2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 2236 of 2339

FRONT HEATER CORE
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove the silencer boot fasteners located
around the base of the lower steering shaft from the
dash panel so that it may be pushed aside.
(2) Remove the brake lamp switch from its mount-
ing bracket (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/
LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the power brake booster input rod
(push rod) from the pin on the brake pedal arm
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - ABS/HYDRAULIC/ME-
CHANICAL/POWER BRAKE BOOSTER -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the heater core tubes (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
HEATER CORE - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the two screws that secure the heater
core mounting plate to the distribution housing.
(6) While pulling the accelerator pedal upward
(Fig. 18) and pushing the brake pedal downward
(Fig. 19) far enough for clearance, pull the heater
core out of the distribution housing.
(7) Use absorbent toweling to mop up any engine
coolant spills from the preceding operation. Also, if
the heater core was leaking, use absorbent toweling
and reach into the heater core opening to mop up
any residual engine coolant within the distribution
housing.
INSTALLATION
FRONT HEATER CORE TUBES
(1) Remove the plugs or tape from both heater core
tube fittings and both heater core ports.
(2) Position the heater core tubes and sealing plate
as a unit beneath the instrument panel.
Fig. 18 Accelerator Pedal - LHD Shown, RHD Typical
1 - HEATER CORE
Fig. 19 Brake Pedal - LHD Shown, RHD Typical
1 - HEATER CORE
2 - BRAKE PEDAL
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-85
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 2243 of 2339

(7) Lubricate a new rubber O-ring seal with clean
refrigerant oil and install it on the liquid line fitting.
(8) Reconnect the A/C liquid line to the receiver/
drier.
(9) Install the bolt that secures the A/C liquid line
to the receiver/drier. Tighten the bolt to 11 N´m (97
in. lbs.).
(10) If equipped, reinstall the A/C ground strap
eyelet terminal connector onto the weld stud on the
top of the right front strut tower (if equipped).
(11) If equipped, install the nut that secures the
A/C ground strap to the weld stud. Tighten the nut
to 12 N´m (106 in. lbs.)
(12) Install the A/C pressure transducer (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS
- FRONT/A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(13) Connect the drain tube to the wiper module
drain on the right side of the engine compartment.
(14) Install the air cleaner housing into the right
side of the engine compartment.
(15) On RHD models, install the liquid line into
the retaining bracket located at the top of the dash
panel.
(16) If the vehicle is equipped with the optional
rear heating-A/C system, go to Step 17. If the vehicle
does not have the optional rear heating-A/C system,
go to Step 23.
(17) Raise and support the vehicle.
(18) Remove the tape or plugs from the A/C liquid
line extension fitting and the underbody liquid line
fitting.
(19) Lubricate a new rubber O-ring seal with clean
refrigerant oil and install it on the underbody liquid
line fitting.
(20) Connect the A/C liquid line extension fitting
to the underbody liquid line fitting. Tighten the fit-
tings to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.).
(21) Install a new tie strap just forward of the con-
nections between the underbody plumbing and the
engine compartment plumbing for the rear heating-
A/C system.
(22) Lower the vehicle.
(23) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
(24) Evacuate the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE).
(25) Charge the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE).RECEIVER / DRIER
DESCRIPTION
The receiver/drier is mounted in a bracket secured
to the right front strut tower in the engine compart-
ment. The receiver/drier is connected between the
front and rear sections of the liquid line between the
condenser outlet and the evaporator inlet. The receiv-
er/drier cannot be repaired. If the receiver/drier is
faulty or damaged, or if the refrigerant system has
been contaminated or left open to the atmosphere for
an indeterminable period or if the A/C compressor
has failed, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The receiver/drier performs a filtering action to
prevent foreign material in the refrigerant from con-
taminating the expansion valve. Desiccant inside the
receiver/drier canister absorbs any moisture which
may have entered and become trapped within the
refrigerant system. In addition, during periods of
high demand air conditioner operation, the receiver/
drier acts as a reservoir to store surplus refrigerant.
Refrigerant enters the receiver/drier as a high-pres-
sure, low temperature liquid.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING) and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY).
(2) Remove the air cleaner housing from the right
side of the engine compartment.
(3) Remove the bolt that secures the liquid line
front section fitting to the top of the receiver/drier
(Fig. 30).
(4) Disconnect the liquid line fitting from the
receiver/drier inlet port.
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the liquid line fit-
ting and discard.
(6) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened liquid
line fitting and the receiver/drier inlet port.
24 - 92 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
LIQUID LINE (Continued)
Page 2245 of 2339

OPERATION
R-134a refrigerant is not compatible with R-12
refrigerant in an air conditioning system. Even a
small amount of R-12 added to an R-134a refrigerant
system will cause compressor failure, refrigerant oil
sludge or poor air conditioning system performance.
In addition, the PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG) synthetic
refrigerant oils used in an R-134a refrigerant system
are not compatible with the mineral-based refriger-
ant oils used in an R-12 refrigerant system. R-134a
refrigerant system service ports, service tool couplers
and refrigerant dispensing bottles have all been
designed with unique fittings to ensure that an
R-134a system is not accidentally contaminated with
the wrong refrigerant (R-12). There are also labels
posted in the engine compartment of the vehicle and
on the compressor identifying to service technicians
that the air conditioning system is equipped with
R-134a.
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant oil used in R-134a refrigerant sys-
tems is a synthetic-based, PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG),
wax-free lubricant. Mineral-based R-12 refrigerant
oils are not compatible with PAG oils, and should
never be introduced to an R-134a refrigerant system.
There are different PAG oils available, and each con-
tains a different additive package. The compressor
used in this vehicle is designed to use an ND-8 PAG
refrigerant oil. Use only refrigerant oil of this same
type to service the refrigerant system.
OPERATION
After performing any refrigerant recovery or recy-
cling operation, always replenish the refrigerant sys-
tem with the same amount of the recommended
refrigerant oil as was removed. Too little refrigerant
oil can cause compressor damage, and too much can
reduce air conditioning system performance. PAG
refrigerant oil is much more hygroscopic than min-
eral oil, and will absorb any moisture it comes into
contact with, even moisture in the air. The PAG oil
container should always be kept tightly capped until
it is ready to be used. After use, recap the oil con-
tainer immediately to prevent moisture contamina-
tion.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING) and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
CAUTION: Use only PAG oils that are designed to
work with R-134a refrigerant and the A/C compres-
sor in the vehicle. Refer to the underhood A/C Sys-
tem Specification Label.
It is important to have the correct amount of lubri-
cant in the A/C refrigerant system to ensure proper
lubrication of the A/C compressor. Too little lubricant
will result in damage to the compressor. Too much
lubricant will reduce the cooling capacity of the A/C
system and consequently result in higher discharge
air temperatures.
The lubricant used in the compressor is polyalka-
lene glycol PAG lubricant. Only the refrigerant lubri-
cant approved for use with this vehicle should be
used to service the system. Do not use any other
lubricant. The lubricant container should be kept
tightly capped until it is ready for use. Refrigerant
lubricant will quickly absorb any moisture it comes
in contact with.
It will not be necessary to check the oil level in the
A/C compressor or to add oil, unless there has been
an oil loss. An oil loss may occur due to a rupture or
leak from a refrigerant line, connector fitting, compo-
nent or component seal. If a leak occurs, add 30 mil-
liliters (1 fluid ounce) of the recommended
refrigerant oil to the refrigerant system after the
repair has been made. Refrigerant oil loss will be evi-
dent at the leak point by the presence of a wet, shiny
surface around the leak.
REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL CHECK
When an air conditioning system is first assembled
at the factory, all components (except the A/C com-
pressor) are refrigerant oil free. After the refrigerant
system has been charged with (R-134a) refrigerant
and operated, the oil in the A/C compressor is dis-
persed through the lines and components. The A/C
evaporator, A/C condenser, and receiver/drier will
retain a significant amount of oil. Refer to the A/C
Component Refrigerant Oil Capacities table. When a
component is replaced, the specified amount of refrig-
erant oil must be added. When the compressor is
replaced, the amount of oil that is retained in the
24 - 94 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
REFRIGERANT (Continued)
Page 2249 of 2339

PLUMBING - REAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
A/C EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................98
OPERATION...........................98
REMOVAL
REAR A/C EVAPORATOR...............98
REAR A/C EVAPORATOR LINE
EXTENSION.........................99
INSTALLATION
REAR A/C EVAPORATOR..............100
REAR A/C EVAPORATOR LINE
EXTENSION........................100
A/C EXPANSION VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................100
OPERATION..........................100
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
REAR A/C EXPANSION VALVE..........101
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................101
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION........................102
OPERATION..........................102
STANDARD PROCEDURE
REAR HEATER CORE FILLING..........102REMOVAL............................103
INSTALLATION........................104
HEATER HOSES
REMOVAL............................104
INSTALLATION........................105
LIQUID LINE
REMOVAL............................105
INSTALLATION........................106
SUCTION LINE
REMOVAL............................106
INSTALLATION........................107
UNDERBODY LINES
DESCRIPTION........................108
OPERATION..........................108
REMOVAL
UNDERBODY HEATER TUBES..........109
UNDERBODY REFRIGERANT LINES......110
INSTALLATION
UNDERBODY HEATER TUBES..........112
UNDERBODY REFRIGERANT LINES......112
A/C EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION
The rear A/C evaporator is located in the rear
HVAC housing, behind the right rear wheel house.
The evaporator is positioned in the rear housing so
that all air that enters the housing must pass over
the fins of the evaporator coils before it is distributed
through the system ducts and outlets. However, air
passing over the evaporator fins will only be condi-
tioned when the compressor is engaged and circulat-
ing refrigerant through the evaporator tubes. The
rear HVAC housing must be removed from the vehi-
cle to access the A/C evaporator for service.
OPERATION
Refrigerant enters the rear evaporator from the
rear expansion valve as a low-temperature, low-pres-
sure liquid. As air flows over the fins of the evapora-
tor, the humidity in the air condenses on the fins,
and the heat from the air is absorbed by the refrig-
erant. Heat absorption causes the refrigerant to boil
and vaporize. The refrigerant becomes a low-pressure
gas when it leaves the evaporator.
REMOVAL
REAR A/C EVAPORATOR
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING), (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING), and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMBING).
(1) Remove the rear HVAC housing from the vehi-
cle (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the rear evaporator line extension from
the expansion valve (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - REAR/EVAPORA-
TOR - REMOVAL - EVAPORATOR LINE EXTEN-
SION).
(3) Remove the rear expansion valve from the rear
evaporator (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
24 - 98 PLUMBING - REARRS
Page 2253 of 2339

(5) Install the rear evaporator line extension onto
the expansion valve (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - REAR/EVAPORA-
TOR - INSTALLATION - EVAPORATOR LINE
EXTENSION).
(6) Install the foam insulator wrap over the rear
expansion valve.
(7) Install the rear HVAC housing (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(8) Run the HVAC Cooldown Test to verify proper
operation.
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The rear heater core is located near the front of
the rear HVAC housing, behind the right rear wheel
house. It is a heat exchanger made of rows of tubes
and fins. One end of the core is fitted with a molded
plastic tank that includes integral heater core inlet
and outlet nipples. The rear heater core can be ser-
viced without removing the rear HVAC housing from
the vehicle.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through underbody
heater hoses to the rear heater core at all times. As
the coolant flows through the rear heater core, heat
removed from the engine is transferred to the heater
core fins and tubes. Air directed through the heater
core picks up the heat from the heater core fins. The
rear blend door allows control of the rear heater out-
put air temperature by controlling how much of the
air flowing through the rear HVAC housing is
directed through the heater core.
The rear heater core cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
REAR HEATER CORE FILLING
In its final installed position, the rear heater core
is positioned higher than the radiator fill cap. There-
fore, when the cooling system is drained and refilled,
gravity will not refill the heater core with coolant to
the proper level. This may result in two problems:1.
Insufficient coolant level in the engine cooling sys-
tem, which may result in engine overheating.2.Air
entrapped within the rear heater core, which may
result in insufficient rear heater performance. There
are two methods that may be employed to prevent
these problems:1.Pre-filling of the rear heater core.
2.Thermal cycling of the engine cooling system. Fol-lowing are descriptions of both prevention methods,
as well as a method to verify rear heater perfor-
mance.
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING
FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMBING).
PRE-FILLING
If the rear heater core or the rear HVAC housing
have been removed from the vehicle for service, the
rear heater core may be pre-filled with the proper
engine coolant mixture prior to reconnecting the
heater hoses to the heater core hose fittings.
(1) The heater core should be installed in the rear
HVAC housing, and the rear HVAC housing should
be installed in the vehicle.
(2) Take the proper precautions to protect the car-
peting below the rear heater core from spilled engine
coolant and have absorbent toweling readily avail-
able to mop up any spills.
(3) Insert the small end of an appropriate funnel
into the upper hose fitting of the heater core (Fig. 4).
(4) Carefully pour the proper pre-mixed engine
coolant solution into the rear heater core through a
funnel until coolant begins to appear at the lower
hose fitting of the heater core.
(5) Use absorbent toweling to clean up any engine
coolant spills from the preceding operation.
(6) Reconnect the heater hoses to the rear heater
core (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER HOSE - INSTAL-
LATION).
Fig. 4 Pre-Filling Heater Core - Typical
1 - REAR HEATER CORE
24 - 102 PLUMBING - REARRS
A/C EXPANSION VALVE (Continued)
Page 2254 of 2339

(7) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
THERMAL CYCLING
If the rear heater core was emptied and was not
pre-filled, it will be necessary to thermal cycle the
vehicle at least two times to ensure that the rear
heater core is properly filled.
(1) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
(2) Start the engine and allow it to operate until
the thermostat opens.
(3) Turn the engine off and allow it to cool.
(4) With the engine cold and not running, check
and top off the engine coolant level as necessary
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- COOLANT LEVEL CHECK) and (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
- ADDING).
(5) Start the engine and allow it to operate until
the thermostat opens again.
(6) Turn the engine off and allow it to cool down
again.
(7) With the engine cold and not running, check
and top off the engine coolant level as necessary
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- COOLANT LEVEL CHECK) and (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
- ADDING).
(8) Check the performance of the rear heater.
Refer to REAR HEATER PERFORMANCE CHECK.
REAR HEATER PERFORMANCE CHECK
Successful completion of the rear heater perfor-
mance check will confirm that the rear heater core is
properly filled with engine coolant. If the check is not
successful, either there is still air trapped in the rear
heater core or the rear heater plumbing is restricted.
This check should be performed with the vehicle in a
shop where the ambient temperature is about 21É C
(70É F).
(1) Start the engine and allow it to idle until it
warms up to normal operating temperature.
(2) Adjust the heater-A/C controls so that the front
heater is turned Off, the rear heater is set for full
Heat, and the rear blower motor is at its highest
speed setting.
(3) Use an accurate test thermometer to measure
the temperature of the air being discharged from the
rear heater outlet located at the base of the right
C-pillar.
(4) Proper discharge air temperature readings
should be from 57É to 63É C (135É to 145É F).REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING
FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMBING).
(1) Drain the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM DRAIN).
(2) Remove the right quarter trim panel and right
D-pillar trim panel from the quarter inner panel
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/QUARTER TRIM
PANEL - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rear heater distribution duct from
the right quarter inner panel (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION -
REAR/REAR HEATER DISTRIBUTION DUCT -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the screw that secures the back of the
rear HVAC housing to the right D-pillar.
(5) Remove the screw that secures the front of the
rear HVAC housing to the right quarter inner panel.
(6) Take the proper precautions to protect the car-
peting below the rear heater core from spilled engine
coolant and have absorbent toweling readily avail-
able to mop up any spills.
(7) Disconnect the heater hoses at the rear heater
core (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER HOSE -
REMOVAL).
(8) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened heater
core fittings and both heater hoses (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 Rear Heater Core
1 - REAR HVAC HOUSING OUTLET
2 - REAR HVAC UNIT HOUSING
3 - LATCH (4)
4 - REAR HEATER CORE
5 - RIGHT REAR WHEEL HOUSE
6 - REAR HEATER HOSES
RSPLUMBING - REAR24 - 103
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 2255 of 2339
(9) Use absorbent toweling to clean up any engine
coolant spills from the preceding operation.
(10) Release the four latch tabs that secure the
heater core into the rear HVAC housing.
(11) Carefully pull the heater core straight out of
the rear HVAC housing.
(12) Use absorbent toweling to clean up any
engine coolant spills from the preceding operation.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If the rear heater core or the rear HVAC
housing have been removed from the vehicle for
service, the rear heater core may be pre-filled with
the proper engine coolant mixture prior to recon-
necting the heater hoses to the heater core hose fit-
tings (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER CORE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - HEATER CORE FILLING).
(1) Carefully slide the heater core into the rear
HVAC housing.
(2) Using hand pressure, press firmly and evenly
on the heater core end plate until the four latch tabs
that secure the heater core in the rear HVAC housing
are fully engaged.
(3) Remove the plugs or tape from the heater core
fittings and both heater hoses.
(4) Reconnect the heater hoses to the rear heater
core (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER HOSE - INSTAL-
LATION).
(5) Install the screw that secures the front of the
rear HVAC housing to the right quarter inner panel.
Tighten the screw to 11 N´m (97 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the screw that secures the back of the
rear HVAC housing to the right D-pillar. Tighten the
screw to 11 N´m (97 in. lbs.).
(7) Install the rear heater distribution duct (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRI-
BUTION - REAR/REAR HEATER DISTRIBUTION
DUCT - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the right quarter trim panel and right
D-pillar trim panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/
QUARTER TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION).
(9) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM REFILL).
HEATER HOSES
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WARNING).
(1) Drain the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM DRAIN).
(2) Using spring tension clamp pliers, compress
and slide the clamps off of each end of the hose being
removed.
CAUTION:
DO NOT apply excessive pressure on heater tubes
or connections when removing heater hoses.
Excessive pressure may damage or deform the
tubes, causing an engine coolant leak.
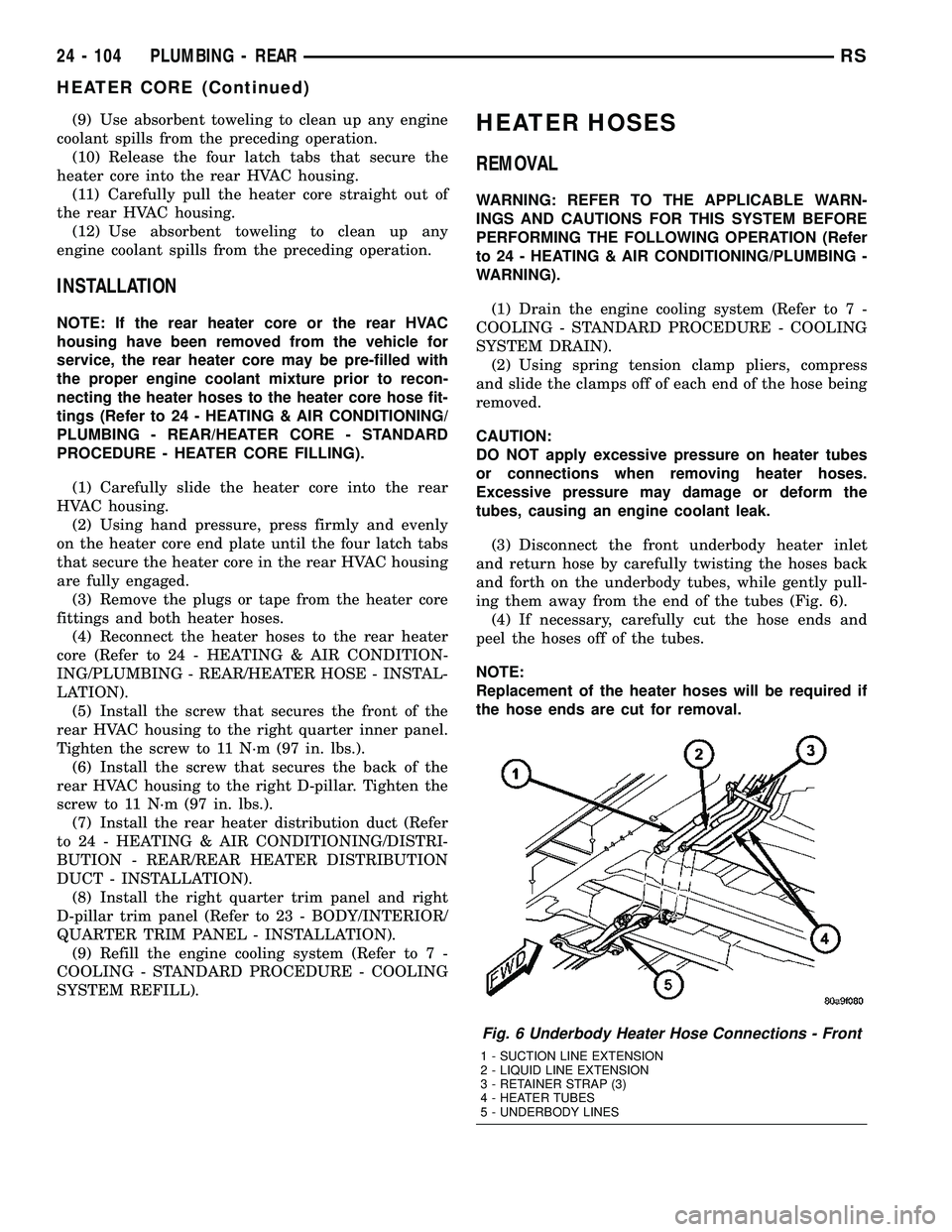
(3) Disconnect the front underbody heater inlet
and return hose by carefully twisting the hoses back
and forth on the underbody tubes, while gently pull-
ing them away from the end of the tubes (Fig. 6).
(4) If necessary, carefully cut the hose ends and
peel the hoses off of the tubes.
NOTE:
Replacement of the heater hoses will be required if
the hose ends are cut for removal.
Fig. 6 Underbody Heater Hose Connections - Front
1 - SUCTION LINE EXTENSION
2 - LIQUID LINE EXTENSION
3 - RETAINER STRAP (3)
4 - HEATER TUBES
5 - UNDERBODY LINES
24 - 104 PLUMBING - REARRS
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 2275 of 2339

The following is a list of the monitored compo-
nents:
²Catalyst Monitor
²Comprehensive Components
²EGR (if equipped)
²Fuel Control (rich/lean)
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Purge
²Misfire
²Natural Vacuum Leak Detection (NVLD)
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS
Along with the major monitors, OBD II requires
that the diagnostic system monitor any component
that could affect emissions levels. In many cases,
these components were being tested under OBD I.
The OBD I requirements focused mainly on testing
emissions-related components for electrical opens and
shorts.
However, OBD II also requires that inputs from
powertrain components to the PCM be tested for
rationality, and that outputs to powertrain compo-
nents from the PCM be tested forfunctionality.
Methods for monitoring the various Comprehensive
Component monitoring include:
(1) Circuit Continuity
²Open
²Shorted high
²Shorted to ground
(2) Rationality or Proper Functioning
²Inputs tested for rationality
²Outputs tested for functionality
NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply. All will set a DTC and illuminate the MIL in 1-
trip.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S) (slow response)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Natural Vacuum Leak Detection (NVLD)
²P/N Switch
²Trans Controls
Output FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
put component, it can verify that the command was
carried out by monitoring specific input signals for
expected changes. For example, when the PCM com-
mands the Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor to a specific
position under certain operating conditions, it expects
to see a specific (target) idle speed (RPM). If it does
not, it stores a DTC.
PCM outputs monitored for functionality include:
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coils
²Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Idle Air Control
²Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid
²Radiator Fan Control
²Trans Controls
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐEffective control of exhaust
emissions is achieved by an oxygen feedback system.
The most important element of the feedback system
is the O2S. The O2S is located in the exhaust path.
Once it reaches operating temperature 300É to 350ÉC
(572É to 662ÉF), the sensor generates a voltage that
is inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen in
the exhaust. When there is a large amount of oxygen
in the exhaust caused by a lean condition, misfire or
exhaust leak, the sensor produces a low voltage,
below 450 mV. When the oxygen content is lower,
caused by a rich condition, the sensor produces a
higher voltage, above 450mV.
The information obtained by the sensor is used to
calculate the fuel injector pulse width. The PCM is
programmed to maintain the optimum air/fuel ratio.
At this mixture ratio, the catalyst works best to
remove hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and nitrous oxide (NOx) from the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
EGR, Catalyst and Fuel Monitors, and purge.
The O2S may fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²Slow response rate (Big Slope)
²Reduced output voltage (Half Cycle)
²Heater Performance
Slow Response Rate (Big Slope)ÐResponse rate
is the time required for the sensor to switch from
lean to rich signal output once it is exposed to a
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLRS
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)