2005 SSANGYONG RODIUS brakes
[x] Cancel search: brakesPage 164 of 502
0-3
DC 5-SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
RODIUS 2005.07
3650-01
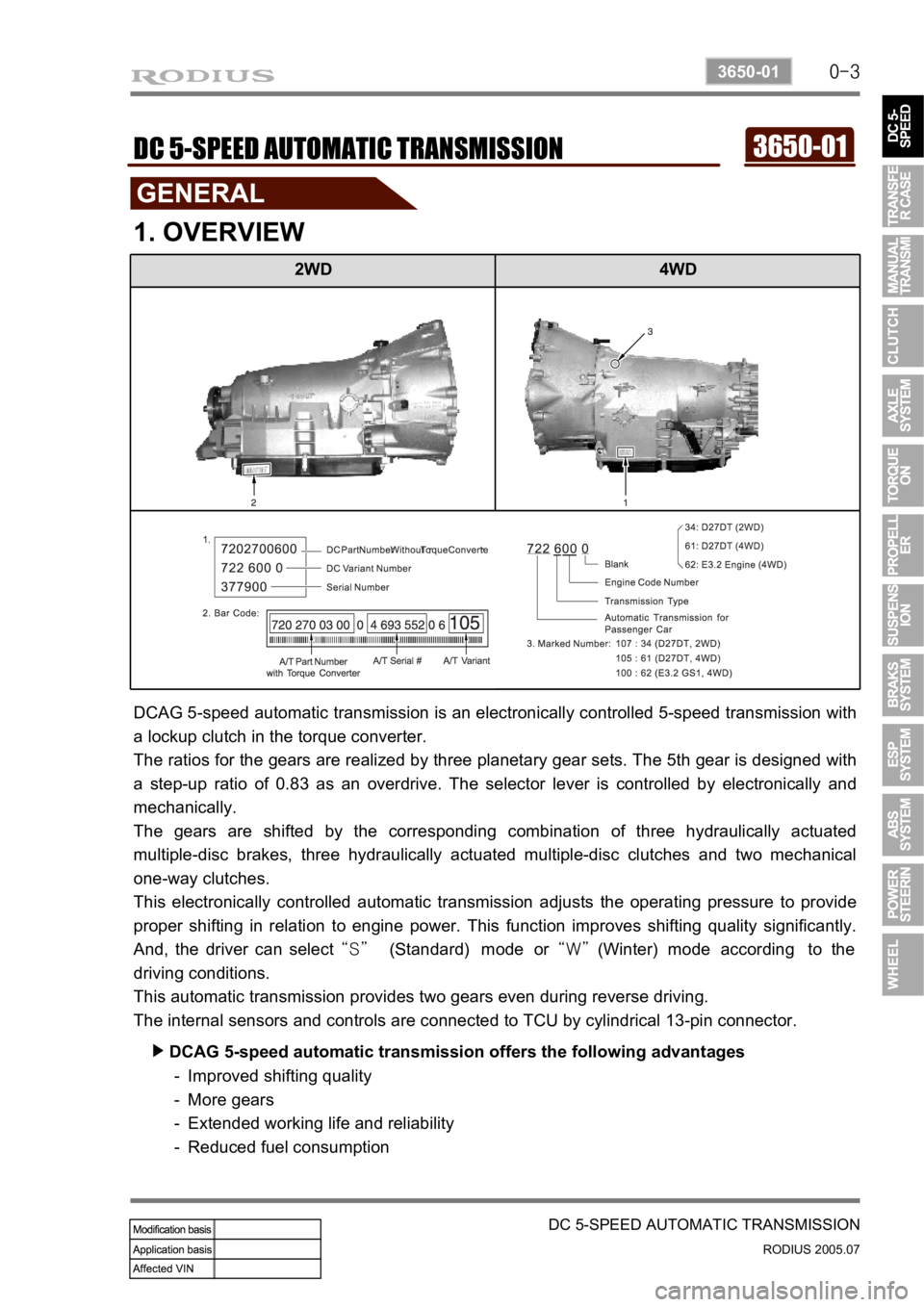
2WD 4WD
3650-01DC 5-SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
1. OVERVIEW
DCAG 5-speed automatic transmission is an electronically controlled 5-speed transmission with
a lockup clutch in the torque converter.
The ratios for the gears are realized by three planetary gear sets. The 5th gear is designed with
a step-up ratio of 0.83 as an overdrive. The selector lever is controlled by electronically and
mechanically.
The gears are shifted by the corresponding combination of three hydraulically actuated
multiple-disc brakes, three hydraulically actuated multiple-disc clutches and two mechanical
one-way clutches.
This electronically controlled automatic transmission adjusts the operating pressure to provide
proper shifting in relation to engine power. This function improves shifting quality significantly.
And, the driver can select “S” (Standard) mode or “W” (Winter) mode according to the
driving conditions.
This automatic transmission provides two gears even during reverse driving.
The internal sensors and controls are connected to TCU by cylindrical 13-pin connector.
DCAG 5-speed automatic transmission offers the following advantages ▶
Improved shifting quality
More gears
Extended working life and reliability
Reduced fuel consumption -
-
-
-
Page 239 of 502

0-6
RODIUS 2005.07
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
3. ESP SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1) Principle of ESP
ESP (Electronic Stability Program) recognizes critical driving conditions, such as panic
reactions in dangerous situations, and stabilizes the vehicle by wheel-individual braking and
engine control intervention with no need for actuating the brake. This system is developed to
help the driver avoid the danger of losing the control of the vehicle stability due to under-
steering or over-steering during cornering.
The yaw rate sensor, lateral sensor and longitudinal sensor in the sensor cluster and the
steering wheel angle sensor under the steering column detect the spin present at any wheels
during over-steering, under-steering or cornering. The ESP ECU controls against over-steering
or under-steering during cornering by controlling the vehicle stability using the input values from
the sensors and applying the brakes independently to the corresponding wheels.
The system also controls during cornering by detecting the moment right before the spin and
automatically limiting the engine output (coupled with the ASR system).
Understeering is when the steering wheel is
steered to a certain angle during driving and
the front tires slip toward the reverse
direction of the desired direction. Generally,
vehicles are designed to have unde
r
steering. The vehicle can return back to
inside of cornering line when the steering
wheel is steered toward the inside even
when the vehicle front is slipped outward.
As
the centrifugal force increases, the tires can
easily lose the traction and the vehicle tends
to slip outward when the curve angle gets
bigger and the speed increases. Under steering
ESP controls during under steering
The ESP system recognizes the directional
angle with the steering wheel angle senso
r
and senses the slipping route that occurs
reversely against the vehicle cornering
direction during understeering with the yaw
rate sensor and the lateral sensor. Then the
ESP system applies the brake at the rea
r
inner wheel to compensate the yaw moment
value.
In this way, the vehicle does not lose its
driving direction and the driver can steer the
vehicle as driver intends.
Page 240 of 502

0-7
ESP SYSTEM
RODIUS 2005.07
4892-01
Over steeringOversteering is when the steering wheel is
steered to a certain angle during driving and
the rear tires slip outward losing traction.
When compared with under steering
vehicles, the controlling of the vehicle is
difficult during cornering and the vehicle can
spin due to rear wheel moment when the
rear tires lose traction and the vehicle speed
increases.
ESP controls during oversteering
The ESP system recognizes the directional
angle with the steering wheel angle senso
r
and senses the slipping route that occurs
towards the vehicle cornering direction
during oversteering with the yaw rate senso
r
and the lateral sensor. Then the ESP system
applies the brake at the front outer wheel to
compensate the yaw moment value.
In this way, the vehicle does not lose its
driving direction and the driver can steer the
vehicle as he or she intends.
2) ESP Control
The ESP system includes the ABS/EBD and ASR systems allowing the system to be able to
operate depending to the vehicle driving conditions. For example, when the brakes are applied
during cornering at the speed of 100 km/h, the ABS system will operate at the same time the
ASR or ABD systems operate to reduce the power from the slipping wheel. And when yaw rate
sensor detects the rate exceeding 4¡Æ/seconds, the ESP system is activated to apply the
brake force to the corresponding wheel to compensate the yaw moment with the vehicle
stability control function. When various systems operate simultaneously under a certain
situation, there may be vehicle control problems due to internal malfunction of a system o
r
simultaneous operations. In order to compensate to this problem, the ESP system sets the
priority among systems. The system operates in the order of TCS (ASR or ABD), ESP and
ABS. The order may be changed depending on the vehicle driving situations and driving
conditions. As the single-track vehicle model used for the calculations is only valid for a vehicle
moving forward, ESP intervention never takes place during backup.
Page 241 of 502

0-8
RODIUS 2005.07
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
2) ESP Control
The ESP system includes the ABS/EBD and ASR systems allowing the system to be able to
operate depending to the vehicle driving conditions. For example, when the brakes are applied
during cornering at the speed of 100 km/h, the ABS system will operate at the same time the
ASR or ABD systems operate to reduce the power from the slipping wheel. And when yaw rate
sensor detects the rate exceeding 4¡Æ/seconds, the ESP system is activated to apply the
brake force to the corresponding wheel to compensate the yaw moment with the vehicle
stability control function. When various systems operate simultaneously under a certain
situation, there may be vehicle control problems due to internal malfunction of a system o
r
simultaneous operations. In order to compensate to this problem, the ESP system sets the
priority among systems. The system operates in the order of TCS (ASR or ABD), ESP and
ABS. The order may be changed depending on the vehicle driving situations and driving
conditions. As the single-track vehicle model used for the calculations is only valid for a vehicle
moving forward, ESP intervention never takes place during backup.
Page 247 of 502

0-14
RODIUS 2005.07
4892-01
ESP SYSTEM
(1) System Overview
When equipped with ABS, the braking force at each wheel will be controlled with 3-channel 4-
sensor method. And when equipped with ESP, 4 wheels will be controlled independently with 4-
channel method. (When controlling ABS system only, it will be operated with 3-channel
method.) When compared to the vehicle equipped with ABS/EBD only, the internal hydraulic
circuit has a normally-open separation valve and a shuttle valve in primary circuit and in
secondary circuit. When the vehicle brakes are not applied during engine running or when
applying the non-ABS operating brakes, the normally-open separation valve and the inlet valve
are open, whereas the normally-closed shuttle valve and the outlet valve are closed. When the
ESP system is operating, the normally-open separation valve will be closed by the solenoid
valve operation and the hydraulic circuit will be established by the shuttle valve. Then, the inlet
and outlet valves will be
closed or open depending on the braking pressure increase, decrease or unchanged
conditions.
<0d96007b008f008c0047009e00880099009500900095008e004700930088009400970047008a00960094008c009a004700960095004700880095008b0047009e00880099009500900095008e00470089008c008c00970047009a0096009c0095008b009a00
47009e008f008c00950047009b008f008c0047006c007a0077> is operating
▶Driving feeling when the ESP is operating
<0d96007500960090009a008c004700880095008b0047009d0090008900990088009b0090009600950047009b008f0088009b0047008b00990090009d008c00990047009a008c0095009a008c009a0047009e008f008c00950047009b008f008c0047006c00
7a007700470090009a004700960097008c00990088009b0090>ng When the ESP operates during vehicle movement, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument
panel flickers and beep comes on every 0.1 seconds. The ESP operation shows that the
vehicle stability is extremely unstable and it is used to warn the driver. The ESP system is just a
supplementary system for the vehicle motion and it cannot control the vehicle when it exceeds
the physical limits. Do not solely rely on the system but be advised to drive the vehicle safely.
When the ESP system activates, the driving feeling can be different depending on vehicle
driving conditions. For example, you will feel differently when the ESP system is activated
during when ABS is operating with the brakes applied and when brakes are not applied on a
curve. Thus, the ESP system would make the driver feel more abruptly when the brakes are
applied during the ESP system activation.
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to the driver due to the pressure changes
caused by the motor and valve operations in a very short period of time. Extreme cornering will
trigger the ESP operation and this will make the driver feel noise and vibration due to sudden
brake application. Also, the ESP system controls the engine output. So, the driver may notice
the engine output decrease even when the accelerator pedal is being applied.
Page 256 of 502

0-4
RODIUS 2005.07
4892-01
ABS SYSTEM
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
The aim of the ABS is to mmaintain steerability and driving stability and to take the burden off
the driver. If the stopping distance is shorter on some road surfaces (carriageway conditions),
this is a gift of physics and not a development aim.
ABS is a device which senses that one or more of the wheels are locking up during braking. It
monitors the rotational speeds of the wheels and reduces hydraulic pressure to any wheel it
senses locking up. It is controlled by both mechanical and electronic components. When you
apply the brakes, the ABS will regulate the flow of brake fluid being delivered to the brake
calipers. By the use of electronic computers, the brakes rapidly alternate (at a rate of 30 times
per second) from full pressure to full release.
1) DRIVING PHYSICS
To give you a better understanding of the tasks and functions of ABS, we will first look at the
physics principles.
(1) The Stopping Distance
The stopping distance depends on the vehicle weight and initial speed when braking starts.
This also applies for vehicle with ABS, where ABS always tries to set an optimum brake force
on each wheel. As great forces are exerted between the tires and the carriageway when
braking, even with ABS the wheels may scream and rubber is left on the road. With an
ABS
skid mark one may be able to clearly recognize the tire profile. The skid mark of an ABS vehicle
does not however leave any hint of the speed of the vehicle in the case of an accident, as it can
only be clearly drawn at the start of braking.
(2) Brake Force on a Wheel
The maximum possible brake force on a wheel depends on the wheel load and the adhesion
coefficient between tire and carriageway. With a low adhesion coefficient the brake force, which
can be obtained is very low. You are bound to know the result already from driving on winte
r
roads. With a high adhesion coefficient on a dry road, the brake force, which can be obtained,
is considerably higher. The brake force, which can be obtained, can be calculated from below
formula:
Page 267 of 502

0-15
ABS SYSTEM
RODIUS 2005.07
4892-01
3. ABS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
1) EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE FORCE DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
(1) System Description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD works in a range in which the intervention
thresholds for ABS control can not be reached. EBD ensures that the rear wheels are
sensitively monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip is detected, the inlet valves fo
r
the rear wheels are switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase in pressure at the
rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically reproducing a pressure-reduction function at the rear-
wheel brakes. ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes control of the brake force
distribution between the front and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake Distribution. In an
unloading car condition the brake efficiency is comparable to the conventional system but for a
fully loaden vehicle the efficiency of the EBD system is higher due to the better use of rear axle
braking capability.
(2) The Benefits of EBD
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve EBD utilizes the existing rear axle wheel
speed sensor to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain
may be triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic (conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable).
“Keep alive” function. -
-
-
-
-
-