Page 96 of 788
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-32
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
IGNITION COIL (WITH BUILT-IN POWER
TRANSISTOR) CHECK
M1163001200324
Check by the following procedure, and replace if
there is a malfunction.
SECONDARY COIL RESISTANCE CHECK
Measure the resistance between the high-voltage
terminals of the ignition coil.
Standard value: 8.5 − 11.5 kΩ
PRIMARY COIL AND POWER
TRANSISTOR CONTINUITY CHECK
NOTE: .•
An analogue-type circuit tester should be used.
•Connect the negative (-) prove of the circuit tester
to terminal No. 1.
CAUTION
This test must be performed quickly (in less than
10 seconds) to prevent coil from burning and
power transistor from breakage.
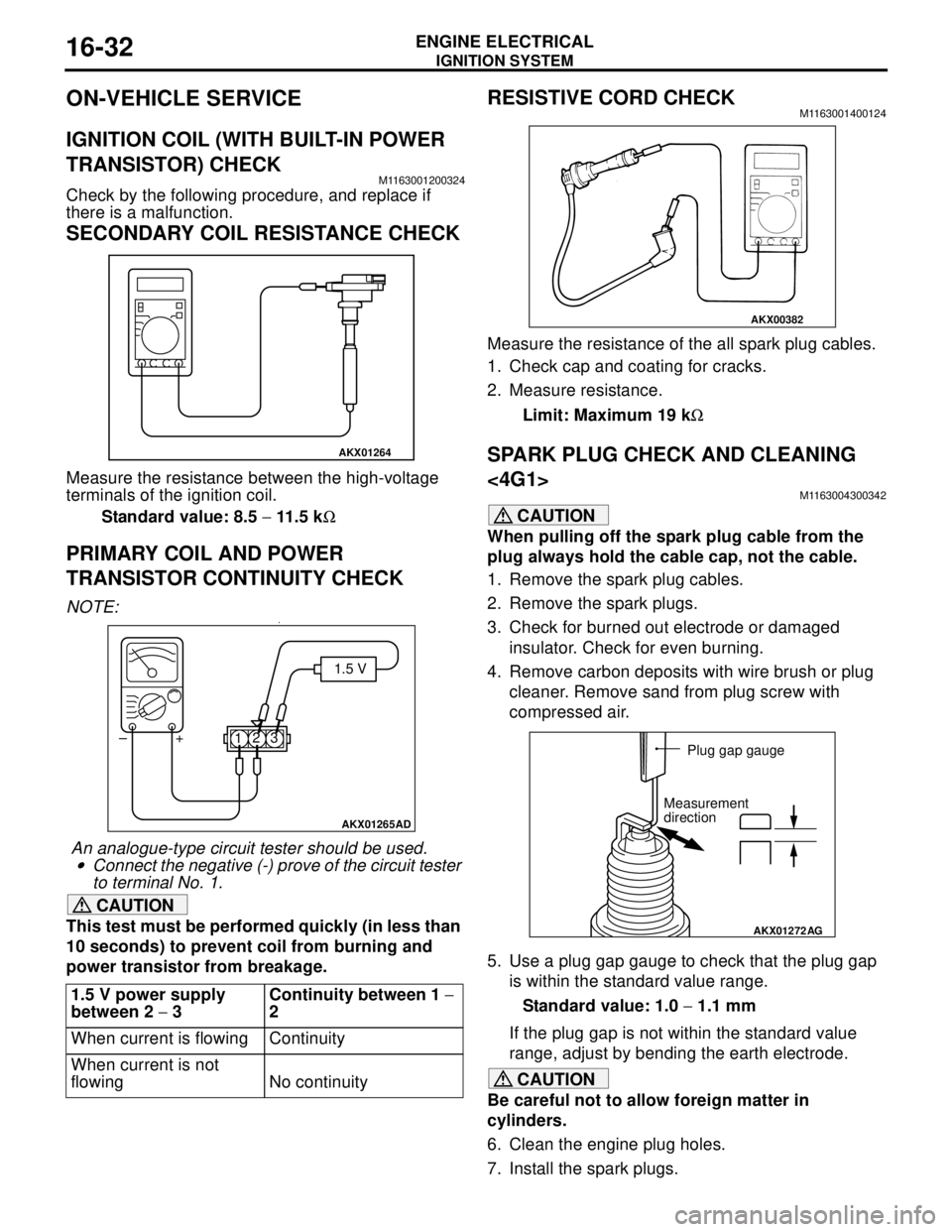
RESISTIVE CORD CHECKM1163001400124
Measure the resistance of the all spark plug cables.
1. Check cap and coating for cracks.
2. Measure resistance.
Limit: Maximum 19 kΩ
SPARK PLUG CHECK AND CLEANING
<4G1>
M1163004300342
CAUTION
When pulling off the spark plug cable from the
plug always hold the cable cap, not the cable.
1. Remove the spark plug cables.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Check for burned out electrode or damaged
insulator. Check for even burning.
4. Remove carbon deposits with wire brush or plug
cleaner. Remove sand from plug screw with
compressed air.
5. Use a plug gap gauge to check that the plug gap
is within the standard value range.
Standard value: 1.0 − 1.1 mm
If the plug gap is not within the standard value
range, adjust by bending the earth electrode.
CAUTION
Be careful not to allow foreign matter in
cylinders.
6. Clean the engine plug holes.
7. Install the spark plugs. 1.5 V power supply
between 2 − 3Continuity between 1 −
2
When current is flowing Continuity
When current is not
flowing No continuity
AKX01264
AKX01265AD
1.5 V
123 +
–
AKX00382
AKX01272
AG
Plug gap gauge
Measurement
direction
Page 99 of 788

IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-35
WAVEFORM OBSERVATION POINTS
Point A: The height, length and slope of the spark line show the following trends (Refer to abnormal
waveform examples, 1, 2, 3 and 4).
Point B: Number of vibration in reduction vibration section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Point C: Number of vibrations at beginning of dwell section (Refer to abnormal waveform example 5)
Point D: Ignition voltage height (distribution per each cylinder) shows the following trends.
AKX01275
kV
Secondary ignition
voltage wave pattern
0
2NO. 1 cylinder
NO. 3 cylinder
ignition noise
Newtral sectionNO. 4 cylinderNO. 2 cylinder
ignition noise
Time
AC
Spark line Plug gap Condition of
electrodeCompression
force Concentration
of air mixtureIgnition
timingSpark plug
cable
Length Long Small Normal Low Rich Advanced Leak
Short Large Large wear High Lean Retarded High
resistance
Height High Large Large wear High Lean Retarded High
resistance
Low Small Normal Low Rich Advanced Leak
Slope Large Plug is fouled
−− −−
Number of vibrations Coil and condenser
3 or more Normal
Except above Abnormal
Number of vibrations Coil
5 − 6 or higher Normal
Except above Abnormal
Ignition
voltagePlug gap Condition of
electrodeCompression
forceConcentration
of air mixtureIgnition
timingSpark plug
cable
High Large Large wear High Lean Retarded High
resistance
Low Small Normal Low Rich Advanced Leak
Page 113 of 788

EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-5
EMISSION CONTROL
GENERAL INFORMATIONM1173000100370
The emission control system consists of the following
subsystems:•Crankcase emission control system
•Evaporative emission control system
•Exhaust emission control system
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICE
REFERENCE TABLE
M1173006600135
SERVICE SPECIFICATION(S)M1173000300288
Items Name Specification
Crankcase emission control
systemPositive crankcase ventilation
(PCV) valveVariable flow type
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Evaporative emission control
systemCanister
Purge control solenoid valveEquipped
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: HC reduction)
Exhaust emission control system Air-fuel ratio control device - MPI
systemOxygen sensor feedback type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Exhaust gas recirculation system
•EGR valve
•EGR control solenoid valveEquipped
Single type
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
(Purpose: NOx reduction)
Catalytic converter Monolith type
(Purpose: CO, HC, NOx reduction)
Related parts Crankcase
emission
control
systemEvaporative
emission
control
systemAir/fuel ratio
control
systemCatalytic
converterExhaust gas
recirculation
system
PCV valve
×
Purge control solenoid valve
×
MPI system component
××
Catalytic converter
×
EGR valve
×
EGR control solenoid valve
×
Items Standard value
Purge control solenoid valve coil resistance (at 20°C) Ω30 − 34
EGR control solenoid valve coil resistance (at 20°C) Ω29 − 35
Page 114 of 788
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-6
VACUUM HOSE
VACUUM HOSE PIPING DIAGRAMM1173000900417
AK300964
To
fuel tankFuel pressure
regulatorFrom
fuel pump
Catalytic
converter
Catalytic
converter Oxygen sensor
(front)
Oxygen sensor (rear)EGR valve <4G1>
EGR control
solenoid valvePurge control
solenoid valveCanisterAir
AB
Air cleaner
AK204364
AC
Air cleaner
Air
Canister
Purge control
solenoid valve EGR control
solenoid valve EGR valve From
fuel pump To
fuel tankFuel pressure
regulator
PCV valve
Oxygen sensor
(front)
Oxygen sensor (rear) Catalytic
converter
Catalytic
converter
<4G6>
Page 115 of 788
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-7
VACUUM CIRCUIT DIAGRAMM1173007100263
AK300765
From
air
cleaner To
combustion
chamberThrottle body
B R
AB
Intake manifold
Y G
G
GR L
Fuel
pressure
regulator
EGR
valveEGR
control
solenoid
valvePurge
control
solenoid
valveCanister
Vacuum hose colour
B: Black
G: Green
R: Red
Y: Yellow
L: Blue
<4G1>
AK300766
From
air
cleaner To
combustion
chamberThrottle body
B B
AB
Intake manifold
Y R
GW L
Fuel
pressure
regulator
EGR
valveEGR
control
solenoid
valve
Purge
control
solenoid
valveCanister
Vacuum hose colour
B: Black
G: Green
R: Red
W: White
Y: Yellow
L: Blue
<4G6>
B
Page 116 of 788

EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-8
VACUUM HOSE CHECKM1173007300159
1. Using the piping diagram as a guide, check to be
sure that the vacuum hoses are correctly
connected.
2. Check the connection condition of the vacuum
hoses, (removed, loose, etc.) and check to be
sure that there are no bends or damage.
VACUUM HOSE INSTALLATIONM1173007200107
1. When connecting the vacuum hoses, they should
be securely inserted onto the nipples.
2. Connect the hoses correctly, using the vacuum
hose piping diagram as a guide.
CRANKCASE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION (CRANKCASE
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM)
M1173005000237
The crankcase emission control system prevents
blow-by gases from escaping inside the crankcase
into the atmosphere.
Fresh air is sent from the air cleaner into the
crankcase through the breather hose.
The air becomes mixed with the blow-by gases
inside the crankcase.
The blow-by gas inside the crankcase is drawn into
the intake manifold through the positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) valve.
The PCV valve lifts the plunger according to the
intake manifold vacuum so as to regulate the flow of
blow-by gas properly.
In other words, the blow-by gas flow is regulated
during low load engine operation to maintain engine
stability, while the flow is increased during high load
operation to improve the ventilation performance.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
AK204365
Air cleaner
Air
Ventilation hose
Breather hose
PCV valve
AB
Page 117 of 788

EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-9
COMPONENT LOCATION (CRANKCASE
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM)
M1173007400208
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION
SYSTEM CHECK
M1173001100179
1. Remove the ventilation hose from the PCV valve.
2. Remove the PCV valve from the rocker cover.
3. Reinstall the PCV valve at the ventilation hose.
4. Start the engine and run at idle.
5. Place a finger at the opening of the PCV valve
and check that vacuum of the intake manifold is
felt.
NOTE: At this moment, the plunger in the PCV
valve moves back and forth.
6. If vacuum is not felt, clean the PCV valve or
replace it.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION
(PCV) VALVE CHECK
M1173001200187
1. Insert a thin rod into the PCV valve from the side
shown in the illustration (rocker cover installation
side), and move the rod back and forth to check
that the plunger moves.
2. If the plunger does not move, there is a clogging
in the PCV valve. In this case, clean or replace
the PCV valve.
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION (EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM)
M1173005100405
The evaporative emission control system prevents
fuel vapours generated in the fuel tank from escaping
into the atmosphere.
Fuel vapours from the fuel tank flow through the fuel
tank pressure control valve and vapour pipe/hose to
be stored temporarily in the canister.
When driving the vehicle, fuel vapours stored in the
canister flow through the purge solenoid and purge
port and go into the intake manifold to be sent to the
combustion chamber.
When the engine coolant temperature is low or when
the intake air quantity is small (when the engine is at
idle, for example), the engine control unit turns the
purge solenoid off to shut off the fuel vapour flow to
the intake manifold.
This does not only insure the driveability when the
engine is cold or running under low load but also
stabilize the emission level.
AK300767
<4G1>
AB
PCV valve
AK204366
<4G6>
AC
PCV valve
AKX00336
PCV valve
AD
AK100010
PCV valve
AC
Page 118 of 788
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-10
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
COMPONENT LOCATION (EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM)
M1173007500216
PURGE CONTROL SYSTEM CHECKM1173001400299
AK204367AC
Throttle body
Canister
From
fuel
tank
OFF
ONPurge
control
solenoid
valveControl
relay
BatteryEngine-ECU <4G1-M/T, 4G6>,
Engine-A/T-ECU <4G1-A/T>
Air flow sensor <4G6>
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Intake air
temperature sensor
Barometric pressure
sensor <4G6> Manifold absolute pressure
(MAP) sensor <4G1>
AK300769
<4G1>
AB
Purge control
solenoid valve
AK300770
<4G6>
AB
Purge control
solenoid valve
AK300771
<4G1>
AB
Plug
Vacuum hose
AK300772
<4G6>
AB
Plug
Vacuum hose