2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN maintenance
[x] Cancel search: maintenancePage 48 of 2339

4 bolts. The driveshaft's constant velocity (C/V) stub
axle is splined through the center of the hub and
bearing and is held in place using a nut, nut lock and
cotter pin.
Service replacement of the front hub and bearing
assembly can be done with the steering knuckle
remaining on the vehicle.
OPERATION
The steering knuckle pivots with the strut assem-
bly between the lower ball joint and the pivot bearing
in the strut assembly. The steering gear outer tie rod
end connects to the trailing end of each knuckle,
allowing the vehicle to be steered.
The center of the knuckle supports the hub and
bearing and axle shaft.
REMOVAL - STEERING KNUCKLE
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly from the
vehicle.
(3) Remove the cotter pin, nut lock and spring
washer from the end of the stub axle and hub nut
(Fig. 8).
(4) Have a helper apply the vehicle's brakes to
keep hub from turning,loosen and removethe hub
nut (Fig. 8).
(5) Remove disc brake caliper and adapter as an
assembly from knuckle as shown (Fig. 9). Hang
assembly out of the way using a bungee cord or wire
(Fig. 10).Do not allow caliper to hang by brake
hose.
(6) Remove nut attaching outer tie rod end to
steering knuckle by holding the tie rod end studwhile loosening and removing nut with a wrench
(Fig. 11).
Fig. 8 Hub Nut
1 - HUB NUT
2 - NUT LOCK
3 - COTTER PIN
4 - SPRING WASHER
Fig. 9 Front Brake Mounting
1 - BRAKE ROTOR
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - BRAKE CALIPER
6 - ADAPTER
7 - CLIP
Fig. 10 Caliper And Driveshaft Suspended
1 - HANGER SUSPENDING CALIPER
2 - HANGER SUSPENDING DRIVESHAFT
3 - DRIVESHAFT
4 - BRAKE CALIPER
RSFRONT SUSPENSION2-7
KNUCKLE (Continued)
Page 51 of 2339
(6) Install tie rod end into knuckle steering arm.
Start nut onto stud of tie rod end. While holding stud
of tie rod end stationary using a socket (Fig. 11),
tighten tie rod end to steering knuckle attaching nut.
Tighten the tie rod end nut to a torque of 75 N´m (55
ft. lbs.).
(7) If equipped with antilock brakes, install wheel
speed sensor and mounting bolt on steering knuckle
(Fig. 13). Tighten the speed sensor bolt to a torque of
7 N´m (60 in. lbs.).
(8) Install brake rotor on hub and bearing (Fig. 9).
(9) Install disc brake caliper and adapter assembly
on steering knuckle. Install adapter amounting bolts
and tighten to 169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
(10) Clean any debris from the threads of the
outer C/V joint stub axle.
(11) Install the washer and hub nut on stub axle.
(12) Have a helper apply the vehicle's brakes to
keep hub from turning, then tighten hub nut to a
torque of 244 N´m (180 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the spring wave washer on the end of
the stub axle.
(14) Install the hub nut lock, and anewcotter pin
(Fig. 8). Wrap cotter pin prongs tightly around the
hub nut lock.
(15) Install wheel and tire assembly. Install and
tighten the wheel mounting nuts in proper sequence
until all nuts are torqued to half the required speci-
fication. Then repeat the tightening sequence to the
full specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(16) Lower vehicle.
(17) Set front wheel alignment camber and toe as
necessary. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/WHEEL
ALIGNMENT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
LOWER BALL JOINT
DESCRIPTION
The ball joint is an integral part of the lower con-
trol arm (Fig. 1). The ball joint has a tapered stud
that is pressed into the aluminum knuckle. The ball
joint stud is threaded on the end for a retainer nut.
The ball joint has a non-vented seal boot. The seal
boot has an integrated heat shield.
The ball joint used in the lower control arm of this
vehicle is a sealed-for-life ball joint and requires no
maintenance lubrication. The ball joint has been
lubricated-for-life during the manufacturing process.
A special fitting cap is installed on the fill port. This
cap must not be removed and replaced with a com-
mon zirc fitting. The special cap is there to eliminate
the possibility of lubrication latter during the ball
joints life, thus damaging the non-vented seal boot.
NOTE: The ball joint does not require any type of
additional lubrication for the life of the vehicle. No
attempt should be made to ever add any lubrication
to the lower ball joint.
OPERATION
The ball joint is a pivotal joint on the lower control
arm that allows the knuckle to move up and down,
and turn with ease.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LOWER BALL
JOINT
With the weight of the vehicle resting on the road
wheels, grasp the special fitting cap on the bottom of
the ball joint and with no mechanical assistance or
added force, attempt to rotate the grease fitting.
If the ball joint is worn, the grease fitting will
rotate easily. If movement is noted, replacement of
the control arm is recommended.
LOWER BALL JOINT SEAL
BOOT
DESCRIPTION - EXPORT
The lower ball joint seal boot is a two piece unit. It
consists of the seal boot, plus a separate shield that
is located in a groove at the top of the seal boot.
NOTE: The seal boot should only be replaced if
damaged during vehicle service. The entire lower
control arm should be replaced if the joint has been
contaminated.
Fig. 16 Correctly Installed Eccentric Attaching Bolt
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - FLANGED BOLT IN TOP HOLE
3 - CAM BOLT IN BOTTOM HOLE
4 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
2 - 10 FRONT SUSPENSIONRS
KNUCKLE (Continued)
Page 53 of 2339
CAUTION: Do not use an arbor press to install the
sealing boot on the ball joint. Damage to the seal-
ing boot will occur if excessive pressure is applied
to the sealing boot when it is being installed.
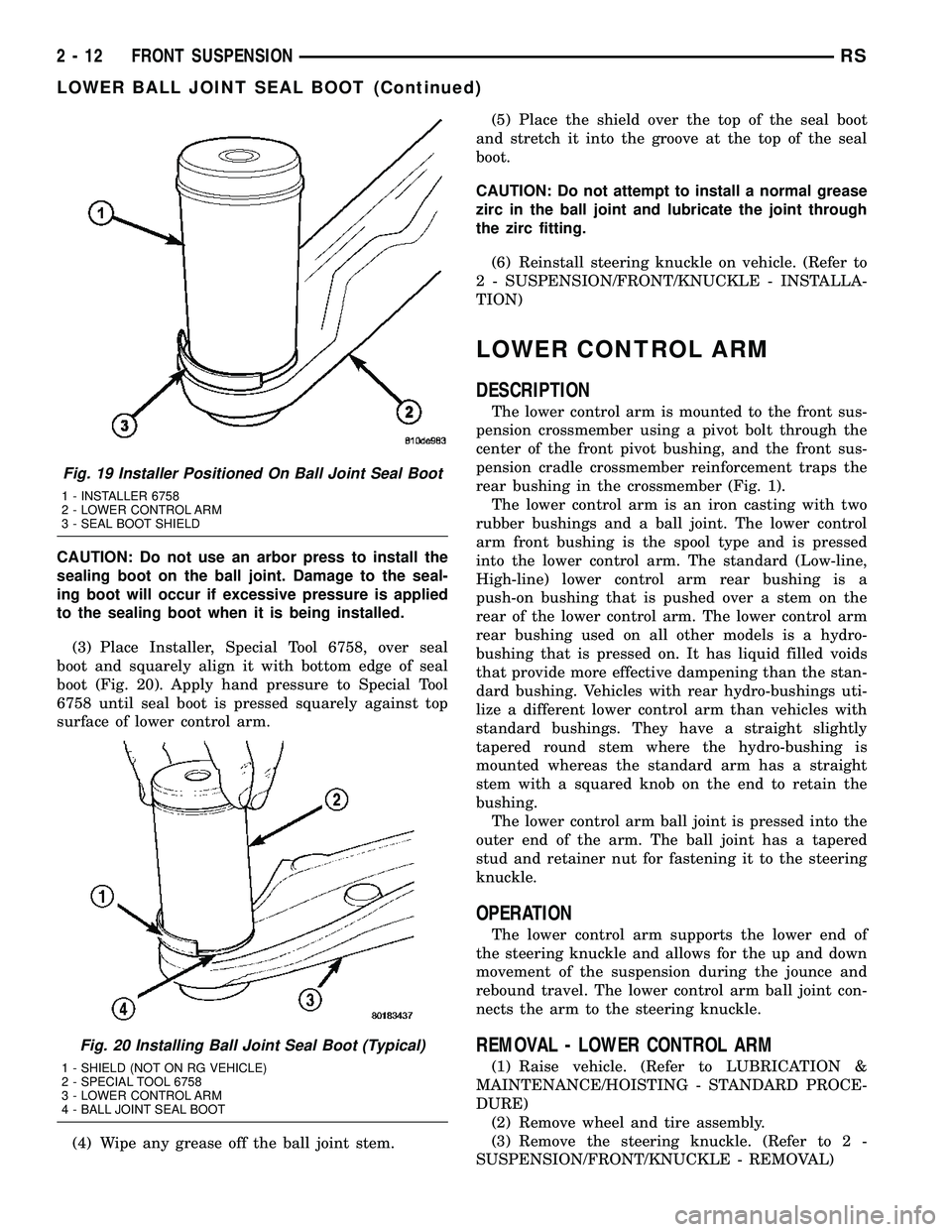
(3) Place Installer, Special Tool 6758, over seal
boot and squarely align it with bottom edge of seal
boot (Fig. 20). Apply hand pressure to Special Tool
6758 until seal boot is pressed squarely against top
surface of lower control arm.
(4) Wipe any grease off the ball joint stem.(5) Place the shield over the top of the seal boot
and stretch it into the groove at the top of the seal
boot.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to install a normal grease
zirc in the ball joint and lubricate the joint through
the zirc fitting.
(6) Reinstall steering knuckle on vehicle. (Refer to
2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
LOWER CONTROL ARM
DESCRIPTION
The lower control arm is mounted to the front sus-
pension crossmember using a pivot bolt through the
center of the front pivot bushing, and the front sus-
pension cradle crossmember reinforcement traps the
rear bushing in the crossmember (Fig. 1).
The lower control arm is an iron casting with two
rubber bushings and a ball joint. The lower control
arm front bushing is the spool type and is pressed
into the lower control arm. The standard (Low-line,
High-line) lower control arm rear bushing is a
push-on bushing that is pushed over a stem on the
rear of the lower control arm. The lower control arm
rear bushing used on all other models is a hydro-
bushing that is pressed on. It has liquid filled voids
that provide more effective dampening than the stan-
dard bushing. Vehicles with rear hydro-bushings uti-
lize a different lower control arm than vehicles with
standard bushings. They have a straight slightly
tapered round stem where the hydro-bushing is
mounted whereas the standard arm has a straight
stem with a squared knob on the end to retain the
bushing.
The lower control arm ball joint is pressed into the
outer end of the arm. The ball joint has a tapered
stud and retainer nut for fastening it to the steering
knuckle.
OPERATION
The lower control arm supports the lower end of
the steering knuckle and allows for the up and down
movement of the suspension during the jounce and
rebound travel. The lower control arm ball joint con-
nects the arm to the steering knuckle.
REMOVAL - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the steering knuckle. (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - REMOVAL)
Fig. 19 Installer Positioned On Ball Joint Seal Boot
1 - INSTALLER 6758
2 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
3 - SEAL BOOT SHIELD
Fig. 20 Installing Ball Joint Seal Boot (Typical)
1 - SHIELD (NOT ON RG VEHICLE)
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6758
3 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 - BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT
2 - 12 FRONT SUSPENSIONRS
LOWER BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT (Continued)
Page 58 of 2339

REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove the bolts fastening the power steering
cooler to the front suspension cradle crossmember
reinforcement (Fig. 31).
(3) Remove the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer bolts located on each side of each lower con-
trol arm rear bushing.
NOTE: The bolts fastening the cradle crossmember
reinforcement are of two different thread sizes. Note
the location of the various sizes.
(4) Remove the bolts attaching the cradle cross-
member reinforcement to the front suspension cradle
crossmember (Fig. 32). Remove the 2 bolts fastening
the reinforcement and rear of cradle crossmember to
the body of the vehicle. Remove the reinforcement.
CAUTION: When removing the nut from the stud of
the stabilizer bar link, do not allow the stud to
rotate in it's socket. Hold the stud from rotating by
placing an open-end wrench on the flat machined
into the stud (Fig. 33).
(5) Remove the stabilizer bar links from each end
of the stabilizer bar (Fig. 33). To do so, place an open-
end wrench on the flat machined into the link's
mounting stud, then remove the nut while holding
the wrench in place. Push each stud out of the hole
in the stabilizer bar.(6) Remove the stabilizer bar bushing (cushion)
retainers from the front suspension cradle crossmem-
ber (Fig. 34).
(7) Remove the stabilizer bar and bushings (cush-
ions) as an assembly from the front suspension cra-
dle crossmember.
INSPECTION
Inspect for broken or distorted stabilizer bar bush-
ings (cushions), bushing retainers, and worn or dam-
aged stabilizer bar links.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Two different diameter stabilizer bars are
available for this vehicle. Therefore, two different
size bushings/cushions are also used. Use the cor-
rect bushing/cushion on the correct stabilizer bar.
Fig. 31 Power Steering Cooler
1 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER REINFORCEMENT
2 - POWER STEERING COOLERFig. 32 Cradle Crossmember Reinforcement
Attachment
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - RIGHT LOWER CONTROL ARM
3 - LEFT LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER REINFORCEMENT
5 - REAR CRADLE CROSSMEMBER ISOLATOR BUSHING
6 - STABILIZER BAR
7 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER
RSFRONT SUSPENSION2-17
STABILIZER BAR (Continued)
Page 61 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STRUT ASSEMBLY
(1) Inspect for damaged or broken coil springs
(Fig. 38).
(2) Inspect for torn or damaged strut assembly
dust boots (Fig. 38).
(3) Inspect the coil spring isolator on the lower
spring seat for any signs of damage or deterioration.
(4) Lift dust boot (Fig. 39) and inspect strut
assembly for evidence of fluid running from the
upper end of fluid reservoir. (Actual leakage will be a
stream of fluid running down the side and dripping
off lower end of unit). A slight amount of seepage
between the strut rod and strut shaft seal is not
unusual and does not affect performance of the strut
assembly (Fig. 39). Also inspect jounce bumpers for
signs of damage or deterioration.
REMOVAL - STRUT ASSEMBLY
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE NUT FROM THE
STRUT ROD WHILE STRUT ASSEMBLY IS
INSTALLED IN VEHICLE, OR BEFORE STRUT
ASSEMBLY SPRING IS COMPRESSED.
(1) Raise the vehicle. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
Fig. 38 STRUT ASSEMBLY
1 - NUT 6 - COIL SPRING
2 - UPPER MOUNT 7 - DUST SHIELD
3 - PIVOT BEARING 8 - JOUNCE BUMPER
4 - UPPER SPRING SEAT 9 - LOWER SPRING ISOLATOR
5 - UPPER SPRING ISOLATOR 10 - STRUT (DAMPER)
Fig. 39 Strut Assembly Leakage Inspection (Typical)
1 - DUST BOOT
2 - STRUT SHAFT
3 - STRUT FLUID RESERVOIR
4 - INSPECT THIS AREA FOR EVIDENCE OF EXCESSIVE FLUID
LEAKAGE
2 - 20 FRONT SUSPENSIONRS
STRUT (Continued)
Page 70 of 2339

BUSHING - LEAF SPRING
FRONT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on frame-contact hoist as follows:
(a) Position the hoist arm supporting the corner
of the vehicle to be serviced against a block of wood
placed on the body sill as shown (Fig. 3).
(b) Position the remaining hoist arms at each
corner of the vehicle in the normal fashion. (Refer
to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(c) Raise the vehicle to a comfortable working
level.
(2) Position an under-hoist utility jack or transmis-
sion jack under rear axle toward the side needing
bushing replacement. Jack pad should just contact
axle.
(3) Remove shock absorber lower mounting bolt.
NOTE: If shock absorber bolt deflects upward dur-
ing removal, raise axle by adjusting support jack. If
shock absorber bolt deflects downward during
removal, lower axle by adjusting support jack (or by
pulling on axle).
(4) Remove four bolts securing leaf spring front
mounting bracket to the body (Fig. 3).
(5) Using jack,slowlylower rear axle, permitting
the forward end of rear spring to hang down. Lower
it enough to allow access to spring pivot bolt. It maybe necessary to place a wooden block between the
spring and vehicle to hold forward end of the spring
in place.
(6) Remove leaf spring forward pivot bolt, then
remove mounting bracket.
(7) Straighten the retainer tabs on the bushing
(Fig. 4).
(8) Place Remover/Installer, Special Tool 8459 on
leaf spring and bushing as shown (Fig. 5) and tighten
Set Screw securing Remover Plate to tool threaded
shaft.
Fig. 3 Lifting Point And Spring Mount
1 - BODY SILL AREA
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - SPRING MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - LEAF SPRING
5 - HOIST LIFT ARM
6 - WOODEN BLOCK
Fig. 4 Straightened Retaining Tabs
1 - SPRING EYE
2 - RETAINING TABS
Fig. 5 Tool 8459 Mounted For Bushing Removal
1 - BUSHING
2 - BEARING
3 - WASHER
4 - NUT
5 - BODY (8459-1)
6 - PIN
7 - REMOVER PLATE (8459-2)
8 - SET SCREW
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-29
Page 72 of 2339

wheel rotates with the hub which is sensed by the
wheel speed sensor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HUB AND
BEARING
The bearing contained in the hub and bearing
assembly will produce noise and vibration when worn
or damaged. The noise will generally change when
the bearings are loaded. A road test of the vehicle is
normally required to determine the location of a
worn or damaged bearing.
Find a smooth level road surface and bring the
vehicle up to a constant speed. When vehicle is at a
constant speed, swerve the vehicle back and forth
from the left and to the right. This will load and
unload the bearings and change the noise level.
When bearing damage is slight, the noise is some-
times noticeable at lower speeds and at other times
is more noticeable at speeds above 105 km/h (65
mph).
REMOVAL
FRONT-WHEEL-DRIVE VEHICLES
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove wheel and tire. (Refer to 22 - TIRES/
WHEELS - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove brake drum or disc brake caliper and
rotor from hub and bearing. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DRUM - REMOVAL-
)(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTOR - REMOVAL)
(4) If equipped with antilock brakes, perform the
following:
(a) Remove secondary (yellow) retaining clip at
rear of wheel speed sensor head (Fig. 8).(b) Push up on metal retaining clip (Fig. 8) until
it bottoms. This will release wheel speed sensor
head from hub and bearing.
(c) While holding metal clip up, pull back on
wheel speed sensor head removing it from hub and
bearing.
(5) Remove the 4 bolts attaching the hub and bear-
ing to the rear axle.
CAUTION: Corrosion may occur between the hub
and bearing, and the axle. If this occurs the hub
and bearing will be difficult to remove from the
axle. If the hub and bearing will not come out of the
axle by pulling on it by hand, do not pound on the
hub and bearing to remove it from the axle. Damage
will occur. Use the following procedure.
(6) If the hub and bearing cannot be removed from
the axle by hand, use Remover, Special Tool 8458
(Fig. 9) and the following procedure to press the hub
and bearing out of the axle.
(a) Remove the two outboard spring plate bolts.
(b) Thread Threaded Guide Pins into hub and
bearing mounting bolt holes.
(c) Using the spring plate bolts, install the
Screw Mount, Special Tool 8458±2, as shown (Fig.
9). Mount the Screw Mount to the spring plate
with the tool number facing the hub and bearing
and the beveled edge on the bottom facing the
spring, otherwise the Forcing Screw will rub the
spring plate when installed.
(d) Place Push Plate, Special Tool 8458±1, on
ends of Threaded Guide Pins
(e) Place a dab of grease in dimple of Push
Plate.
Fig. 7 Hub And Bearing - FWD With ABS
Fig. 8 Sensor Connector At Hub And Bearing
1 - SECONDARY SENSOR RETAINING CLIP
2 - METAL SENSOR RETAINING CLIP
3 - HUB AND BEARING
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-31
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
Page 73 of 2339

(f) Install Forcing Screw, Special Tool 8458±3,
through Screw Mount from rear.
(g) Tighten the Forcing Screw up against dimple
in Push Plate and press hub and bearing out of
axle by continuing to tighten screw.
(h) Remove the tool.
(i) Reinstall the two outboard spring plate bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Remove the hub/bearing from the rear axle and
brake support plate.
ALL-WHEEL-DRIVE VEHICLES
(1) Set the parking brake.The parking brake is
set to keep the hub and bearing, and axle shaft
from rotating when loosening the hub nut.
(2) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(3) Remove the wheel/tire assembly. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the cotter pin and nut retainer (Fig.
18) from the stub shaft of the outer C/V joint.
(5) Remove the spring washer (Fig. 17) from the
stub shaft of the outer C/V joint.
(6) Remove the hub nut and washer (Fig. 16) from
the stub shaft of the outer C/V joint.
(7) Remove the 6 bolts mounting the driveshaft
inner joint to the output shaft of the rear drive line
module.
(8) Remove the rear wheel speed sensor (Fig. 19)
from the rear hub/bearing.(9) Release the parking brake.
(10) Remove the disc brake caliper to adapter
guide pin bolts (Fig. 15).
(11) Remove rear caliper from adapter using the
following procedure. First rotate front of caliper up
from the adapter. Then pull the rear of the caliper
and the outboard brake shoe anti-rattle clip out from
under the rear abutment on the adapter (Fig. 14).
(12) Support caliper to prevent the weight of the
caliper from damaging the flexible brake hose (Fig.
10).
(13) Remove the rotor from the hub/bearing.
(14)
Remove driveshaft from rear drive line module
and hub/bearing. Driveshaft is removed by first com-
pressing the inner joint on the driveshaft and remov-
ing it from the drive line module. Then, slide the
outer joint of the driveshaft out of the hub/bearing.
(15) Remove the hub/bearing to axle mounting
bolts (Fig. 13).
CAUTION: Corrosion may occur between the hub/
bearing and the axle. If this occurs the hub/bearing
will be difficult to remove from the axle. If the hub/
bearing will not come out of the axle by pulling on
it by hand, do not pound on the hub/bearing to
remove it from the axle. Pounding on the hub/bear-
ing to remove it from the axle will damage the hub/
bearing. This damage will result in noise or failure
of the hub/bearing. To remove a hub/bearing which
is corroded to the axle, lightly tap the disc brake
caliper adapter using a soft faced hammer. This will
remove both the disc brake caliper adapter and
hub/bearing from the axle. The hub/bearing will
then need to be removed from the caliper adapter.
Fig. 9 Removal Using Special Tool 8458
1 - THREADED GUIDE PINS 8458-4
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - LEAF SPRING PLATE
4 - FORCING SCREW 8458-3
5 - SCREW MOUNT 8458-2
6 - PUSH PLATE 8458-1
Fig. 10 Correctly Supported Caliper
1 - WIRE
2 - CALIPER
3 - ADAPTER
4 - ROTOR
5 - INNER FENDER
2 - 32 REAR SUSPENSIONRS
HUB / BEARING (Continued)