2005 SUZUKI JIMNY ATE
[x] Cancel search: ATEPage 113 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3-4 STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS AND TIRES
Abnormal Noise,
Front EndWorn, sticky or loose tie rod ends, drug rod ball
joints, king pin bearings or axle shaft jointsReplace tie rod end, king pin bear-
ing or axle shaft joint.
Damaged shock absorbers or mountings Replace or repair.
Worn leading arm bushings Replace.
Worn stabilizer bar bushings Replace.
Worn Iateral rod bushings Replace.
Loose stabilizer bar Tighten bolts or replace bushes.
Loose wheel nuts Tighten wheel nuts.
Loose suspension bolts or nuts Tighten suspension bolts or nuts.
Broken or otherwise damaged wheel bearings Replace wheel bearing.
Broken suspension springs Replace spring.
Wander or Poor
Steering StabilityMismatched or uneven tires Replace tire or inflate tires to
proper pressure.
Loose king pin bearings and tie rod ends Replace king pin bearing or tie rod
end.
Faulty shock absorbers or mounting Replace absorber or repair mount-
ing.
Loose stabilizer bar Tighten or replace stabilizer bar or
bushes.
Broken or sagging springs Replace spring.
Steering gear box not properly adjusted Check or adjust steering gear box
torque.
Front wheel alignment Check and adjust front wheel align-
ment.
Erratic Steering when
BrakingWorn wheel bearings Replace wheel bearing.
Broken or sagging springs Replace spring.
Leaking wheel cylinder or caliper Repair or replace wheel cylinder or
caliper.
Warped discs Replace brake disc.
Badly worn brake linings Replace brake shoe lining.
Drum is out of round in some brakes Replace brake drum.
Wheel tires are inflated unequally Inflate tires to proper pressure.
Defective wheel cylinders Replace or repair wheel cylinder.
Disturbed front wheel alignment Check front wheel alignment
Ride Too Soft
Faulty shock absorber Replace shock absorber.
Suspension bottoms
Overloaded Check loading.
Faulty shocks absorber Replace shock absorber.
Incorrect, broken or sagging springs Replace spring.
Body Leans or Sways
in CornersLoose stabilizer bar Tighten stabilizer bar bolts or
replace bushes.
Faulty shocks absorbers or mounting Replace shock absorber or tighten
mounting.
Broken or sagging springs Replace spring.
Overloaded Check loading.
Cupped Tires
Worn wheel bearings Replace wheel bearing.
Excessive tire or wheel run-out Replace tire or wheel disc.
Tire out of balance Adjust tire balance. Condition Possible Cause Correction
Page 114 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS AND TIRES 3-5
Tire Diagnosis
Irregular and/or Premature Wear
Irregular and premature wear has many possible causes. Some
of them are: incorrect inflation pressures lack of tire rotation, driv-
ing habits, improper alignment.
If the following conditions are noted rotation is in order:
Front tire wear is different from rear.
Uneven wear exists across the tread of any tire.
Left front and right front tire wear is unequal.
Left rear and right rear tire wear is unequal.
There is cupping, flat spotting, etc.
A wheel alignment check is in order if the following conditions are
noted:
Left front and right front tire wear is unequal.
Wear is uneven across the tread of any front tire.
Front tire treads have scuffed appearance with “feather”
edges on one side of tread ribs or blocks.
Wear Indicators
The original equipment tires have built-in tread wear indicators to
show when tires need replacement. These indicators will appear
as 12 mm (0.47 inch) wide bands when the tire tread depth
becomes 1.6 mm (0.063 inch). When the indicators appear in 3 or
more grooves at 6 locations, tire replacement is recommended.
Radial Tire Waddle
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear of the
vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being straight within the
tire. It is most noticeable at low speed, 5 to 30 mph. It is possible
to road test a vehicle and tell on which end of the vehicle the
faulty tire is located. If the waddle tire is on the rear, the rear end
of the vehicle will shake from side to side or “waddle”. From the
driver’s seat it feels as though someone is pushing on the side of
the vehicle. If the faulty tire is on the front, the waddle is more
visual. The front sheet metal appears to be moving back and forth
and the driver feels as though he is at the pivot point in the vehi-
cle. Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using a Tire Problem
Detector (TPD) and following the equipment manufacturer’s rec-
ommendations.
If a TPD is not available, the more time consuming method of sub-
stituting known good tire / wheel assemblies on the problem vehi-
cle can be used as follows:
[A] : Hard cornering, under inflation or lack of tire rotation
[B] : Incorrect wheel alignment, tire construction not uniform or wheel heavy acceleration
Page 115 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3-6 STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS AND TIRES
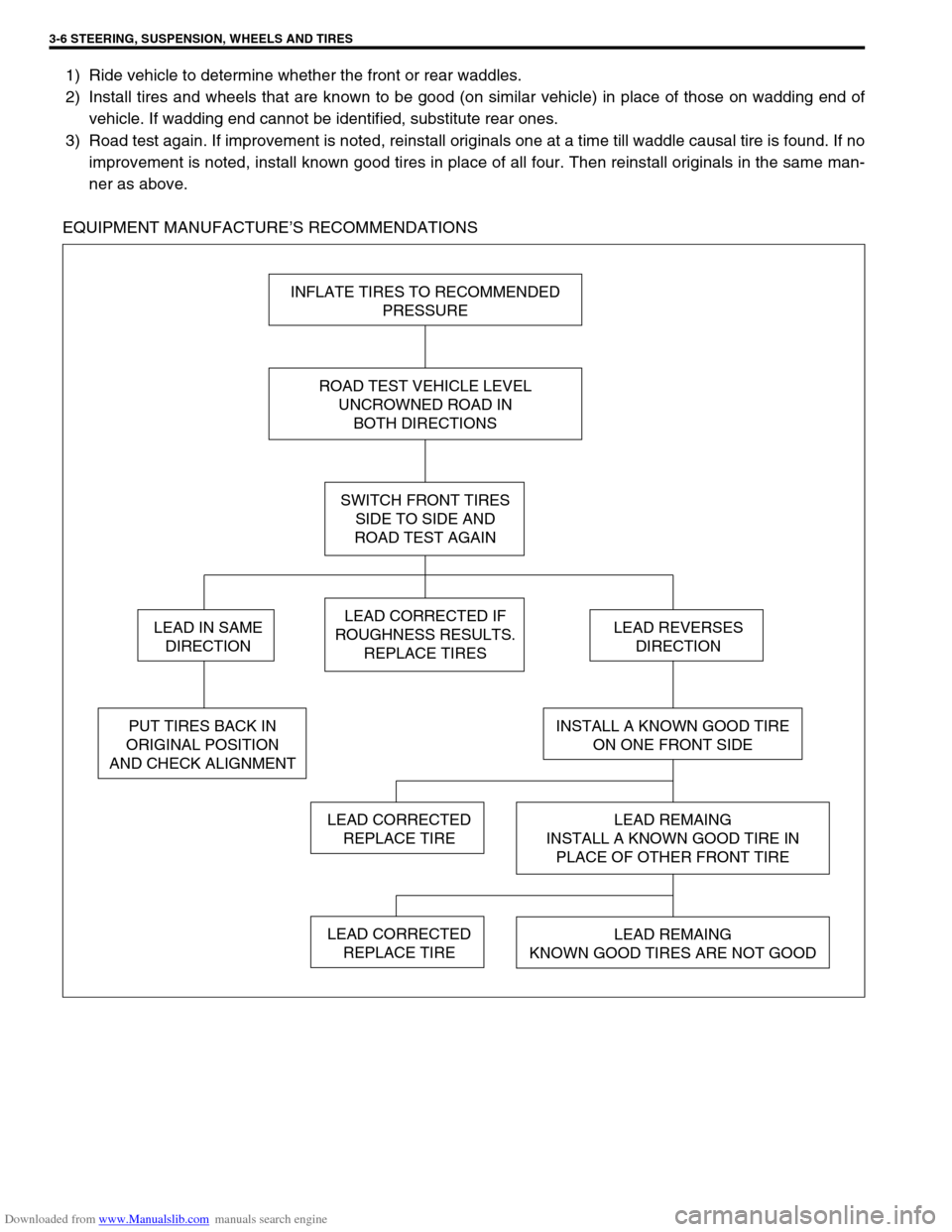
1) Ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear waddles.
2) Install tires and wheels that are known to be good (on similar vehicle) in place of those on wadding end of
vehicle. If wadding end cannot be identified, substitute rear ones.
3) Road test again. If improvement is noted, reinstall originals one at a time till waddle causal tire is found. If no
improvement is noted, install known good tires in place of all four. Then reinstall originals in the same man-
ner as above.
EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURE’S RECOMMENDATIONS
INFLATE TIRES TO RECOMMENDED
PRESSURE
ROAD TEST VEHICLE LEVEL
UNCROWNED ROAD IN
BOTH DIRECTIONS
SWITCH FRONT TIRES
SIDE TO SIDE AND
ROAD TEST AGAIN
LEAD CORRECTED IF
ROUGHNESS RESULTS.
REPLACE TIRES
INSTALL A KNOWN GOOD TIRE
ON ONE FRONT SIDE
LEAD REMAING
INSTALL A KNOWN GOOD TIRE IN
PLACE OF OTHER FRONT TIRE
LEAD REMAING
KNOWN GOOD TIRES ARE NOT GOOD
LEAD CORRECTED
REPLACE TIRE
LEAD REVERSES
DIRECTION
PUT TIRES BACK IN
ORIGINAL POSITION
AND CHECK ALIGNMENT
LEAD IN SAME
DIRECTION
LEAD CORRECTED
REPLACE TIRE
Page 120 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT 3A-3
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Table
For the details, refer to “Diagnosis Table” in Section 3.
Preliminary Checks Prior To Adjusting Front Wheel Alignment
Steering and vibration complaints are not always the result of improper alignment. An additional item to be
checked is the possibility of tire lead due to worn or improperly manufactured tires. “Lead” is the deviation of the
vehicle from a straight path on a level road without hand pressure on the steering wheel. Section 3 of this man-
ual contains a procedure for determining the presence of a tire lead problem. Before making any adjustment
affecting toe setting, the following checks and inspections should be made to ensure correctness of alignment
readings and alignment adjustments:
1) Check all tires for proper inflation pressures and approximately the same tread wear.
2) Check for loose of king pin bearings. Check tie rod ends; if excessive looseness is noted, it must be cor-
rected before adjusting.
3) Check for run-out of wheels and tires.
4) Check vehicle trim heights; if out of limits and a correction is to be made, it must be made before adjusting
toe.
5) Check for loose of suspension arms.
6) Check for loose or missing stabilizer bar attachments.
7) Consideration must be given to excess loads, such as tool boxes. If this excess load is normally carried in
vehicle, it should remain in vehicle during alignment checks.
8) Consider condition of equipment being used to check alignment and follow manufacturer's instructions.
9) Regardless of equipment used to check alignment, vehicle must be on a level surface both fore and aft and
transversely.
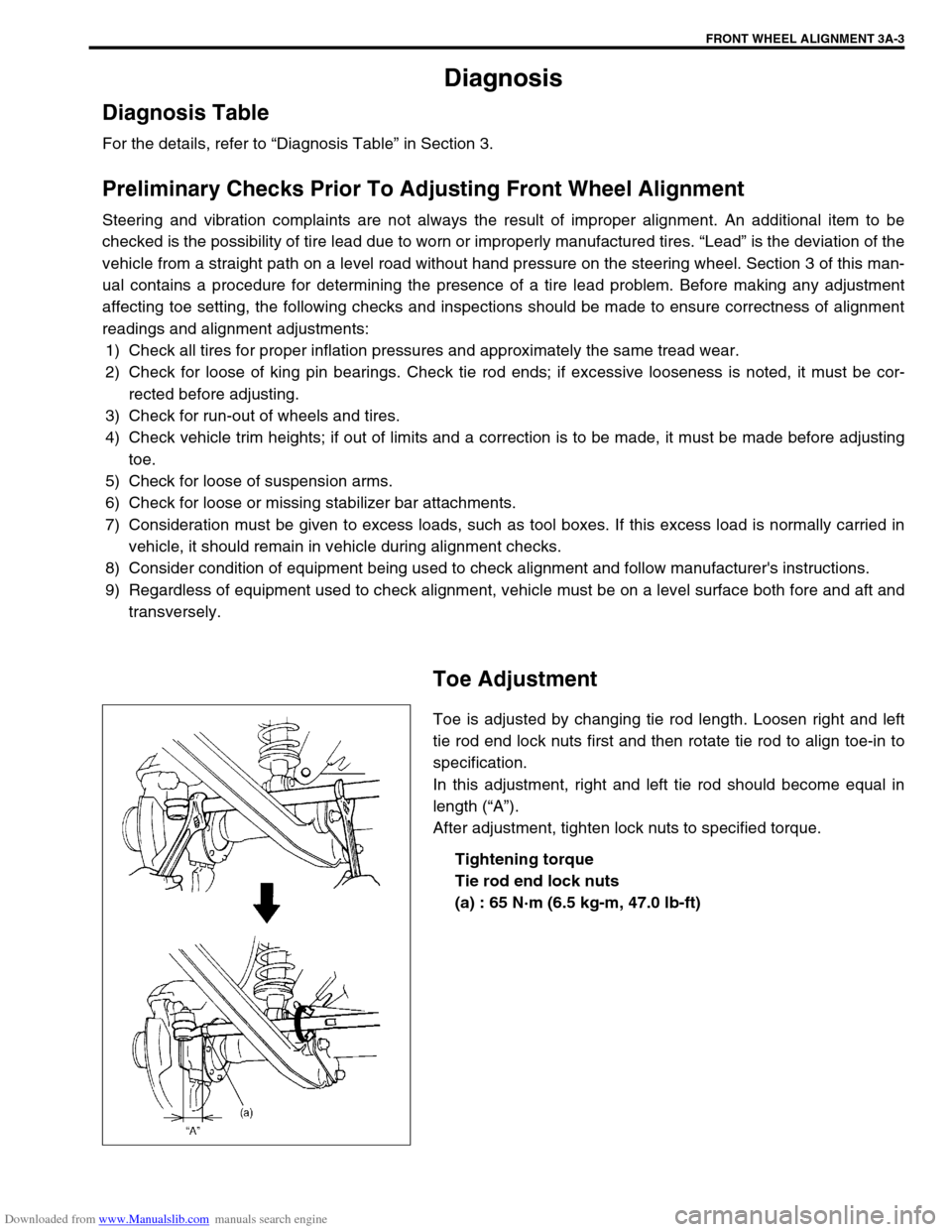
Toe Adjustment
Toe is adjusted by changing tie rod length. Loosen right and left
tie rod end lock nuts first and then rotate tie rod to align toe-in to
specification.
In this adjustment, right and left tie rod should become equal in
length (“A”).
After adjustment, tighten lock nuts to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Tie rod end lock nuts
(a) : 65 N·m (6.5 kg-m, 47.0 lb-ft)
Page 121 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3A-4 FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Camber And Caster Check And Adjustment
Should camber or caster be found out of specifications upon
inspection, locate its cause first. If it is in damaged, loose, bent,
dented or worn suspension parts and axle housing, they should
be replaced. If it is in vehicle body, repair it so as to attain specifi-
cations.
Steering Angle Check And Adjustment
When tie rod (2) or tie rod end (3) was replaced, check toe and
then also steering angle with turning radius gauge (1).
If steering angle is not correct, check if right and left tie rods are
equal in length “A”.
Steering angle
Inside : 35° ± 3°
Outside : 32° ± 3°
Side Slip(Reference)
For inspecting front wheel side slip with side slip tester:
If side slip exceeds limit, toe or front wheel alignment may out not
be correct.
Side slip limit
: Less than 3 mm/m (Less than 0.118 in/3 ft) NOTE:
To prevent possible incorrect reading of camber or
caster, vehicle front end must be moved up and down a
few times before inspection.
NOTE:
If tie rod lengths were changed to adjust steering angle,
reinspect toe-in.
Page 122 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine STEERING GEAR BOX (MANUAL TYPE) AND LINKAGE 3B-1
6F1
6F2
6G
6H
3B
7C1
7D
7E
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 3B
STEERING GEAR BOX (MANUAL TYPE)
AND LINKAGE
CONTENTS
General Description ....................................... 3B-2
Diagnosis ........................................................ 3B-3
Diagnosis Table ........................................... 3B-3
Steering Wheel Play Check ......................... 3B-3
Tie Rod And Drag Rod Check ...................... 3B-3
Steering Gear Box Oil Level Check ............. 3B-4
Adjustment of Worm Shaft Starting Torque . 3B-4On-Vehicle Service ........................................ 3B-6
Steering Gear Box ....................................... 3B-6
Tie Rod And Drag Rod................................. 3B-8
Tightening Torque Specifications .............. 3B-10
Required Service Material ........................... 3B-10
Special Tools ................................................ 3B-10 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system may
be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM)
NOTE:
All steering gear fasteners are important attaching parts in that they could affect the performance of
vital parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one
of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified dur-
ing reassembly to assure proper retention of these parts.
Page 125 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3B-4 STEERING GEAR BOX (MANUAL TYPE) AND LINKAGE
Steering Gear Box Oil Level Check
Oil surface should be up to the level as shown in figure. If not, add
prescribed gear oil, SAE 90.
Steering gear box oil level
“a” : 23 mm (0.91 in.)
Apply sealant to thread parts of breathing plug and tighten breath-
ing plug to specified torque.
(A) : Sealant 99000-31110
Tightening torque
Breathing plug
(a) : 4 N·m (0.4 kg-m, 3.0 lb-ft)
Adjustment of Worm Shaft Starting Torque
Steering gear box has adjusting bolt (1) which gives preload to
sector shaft.
Special tool
(A) : 09944-18211
MAKE ADJUSTMENT ACCORDING TO FOLLOWING PRO-
CEDURE.
1) Check worm shaft (1) to ensure that it is free from thrust
play.
2) Position pitman arm (2) in nearly parallel with worm shaft (1)
as shown. (With pitman arm (2) in this position, front wheels
are in straightforward state.)
Page 126 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine STEERING GEAR BOX (MANUAL TYPE) AND LINKAGE 3B-5
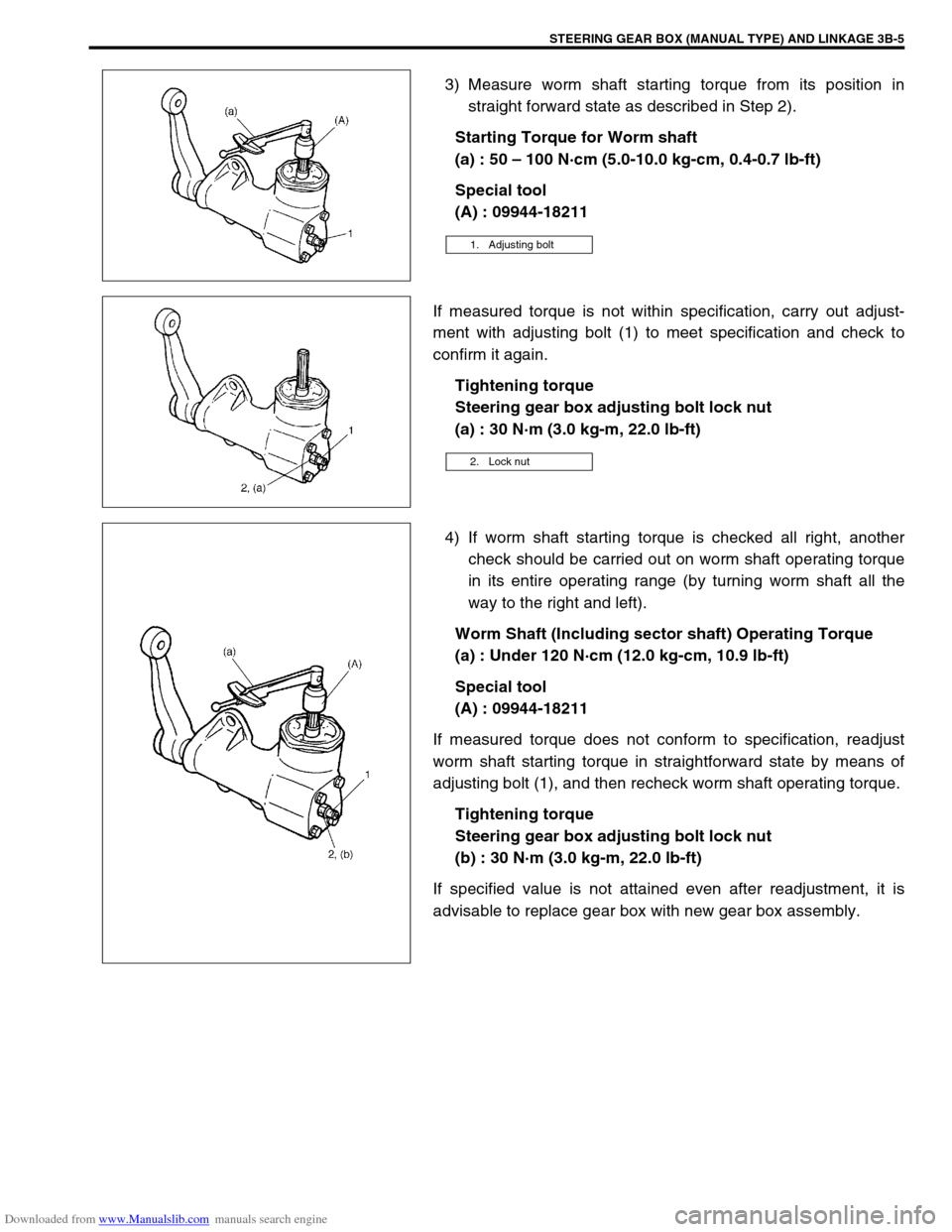
3) Measure worm shaft starting torque from its position in
straight forward state as described in Step 2).
Starting Torque for Worm shaft
(a) : 50 – 100 N·cm (5.0-10.0 kg-cm, 0.4-0.7 lb-ft)
Special tool
(A) : 09944-18211
If measured torque is not within specification, carry out adjust-
ment with adjusting bolt (1) to meet specification and check to
confirm it again.
Tightening torque
Steering gear box adjusting bolt lock nut
(a) : 30 N·m (3.0 kg-m, 22.0 lb-ft)
4) If worm shaft starting torque is checked all right, another
check should be carried out on worm shaft operating torque
in its entire operating range (by turning worm shaft all the
way to the right and left).
Worm Shaft (Including sector shaft) Operating Torque
(a) : Under 120 N·cm (12.0 kg-cm, 10.9 lb-ft)
Special tool
(A) : 09944-18211
If measured torque does not conform to specification, readjust
worm shaft starting torque in straightforward state by means of
adjusting bolt (1), and then recheck worm shaft operating torque.
Tightening torque
Steering gear box adjusting bolt lock nut
(b) : 30 N·m (3.0 kg-m, 22.0 lb-ft)
If specified value is not attained even after readjustment, it is
advisable to replace gear box with new gear box assembly.
1. Adjusting bolt
2. Lock nut