2005 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 1466 of 2339
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTE TRANSAXLE
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Before attempting any repair on a 4XTE four-
speed automatic transaxle, check for diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC's) using the DRB scan tool.
Refer to the Transmission Diagnostic Procedures
Manual.
Transaxle malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or that more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, verify that the
fluid level, fluid condition, and linkage adjustment
have been approved.
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
If the vehicle operates properly at highway speeds,
but has poor acceleration, the converter stator over-
running clutch may be slipping. If acceleration is nor-
mal, but high throttle opening is needed to maintain
highway speeds, the converter stator clutch may
have seized. Both of these stator defects require
replacement of the torque converter and thorough
transaxle cleaning.
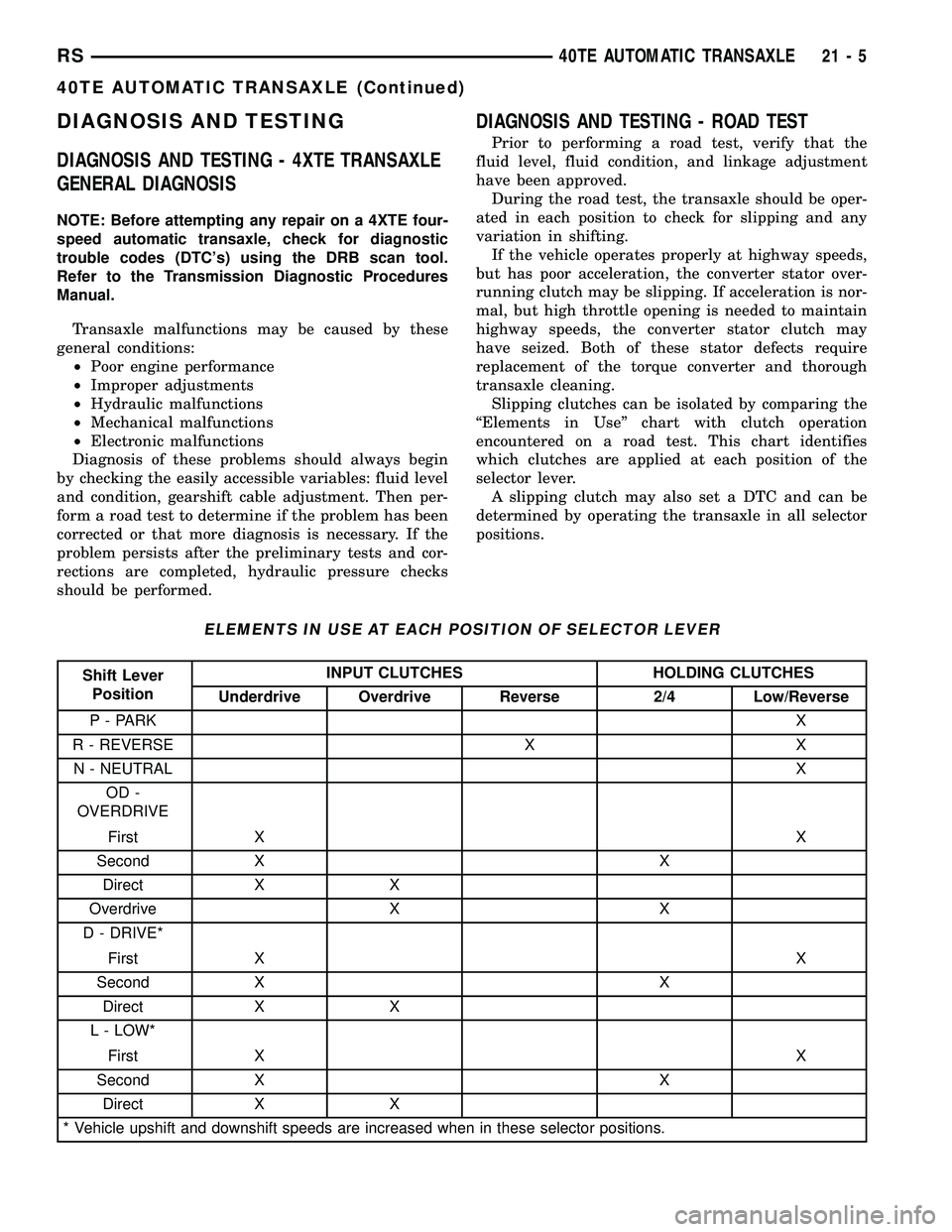
Slipping clutches can be isolated by comparing the
ªElements in Useº chart with clutch operation
encountered on a road test. This chart identifies
which clutches are applied at each position of the
selector lever.
A slipping clutch may also set a DTC and can be
determined by operating the transaxle in all selector
positions.
ELEMENTS IN USE AT EACH POSITION OF SELECTOR LEVER
Shift Lever
PositionINPUT CLUTCHES HOLDING CLUTCHES
Underdrive Overdrive Reverse 2/4 Low/Reverse
P - PARKX
R - REVERSE X X
N - NEUTRALX
OD -
OVERDRIVE
First XX
Second X X
Direct X X
Overdrive X X
D - DRIVE*
First XX
Second X X
Direct X X
L - LOW*
First XX
Second X X
Direct X X
* Vehicle upshift and downshift speeds are increased when in these selector positions.
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-5
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1467 of 2339
The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road test analysis can diagnose slip-
ping units, but the cause of the malfunction cannot
be determined. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most hydraulic transaxle problems.
Before performing pressure tests, be certain that
fluid level and condition, and shift cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. Fluid must be at
operating temperature (150 to 200 degrees F.).
Install an engine tachometer, raise vehicle on hoist
which allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read.
Attach 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP) to port(s)
required for test(s) being conducted. Use adapter set
L-4559 to adapt gauge(s) to transaxle.
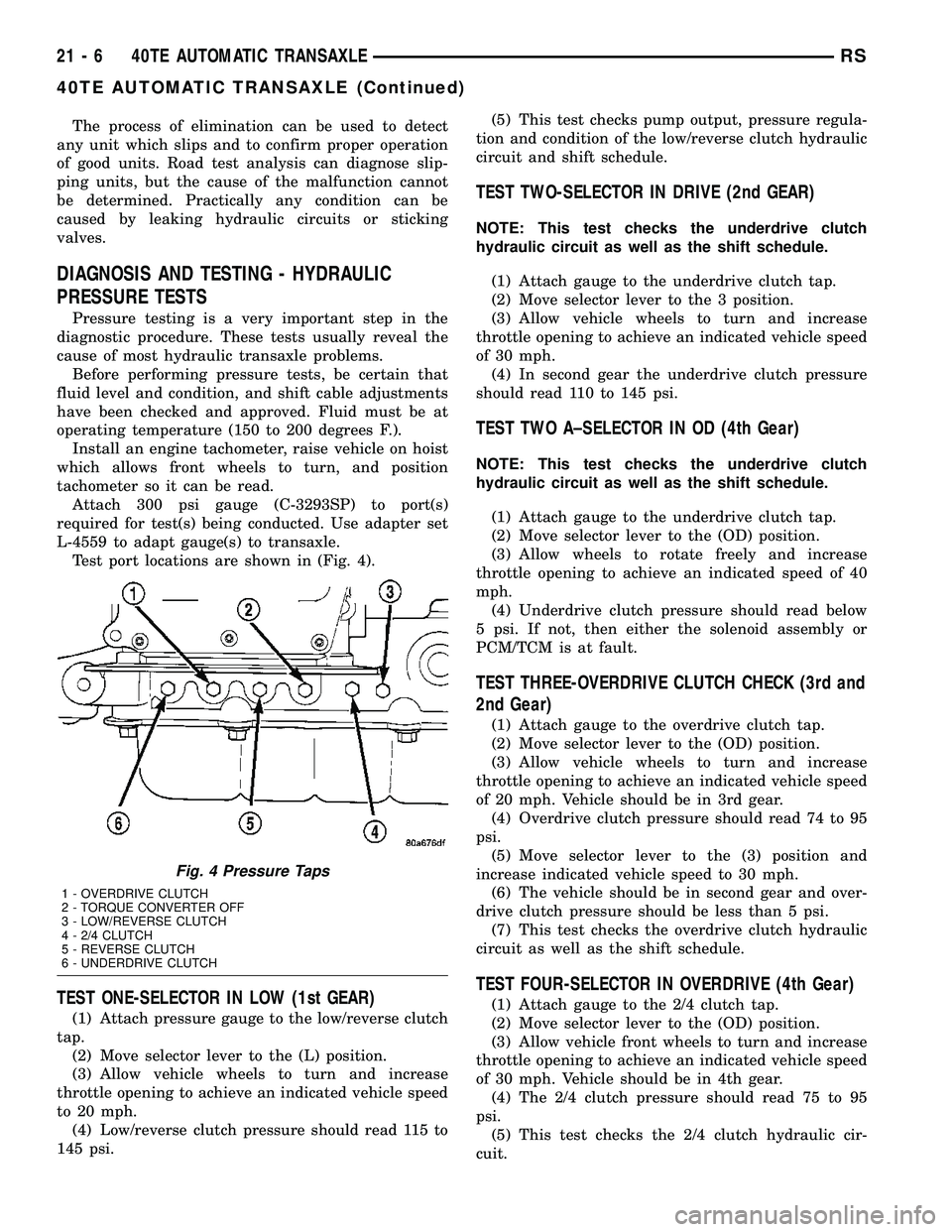
Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 4).
TEST ONE-SELECTOR IN LOW (1st GEAR)
(1) Attach pressure gauge to the low/reverse clutch
tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (L) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
to 20 mph.
(4) Low/reverse clutch pressure should read 115 to
145 psi.(5) This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion and condition of the low/reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit and shift schedule.
TEST TWO-SELECTOR IN DRIVE (2nd GEAR)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the 3 position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph.
(4) In second gear the underdrive clutch pressure
should read 110 to 145 psi.
TEST TWO A±SELECTOR IN OD (4th Gear)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow wheels to rotate freely and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated speed of 40
mph.
(4) Underdrive clutch pressure should read below
5 psi. If not, then either the solenoid assembly or
PCM/TCM is at fault.
TEST THREE-OVERDRIVE CLUTCH CHECK (3rd and
2nd Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the overdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 20 mph. Vehicle should be in 3rd gear.
(4) Overdrive clutch pressure should read 74 to 95
psi.
(5) Move selector lever to the (3) position and
increase indicated vehicle speed to 30 mph.
(6) The vehicle should be in second gear and over-
drive clutch pressure should be less than 5 psi.
(7) This test checks the overdrive clutch hydraulic
circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST FOUR-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the 2/4 clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle front wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear.
(4) The 2/4 clutch pressure should read 75 to 95
psi.
(5) This test checks the 2/4 clutch hydraulic cir-
cuit.
Fig. 4 Pressure Taps
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER OFF
3 - LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
4 - 2/4 CLUTCH
5 - REVERSE CLUTCH
6 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
21 - 6 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1468 of 2339
TEST FIVE-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear-CC
on)
(1) Attach gauge to the torque converter clutch off
pressure tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 50 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear, CC on.
CAUTION: Both wheels must turn at the same
speed.
(4) Torque converter clutch off pressure should be
less than 5 psi.
(5) This test checks the torque converter clutch
hydraulic circuit.
TEST SIX-SELECTOR IN REVERSE
(1) Attach gauges to the reverse and LR clutch
tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (R) position.
(3) Read reverse clutch pressure with output sta-
tionary (foot on brake) and throttle opened to achieve
1500 rpm.(4) Reverse and LR clutch pressure should read
165 to 235 psi.
(5) This test checks the reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure is found in any one test,
the pump and pressure regulator are working prop-
erly.
(2) Low pressure in all positions indicates a defec-
tive pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure regu-
lator valve.
(3) Clutch circuit leaks are indicated if pressures
do not fall within the specified pressure range.
(4) If the overdrive clutch pressure is greater than
5 psi in Step 4 of Test Three, a worn reaction shaft
seal ring or a defective solenoid assembly is indi-
cated.
(5) If the underdrive clutch pressure is greater
than 5 psi in Step 4 of Test Two A, a defective sole-
noid assembly or PCM/TCM is the cause.
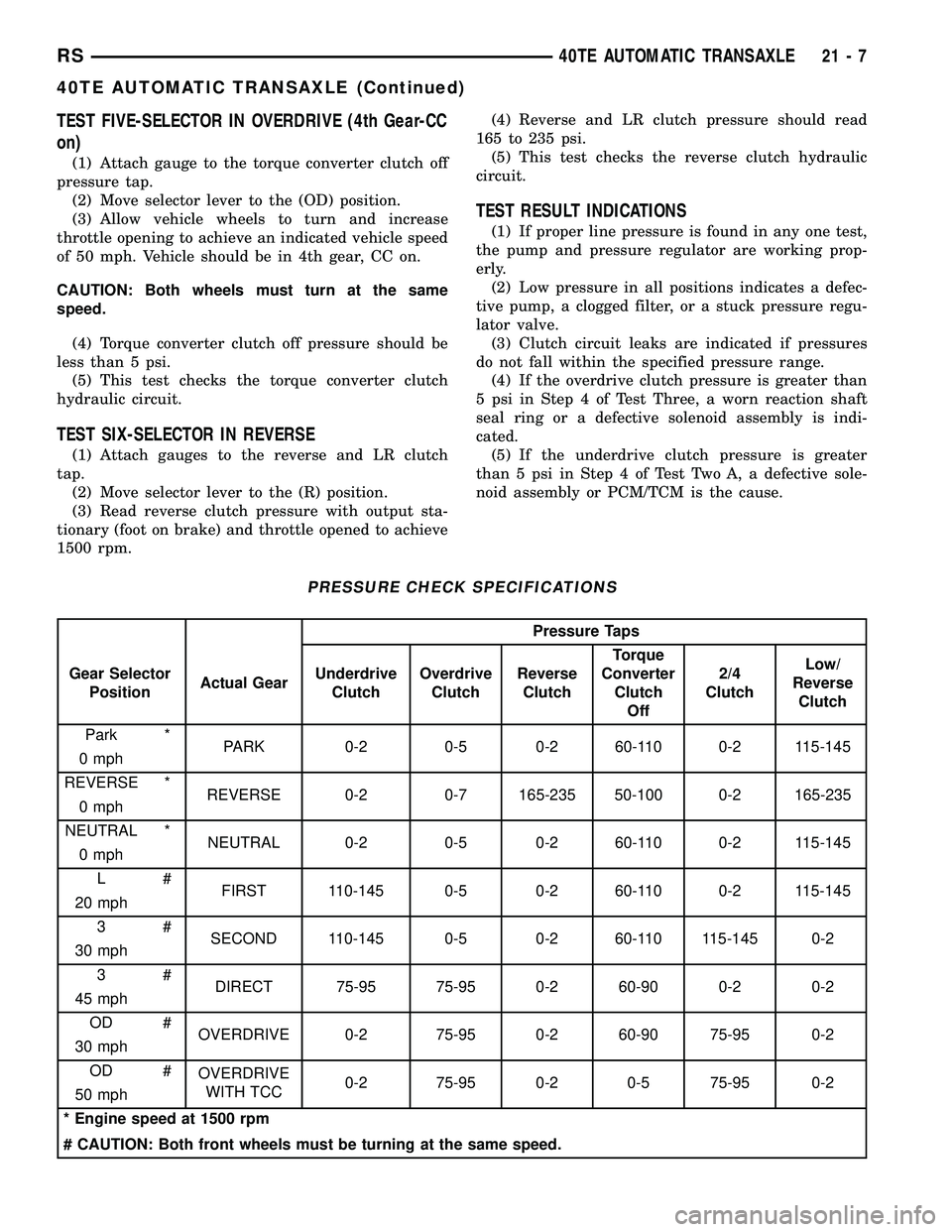
PRESSURE CHECK SPECIFICATIONS
Pressure Taps
Gear Selector
PositionActual GearUnderdrive
ClutchOverdrive
ClutchReverse
ClutchTorque
Converter
Clutch
Off2/4
ClutchLow/
Reverse
Clutch
Park *
PARK 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
REVERSE *
REVERSE 0-2 0-7 165-235 50-100 0-2 165-235
0 mph
NEUTRAL *
NEUTRAL 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
L#
FIRST 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
20 mph
3#
SECOND 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 115-145 0-2
30 mph
3#
DIRECT 75-95 75-95 0-2 60-90 0-2 0-2
45 mph
OD #
OVERDRIVE 0-2 75-95 0-2 60-90 75-95 0-2
30 mph
OD #
OVERDRIVE
WITH TCC0-2 75-95 0-2 0-5 75-95 0-2
50 mph
* Engine speed at 1500 rpm
# CAUTION: Both front wheels must be turning at the same speed.
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-7
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1470 of 2339
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
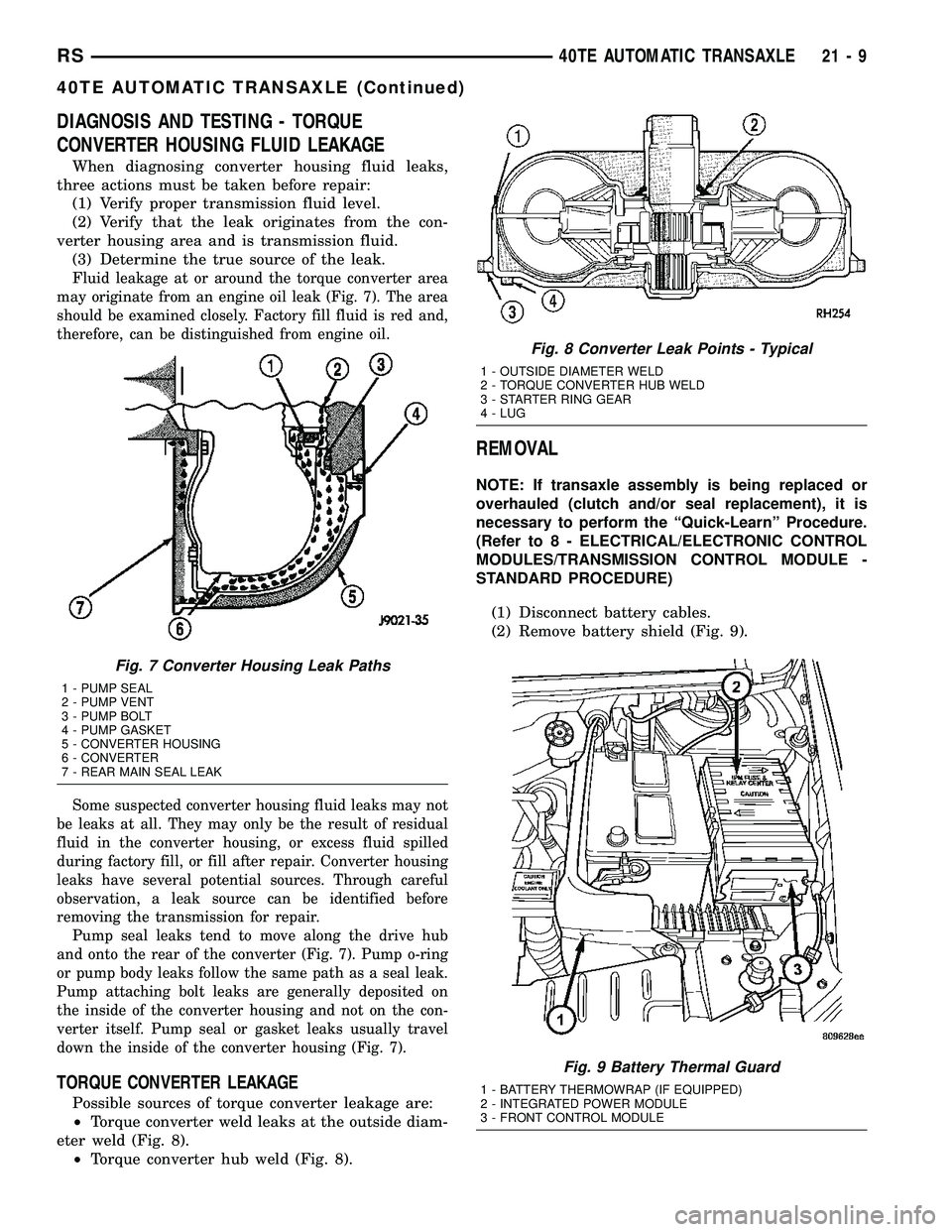
F
luid leakage at or around the torque converter area
may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 7). The area
should be examined closely. Factory fill fluid is red and,
therefore, can be distinguished from engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may not
be leaks at all. They may only be the result of residual
fluid in the converter housing, or excess fluid spilled
during factory fill, or fill after repair. Converter housing
leaks have several potential sources. Through careful
observation, a leak source can be identified before
removing the transmission for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 7). Pump o-ring
or pump body leaks follow the same path as a seal leak.
Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally deposited on
the inside of the converter housing and not on the con-
verter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaks usually travel
down the inside of the converter housing (Fig. 7).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 8).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transaxle assembly is being replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perform the ªQuick-Learnº Procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield (Fig. 9).
Fig. 7 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 8 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
Fig. 9 Battery Thermal Guard
1 - BATTERY THERMOWRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-9
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1472 of 2339
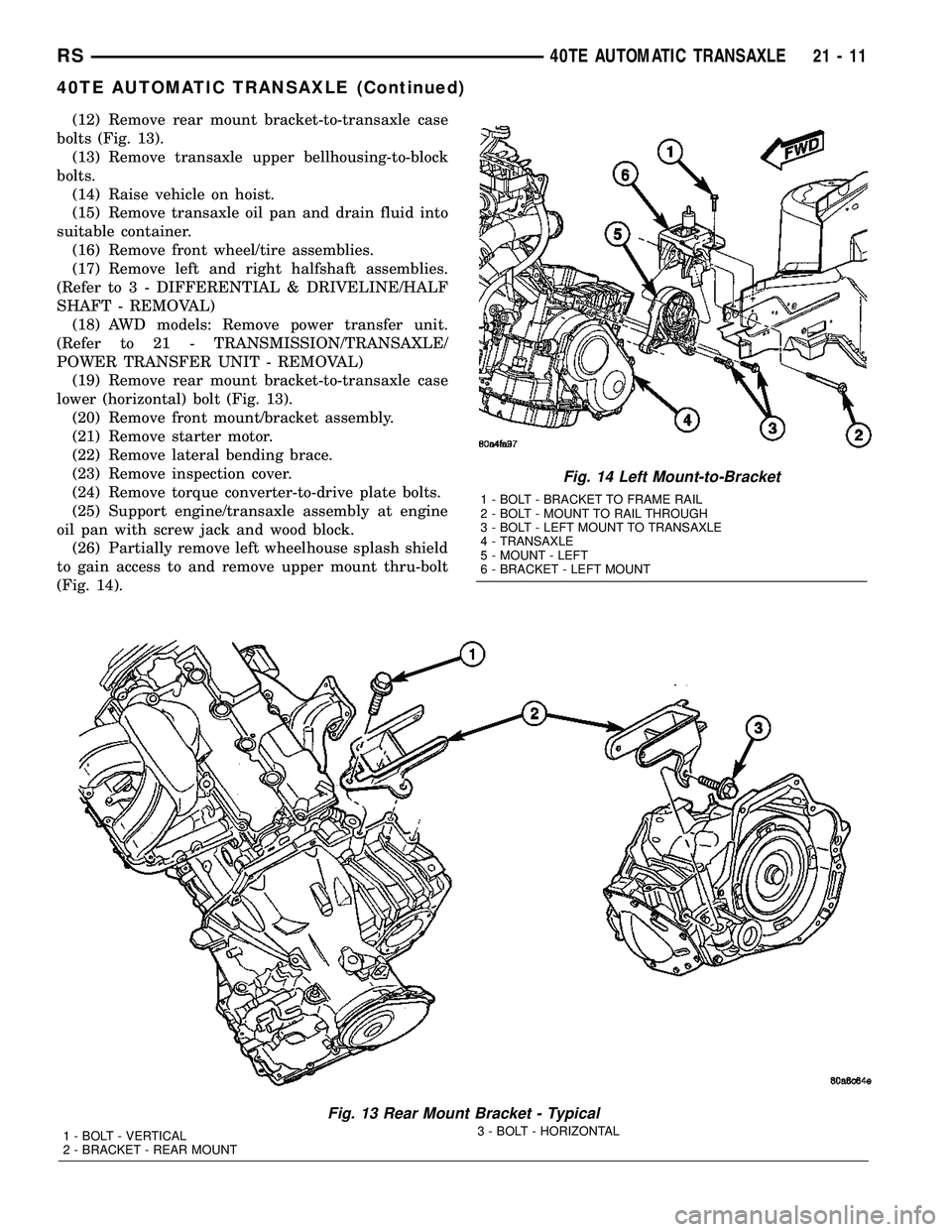
(12) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 13).
(13) Remove transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts.
(14) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(15) Remove transaxle oil pan and drain fluid into
suitable container.
(16) Remove front wheel/tire assemblies.
(17) Remove left and right halfshaft assemblies.
(Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF
SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(18) AWD models: Remove power transfer unit.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
POWER TRANSFER UNIT - REMOVAL)
(19) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
lower (horizontal) bolt (Fig. 13).
(20) Remove front mount/bracket assembly.
(21) Remove starter motor.
(22) Remove lateral bending brace.
(23) Remove inspection cover.
(24) Remove torque converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(25) Support engine/transaxle assembly at engine
oil pan with screw jack and wood block.
(26) Partially remove left wheelhouse splash shield
to gain access to and remove upper mount thru-bolt
(Fig. 14).
Fig. 13 Rear Mount Bracket - Typical
1 - BOLT - VERTICAL
2 - BRACKET - REAR MOUNT3 - BOLT - HORIZONTAL
Fig. 14 Left Mount-to-Bracket
1 - BOLT - BRACKET TO FRAME RAIL
2 - BOLT - MOUNT TO RAIL THROUGH
3 - BOLT - LEFT MOUNT TO TRANSAXLE
4 - TRANSAXLE
5 - MOUNT - LEFT
6 - BRACKET - LEFT MOUNT
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-11
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1473 of 2339
(27) Lower engine/transaxle assembly with screw
jack.
(28) Obtain helper and/or transmission jack.
Secure transmission jack to transaxle assembly.
(29) Remove upper mount bracket from transaxle
(Fig. 14).
(30) Remove remaining transaxle bellhousing-to-
engine bolts.
(31) Remove transaxle assembly from vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: If transaxle is being overhauled (clutch
and/or seal replacement) or replaced, it is neces-
sary to perform the PCM/TCM Quick Learn Proce-
dure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN/TRANSMIS-
SION CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
NOTE: This procedure does not include final drive
(differential) disassembly.
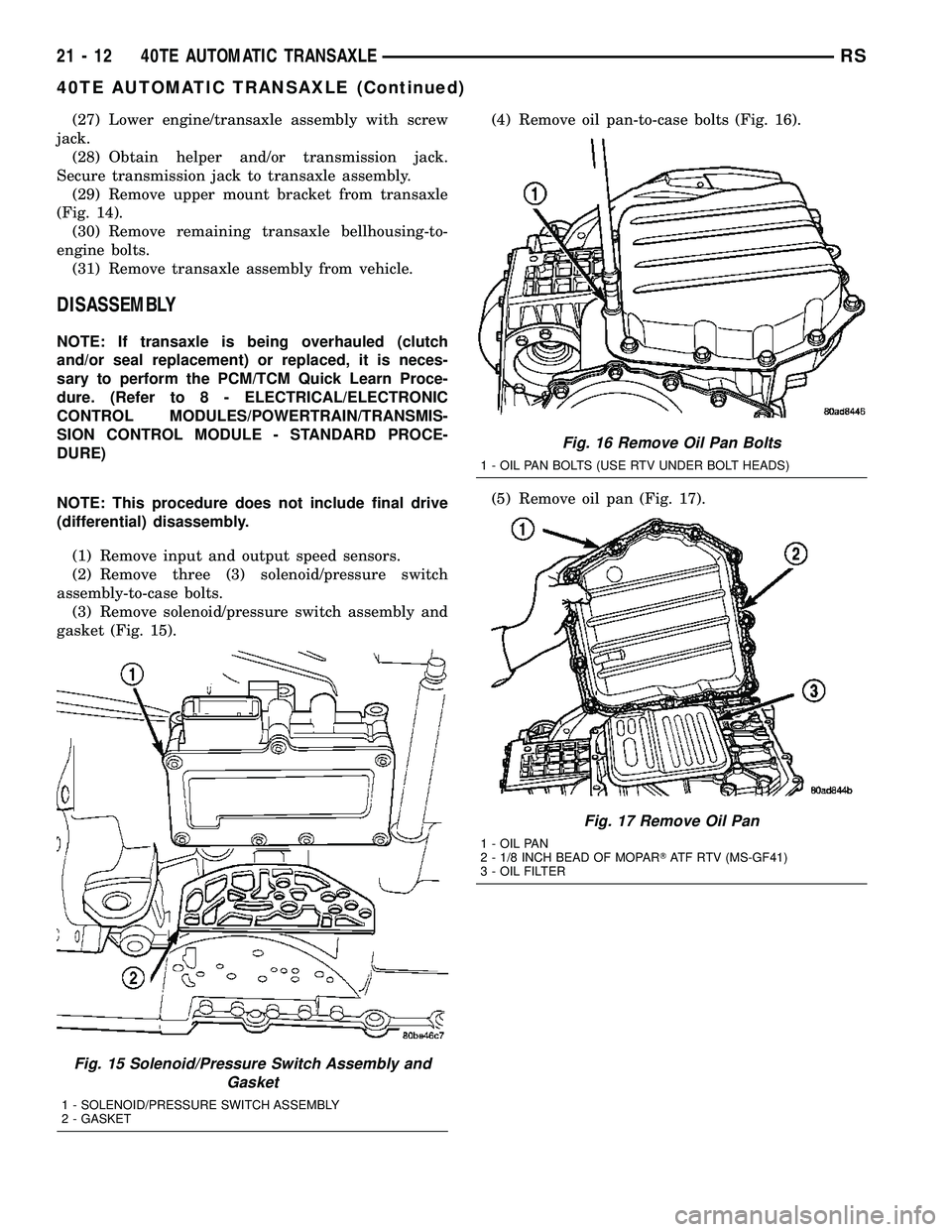
(1) Remove input and output speed sensors.
(2) Remove three (3) solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-case bolts.
(3) Remove solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
gasket (Fig. 15).(4) Remove oil pan-to-case bolts (Fig. 16).
(5) Remove oil pan (Fig. 17).
Fig. 15 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly and
Gasket
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - GASKET
Fig. 16 Remove Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
Fig. 17 Remove Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF MOPARTATF RTV (MS-GF41)
3 - OIL FILTER
21 - 12 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1475 of 2339
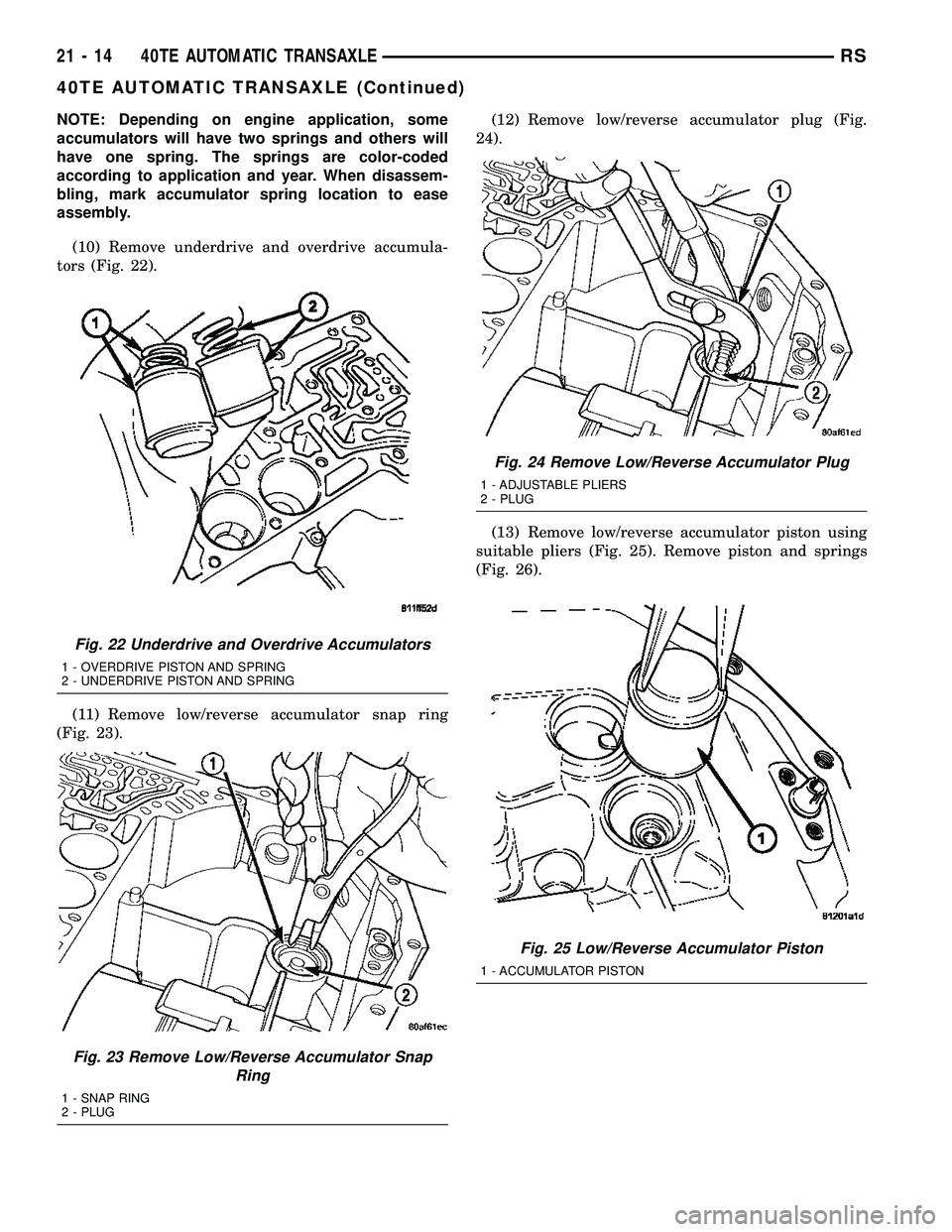
NOTE: Depending on engine application, some
accumulators will have two springs and others will
have one spring. The springs are color-coded
according to application and year. When disassem-
bling, mark accumulator spring location to ease
assembly.
(10) Remove underdrive and overdrive accumula-
tors (Fig. 22).
(11) Remove low/reverse accumulator snap ring
(Fig. 23).(12) Remove low/reverse accumulator plug (Fig.
24).
(13) Remove low/reverse accumulator piston using
suitable pliers (Fig. 25). Remove piston and springs
(Fig. 26).
Fig. 22 Underdrive and Overdrive Accumulators
1 - OVERDRIVE PISTON AND SPRING
2 - UNDERDRIVE PISTON AND SPRING
Fig. 23 Remove Low/Reverse Accumulator Snap
Ring
1 - SNAP RING
2 - PLUG
Fig. 24 Remove Low/Reverse Accumulator Plug
1 - ADJUSTABLE PLIERS
2 - PLUG
Fig. 25 Low/Reverse Accumulator Piston
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
21 - 14 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1510 of 2339
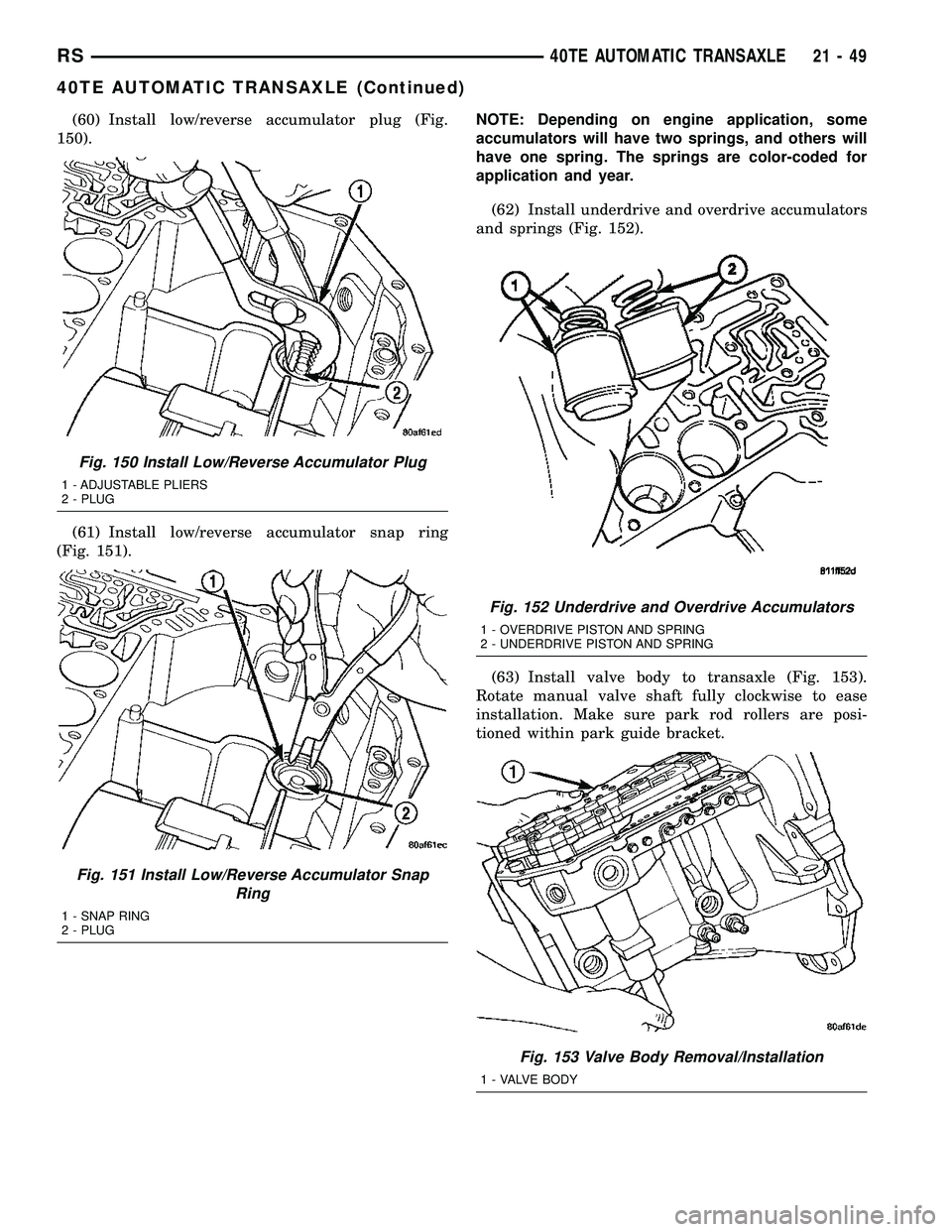
(60) Install low/reverse accumulator plug (Fig.
150).
(61) Install low/reverse accumulator snap ring
(Fig. 151).NOTE: Depending on engine application, some
accumulators will have two springs, and others will
have one spring. The springs are color-coded for
application and year.
(62) Install underdrive and overdrive accumulators
and springs (Fig. 152).
(63) Install valve body to transaxle (Fig. 153).
Rotate manual valve shaft fully clockwise to ease
installation. Make sure park rod rollers are posi-
tioned within park guide bracket.
Fig. 150 Install Low/Reverse Accumulator Plug
1 - ADJUSTABLE PLIERS
2 - PLUG
Fig. 151 Install Low/Reverse Accumulator Snap
Ring
1 - SNAP RING
2 - PLUG
Fig. 152 Underdrive and Overdrive Accumulators
1 - OVERDRIVE PISTON AND SPRING
2 - UNDERDRIVE PISTON AND SPRING
Fig. 153 Valve Body Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE BODY
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-49
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)