2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 1689 of 2339
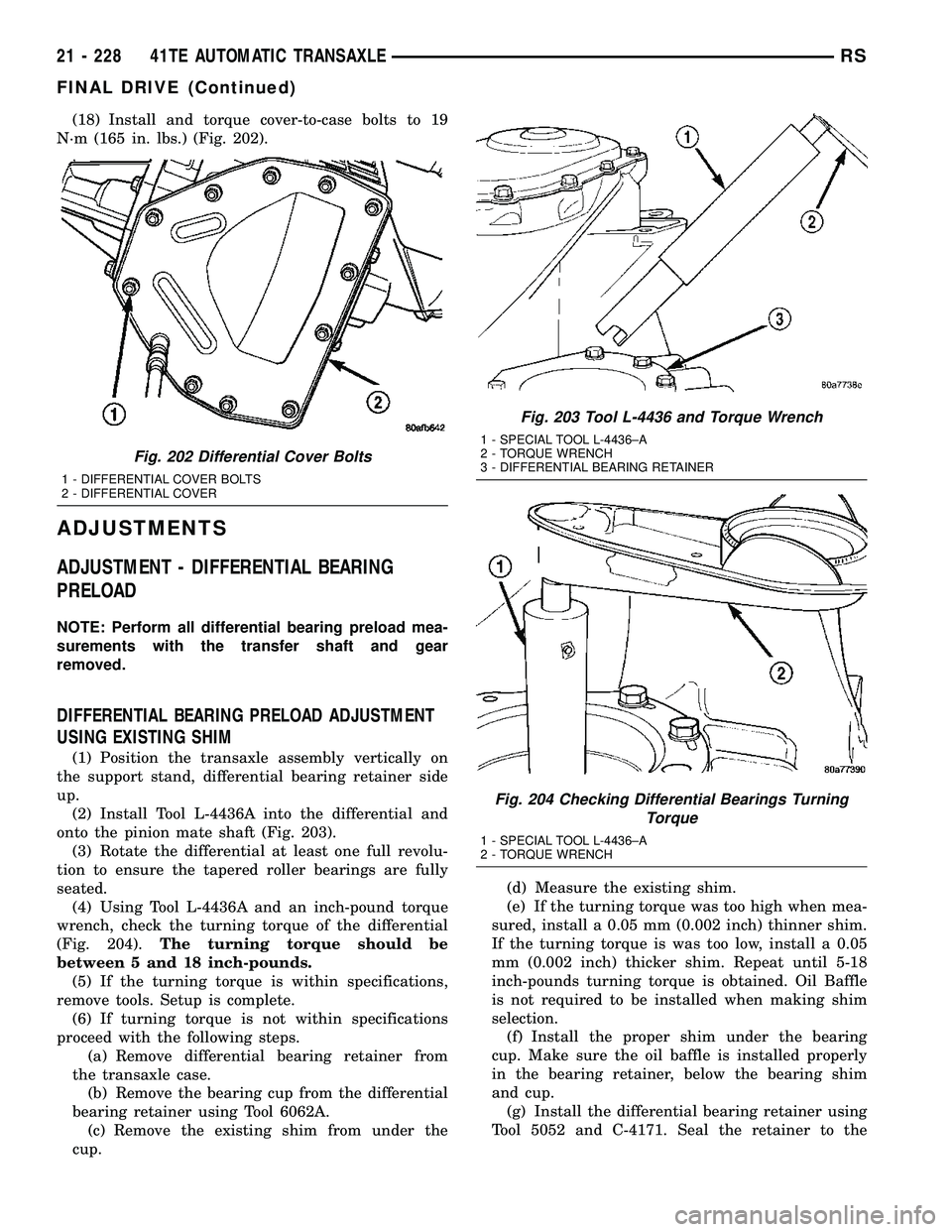
(18) Install and torque cover-to-case bolts to 19
N´m (165 in. lbs.) (Fig. 202).
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
PRELOAD
NOTE: Perform all differential bearing preload mea-
surements with the transfer shaft and gear
removed.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD ADJUSTMENT
USING EXISTING SHIM
(1) Position the transaxle assembly vertically on
the support stand, differential bearing retainer side
up.
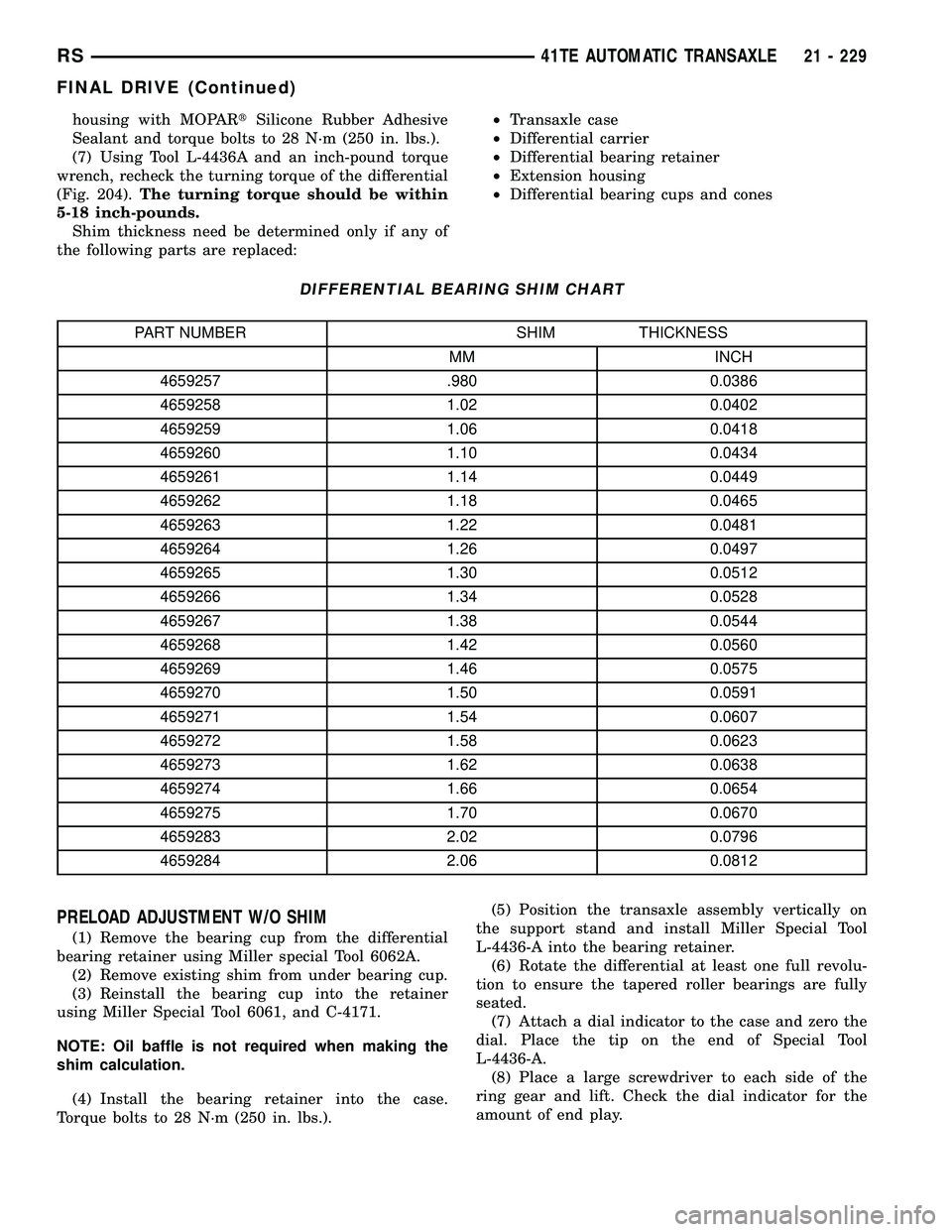
(2) Install Tool L-4436A into the differential and
onto the pinion mate shaft (Fig. 203).
(3) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated.
(4) Using Tool L-4436A and an inch-pound torque
wrench, check the turning torque of the differential
(Fig. 204).The turning torque should be
between 5 and 18 inch-pounds.
(5) If the turning torque is within specifications,
remove tools. Setup is complete.
(6) If turning torque is not within specifications
proceed with the following steps.
(a) Remove differential bearing retainer from
the transaxle case.
(b) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Tool 6062A.
(c) Remove the existing shim from under the
cup.(d) Measure the existing shim.
(e) If the turning torque was too high when mea-
sured, install a 0.05 mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
If the turning torque is was too low, install a 0.05
mm (0.002 inch) thicker shim. Repeat until 5-18
inch-pounds turning torque is obtained. Oil Baffle
is not required to be installed when making shim
selection.
(f) Install the proper shim under the bearing
cup. Make sure the oil baffle is installed properly
in the bearing retainer, below the bearing shim
and cup.
(g) Install the differential bearing retainer using
Tool 5052 and C-4171. Seal the retainer to the
Fig. 202 Differential Cover Bolts
1 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER BOLTS
2 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER
Fig. 203 Tool L-4436 and Torque Wrench
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4436±A
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
3 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING RETAINER
Fig. 204 Checking Differential Bearings Turning
Torque
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4436±A
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
21 - 228 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
Page 1690 of 2339
housing with MOPARtSilicone Rubber Adhesive
Sealant and torque bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(7) Using Tool L-4436A and an inch-pound torque
wrench, recheck the turning torque of the differential
(Fig. 204).The turning torque should be within
5-18 inch-pounds.
Shim thickness need be determined only if any of
the following parts are replaced:²Transaxle case
²Differential carrier
²Differential bearing retainer
²Extension housing
²Differential bearing cups and cones
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM CHART
PART NUMBER SHIM THICKNESS
MM INCH
4659257 .980 0.0386
4659258 1.02 0.0402
4659259 1.06 0.0418
4659260 1.10 0.0434
4659261 1.14 0.0449
4659262 1.18 0.0465
4659263 1.22 0.0481
4659264 1.26 0.0497
4659265 1.30 0.0512
4659266 1.34 0.0528
4659267 1.38 0.0544
4659268 1.42 0.0560
4659269 1.46 0.0575
4659270 1.50 0.0591
4659271 1.54 0.0607
4659272 1.58 0.0623
4659273 1.62 0.0638
4659274 1.66 0.0654
4659275 1.70 0.0670
4659283 2.02 0.0796
4659284 2.06 0.0812
PRELOAD ADJUSTMENT W/O SHIM
(1) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Miller special Tool 6062A.
(2) Remove existing shim from under bearing cup.
(3) Reinstall the bearing cup into the retainer
using Miller Special Tool 6061, and C-4171.
NOTE: Oil baffle is not required when making the
shim calculation.
(4) Install the bearing retainer into the case.
Torque bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).(5) Position the transaxle assembly vertically on
the support stand and install Miller Special Tool
L-4436-A into the bearing retainer.
(6) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated.
(7) Attach a dial indicator to the case and zero the
dial. Place the tip on the end of Special Tool
L-4436-A.
(8) Place a large screwdriver to each side of the
ring gear and lift. Check the dial indicator for the
amount of end play.
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 229
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
Page 1691 of 2339

CAUTION: Do not damage the transaxle case and/or
differential retainer sealing surface.
(9) Using the end play measurement that was
determined, add 0.18mm (0.007 inch). This should
give you between 5-18 inch pounds of bearing pre-
load. Refer to the Differential Bearing Shim Chart to
determine which shim to use.
(10) Remove the differential bearing retainer.
Remove the bearing cup.
(11) Install the oil baffle. Install the proper shim
combination under the bearing cup.
(12) Install the differential bearing retainer. Seal
the retainer to the housing with MopartSilicone
Rubber Adhesive Sealant. Torque bolts to 28 N´m
(250 in. lbs.).
(13) Using Miller Special Tool L-4436-A and an
inch-pound torque wrench, check the turning torque
of the differential (Fig. 204). The turning torque
should be between 5-18 inch-pounds.
NOTE: If turning torque is too high install a 0.05mm
(0.002 inch) thicker shim. If the turning torque is too
low, install a 0.05mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
Repeat until 5-18 inch-pounds of turning torque is
obtained.
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature 82É C
(180É F), the fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT
region on the oil level indicator (Fig. 205). The fluid
level should be within the COLD region of the dip-
stick at 27É C (80É F) fluid temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.
(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 206).
(6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart.
(7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
Fig. 205 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21 - 230 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
Page 1722 of 2339
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
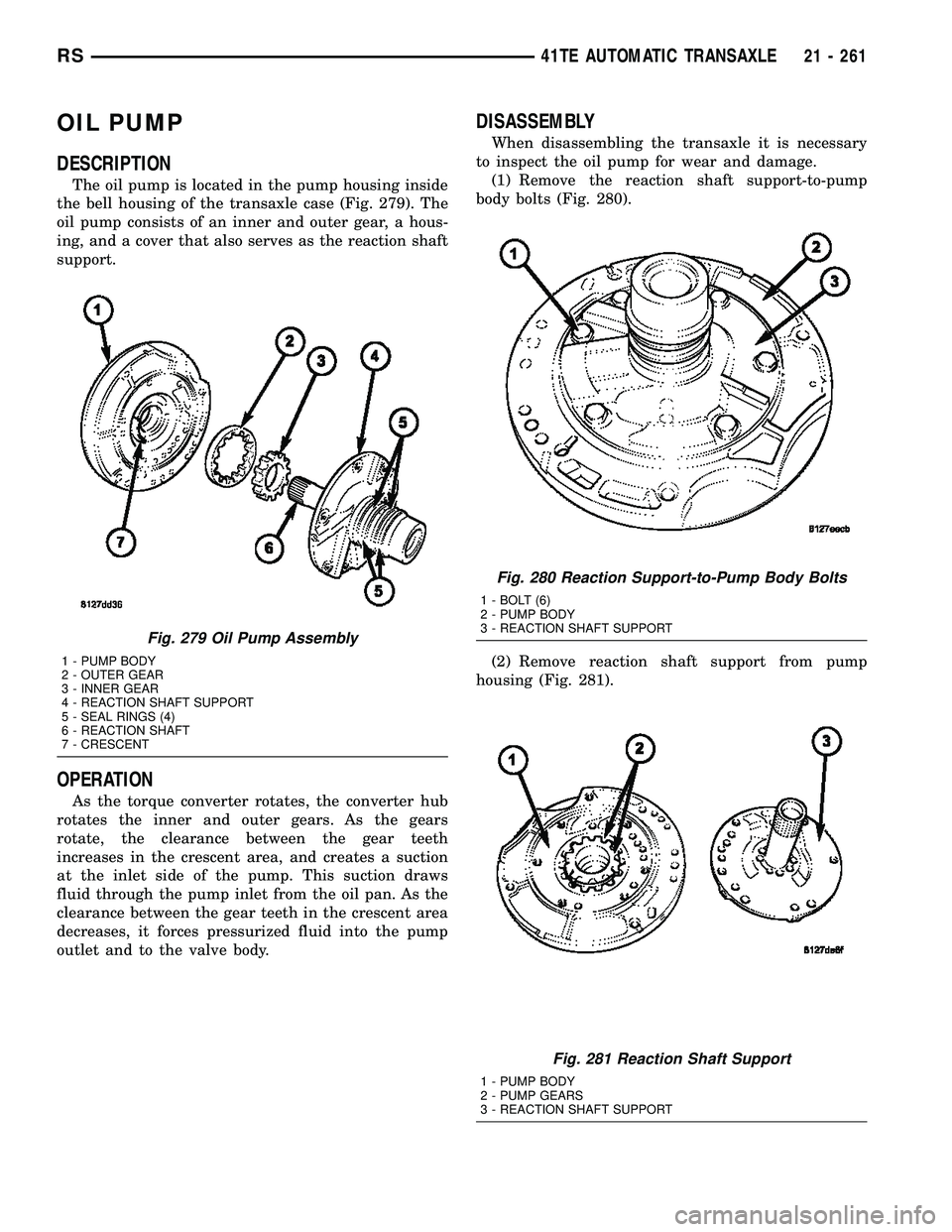
The oil pump is located in the pump housing inside
the bell housing of the transaxle case (Fig. 279). The
oil pump consists of an inner and outer gear, a hous-
ing, and a cover that also serves as the reaction shaft
support.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the inner and outer gears. As the gears
rotate, the clearance between the gear teeth
increases in the crescent area, and creates a suction
at the inlet side of the pump. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
clearance between the gear teeth in the crescent area
decreases, it forces pressurized fluid into the pump
outlet and to the valve body.
DISASSEMBLY
When disassembling the transaxle it is necessary
to inspect the oil pump for wear and damage.
(1) Remove the reaction shaft support-to-pump
body bolts (Fig. 280).
(2) Remove reaction shaft support from pump
housing (Fig. 281).
Fig. 279 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP BODY
2 - OUTER GEAR
3 - INNER GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
Fig. 280 Reaction Support-to-Pump Body Bolts
1 - BOLT (6)
2 - PUMP BODY
3 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
Fig. 281 Reaction Shaft Support
1 - PUMP BODY
2 - PUMP GEARS
3 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 261
Page 1724 of 2339
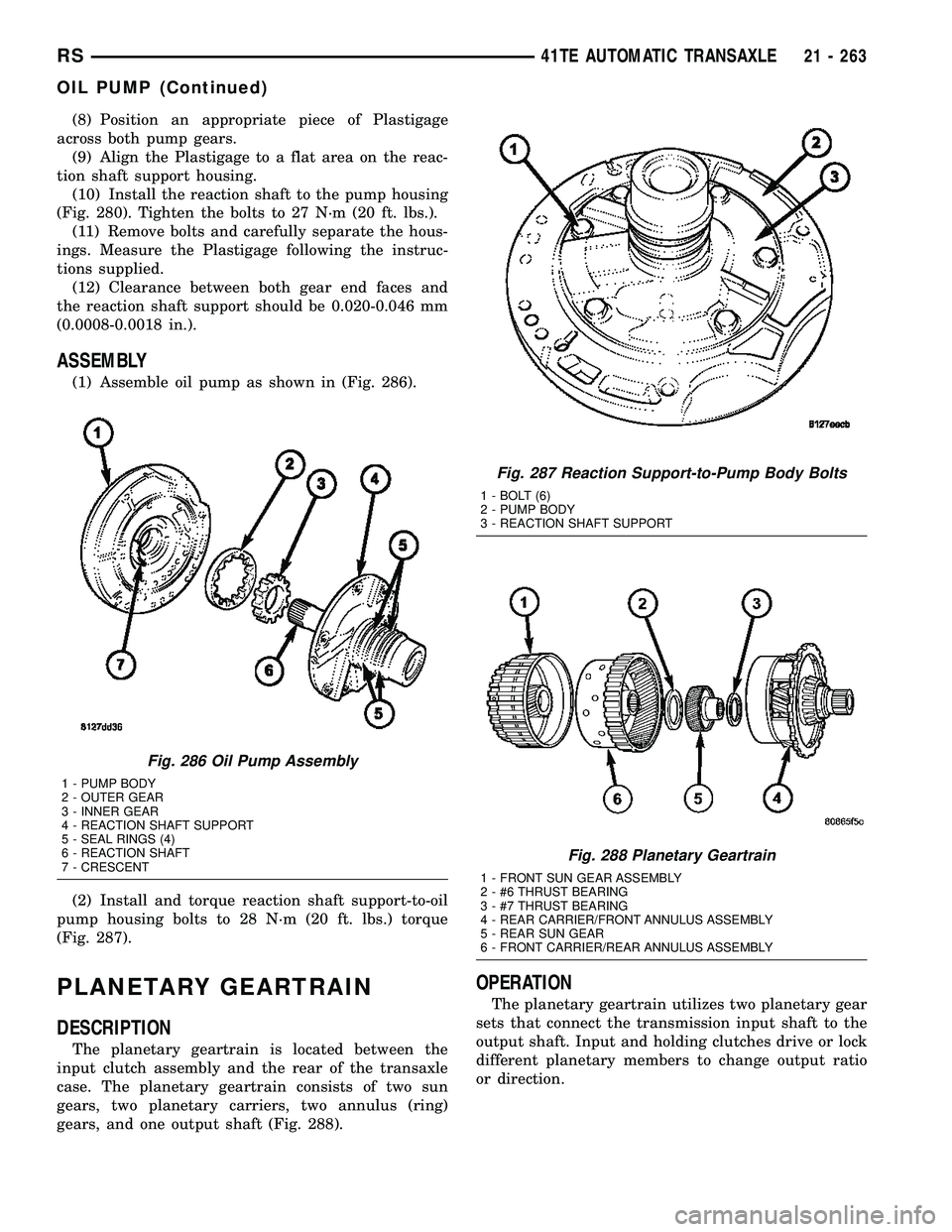
(8) Position an appropriate piece of Plastigage
across both pump gears.
(9) Align the Plastigage to a flat area on the reac-
tion shaft support housing.
(10) Install the reaction shaft to the pump housing
(Fig. 280). Tighten the bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(11) Remove bolts and carefully separate the hous-
ings. Measure the Plastigage following the instruc-
tions supplied.
(12) Clearance between both gear end faces and
the reaction shaft support should be 0.020-0.046 mm
(0.0008-0.0018 in.).
ASSEMBLY
(1) Assemble oil pump as shown in (Fig. 286).
(2) Install and torque reaction shaft support-to-oil
pump housing bolts to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque
(Fig. 287).
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION
The planetary geartrain is located between the
input clutch assembly and the rear of the transaxle
case. The planetary geartrain consists of two sun
gears, two planetary carriers, two annulus (ring)
gears, and one output shaft (Fig. 288).
OPERATION
The planetary geartrain utilizes two planetary gear
sets that connect the transmission input shaft to the
output shaft. Input and holding clutches drive or lock
different planetary members to change output ratio
or direction.
Fig. 286 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP BODY
2 - OUTER GEAR
3 - INNER GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
Fig. 287 Reaction Support-to-Pump Body Bolts
1 - BOLT (6)
2 - PUMP BODY
3 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
Fig. 288 Planetary Geartrain
1 - FRONT SUN GEAR ASSEMBLY
2 - #6 THRUST BEARING
3 - #7 THRUST BEARING
4 - REAR CARRIER/FRONT ANNULUS ASSEMBLY
5 - REAR SUN GEAR
6 - FRONT CARRIER/REAR ANNULUS ASSEMBLY
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 263
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1731 of 2339
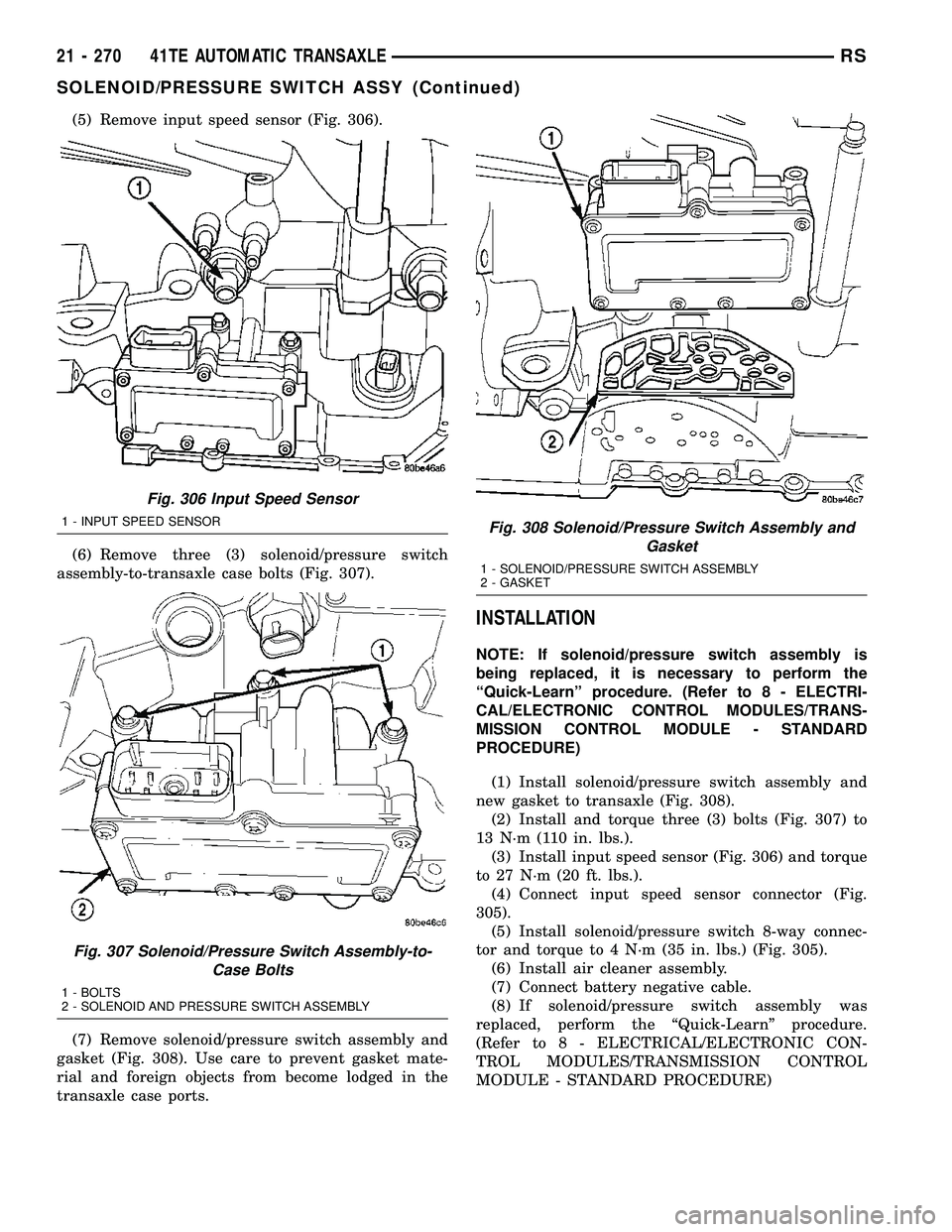
(5) Remove input speed sensor (Fig. 306).
(6) Remove three (3) solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 307).
(7) Remove solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
gasket (Fig. 308). Use care to prevent gasket mate-
rial and foreign objects from become lodged in the
transaxle case ports.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, it is necessary to perform the
ªQuick-Learnº procedure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANS-
MISSION CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(1) Install solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
new gasket to transaxle (Fig. 308).
(2) Install and torque three (3) bolts (Fig. 307) to
13 N´m (110 in. lbs.).
(3) Install input speed sensor (Fig. 306) and torque
to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(4) Connect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
305).
(5) Install solenoid/pressure switch 8-way connec-
tor and torque to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) (Fig. 305).
(6) Install air cleaner assembly.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
(8) If solenoid/pressure switch assembly was
replaced, perform the ªQuick-Learnº procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 306 Input Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 307 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly-to-
Case Bolts
1 - BOLTS
2 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 308 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly and
Gasket
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - GASKET
21 - 270 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY (Continued)
Page 1732 of 2339
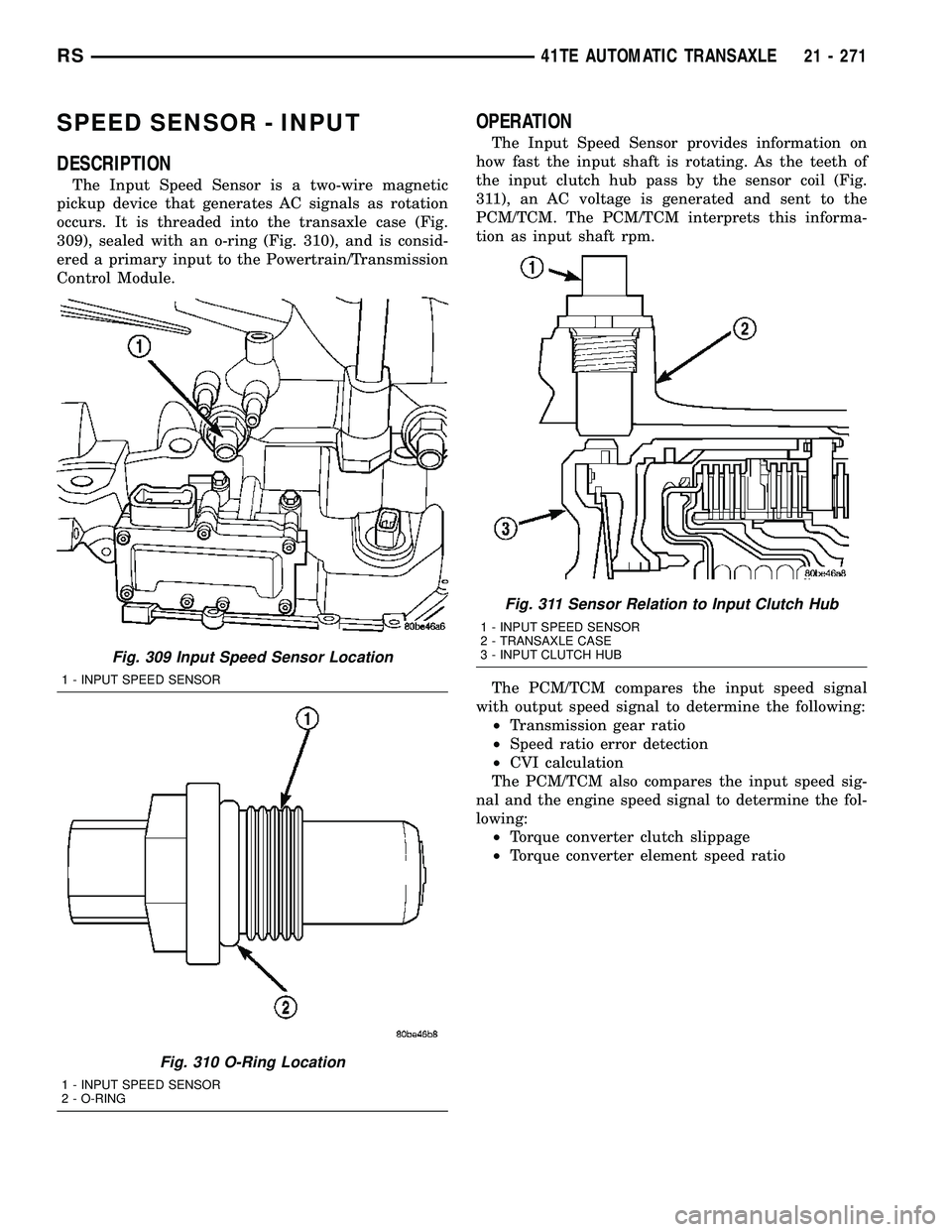
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Input Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates AC signals as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
309), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 310), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powertrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil (Fig.
311), an AC voltage is generated and sent to the
PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this informa-
tion as input shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input speed signal
with output speed signal to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The PCM/TCM also compares the input speed sig-
nal and the engine speed signal to determine the fol-
lowing:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
Fig. 309 Input Speed Sensor Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 310 O-Ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 311 Sensor Relation to Input Clutch Hub
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - TRANSAXLE CASE
3 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 271
Page 1736 of 2339
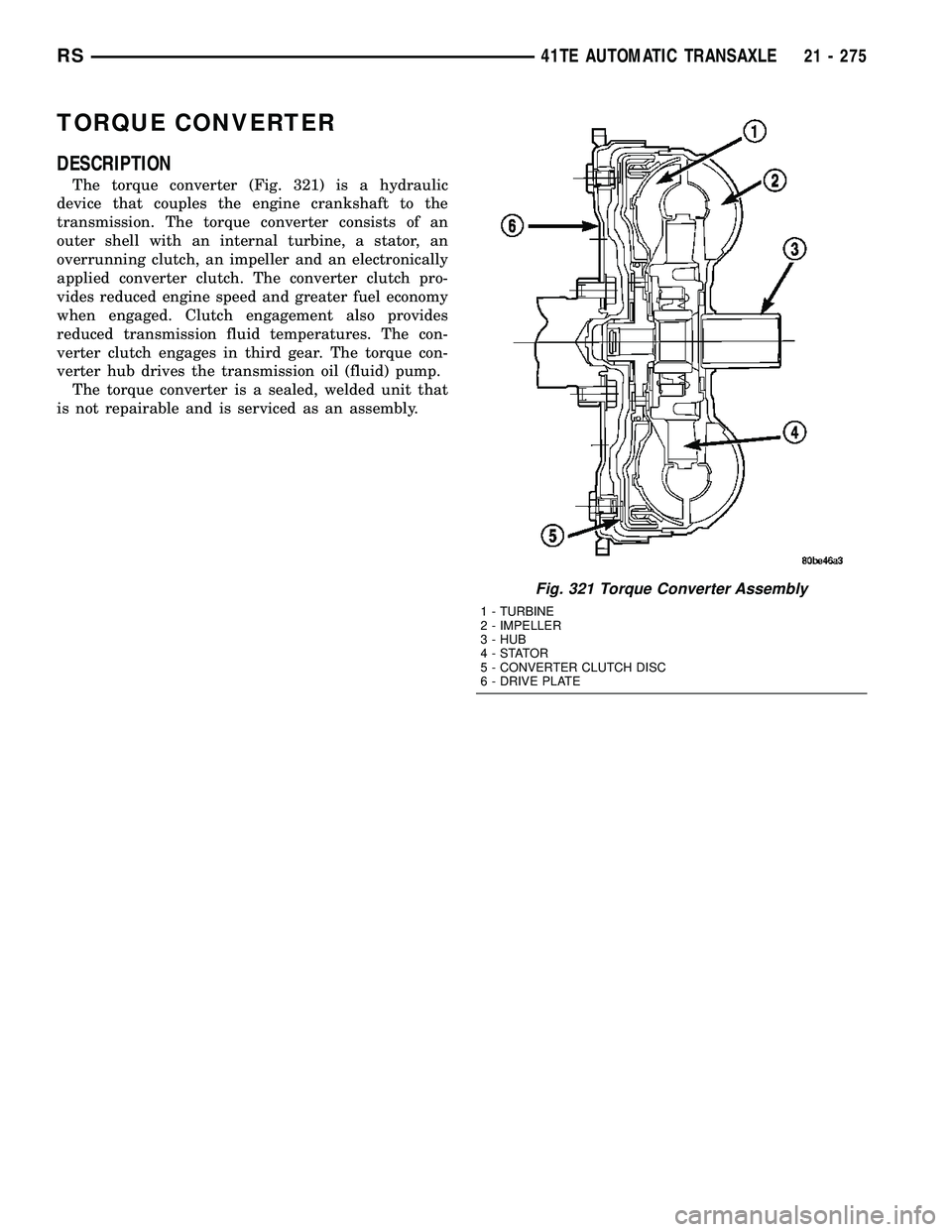
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 321) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
Fig. 321 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 275