2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN tire type
[x] Cancel search: tire typePage 374 of 2339

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SELF-
DIAGNOSTICS.........................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUSTER
DIAGNOSIS...........................3REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
CLUSTER LENS
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION
The instrumentation gauges are contained in a
subdial assembly within the instrument cluster. The
individual gauges are not serviceable. If one of the
cluster gauges becomes faulty, the entire cluster
would require replacement.
The Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC) with a
tachometer is equipped with a electronic vacuum flu-
orescent transmission range indicator (PRND3L),
odometer, and trip odometer display.
The MIC without a tachometer is equipped with a
Light Emitting Diode (LED) transmission range indi-
cator (PRND3L) and a vacuum fluorescent odometer
display.
The MIC is equipped with the following warning
lamps.
²Lift Gate Ajar
²Low Fuel Level
²Low Windshield Washer Fluid Level
²Cruise
²Battery Voltage
²Fasten Seat Belt
²Door Ajar
²Coolant Temperature
²Anti-Lock Brake
²Brake
²Oil Pressure
²MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
²VTSS/SKIS Indicator
²Airbag
²Traction Control
²Autostick
Export Only- uses a message center that displays
the following telltales:
²Turns Signals
²High Beam
²Tire Pressure Monitoring (TPM)²Glow Plug (Export Only)
²Supplemental Cabin Heater (Export Only)WATER IN FUEL LAMP - EXPORT
The Water In Fuel Lamp is located in the message
center. When moisture is found within the fuel sys-
tem, the sensor sends a message via the PCI data
bus to the instrument cluster. The MIC illuminates
the bulb in the message center, The sensor is located
underneath the vehicle, directly above the rear axle.
The sensor is housed within the fuel filter/water sep-
arator assembly cover. The sensor is not serviced sep-
arately. If found defective, the entire assembly cover
must be replaced.
OPERATION
Refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual for operation
instructions and conditions for the Instrument Clus-
ter Gauges.
WATER IN FUEL LAMP/SENSOR - EXPORT
The Water In Fuel Sensor is a resistive type
switch. It is calibrated to sense the different resis-
tance between diesel fuel and water. When water
enters the fuel system, it is caught in the bottom of
the fuel filter/water separator assembly, where the
sensor is located. Water has less resistance than die-
sel fuel. The sensor then sends a PCI data bus mes-
sage to the instrument cluster to illuminate the
lamp.
If the lamp is inoperative, perform the self diag-
nostic test on the instrument cluster to check the
lamp operation before continuing diagnosis.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-1
Page 460 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
MEMORY SWITCH
(1) Remove the memory switch from the drivers
door panel (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
SEATS/MEMORY SET SWITCH - REMOVAL).
(2) Using an ohmmeter, check the continuity of the
memory select switch MUX circuit between the C2
wire harness connector for the Body Control Module
(BCM) and the wire harness connector for the mem-
ory switch. There should be continuity. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, repair the open or shorted MUX
circuit as required.
(3) Using an ohmmeter, check the continuity of the
memory select switch return circuit between the C2
wire harness connector for the BCM and the wire
harness connector for the memory switch. There
should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK,
repair the open or shorted return circuit as required.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, test the resistances of the
memory switch, refer to the MEMORY SWITCH
TEST TABLE. If OK, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
POWER SEATS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
MEMORY SYSTEM). If not OK, replace the memory
switch, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER SEATS/
MEMORY SET SWITCH - REMOVAL).
MEMORY SWITCH TEST TABLE
MEMORY
SWITCH
POSITIONRESISTANCE
BETWEEN
PINSRESISTANCE
RANGE
(OHMS)
NEUTRAL 1&2 24650 5%
(24.65 k)
MEMORY 1 1&2 6850 5%
(6.85 k)
MEMORY 2 1&2 2100 5%
(2.10 k)
SET 1&2 4490 5%
(4.49 k)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the front door trim panel switch bezel
from the driver side front door. Using a thin flat-
bladed pry tool, gently pry the switch bezel away
from the drivers door trim panel.
(3) Disconnect the memory switch wire harness
connector from the memory switch.
(4) Remove the two screws that secure the memory
switch to the back of the driver side front door trim
panel switch bezel.
(5) Remove the memory switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the memory switch and install and
tighten the two screws that secure the memory
switch to the back of the driver side front door trim
panel switch bezel. Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20
in. lbs.).
(2) Reconnect the memory switch wire harness
connector to the memory switch.
(3) Install the trim panel switch bezel onto the
driver side front door.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
POWER SEAT TRACK
DESCRIPTION
The power seat option includes an electrically oper-
ated power seat track located under the front seat. If
equipped with Memory System, the front power seat
track on the driver side of the vehicle also provides
the mounting location for the Memory Seat/Mirror
Module (MSMM). The power seat circuit breakers are
mounted on the rear of the power seat track, just
behind the seat rear trim panel. The lower half of the
power seat track is secured to the floor panel via four
studs and nuts that must be accessed from the
underside of the vehicle. Four bolts secure the bot-
tom of the seat cushion pan to the upper half of the
power seat track unit. Four additional bolts secure
the seat back frame to the power seat track unit.
The eight-way power seat track unit includes four
reversible electric motors that are secured to the
upper half of the track unit. Each motor moves the
seat adjuster through a combination of worm-drive
gearboxes and screw-type drive units. Each of the
four power seat track motors used on models
equipped with the optional memory system incorpo-
rate a position potentiometer integral to the motor
assembly, which electronically monitors the motor
position. This enables the memory system to function
by referencing the motor positions programmed into
the memory seat/mirror module.
The front and rear of the seat are operated by two
separate vertical adjustment motors. These motors
can be operated independently of each other, tilting
the entire seat assembly forward or rearward. They
can also be operated in unison by selecting the
proper power seat switch functions, which will raise
or lower the entire seat assembly. A third motor is
the horizontal adjustment motor, which moves the
seat track in the forward and aft directions. The
forth motor is the recliner adjustment motor, which
moves the seat back in the forward and rearward
directions.
The four-way power seat track unit includes two
reversible electric motors that are secured to the
RSPOWER SEAT SYSTEM8N-37
MEMORY SWITCH (Continued)
Page 461 of 2339

upper half of the track unit. Each motor moves the
seat adjuster through a combination of worm-drive
gearboxes and screw-type drive units. The horizontal
adjustment motor moves the seat track in the for-
ward and aft directions. The recliner adjustment
motor moves the seat back in the forward and rear-
ward directions.
The power seat track unit cannot be repaired, and
is serviced only as a complete unit. If any component
in this unit is faulty or damaged, the entire power
seat track unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
When the power seat switch control knob or knobs
are actuated, a battery feed and a ground path are
applied through the switch contacts to the power seat
track or recliner adjuster motor. The selected
adjuster motor operates to move the seat track or
recliner through its drive unit in the selected direc-
tion until the switch is released, or until the travel
limit of the adjuster is reached. When the switch is
moved in the opposite direction, the battery feed and
ground path to the motor are reversed through the
switch contacts. This causes the adjuster motor to
run in the opposite direction.
No power seat switch should be held applied in any
direction after the adjuster has reached its travel
limit. The power seat adjuster motors each contain a
self-resetting circuit breaker to protect them from
overload. However, consecutive or frequent resetting
of the circuit breaker must not be allowed to con-
tinue, or the motor may be damaged.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
POWER SEAT TRACK
WARNING: SOME VEHICLES ARE EQUIPPED WITH
SEATBACK MOUNTED AIRBAGS. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE OR SERVICE ANY
SEAT OR POWER SEAT SYSTEM COMPONENT
YOU MUST FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO MIN-
UTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE BEFORE FURTHER SYSTEM SERVICE.
THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE
AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
Actuate the power seat switch to move the power
seat track adjusters in each direction. The power seat
track adjusters should move in each of the selected
directions. If a power seat track adjuster operates in
one direction only, move the adjuster a short distance
in the opposite direction and test again to be certainthat the adjuster is not at its travel limit. If the
power seat track adjuster still operates in one direc-
tion only, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
SEATS/DRIVER SEAT SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). If the power seat track adjuster does not
operate in more than one direction, perform the fol-
lowing tests.
TESTING POWER SEAT TRACK MOTORS
(1) Check the power seat circuit breaker under the
seat. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace the
faulty power seat circuit breaker.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the power seat cir-
cuit breaker under the seat. If OK, go to Step 3. If
not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the fuse
in the Integrated Power Module (IPM) as required.
(3) Remove the outboard seat cushion side cover,
(Refer to 23 - BODY/SEATS/SEAT CUSHION SIDE
COVERS - REMOVAL). Disconnect the wire harness
connector from the power seat switch. Check for bat-
tery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit cavity of the
power seat switch wire harness connector. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open fused B(+) cir-
cuit to the power seat circuit breaker under the seat
as required.
(4) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity of the power seat switch wire harness con-
nector and a known good ground. There should be
continuity. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the
open ground circuit as required.
(5) Test the power seat switch, (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/POWER SEATS/DRIVER SEAT SWITCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). If the switch tests OK,
test the circuits of the power seat wire harness
between the inoperative power seat track adjuster
motor and the power seat switch for shorts or opens.
If the circuits check OK, replace the faulty power
seat track unit. If the circuits are not OK, repair the
power seat wire harness as required.
REMOVAL
WARNING: SOME VEHICLES ARE EQUIPPED WITH
SEATBACK MOUNTED AIRBAGS. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE OR SERVICE ANY
SEAT OR POWER SEAT SYSTEM COMPONENT
YOU MUST FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO MIN-
UTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE BEFORE FURTHER SYSTEM SERVICE.
THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE
AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
8N - 38 POWER SEAT SYSTEMRS
POWER SEAT TRACK (Continued)
Page 580 of 2339

WIRE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WIRE SPLICING
When splicing a wire, it is important that the cor-
rect gage be used as shown in the wiring diagrams.
(1) Remove one-half (1/2) inch of insulation from
each wire that needs to be spliced.
(2) Place a piece of adhesive lined heat shrink tub-
ing on one side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will
be long enough to cover and seal the entire repair
area.
(3) Place the strands of wire overlapping each
other inside of the splice clip (Fig. 14).
(4) Using crimping tool, Mopar p/n 05019912AA,
crimp the splice clip and wires together (Fig. 15).(5) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only (Fig. 16).
CAUTION: DO NOT USE ACID CORE SOLDER.
(6) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both
ends of the tubing (Fig. 17).
Fig. 14 SPLICE BAND
1 - SPLICE BAND
Fig. 15 CRIMPING TOOL
1 - CRIMPING TOOL
Fig. 16 SOLDER SPLICE
1 - SOLDER
2 - SPLICE BAND
3 - SOLDERING IRON
Fig. 17 HEAT SHRINK TUBE
1 - SEALANT
2 - HEAT SHRINK TUBE
RS8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION8W-01-15
Page 1189 of 2339

²Drill motor with 3M RolocŸ Bristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 3)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 4). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap/bed plate bolts of the
bearing being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Compare the clearance measurements to specsifica-
tions found in the engine specifications table(Refer to9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).Plastigage gen-
erally is accompanied by two scales. One scale
is in inches, the other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
(4) Install the proper crankshaft bearings to
achieve the specified bearing clearances.
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Remove air cleaner housing and inlet tube.
(4) Disconnect the fuel line from fuel rail. (Refer to
14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(5) Disconnect all vacuum hoses.
(6) Drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(7) Remove radiator fans. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL)
(8) Remove radiator upper and lower hoses.
NOTE: When the transaxle cooler lines are removed
from the rolled-groove type fittings at the transaxle,
damage to the inner wall of the hose will occur. To
prevent prevent potential leakage, the cooler hoses
must be cut off flush at the transaxle fitting, and a
service cooler hose splice kit must be installed
upon reassembly.
Fig. 3 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCŸ BRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
Fig. 4 Plastigage Placed in Lower ShellÐTypical
1 - PLASTIGAGE
9 - 12 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1263 of 2339

Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 3). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap/bed plate bolts of the
bearing being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Compare the clearance measurements to specsifica-
tions found in the engine specifications table(Refer to
9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).Plastigage gen-
erally is accompanied by two scales. One scale
is in inches, the other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
(4) Install the proper crankshaft bearings to
achieve the specified bearing clearances.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN IIis used to seal
components exposed to engine oil. This material is a
specially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTVis a specifically designed
black silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and
sealing properties to seal components exposed to
automatic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKERis an anaerobic type
gasket material. The material cures in the absence of
air when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It
will not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The
anaerobic material is for use between two machined
surfaces. Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
Fig. 3 Plastigage Placed in Lower ShellÐTypical
1 - PLASTIGAGE
9 - 86 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1413 of 2339
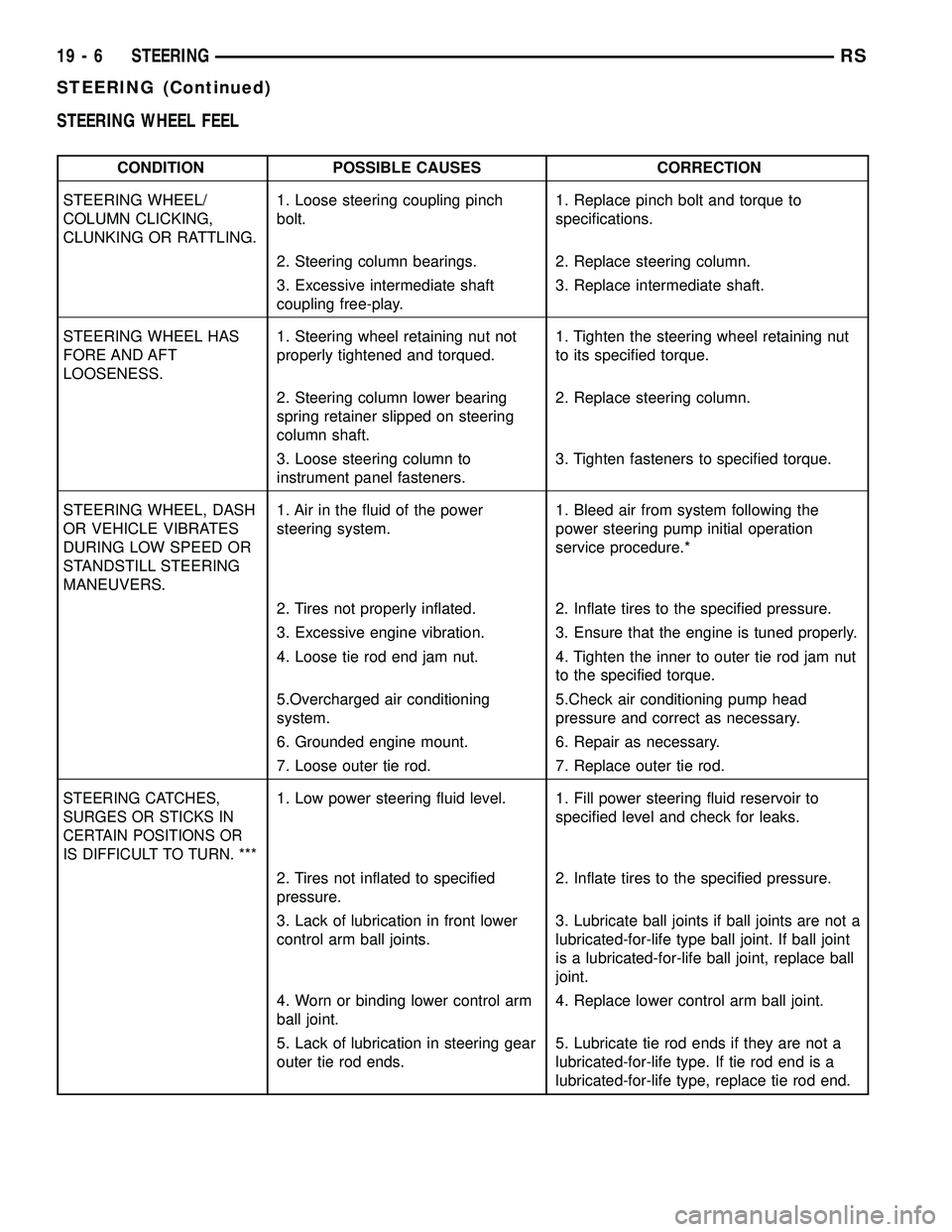
STEERING WHEEL FEEL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STEERING WHEEL/
COLUMN CLICKING,
CLUNKING OR RATTLING.1. Loose steering coupling pinch
bolt.1. Replace pinch bolt and torque to
specifications.
2. Steering column bearings. 2. Replace steering column.
3. Excessive intermediate shaft
coupling free-play.3. Replace intermediate shaft.
STEERING WHEEL HAS
FORE AND AFT
LOOSENESS.1. Steering wheel retaining nut not
properly tightened and torqued.1. Tighten the steering wheel retaining nut
to its specified torque.
2. Steering column lower bearing
spring retainer slipped on steering
column shaft.2. Replace steering column.
3. Loose steering column to
instrument panel fasteners.3. Tighten fasteners to specified torque.
STEERING WHEEL, DASH
OR VEHICLE VIBRATES
DURING LOW SPEED OR
STANDSTILL STEERING
MANEUVERS.1. Air in the fluid of the power
steering system.1. Bleed air from system following the
power steering pump initial operation
service procedure.*
2. Tires not properly inflated. 2. Inflate tires to the specified pressure.
3. Excessive engine vibration. 3. Ensure that the engine is tuned properly.
4. Loose tie rod end jam nut. 4. Tighten the inner to outer tie rod jam nut
to the specified torque.
5.Overcharged air conditioning
system.5.Check air conditioning pump head
pressure and correct as necessary.
6. Grounded engine mount. 6. Repair as necessary.
7. Loose outer tie rod. 7. Replace outer tie rod.
STEERING CATCHES,
SURGES OR STICKS IN
CERTAIN POSITIONS OR
IS DIFFICULT TO TURN. ***1. Low power steering fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
specified level and check for leaks.
2. Tires not inflated to specified
pressure.2. Inflate tires to the specified pressure.
3. Lack of lubrication in front lower
control arm ball joints.3. Lubricate ball joints if ball joints are not a
lubricated-for-life type ball joint. If ball joint
is a lubricated-for-life ball joint, replace ball
joint.
4. Worn or binding lower control arm
ball joint.4. Replace lower control arm ball joint.
5. Lack of lubrication in steering gear
outer tie rod ends.5. Lubricate tie rod ends if they are not a
lubricated-for-life type. If tie rod end is a
lubricated-for-life type, replace tie rod end.
19 - 6 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1414 of 2339
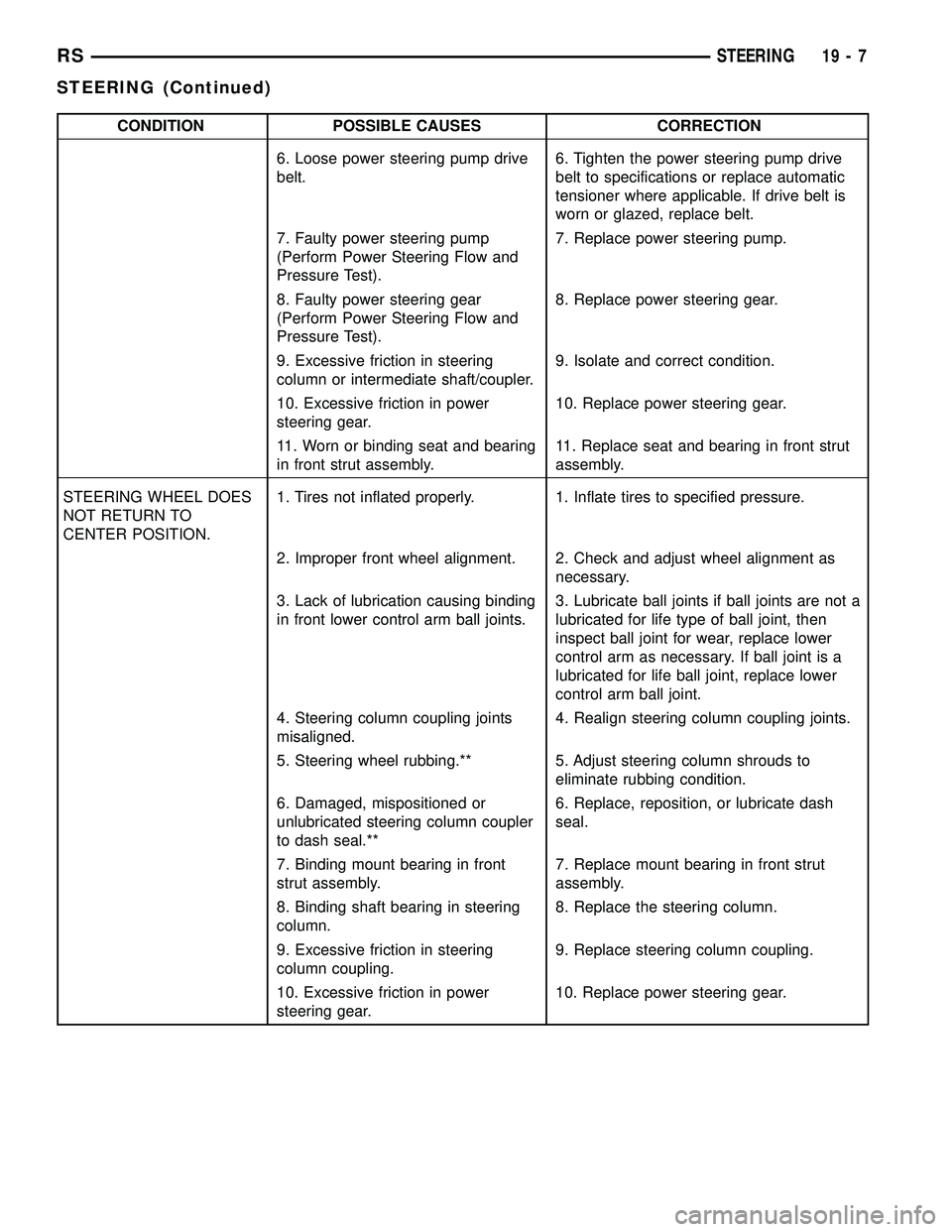
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
6. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.6. Tighten the power steering pump drive
belt to specifications or replace automatic
tensioner where applicable. If drive belt is
worn or glazed, replace belt.
7. Faulty power steering pump
(Perform Power Steering Flow and
Pressure Test).7. Replace power steering pump.
8. Faulty power steering gear
(Perform Power Steering Flow and
Pressure Test).8. Replace power steering gear.
9. Excessive friction in steering
column or intermediate shaft/coupler.9. Isolate and correct condition.
10. Excessive friction in power
steering gear.10. Replace power steering gear.
11. Worn or binding seat and bearing
in front strut assembly.11. Replace seat and bearing in front strut
assembly.
STEERING WHEEL DOES
NOT RETURN TO
CENTER POSITION.1. Tires not inflated properly. 1. Inflate tires to specified pressure.
2. Improper front wheel alignment. 2. Check and adjust wheel alignment as
necessary.
3. Lack of lubrication causing binding
in front lower control arm ball joints.3. Lubricate ball joints if ball joints are not a
lubricated for life type of ball joint, then
inspect ball joint for wear, replace lower
control arm as necessary. If ball joint is a
lubricated for life ball joint, replace lower
control arm ball joint.
4. Steering column coupling joints
misaligned.4. Realign steering column coupling joints.
5. Steering wheel rubbing.** 5. Adjust steering column shrouds to
eliminate rubbing condition.
6. Damaged, mispositioned or
unlubricated steering column coupler
to dash seal.**6. Replace, reposition, or lubricate dash
seal.
7. Binding mount bearing in front
strut assembly.7. Replace mount bearing in front strut
assembly.
8. Binding shaft bearing in steering
column.8. Replace the steering column.
9. Excessive friction in steering
column coupling.9. Replace steering column coupling.
10. Excessive friction in power
steering gear.10. Replace power steering gear.
RSSTEERING19-7
STEERING (Continued)