2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN key battery
[x] Cancel search: key batteryPage 1400 of 2339

Also like the cam and crank sensors, a 5 volt ref-
erence is supplied from the PCM and returns a volt-
age signal to the PCM that reflects manifold
pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V and full
scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of0Ð15psithe
voltage changes 4.0V. The sensor is supplied a regu-
lated 4.8 to 5.1 volts to operate the sensor. Like the
cam and crank sensors ground is provided through
the sensor return circuit.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to pulse width. The most important function of
the MAP sensor is to determine barometric pressure.
The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is at sea level
or is it in Denver at 5000 feet above sea level,
because the air density changes with altitude. It will
also help to correct for varying weather conditions. If
a hurricane was coming through the pressure would
be very, very low or there could be a real fair
weather, high pressure area. This is important
because as air pressure changes the barometric pres-
sure changes. Barometric pressure and altitude have
a direct inverse correlation, as altitude goes up baro-
metric goes down. The first thing that happens as
the key is rolled on, before reaching the crank posi-
tion, the PCM powers up, comes around and looks at
the MAP voltage, and based upon the voltage it sees,
it knows the current barometric pressure relative to
altitude. Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at
the voltage again, continuously every 12 milliseconds,
and compares the current voltage to what it was at
key on. The difference between current and what it
was at key on is manifold vacuum.
During key On (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring known good sensor in
you work area.As the altitude increases the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to a
very different altitude than where it was at key On
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open throttle, based upon
TPS angle and RPM it will update barometric pres-
sure in the MAP memory cell. With periodic updates,
the PCM can make its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor to aid in calculat-
ing the following:
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Manifold pressure
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (F4AC1 transmissions
only, via the PCI bus)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; as pressure
changes, voltage changes proportionately. The range
of voltage output from the sensor is usually between
4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3 volts at 26 in. of
Hg. Barometric pressure is the pressure exerted by
the atmosphere upon an object. At sea level on a
standard day, no storm, barometric pressure is 29.92
in Hg. For every 100 feet of altitude barometric pres-
sure drops .10 in. Hg. If a storm goes through it can
either add, high pressure, or decrease, low pressure,
from what should be present for that altitude. You
should make a habit of knowing what the average
pressure and corresponding barometric pressure is
for your area.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector and vacuum
hose from MAP sensor (Fig. 20).
(3) Remove two screws holding sensor to the
intake manifold.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove vacuum hose and mounting screws
from manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig.
21).
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
Remove sensor.
Fig. 21 MAP SENSOR - 3.3/3.8L
RSFUEL INJECTION14-35
MAP SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1417 of 2339
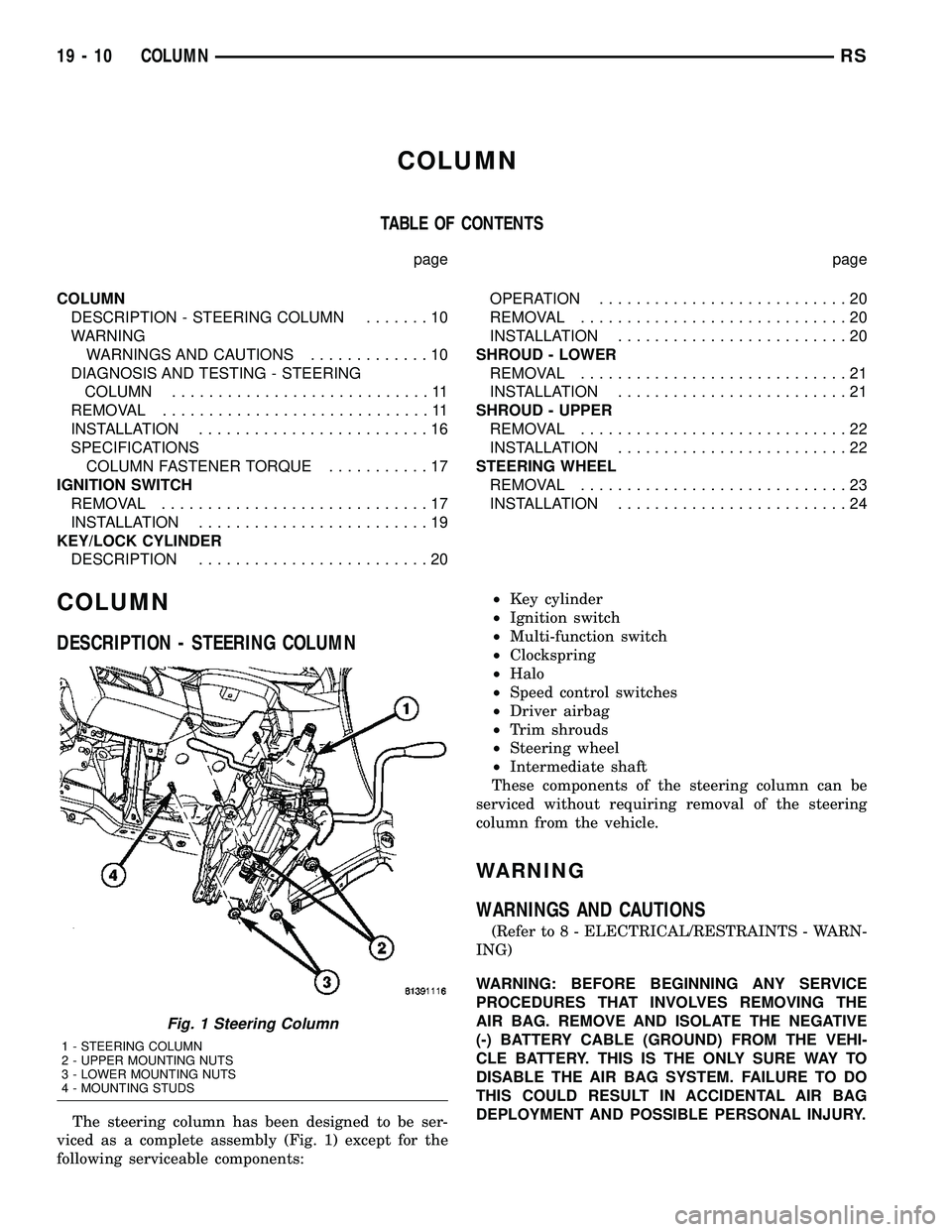
COLUMN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION - STEERING COLUMN.......10
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS.............10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
COLUMN............................11
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................16
SPECIFICATIONS
COLUMN FASTENER TORQUE...........17
IGNITION SWITCH
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................19
KEY/LOCK CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION.........................20OPERATION...........................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................20
SHROUD - LOWER
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
SHROUD - UPPER
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
STEERING WHEEL
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................24
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION - STEERING COLUMN
The steering column has been designed to be ser-
viced as a complete assembly (Fig. 1) except for the
following serviceable components:²Key cylinder
²Ignition switch
²Multi-function switch
²Clockspring
²Halo
²Speed control switches
²Driver airbag
²Trim shrouds
²Steering wheel
²Intermediate shaft
These components of the steering column can be
serviced without requiring removal of the steering
column from the vehicle.
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - WARN-
ING)
WARNING: BEFORE BEGINNING ANY SERVICE
PROCEDURES THAT INVOLVES REMOVING THE
AIR BAG. REMOVE AND ISOLATE THE NEGATIVE
(-) BATTERY CABLE (GROUND) FROM THE VEHI-
CLE BATTERY. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO
DISABLE THE AIR BAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO DO
THIS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
Fig. 1 Steering Column
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - UPPER MOUNTING NUTS
3 - LOWER MOUNTING NUTS
4 - MOUNTING STUDS
19 - 10 COLUMNRS
Page 1427 of 2339
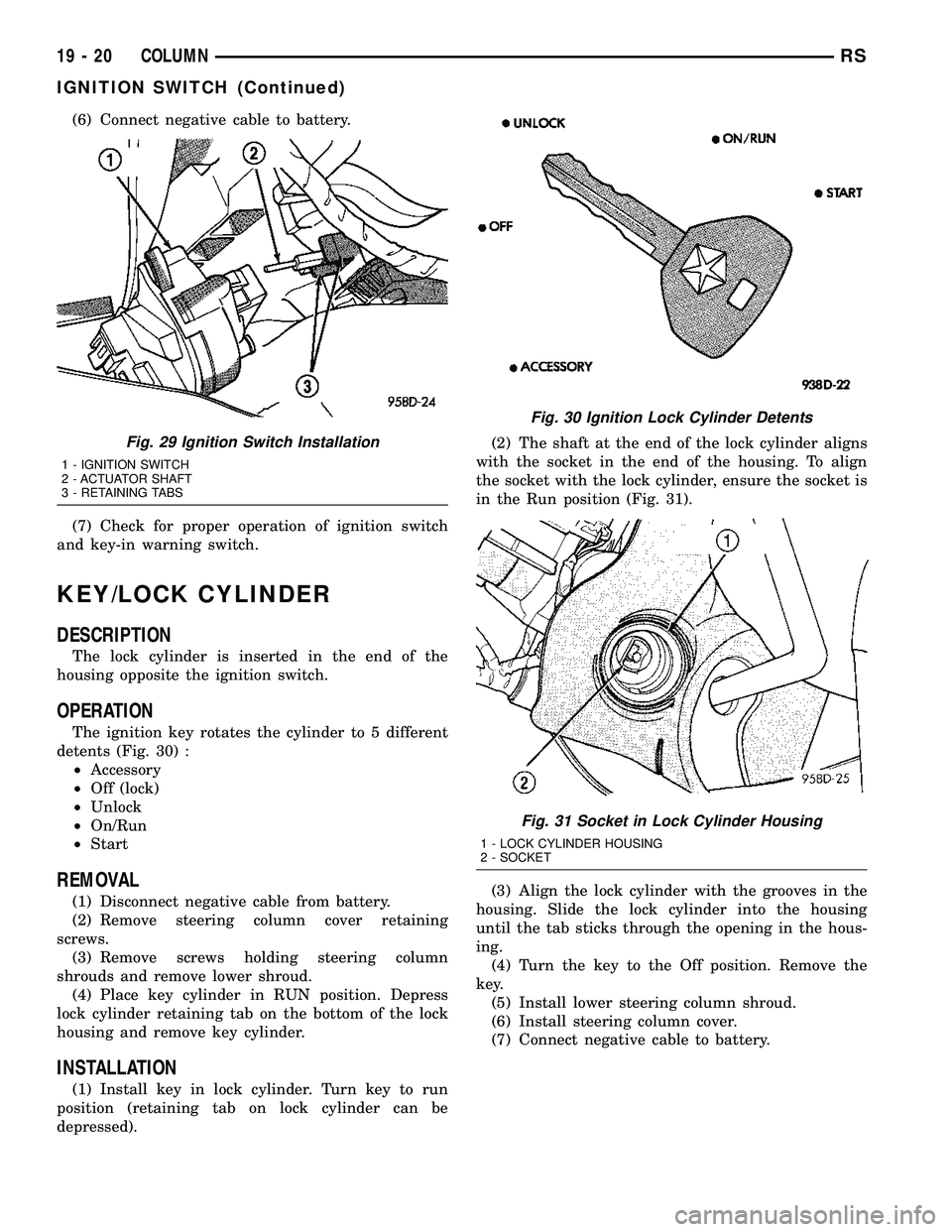
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
(7) Check for proper operation of ignition switch
and key-in warning switch.
KEY/LOCK CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
The lock cylinder is inserted in the end of the
housing opposite the ignition switch.
OPERATION
The ignition key rotates the cylinder to 5 different
detents (Fig. 30) :
²Accessory
²Off (lock)
²Unlock
²On/Run
²Start
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove steering column cover retaining
screws.
(3) Remove screws holding steering column
shrouds and remove lower shroud.
(4) Place key cylinder in RUN position. Depress
lock cylinder retaining tab on the bottom of the lock
housing and remove key cylinder.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install key in lock cylinder. Turn key to run
position (retaining tab on lock cylinder can be
depressed).(2) The shaft at the end of the lock cylinder aligns
with the socket in the end of the housing. To align
the socket with the lock cylinder, ensure the socket is
in the Run position (Fig. 31).
(3) Align the lock cylinder with the grooves in the
housing. Slide the lock cylinder into the housing
until the tab sticks through the opening in the hous-
ing.
(4) Turn the key to the Off position. Remove the
key.
(5) Install lower steering column shroud.
(6) Install steering column cover.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 29 Ignition Switch Installation
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - ACTUATOR SHAFT
3 - RETAINING TABS
Fig. 30 Ignition Lock Cylinder Detents
Fig. 31 Socket in Lock Cylinder Housing
1 - LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
2 - SOCKET
19 - 20 COLUMNRS
IGNITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1575 of 2339
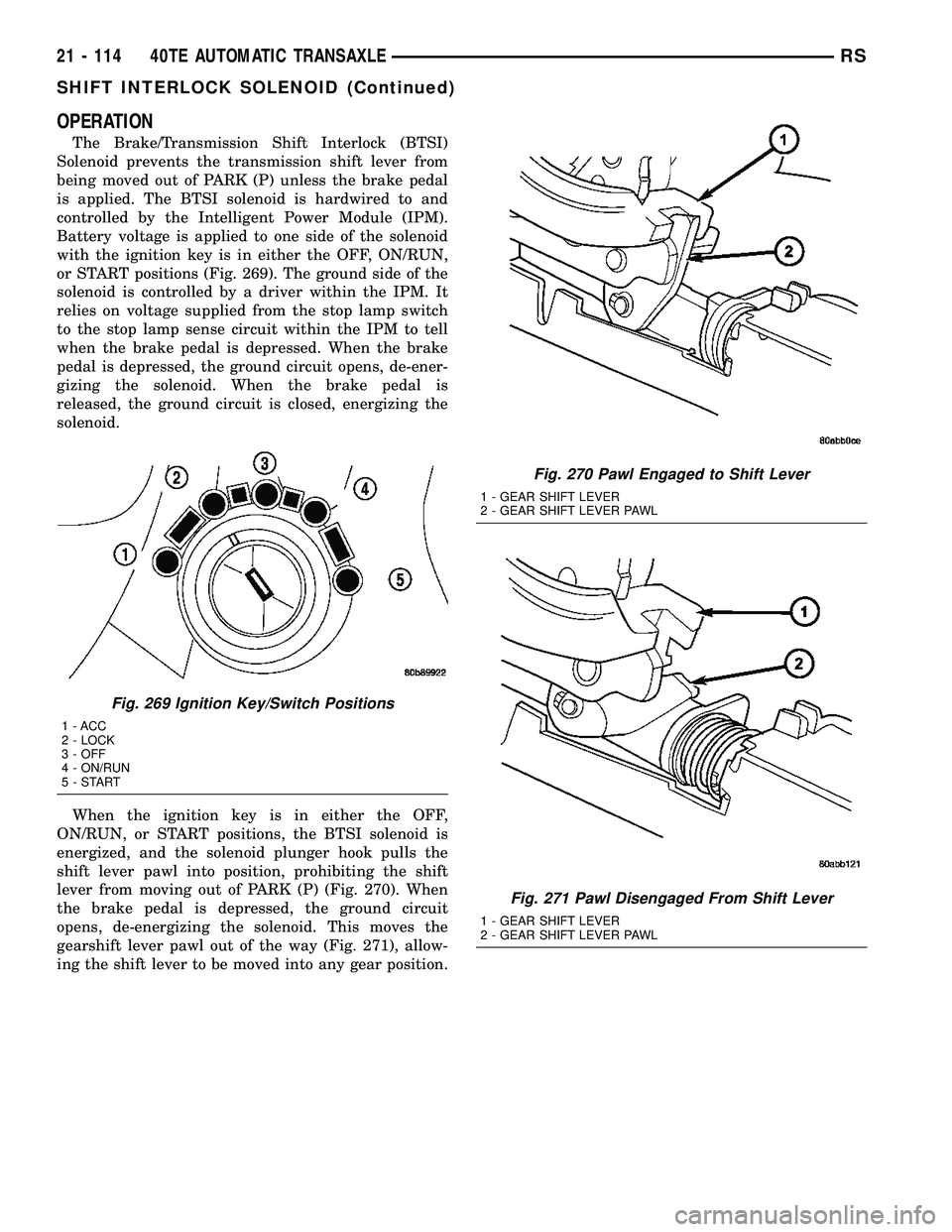
OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the OFF, ON/RUN,
or START positions (Fig. 269). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 270). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 271), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position.
Fig. 269 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 270 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 271 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
21 - 114 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1576 of 2339
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
272).
(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 273).
Fig. 272 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 273 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 115
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1591 of 2339

TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission control relay (Fig. 306) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized by
the PCM/TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal operating
mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to
the solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset (ignition key turned to the
ªrunº position or after cranking engine), the PCM/TCM
energizes the relay. Prior to this, the PCM/TCM verifies
that the contacts are open by checking for no voltage at
the switched battery terminals. After this is verified,
the voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the PCM/TCM
monitors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle andcan only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 307).
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the PCM/TCM.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 308).
Fig. 306 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERY
Fig. 307 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 308 Transmission Temperature Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - TEMPERATURE SENSOR
21 - 130 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1696 of 2339
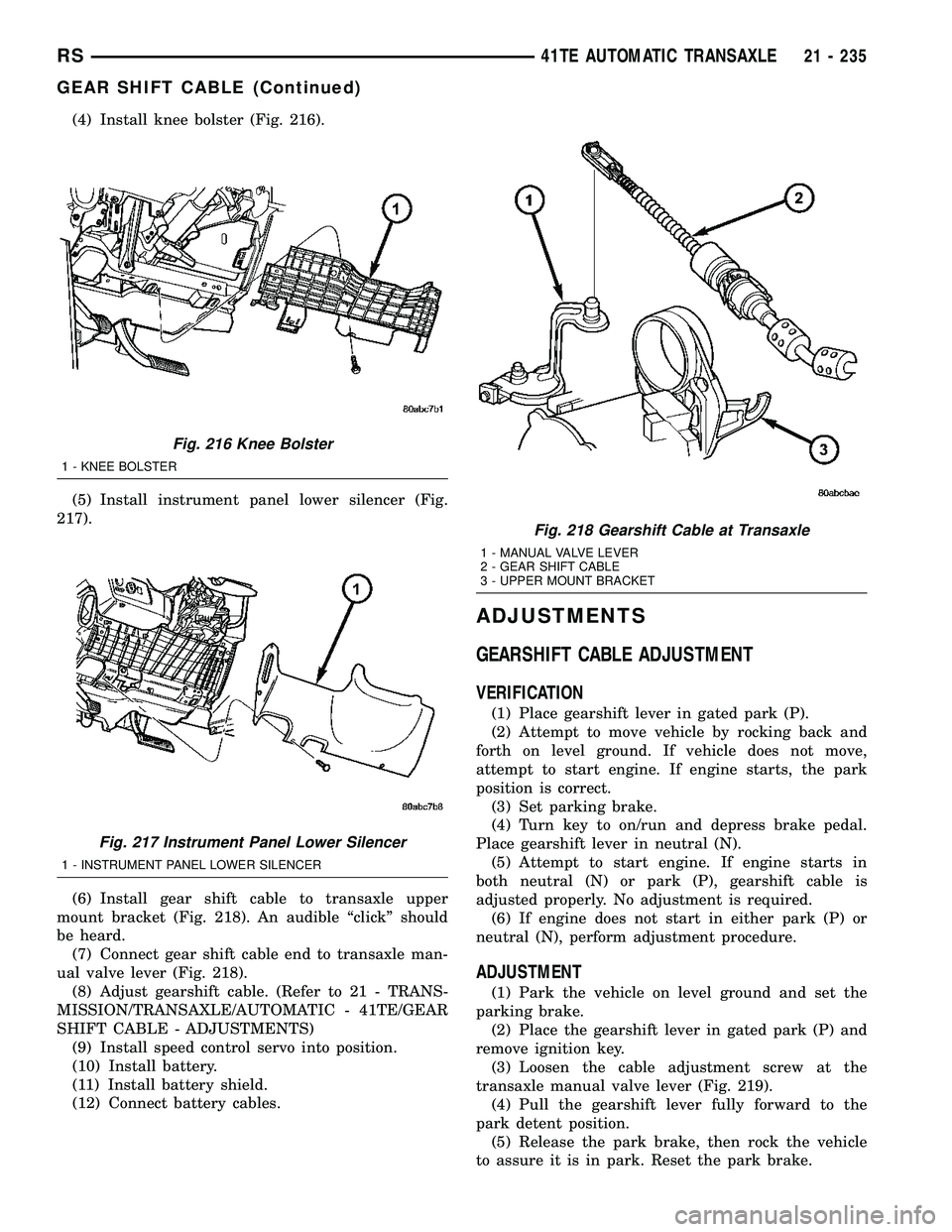
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 216).
(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
217).
(6) Install gear shift cable to transaxle upper
mount bracket (Fig. 218). An audible ªclickº should
be heard.
(7) Connect gear shift cable end to transaxle man-
ual valve lever (Fig. 218).
(8) Adjust gearshift cable. (Refer to 21 - TRANS-
MISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/GEAR
SHIFT CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS)
(9) Install speed control servo into position.
(10) Install battery.
(11) Install battery shield.
(12) Connect battery cables.
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
VERIFICATION
(1) Place gearshift lever in gated park (P).
(2) Attempt to move vehicle by rocking back and
forth on level ground. If vehicle does not move,
attempt to start engine. If engine starts, the park
position is correct.
(3) Set parking brake.
(4) Turn key to on/run and depress brake pedal.
Place gearshift lever in neutral (N).
(5) Attempt to start engine. If engine starts in
both neutral (N) or park (P), gearshift cable is
adjusted properly. No adjustment is required.
(6) If engine does not start in either park (P) or
neutral (N), perform adjustment procedure.
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Park the vehicle on level ground and set the
parking brake.
(2) Place the gearshift lever in gated park (P) and
remove ignition key.
(3) Loosen the cable adjustment screw at the
transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 219).
(4) Pull the gearshift lever fully forward to the
park detent position.
(5) Release the park brake, then rock the vehicle
to assure it is in park. Reset the park brake.
Fig. 216 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 217 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 218 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 235
GEAR SHIFT CABLE (Continued)
Page 1726 of 2339
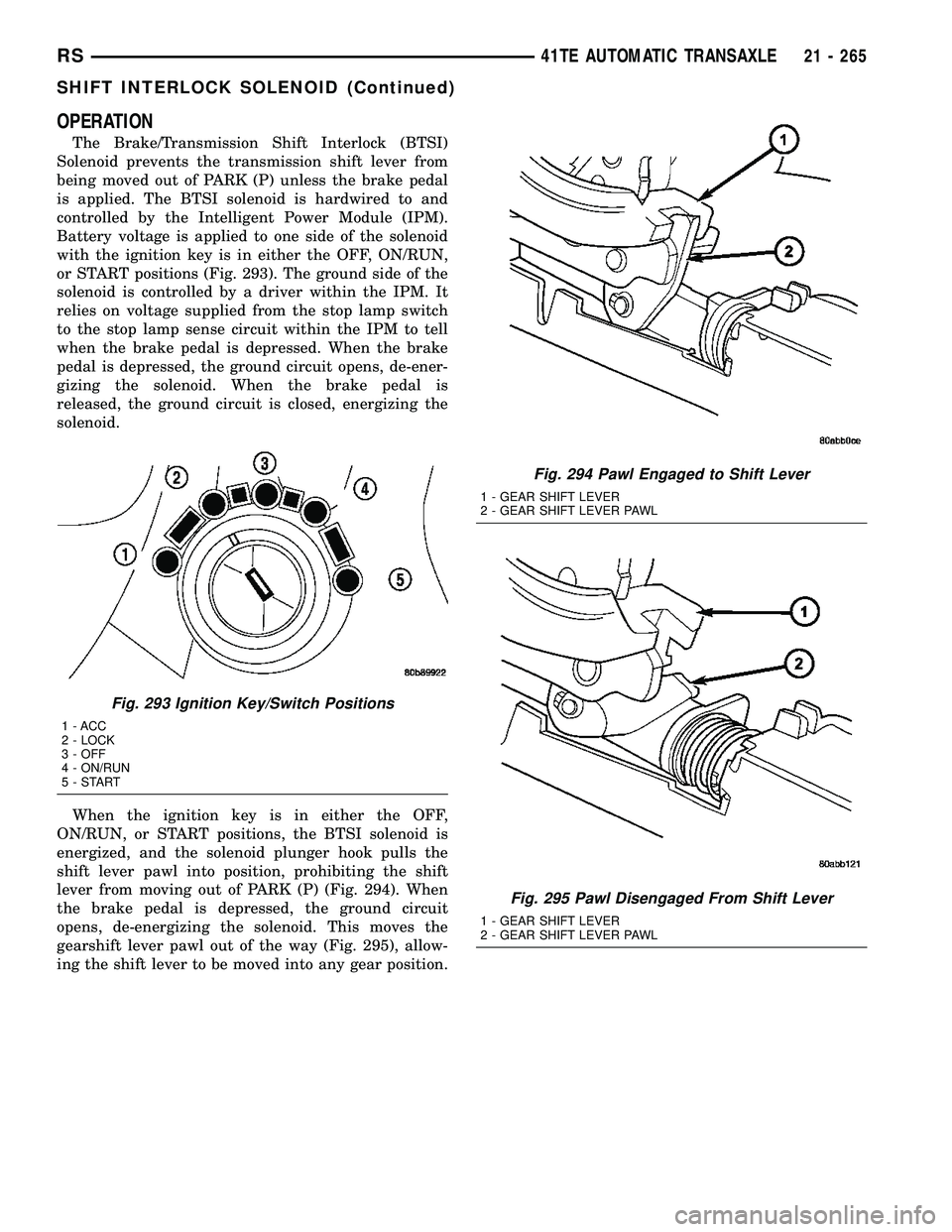
OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the OFF, ON/RUN,
or START positions (Fig. 293). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 294). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 295), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position.
Fig. 293 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 294 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 295 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 265
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)