2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN body
[x] Cancel search: bodyPage 1368 of 2339
(6) Open fuel fill door and remove screws mount-
ing fuel filler tube assembly to body. Do not discon-
nect rubber fuel fill or vent hoses from tank at this
time.
(7) Place a transmission jack under center of fuel
tank. Apply a slight amount of pressure to fuel tank
with transmission jack.
(8) Remove fuel tank mounting straps.
(9)Lower the tank just enough so that the
filler tube fitting is the highest point of the fuel
tank.
(10) Remove filler tube from fuel tank. Tank will
be drained through this fitting.
NOTE: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND HOSES TO
CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(11) Drain fuel tank into holding tank or a prop-
erly labeledGasolinesafety container.
WARNING: GASOLINE OR GASOLINE VAPORS ARE
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE. A FIRE COULD OCCUR IF AN
IGNITION SOURCE IS PRESENT. NEVER DRAIN OR
STORE GASOLINE OR DIESEL FUEL IN AN OPEN
CONTAINER, DUE TO THE POSSIBILITY OF FIRE
OR EXPLOSION. THIS MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
(12) If fuel pump module removal is necessary,
refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation in
this section.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL PRESSURE
GAUGE
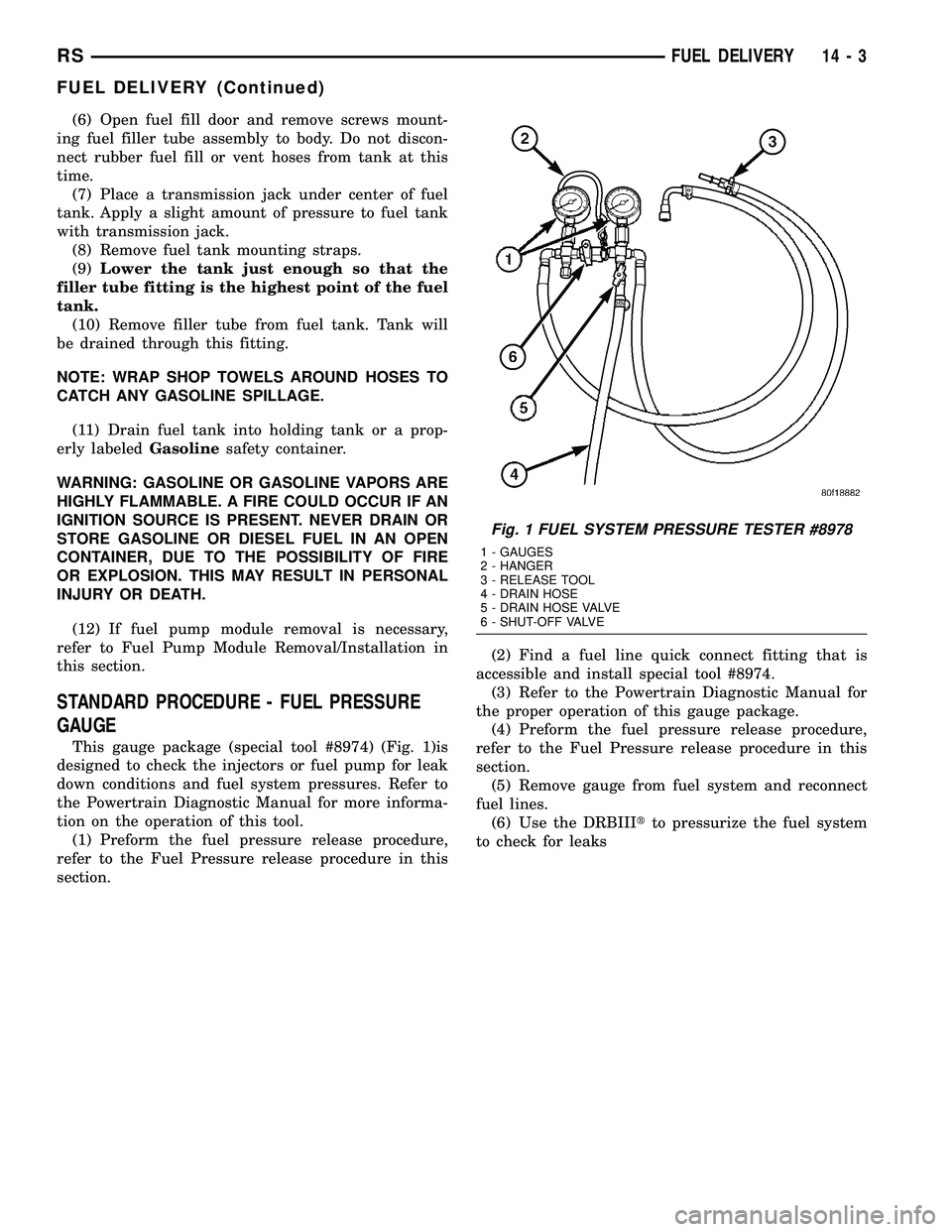
This gauge package (special tool #8974) (Fig. 1)is
designed to check the injectors or fuel pump for leak
down conditions and fuel system pressures. Refer to
the Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for more informa-
tion on the operation of this tool.
(1) Preform the fuel pressure release procedure,
refer to the Fuel Pressure release procedure in this
section.(2) Find a fuel line quick connect fitting that is
accessible and install special tool #8974.
(3) Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for
the proper operation of this gauge package.
(4) Preform the fuel pressure release procedure,
refer to the Fuel Pressure release procedure in this
section.
(5) Remove gauge from fuel system and reconnect
fuel lines.
(6) Use the DRBIIItto pressurize the fuel system
to check for leaks
Fig. 1 FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER #8978
1 - GAUGES
2 - HANGER
3 - RELEASE TOOL
4 - DRAIN HOSE
5 - DRAIN HOSE VALVE
6 - SHUT-OFF VALVE
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-3
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1382 of 2339
(8)For RGDisconnect the vent at the top of the
filler tube.
(9) Remove the ground strap.
(10) Remove filler tube at tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install filler tube to tank (Fig. 32).
(2) Install filler tube shield (Fig. 34).
(3) Install the ground strap.
(4)For RGConnect the vent at the top of the filler
tube.
(5) Install the 3 screws at the filler door.(6)For RGInstall the canister from filler tube
(Fig. 33).
(7) Install the splash shield.
(8) Install the left rear tire.
(9) lower vehicle.
(10) Connect the negative battery cable.
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal in this section.
(2) Using a thin straight blade screwdriver, pry
back the locking tabs on fuel pump reservoir and
remove the strainer (Fig. 35).
(3) Remove strainer O-ring from the fuel pump
reservoir body.
(4) Remove any contaminants in the fuel tank by
washing the inside of the fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the strainer O-ring with clean engine
oil.
(2) Insert strainer O-ring into outlet of strainer so
that it sits evenly on the step inside the outlet.
(3) Push strainer onto the inlet of the fuel pump
reservoir body. Make sure the locking tabs on the
reservoir body lock over the locking tangs on the
strainer.
(4) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Installation in this section.
Fig. 33 FUEL TUBE VENT CANISTER (RG)
Fig. 34 FILLER TUBE SHIELD
Fig. 35 Inlet
1 - TABS
2 - INLET STRAINER
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-17
FUEL TANK FILLER TUBE (Continued)
Page 1384 of 2339
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP. THIS MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
OR DEATH.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To disconnect quick-connect fitting, squeeze
plastic retainer tabs (Fig. 37) against sides of quick-
connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is not
required for removal and may damage plastic
retainer. Pull fitting from fuel system component
being serviced. The plastic retainer will remain on
component being serviced after fitting is discon-
nected. The O-rings and spacer will remain in quick-
connect fitting connector body.
(5) Inspect quick-connect fitting body and compo-
nent for damage. Replace as necessary.
CAUTION: When the quick-connect fitting was dis-
connected, the plastic retainer will remain on the
component being serviced. If this retainer must be
removed, very carefully release the retainer from
the component with two small screwdrivers. After
removal, inspect the retainer for cracks or any dam-
age.
(6) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert quick-connect fitting to component being
serviced and into plastic retainer. When a connection
is made, a click will be heard.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly push-pull-
ing-push on fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(10) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
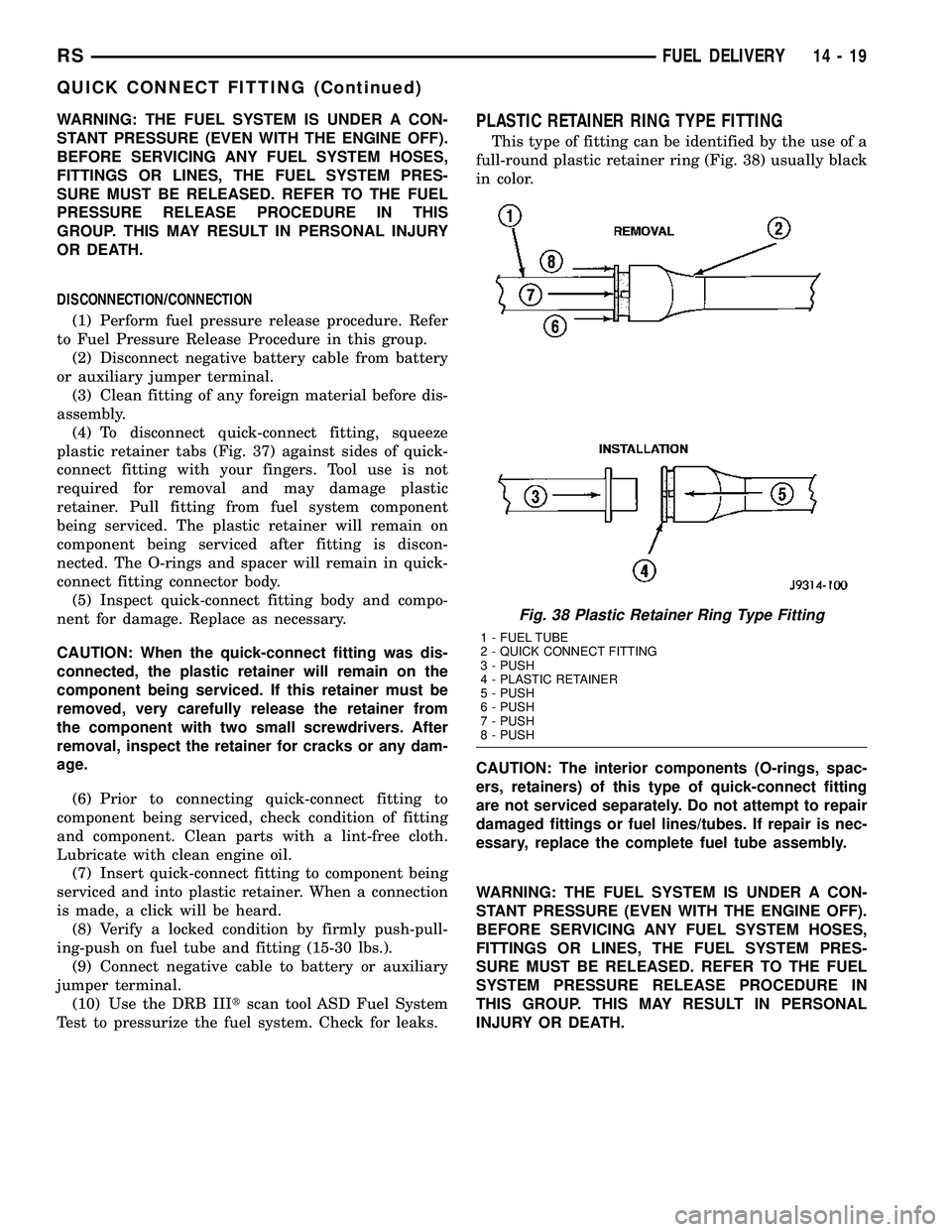
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 38) usually black
in color.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP. THIS MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
Fig. 38 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 - FUEL TUBE
2 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 - PUSH
4 - PLASTIC RETAINER
5 - PUSH
6 - PUSH
7 - PUSH
8 - PUSH
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-19
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 1385 of 2339

DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-
nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 38). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plastic
retainer ring must be pressed squarely into fit-
ting body. If this retainer is cocked during
removal, it may be difficult to disconnect fit-
ting. Use an open-end wrench on shoulder of
plastic retainer ring to aid in disconnection.(5) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(6) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(7) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(8) Insert quick-connect fitting into component
being serviced until a click is felt.
(9) Verify a locked condition by firmly push-pull-
ing-push on fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery or
auxiliary jumper terminal.
(11) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
14 - 20 FUEL DELIVERYRS
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 1386 of 2339

FUEL INJECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL INJECTION
OPERATION
OPERATION - INJECTION SYSTEM.......22
OPERATION - MODES OF OPERATION....22
FUEL CORRECTION or ADAPTIVE
MEMORIES..........................24
PROGRAMMABLE COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (PCI) BUS.................25
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS..................26
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................26
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL...............................27
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................30
INSTALLATION - 2.4L....................30
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................30
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L......................31
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L...................31
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L..................32
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L................32
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................32
OPERATION...........................32
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................33REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................33
INLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................34
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L......................35
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L...................35
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L..................36
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L................36
O2 SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................36
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 2.4L........37
REMOVAL - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 3.3/3.8L.....38
REMOVAL - DOWNSTREAM 1/2 - 2.4/3.3/
3.8L................................38
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 2.4L.....38
INSTALLATION - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 3.3/3.8L . . 39
INSTALLATION DOWNSTREAM 2/1 -
2.4/3.3/3.8L..........................39
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................40
OPERATION...........................41
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L.....................41
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L.................41
RSFUEL INJECTION14-21
Page 1390 of 2339
opposite preset limit or switch point. The process
then repeats itself in the opposite direction.
Short term fuel correction will keep increasing or
decreasing injector pulse-width based upon the
upstream O2 Sensor input. The maximum range of
authority for short term memory is 25% (+/-) of base
pulse-width. Short term is violated and is lost when
ignition is turned OFF.
Long Term
The second fuel correction program is the long
term adaptive memory. In order to maintain correct
emission throughout all operating ranges of the
engine, a cell structure based on engine rpm and load
(MAP) is used.
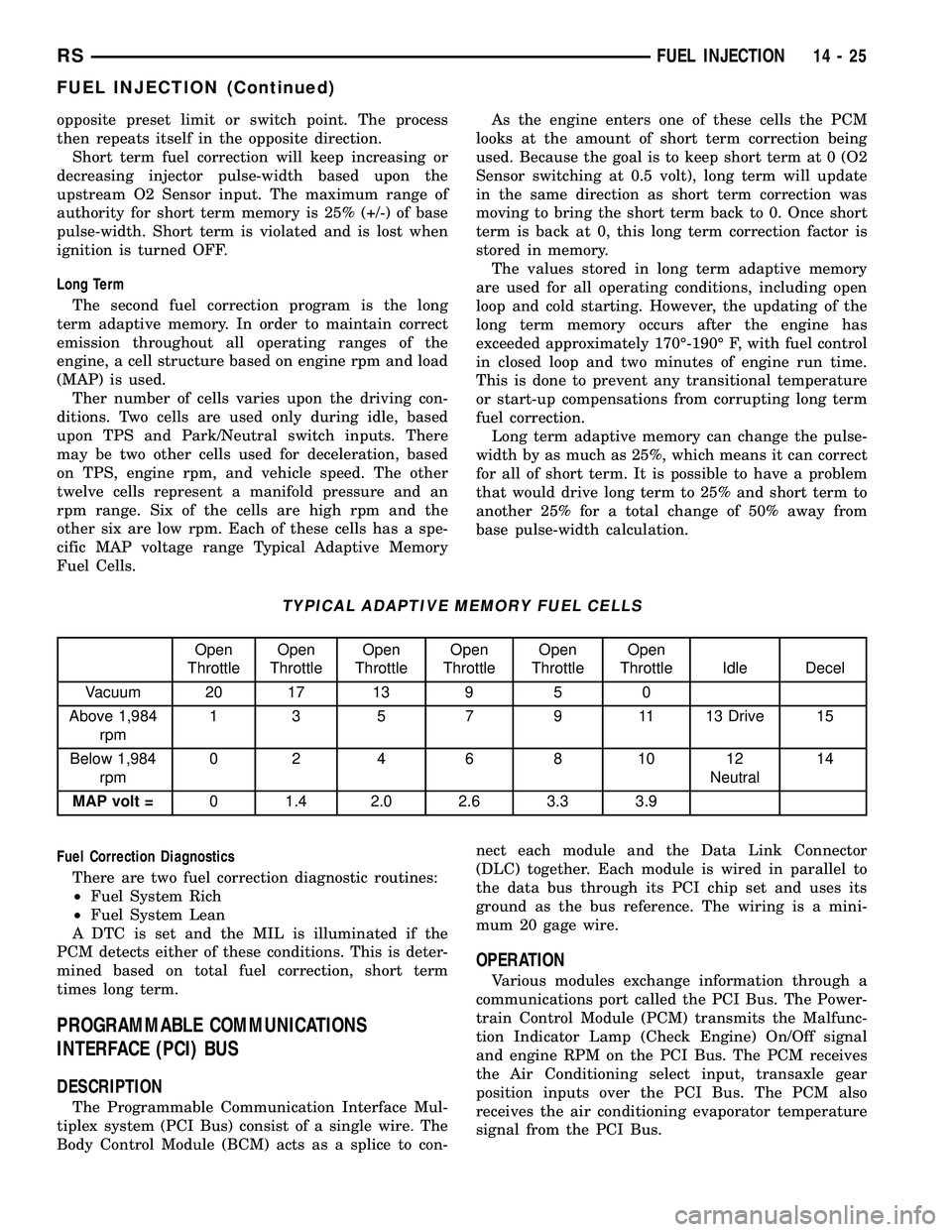
Ther number of cells varies upon the driving con-
ditions. Two cells are used only during idle, based
upon TPS and Park/Neutral switch inputs. There
may be two other cells used for deceleration, based
on TPS, engine rpm, and vehicle speed. The other
twelve cells represent a manifold pressure and an
rpm range. Six of the cells are high rpm and the
other six are low rpm. Each of these cells has a spe-
cific MAP voltage range Typical Adaptive Memory
Fuel Cells.As the engine enters one of these cells the PCM
looks at the amount of short term correction being
used. Because the goal is to keep short term at 0 (O2
Sensor switching at 0.5 volt), long term will update
in the same direction as short term correction was
moving to bring the short term back to 0. Once short
term is back at 0, this long term correction factor is
stored in memory.
The values stored in long term adaptive memory
are used for all operating conditions, including open
loop and cold starting. However, the updating of the
long term memory occurs after the engine has
exceeded approximately 170É-190É F, with fuel control
in closed loop and two minutes of engine run time.
This is done to prevent any transitional temperature
or start-up compensations from corrupting long term
fuel correction.
Long term adaptive memory can change the pulse-
width by as much as 25%, which means it can correct
for all of short term. It is possible to have a problem
that would drive long term to 25% and short term to
another 25% for a total change of 50% away from
base pulse-width calculation.
TYPICAL ADAPTIVE MEMORY FUEL CELLS
Open
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
Throttle Idle Decel
Vacuum 20 17 13 9 5 0
Above 1,984
rpm1 3 5 7 9 11 13 Drive 15
Below 1,984
rpm02 4 6 8 1012
Neutral14
MAP volt =0 1.4 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9
Fuel Correction Diagnostics
There are two fuel correction diagnostic routines:
²Fuel System Rich
²Fuel System Lean
A DTC is set and the MIL is illuminated if the
PCM detects either of these conditions. This is deter-
mined based on total fuel correction, short term
times long term.
PROGRAMMABLE COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (PCI) BUS
DESCRIPTION
The Programmable Communication Interface Mul-
tiplex system (PCI Bus) consist of a single wire. The
Body Control Module (BCM) acts as a splice to con-nect each module and the Data Link Connector
(DLC) together. Each module is wired in parallel to
the data bus through its PCI chip set and uses its
ground as the bus reference. The wiring is a mini-
mum 20 gage wire.
OPERATION
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the PCI Bus. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) transmits the Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp (Check Engine) On/Off signal
and engine RPM on the PCI Bus. The PCM receives
the Air Conditioning select input, transaxle gear
position inputs over the PCI Bus. The PCM also
receives the air conditioning evaporator temperature
signal from the PCI Bus.
RSFUEL INJECTION14-25
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1391 of 2339
The following components access or send informa-
tion on the PCI Bus.
²Instrument Panel
²Body Control Module
²Air Bag System Diagnostic Module
²Full ATC Display Head (if equipped)
²ABS Module
²Transmission Control Module
²Powertrain Control Module
²Travel Module
²SKIMSYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
OPERATION
The PCM can test many of its own input and out-
put circuits. If the PCM senses a fault in a major
system, the PCM stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in memory.
For DTC information see On-Board Diagnostics
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MOD-
ULE - DESCRIPTION) .
SPECIFICATIONS
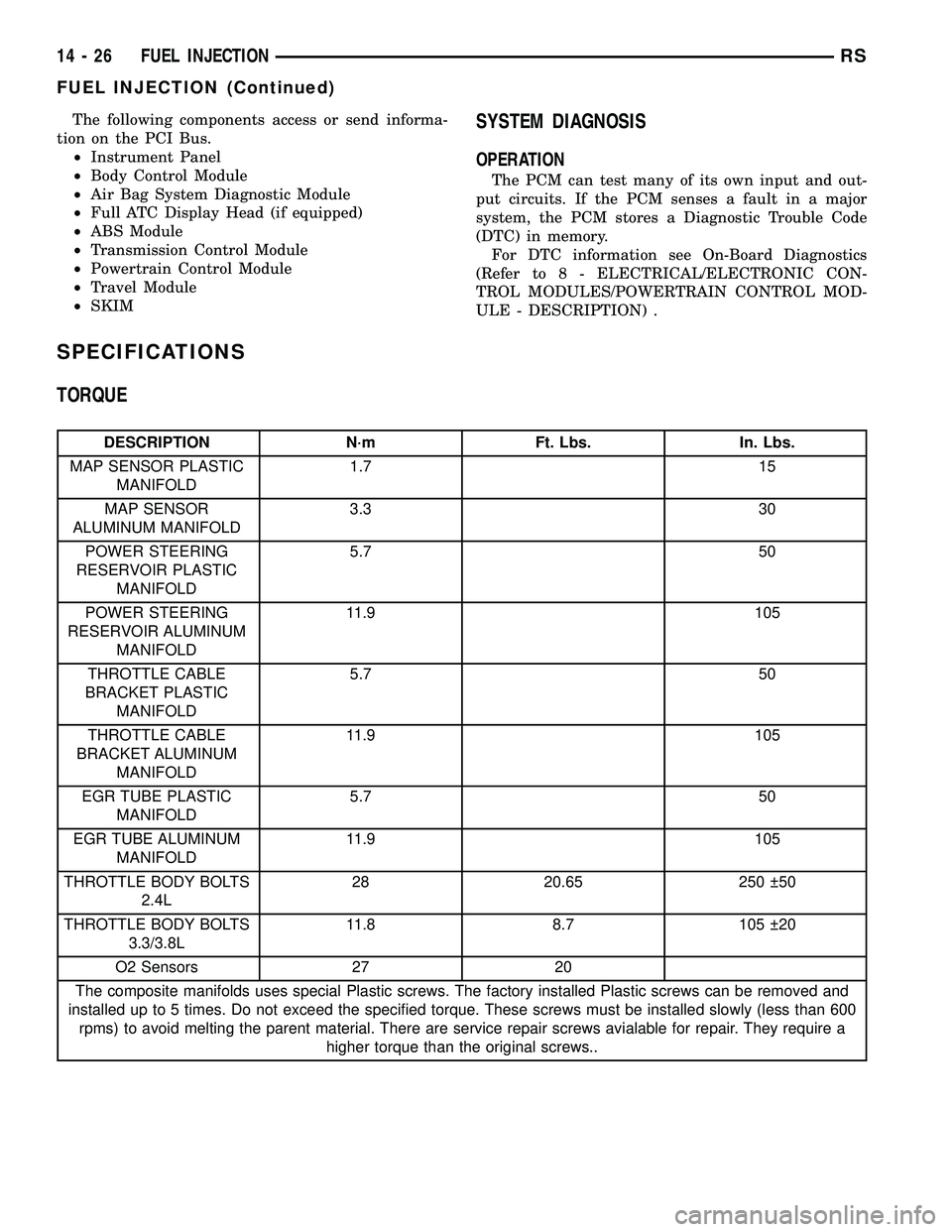
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
MAP SENSOR PLASTIC
MANIFOLD1.7 15
MAP SENSOR
ALUMINUM MANIFOLD3.3 30
POWER STEERING
RESERVOIR PLASTIC
MANIFOLD5.7 50
POWER STEERING
RESERVOIR ALUMINUM
MANIFOLD11.9 105
THROTTLE CABLE
BRACKET PLASTIC
MANIFOLD5.7 50
THROTTLE CABLE
BRACKET ALUMINUM
MANIFOLD11.9 105
EGR TUBE PLASTIC
MANIFOLD5.7 50
EGR TUBE ALUMINUM
MANIFOLD11.9 105
THROTTLE BODY BOLTS
2.4L28 20.65 250 50
THROTTLE BODY BOLTS
3.3/3.8L11.8 8.7 105 20
O2 Sensors 27 20
The composite manifolds uses special Plastic screws. The factory installed Plastic screws can be removed and
installed up to 5 times. Do not exceed the specified torque. These screws must be installed slowly (less than 600
rpms) to avoid melting the parent material. There are service repair screws avialable for repair. They require a
higher torque than the original screws..
14 - 26 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1393 of 2339
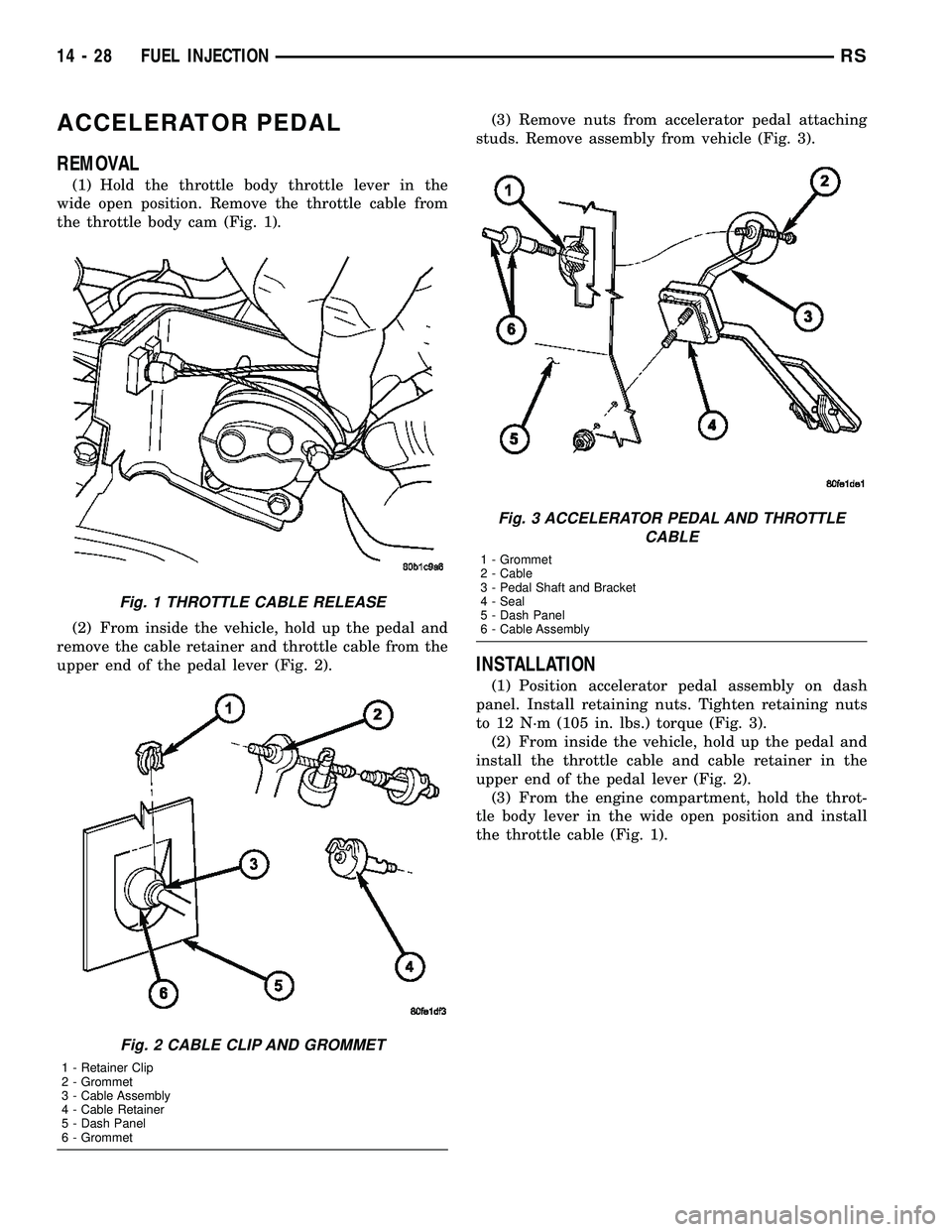
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL
(1) Hold the throttle body throttle lever in the
wide open position. Remove the throttle cable from
the throttle body cam (Fig. 1).
(2) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
remove the cable retainer and throttle cable from the
upper end of the pedal lever (Fig. 2).(3) Remove nuts from accelerator pedal attaching
studs. Remove assembly from vehicle (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position accelerator pedal assembly on dash
panel. Install retaining nuts. Tighten retaining nuts
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 3).
(2) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
install the throttle cable and cable retainer in the
upper end of the pedal lever (Fig. 2).
(3) From the engine compartment, hold the throt-
tle body lever in the wide open position and install
the throttle cable (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 THROTTLE CABLE RELEASE
Fig. 2 CABLE CLIP AND GROMMET
1 - Retainer Clip
2 - Grommet
3 - Cable Assembly
4 - Cable Retainer
5 - Dash Panel
6 - Grommet
Fig. 3 ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE
CABLE
1 - Grommet
2 - Cable
3 - Pedal Shaft and Bracket
4 - Seal
5 - Dash Panel
6 - Cable Assembly
14 - 28 FUEL INJECTIONRS