2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 559 of 2339

(7) Disconnect the wire connectors from back of
the wiper motor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect the wire harness connector.
(2) Install the linkage on the wiper unit.
(3) Install the nut holding the linkage to the wiper
unit.
(4) Install the cowl cover brackets to the wiper
nut.
(5) Install the front wiper unit (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the cowl cover.
(7) Install the wiper arms and blades.
WIPER MODULE
REMOVAL
(1) Release the hood latch and open hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the wiper arms.
(4) Remove the cowl cover (Refer to 23 - BODY/
EXTERIOR/COWL GRILLE - REMOVAL).
(5) Disconnect the positive lock on the wiper mod-
ule wire connector (Fig. 7).
(6) Disconnect the wiper module wire connector
from the engine compartment wire harness.
(7) Disconnect the windshield washer hose from
coupling outside the module.
(8) Disconnect the drain tubes from nipples on bot-
tom of the wiper module.(9) Remove nuts holding wiper module to lower
windshield fence.
(10) Remove bolts holding the wiper module to the
dash panel (Fig. 8).
(11) Lift wiper module from weld-studs on lower
windshield fence.
CAUTION: Do not allow wiper module to rest on
brake master cylinder reservoir, damage to brake
system can result.
(12) Remove wiper module.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the wiper module into the cowl.
(2) Install the bolts that secure the wiper module
to the dash (Fig. 8).
(3) Install the nuts that retain the wiper module.
(4) Connect the drain tubes to the nipples on the
wiper module.
(5) Connect the windshield washer tube.
(6) Connect the wire harness connector to the
wiper module (Fig. 8).
(7) Connect the positive lock on the wiper module
wire connector (Fig. 7).
CAUTION: Do not allow wiper module to rest on
brake master cylinder reservoir, damage to brake
system can result.
(8) Install the cowl cover (Refer to 23 - BODY/EX-
TERIOR/COWL GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the wiper arms and blades.
(10) Connect the battery negative cable.
(11) Close the hood.
Fig. 7 WIPER MODULE WIRE CONNECTOR
1 - WIPER SYSTEM WIRE CONNECTOR
2 - LOCK TAB
3 - POSITIVE LOCK
4 - WIPER MODULE
Fig. 8 WIPER MODULE
1 - BOLT
2 - NUTS
3 - BOLT
4 - WIPER MODULE
5 - WINDSHIELD
8R - 14 WIPERS/WASHERSRS
WIPER LINKAGE (Continued)
Page 564 of 2339

WIRING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION....... 8W-01-1
COMPONENT INDEX.................. 8W-02-1
POWER DISTRIBUTION............... 8W-10-1
GROUND DISTRIBUTION.............. 8W-15-1
BUS COMMUNICATIONS.............. 8W-18-1
CHARGING SYSTEM.................. 8W-20-1
STARTING SYSTEM.................. 8W-21-1
FUEL/IGNITION SYSTEM.............. 8W-30-1
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM..... 8W-31-1
VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL............ 8W-33-1
ANTILOCK BRAKES................... 8W-35-1
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM..... 8W-39-1
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER............... 8W-40-1
HORN/CIGAR LIGHTER/POWER OUTLET . . 8W-41-1
AIR CONDITIONING-HEATER........... 8W-42-1
OCCUPANT RESTRAINT SYSTEM........ 8W-43-1
INTERIOR LIGHTING.................. 8W-44-1
BODY CONTROL MODULE............. 8W-45-1
MESSAGE CENTER................... 8W-46-1
AUDIO SYSTEM..................... 8W-47-1REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER............ 8W-48-1
OVERHEAD CONSOLE................. 8W-49-1
FRONT LIGHTING.................... 8W-50-1
REAR LIGHTING..................... 8W-51-1
TURN SIGNALS...................... 8W-52-1
WIPERS............................ 8W-53-1
TRAILER TOW....................... 8W-54-1
NAVIGATION/TELECOMMUNICATIONS.... 8W-55-1
CONVENIENCE SYSTEMS.............. 8W-56-1
POWER WINDOWS................... 8W-60-1
POWER DOOR LOCKS................ 8W-61-1
POWER MIRRORS................... 8W-62-1
POWER SEATS...................... 8W-63-1
POWER SUNROOF................... 8W-64-1
SPLICE INFORMATION................ 8W-70-1
CONNECTOR PIN-OUTS............... 8W-80-1
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE
LOCATION........................ 8W-91-1
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM........ 8W-97-1 RSWIRING
8W-1
Page 754 of 2339

8W-39 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM
Component Page
Body Control Module........... 8W-39-2, 3, 6, 7,
8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13
Clockspring........................ 8W-39-5
Driver Door Lock Switch........... 8W-39-11, 12
Front Control Module............. 8W-39-2, 3, 5
Front Intrusion Sensor................ 8W-39-4
Fuse 8............................ 8W-39-5
Fuse 14............................ 8W-39-2
G102.............................. 8W-39-5
G200.......................... 8W-39-2, 3, 5
G300.............. 8W-39-6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13
G301................. 8W-39-6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12
G302............................. 8W-39-13
G303............................. 8W-39-13
High Note Horn..................... 8W-39-5
Hood Ajar Switch................... 8W-39-13
Horn Relay......................... 8W-39-5
Horn Switch........................ 8W-39-5
Ignition Switch.................... 8W-39-2, 3
Integrated Power Module.......... 8W-39-2, 3, 5
Left Cylinder Lock Switch......... 8W-39-11, 12
Left Front Door Ajar Switch............ 8W-39-6
Left Front Door Lock Motor/Ajar
Switch........................ 8W-39-6, 7Component Page
Left Sliding Door Control Module...... 8W-39-8, 9
Left Sliding Door Latch Sensing Switch . . . 8W-39-8
Left Sliding Door Lock Motor........... 8W-39-9
Left Sliding Door Lock Motor/Ajar
Switch......................... 8W-39-10
Liftgate Ajar Switch................. 8W-39-13
Liftgate Cinch/Release Motor.......... 8W-39-13
Passenger Door Lock Switch........ 8W-39-11, 12
Power Liftgate Module............... 8W-39-13
Rear Intrusion Sensor................ 8W-39-4
Right Cylinder Lock Switch........ 8W-39-11, 12
Right Front Door Ajar Switch........... 8W-39-6
Right Front Door Lock Motor/Ajar
Switch........................ 8W-39-6, 7
Right Sliding Door Control Module.... 8W-39-8, 9
Right Sliding Door Latch Sensing Switch . . 8W-39-8
Right Sliding Door Lock Motor.......... 8W-39-9
Right Sliding Door Lock Motor/Ajar
Switch......................... 8W-39-10
Sentry Key Remote Entry Module....... 8W-39-2
Siren............................. 8W-39-3
Thatcham Alarm Indicator............. 8W-39-4
Thatcham Alarm Module............ 8W-39-3, 4
RS8W-39 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM8W-39-1
Page 1174 of 2339
8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS.........1
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
REMOVAL.............................2
INSTALLATION..........................2IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - POWER OUTLET . . 3
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
POWER DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The power distribution system for this vehicle con-
sists of the following components:
²Integrated Power Module (IPM)
²Front Control Module (FCM)
²Power Outlets
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit sche-
matics.
The power distribution system also incorporates
various types of circuit control and protection fea-
tures, including:
²Automatic resetting circuit breakers
²Blade-type fuses
²Bus bars
²Cartridge fuses
²Circuit splice blocks
²Flashers
²Fusible links
²Relays
OPERATION
The power distribution system for this vehicle is
designed to provide safe, reliable, and centralized dis-
tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the many standard and optional facto-
ry-installed electrical and electronic powertrain,
chassis, safety, security, comfort and convenience sys-
tems. At the same time, the power distribution sys-
tem was designed to provide ready access to these
electrical distribution points for the vehicle techni-
cian to use when conducting diagnosis and repair of
faulty circuits. The power distribution system can
also prove useful for the sourcing of additional elec-
trical circuits that may be required to provide theelectrical current needed to operate many accessories
that the vehicle owner may choose to have installed.
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Integrated Power Module (IPM) is a combina-
tion of the Power Distribution Center (PDC) and the
Front Control Module (FCM). The IPM is located in
the engine compartment, next to the battery. (Fig. 1).
The PDC mates directly with the FCM to form the
IPM. The PDC is a printed circuit board based mod-
ule that contains fuses and relays, while the FCM
contains the electronics controlling the IPM and
other functions. This IPM connects directly to the
battery positive through a four pin connector. The
ground connection is through two other connectors.
Terminal Pick Kit 6680
RS8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM8W-97-1
Page 1175 of 2339

The IPM provides the primary means of voltage dis-
tribution and protection for the entire vehicle.
OPERATION
All of the current from the battery and the gener-
ator output enters the Integrated Power Module
(IPM) through a four- pin connector on the bottom of
the module. Internal connections of all of the power
distribution center circuits is accomplished by a com-
bination of bus bars and a printed circuit board.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative and positive battery
cables.
(2) Remove the battery thermal guard.
(3) Remove the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(4) Using a flat-bladed screwdriver, twist the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM) bracket retaining latch
outward to free the IPM from its mounting bracket
(Fig. 2).
(5) Rotate the IPM counter-clockwise to access and
disconnect the electrical connectors (Fig. 3).
(6) Remove the IPM bracket clips from the hinge.
INSTALLATION
(1) Snap the left side of the Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM) housing in its mounting bracket and con-
nect the various electrical connectors.NOTE: Ensure that the Connector Positive Assur-
ance (CPA) on the five-pin B+ connector is posi-
tively engaged to prevent generating a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
(2) Rotate the IPM clock-wise until secured in
mounting bracket. An audible click may be heard.
(3) Install the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the battery thermal guard.
Fig. 1 INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
Fig. 2 INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
Fig. 3 DISCONNECTING IPM
1 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
8W - 97 - 2 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMRS
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (Continued)
Page 1176 of 2339

(5) Connect the negative and positive battery
cables.
(6) Using a scan tool, check for any stored diagnos-
tic trouble codes. Ensure that all vehicle options are
operational.
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse that is removed from its normal
cavity in the Integrated Power Module (IPM) when
the vehicle is shipped from the factory. Dealer per-
sonnel are to remove the IOD fuse from the storage
location and install it into the IPM fuse cavity
marked IOD as part of the preparation procedures
performed just prior to new vehicle delivery.
The IOD fuse is a 20 ampere blade-type mini fuse
and, when removed, it is stored in a fuse cavity adja-
cent to the washer fuse within the IPM.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw (IOD) identifies a nor-
mal condition where power is being drained from the
battery with the ignition switch in the Off position.
The IOD fuse feeds the memory and sleep mode func-
tions for some of the electronic modules in the vehicle
as well as various other accessories that require bat-
tery current when the ignition switch is in the Off
position, including the clock. The only reason the
IOD fuse is removed is to reduce the normal IOD of
the vehicle electrical system during new vehicle
transportation and pre-delivery storage to reduce
battery depletion, while still allowing vehicle opera-
tion so that the vehicle can be loaded, unloaded and
moved as needed by both vehicle transportation com-
pany and dealer personnel.
The IOD fuse is removed from the Integrated
Power Module (IPM) fuse cavity when the vehicle is
shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer personnel
must install the IOD fuse when the vehicle is being
prepared for delivery in order to restore full electrical
system operation. Once the vehicle is prepared for
delivery, the IOD function of this fuse becomes trans-
parent and the fuse that has been assigned the IOD
designation becomes only another Fused B(+) circuit
fuse. The IOD fuse serves no useful purpose to the
dealer technician in the service or diagnosis of any
vehicle system or condition, other than the same pur-
pose as that of any other standard circuit protection
device.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not to
exceed approximately thirty days. However, it mustbe remembered that removing the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
If a vehicle will be stored for more than thirty days,
the battery negative cable should be disconnected to
eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery should be
tested and recharged at regular intervals during the
vehicle storage period to prevent the battery from
becoming discharged or damaged.
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
Two power outlets are installed in the instrument
panel center lower bezel. Two additional power out-
lets are incorporated into the left rear C-pillar and
the center console (if equipped). The power outlets
bases are secured by a snap fit. A hinged plug flips
closed to conceal and protect the power outlet base
when not in use.
OPERATION
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a battery receives battery voltage from a fuse in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM) at all times. The
other power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a key receives battery voltage only when the
key is in the on position.
The power outlet located in the center console
receives battery voltage all the time when positioned
between thefront seatsand key-on voltage when
positioned between therear seats. The power outlet
located on the C-pillar receives battery voltage only
when the key is in the ON position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - POWER OUTLET
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO RESTRAINTS BEFORE ATTEMPT-
ING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN,
SEAT OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAG-
NOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the Integrated
Power Module (IPM). If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK,
repair the shorted circuit or component as required
and replace the faulty fuse.
RS8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM8W-97-3
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (Continued)
Page 1267 of 2339
(41) Disconnect the knock sensor electrical connec-
tor (3.8L only).
(42) Disconnect the engine block heater electrical
connector (if equipped).
(43) Remove the accessory belt splash shield.
(44) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(45) Disconnect the radiator lower hose.
(46) Remove air conditioning compressor from
engine.
(47) Remove the generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(48) Remove the water pump pulley attaching
bolts and position pulley between pump hub and
housing.
(49) Disconnect the oil pressure switch electrical
connector.
(50) Disconnect wiring harness support clip from
engine oil dipstick tube.
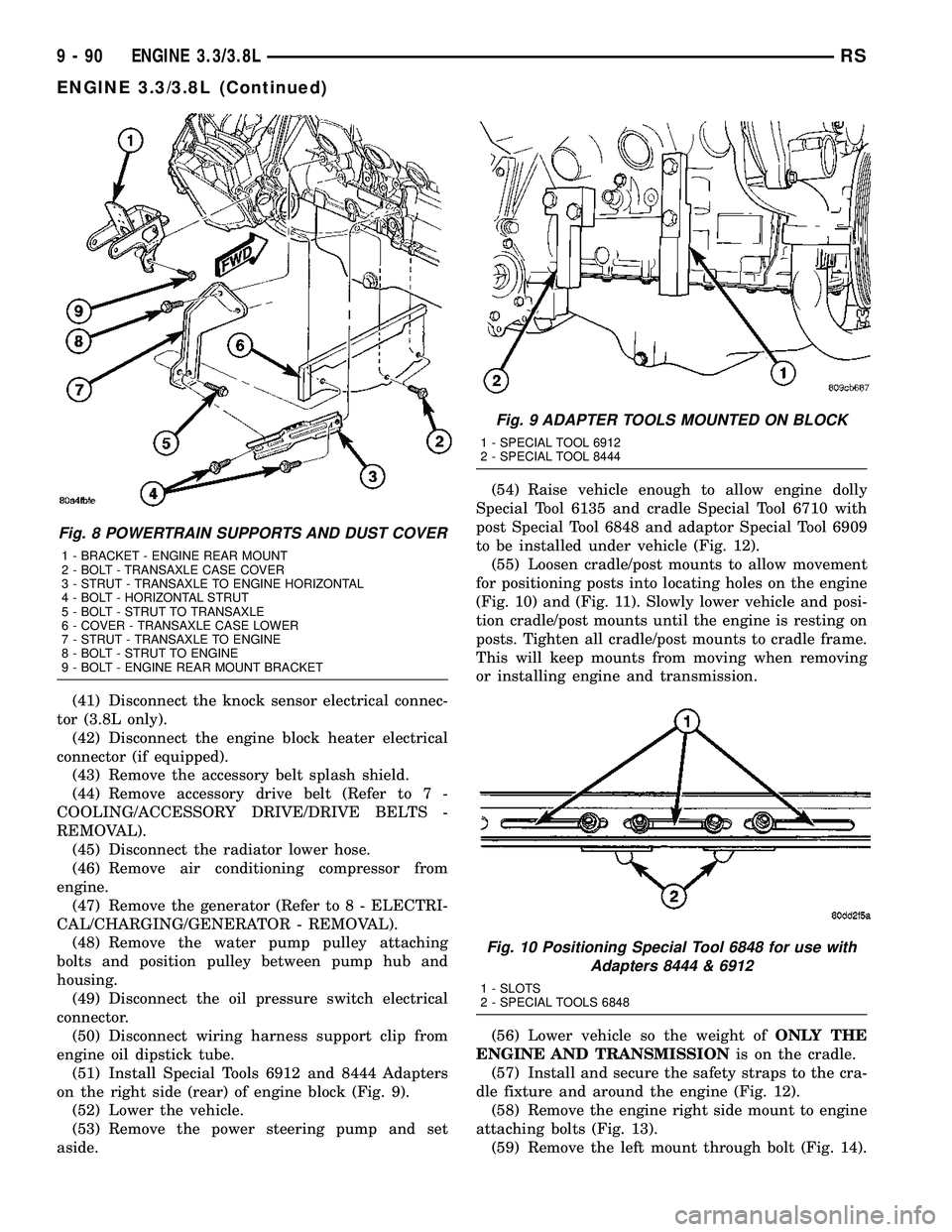
(51) Install Special Tools 6912 and 8444 Adapters
on the right side (rear) of engine block (Fig. 9).
(52) Lower the vehicle.
(53) Remove the power steering pump and set
aside.(54) Raise vehicle enough to allow engine dolly
Special Tool 6135 and cradle Special Tool 6710 with
post Special Tool 6848 and adaptor Special Tool 6909
to be installed under vehicle (Fig. 12).
(55) Loosen cradle/post mounts to allow movement
for positioning posts into locating holes on the engine
(Fig. 10) and (Fig. 11). Slowly lower vehicle and posi-
tion cradle/post mounts until the engine is resting on
posts. Tighten all cradle/post mounts to cradle frame.
This will keep mounts from moving when removing
or installing engine and transmission.
(56) Lower vehicle so the weight ofONLY THE
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSIONis on the cradle.
(57) Install and secure the safety straps to the cra-
dle fixture and around the engine (Fig. 12).
(58) Remove the engine right side mount to engine
attaching bolts (Fig. 13).
(59) Remove the left mount through bolt (Fig. 14).
Fig. 8 POWERTRAIN SUPPORTS AND DUST COVER
1 - BRACKET - ENGINE REAR MOUNT
2 - BOLT - TRANSAXLE CASE COVER
3 - STRUT - TRANSAXLE TO ENGINE HORIZONTAL
4 - BOLT - HORIZONTAL STRUT
5 - BOLT - STRUT TO TRANSAXLE
6 - COVER - TRANSAXLE CASE LOWER
7 - STRUT - TRANSAXLE TO ENGINE
8 - BOLT - STRUT TO ENGINE
9 - BOLT - ENGINE REAR MOUNT BRACKET
Fig. 9 ADAPTER TOOLS MOUNTED ON BLOCK
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6912
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8444
Fig. 10 Positioning Special Tool 6848 for use with
Adapters 8444 & 6912
1 - SLOTS
2 - SPECIAL TOOLS 6848
9 - 90 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1293 of 2339
46) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). If
the cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the
cylinder block should be replaced, and new pistons
and rings fitted.
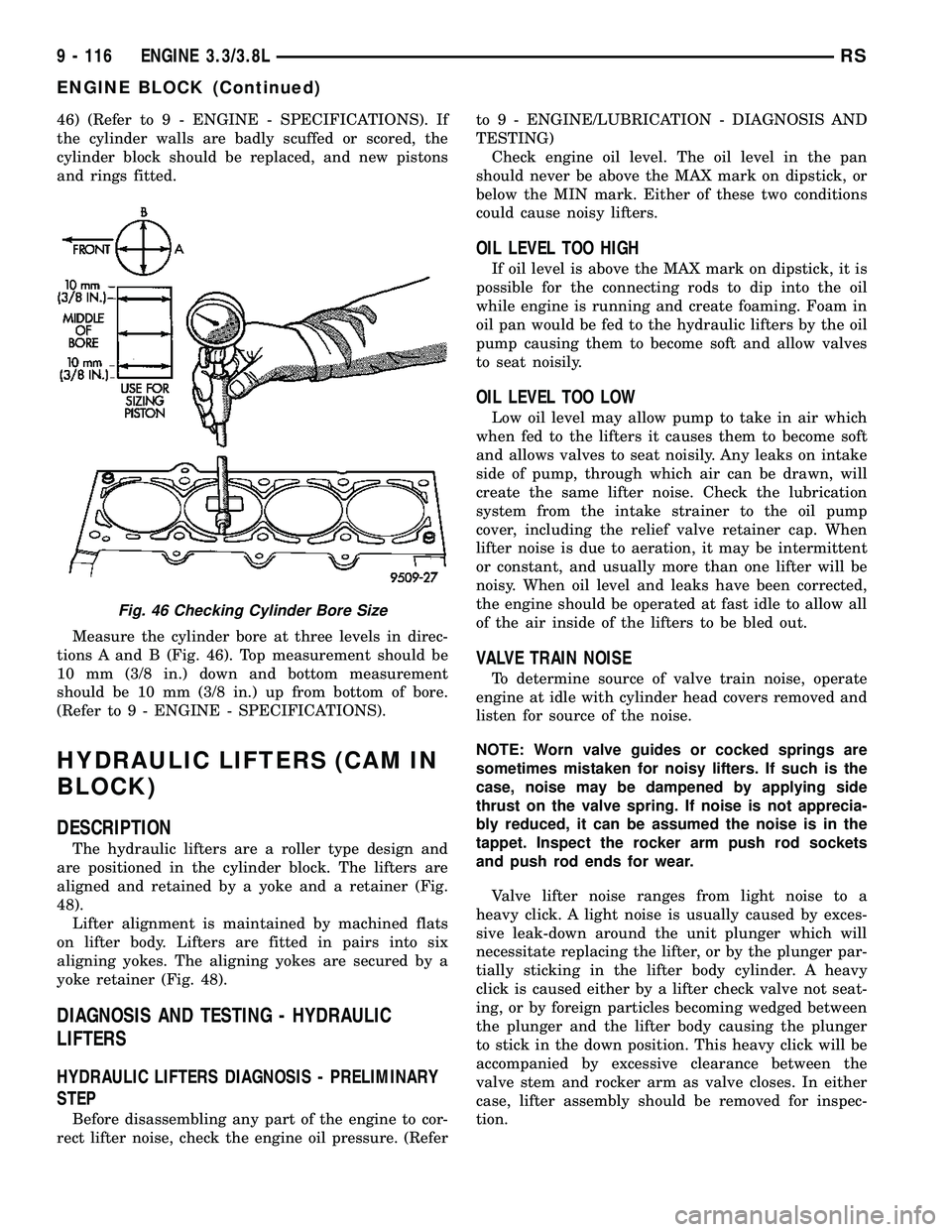
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 46). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 in.) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 in.) up from bottom of bore.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN
BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION
The hydraulic lifters are a roller type design and
are positioned in the cylinder block. The lifters are
aligned and retained by a yoke and a retainer (Fig.
48).
Lifter alignment is maintained by machined flats
on lifter body. Lifters are fitted in pairs into six
aligning yokes. The aligning yokes are secured by a
yoke retainer (Fig. 48).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LIFTERS
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS DIAGNOSIS - PRELIMINARY
STEP
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect lifter noise, check the engine oil pressure. (Referto 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
Check engine oil level. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the MAX mark on dipstick, or
below the MIN mark. Either of these two conditions
could cause noisy lifters.
OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dipstick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foaming. Foam in
oil pan would be fed to the hydraulic lifters by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the lifters it causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump, through which air can be drawn, will
create the same lifter noise. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the oil pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
lifter noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one lifter will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
the engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all
of the air inside of the lifters to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy lifters. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve lifter noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the lifter, or by the plunger par-
tially sticking in the lifter body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a lifter check valve not seat-
ing, or by foreign particles becoming wedged between
the plunger and the lifter body causing the plunger
to stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the
valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either
case, lifter assembly should be removed for inspec-
tion.
Fig. 46 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
9 - 116 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)