2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 1324 of 2339

(2) Install timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION) and oil pan (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake system is made up of an upper and
lower intake manifold. The upper intake manifold is
made of a composite for both the 3.3L engine and for
the 3.8L engine (Fig. 118). The lower intake manifold
is common between the two engines (Fig. 122). It also
provides coolant crossover between cylinder heads
and houses the coolant thermostat (Fig. 122).
The intake manifold utilizes a compact design with
very low restriction and outstanding flow balance.
This design allows the engine to perform with a wide
torque curve while increasing higher rpm horse-
power.
If, for some reason, the molded-in vacuum ports
break, the composite manifold can be salvaged. The
vacuum ports are designed to break at the shoulder,
if overloaded. Additional material in the shoulder
area provides sufficient stock to repair. For more
information and procedure, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - STANDARD
PROCEDURE). Also, if the special screws that attach
the MAP sensor, power steering reservoir, throttle
cable bracket, and the EGR tube become stripped, an
oversized screw is available to repair the stripped-out
condition. For more information and procedure,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANIFOLD
STRIPPED THREAD REPAIR
The composite upper intake manifold thread
bosses, if stripped out, can be repaired by utilizing a
repair screw available through Mopartparts. Repair
screws are available for the following manifold
attached components:
²MAP sensor
²Power steering reservoir
²EGR tube
²Throttle cable bracket
The repair screws require a unique tightening
torque specification from the original screw. Refer to
the following chart for specification.
DESCRIPTION TORQUE*
STRIP-OUT REPAIR SCREWS ONLY
MAP Sensor Repair
Screw4 N´m (35 in. lbs.)
Power Steering Reservoir
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
EGR Tube Attaching
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
Throttle Cable Bracket
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
*Install Slowly Using Hand Tools Only
Fig. 113 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 - RELIEF VALVE
2 - SPRING
3 - RETAINER CAP
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 147
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1327 of 2339
(5) Connect the MAP sensor electrical connector.
(6) Connect the brake booster and LDP vacuum
hose to intake manifold (Fig. 117).CAUTION: The special screws used for attaching
the EGR tube and power steering reservoir to the
manifold must be installed slowly using hand tools
only. This requirement is to prevent the melting of
material that causes stripped threads. If threads
become stripped, an oversize repair screw is avail-
able. For more information and procedure (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - MANIFOLD STRIPPED
THREAD REPAIR).
(7) Install the power steering reservoir (Fig. 116).
Tighten screws to manifold to 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
(8) Connect throttle and speed control cables to
throttle body (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE -
INSTALLATION)
(9) Attach make up air hose clip into the hole in
the throttle cable bracket.
(10) Connect the wiring connectors to the throttle
position sensor (TPS) and Automatic Idle Speed (AIS)
motor.
(11) Install air cleaner and air inlet hose assembly.
(12) Connect the inlet air temperature (IAT) sen-
sor electrical connector.
(13) Connect battery negative cable.
INTAKE MANIFOLD - LOWER
REMOVAL - LOWER INTAKE MANIFOLD
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
(before attempting any repairs).(Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(2) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(3) Remove the upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the fuel line. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES - STANDARD
PROCEDURE) (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
(5) Remove ignition coil and bracket (Fig. 120).
(6) Disconnect heater supply hose and engine cool-
ant temperature sensor (Fig. 121).
(7) Disconnect the fuel injector wire harness.
(8) Remove the fuel injectors and rail assembly
(Fig. 120).
(9) Remove radiator upper hose.
(10) Remove the intake manifold bolts.
(11) Remove lower intake manifold (Fig. 122).
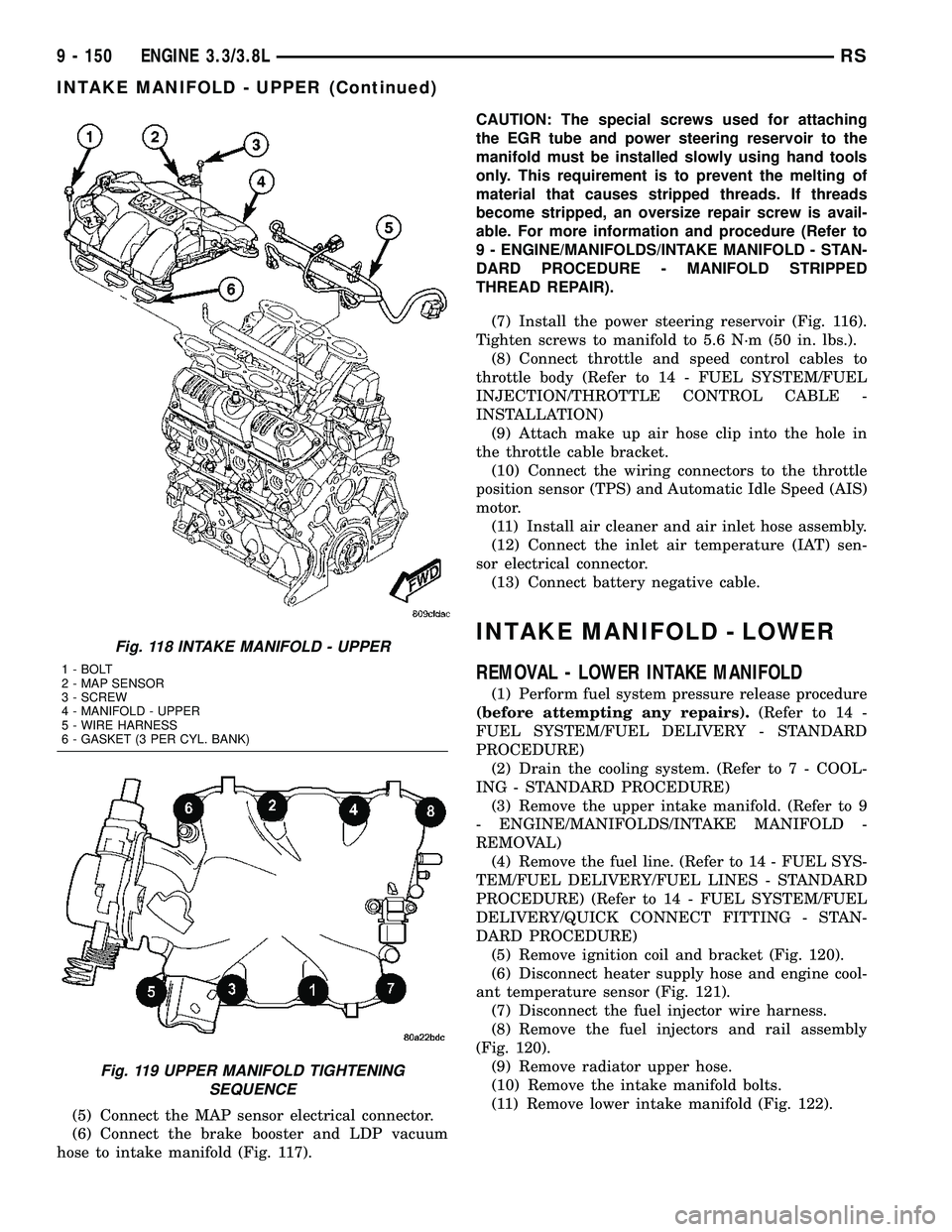
Fig. 118 INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
1 - BOLT
2 - MAP SENSOR
3 - SCREW
4 - MANIFOLD - UPPER
5 - WIRE HARNESS
6 - GASKET (3 PER CYL. BANK)
Fig. 119 UPPER MANIFOLD TIGHTENING
SEQUENCE
9 - 150 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER (Continued)
Page 1362 of 2339
REMOVAL
The front cradle crossmember must be installed in
the design location to achieve proper front end sus-
pension alignment. If the cradle crossmember is
removed without applying reference marks on the
frame rails, align the cradle crossmember according
to the dimensions provided in this group.
NOTE: If the caged nuts in the frame rails become
damaged and cannot be reused, a replacement nut
can be obtained through MoparT(Fig. 14).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove steering column lower cover from
instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPENING
COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove steering column cover backing plate
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN COVER BACKING PLATE -
REMOVAL).
(4) Position steering so front wheels are straight
ahead.
CAUTION: Do not rotate steering wheel after disen-
gaging lower coupling from steering gear, damage
to air bag clock spring can result.
(5) Remove clinch bolt attaching steering column
coupling to steering gear shaft (Fig. 15).
(6) Remove steering column coupling from tele-
scoping steering gear shaft.(7) Hoist vehicle and support on safety stands.
(8) Position a drain pan under power steering
pump and oil return hose coupling.
(9) Using a hose pinch-off pliers (C-4390), pinch
power steering oil return hose off between the cross-
member coupling and the pump.
(10) Loosen hose clamp at the cradle crossmember
coupling.
(11) Disconnect return hose from metal tube.
(12) While holding pressure relief valve nut on
back of power steering pump, Remove flare nut
attaching high pressure hose to back of pump.
(13) Remove high pressure hose from pump.
(14) Allow power steering fluid to drain into pan.
(15) Remove bolts attaching anti-lock brake sensor
leads to cradle crossmember.
(16) Position anti-lock brake leads out of the way.
(17) Disconnect stabilizer bar links from ends of
stabilizer bar.
(18) Disconnect lower ball joints from lower steer-
ing knuckles (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/
LOWER BALL JOINT - REMOVAL).
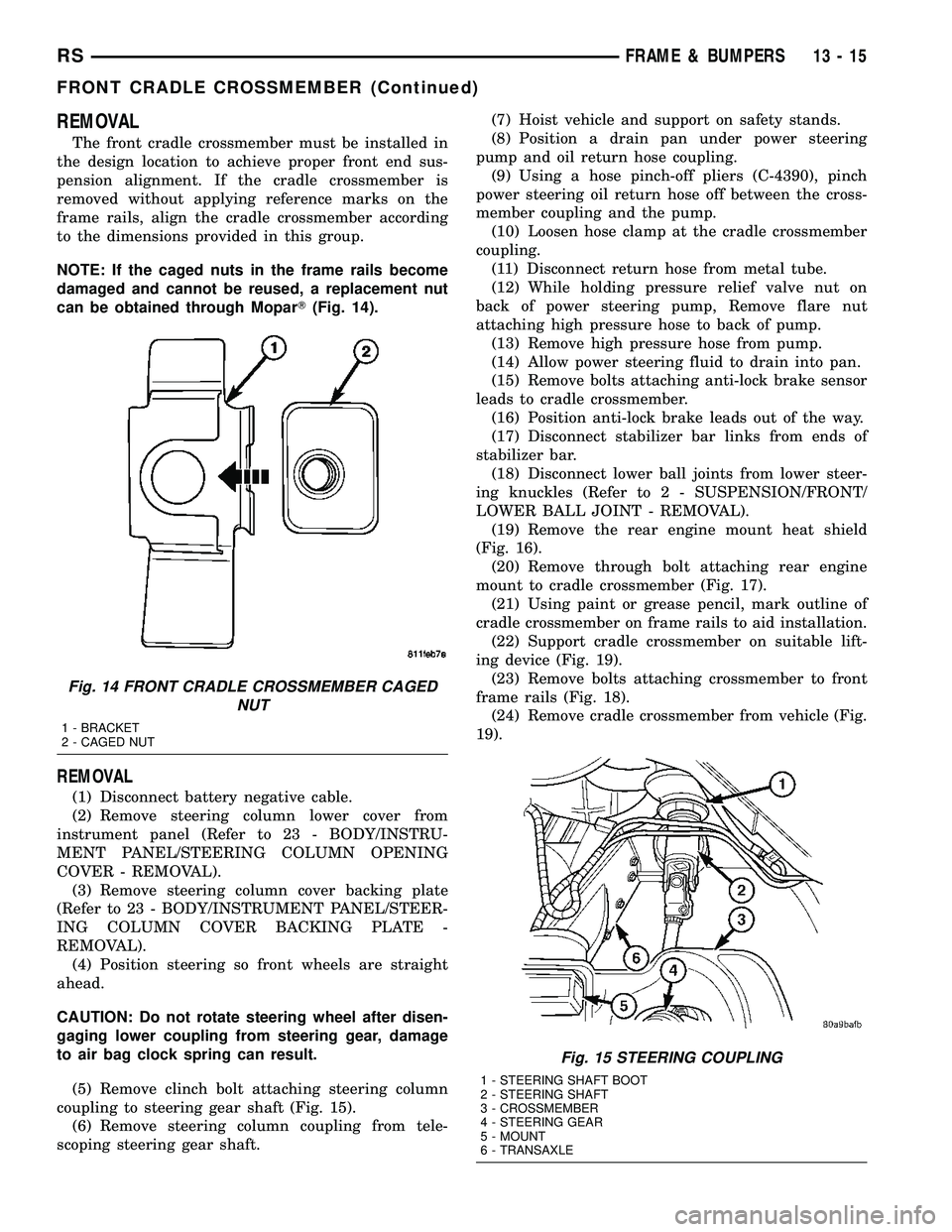
(19) Remove the rear engine mount heat shield
(Fig. 16).
(20) Remove through bolt attaching rear engine
mount to cradle crossmember (Fig. 17).
(21) Using paint or grease pencil, mark outline of
cradle crossmember on frame rails to aid installation.
(22) Support cradle crossmember on suitable lift-
ing device (Fig. 19).
(23) Remove bolts attaching crossmember to front
frame rails (Fig. 18).
(24) Remove cradle crossmember from vehicle (Fig.
19).
Fig. 14 FRONT CRADLE CROSSMEMBER CAGED
NUT
1 - BRACKET
2 - CAGED NUT
Fig. 15 STEERING COUPLING
1 - STEERING SHAFT BOOT
2 - STEERING SHAFT
3 - CROSSMEMBER
4 - STEERING GEAR
5 - MOUNT
6 - TRANSAXLE
RSFRAME & BUMPERS13-15
FRONT CRADLE CROSSMEMBER (Continued)
Page 1373 of 2339
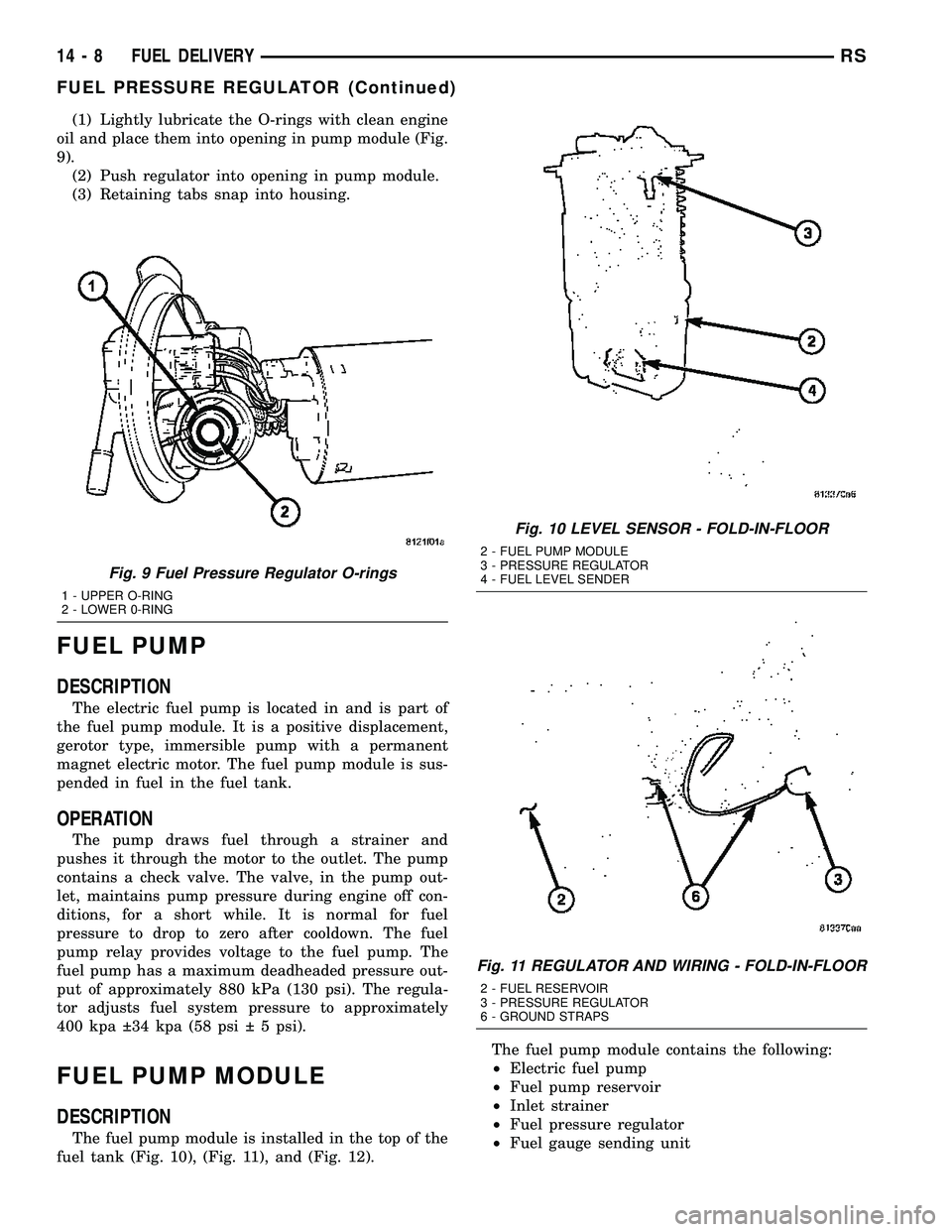
(1) Lightly lubricate the O-rings with clean engine
oil and place them into opening in pump module (Fig.
9).
(2) Push regulator into opening in pump module.
(3) Retaining tabs snap into housing.
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located in and is part of
the fuel pump module. It is a positive displacement,
gerotor type, immersible pump with a permanent
magnet electric motor. The fuel pump module is sus-
pended in fuel in the fuel tank.
OPERATION
The pump draws fuel through a strainer and
pushes it through the motor to the outlet. The pump
contains a check valve. The valve, in the pump out-
let, maintains pump pressure during engine off con-
ditions, for a short while. It is normal for fuel
pressure to drop to zero after cooldown. The fuel
pump relay provides voltage to the fuel pump. The
fuel pump has a maximum deadheaded pressure out-
put of approximately 880 kPa (130 psi). The regula-
tor adjusts fuel system pressure to approximately
400 kpa 34 kpa (58 psi 5 psi).
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank (Fig. 10), (Fig. 11), and (Fig. 12).The fuel pump module contains the following:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²Inlet strainer
²Fuel pressure regulator
²Fuel gauge sending unit
Fig. 9 Fuel Pressure Regulator O-rings
1 - UPPER O-RING
2 - LOWER 0-RING
Fig. 10 LEVEL SENSOR - FOLD-IN-FLOOR
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
3 - PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - FUEL LEVEL SENDER
Fig. 11 REGULATOR AND WIRING - FOLD-IN-FLOOR
2 - FUEL RESERVOIR
3 - PRESSURE REGULATOR
6 - GROUND STRAPS
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR (Continued)
Page 1376 of 2339
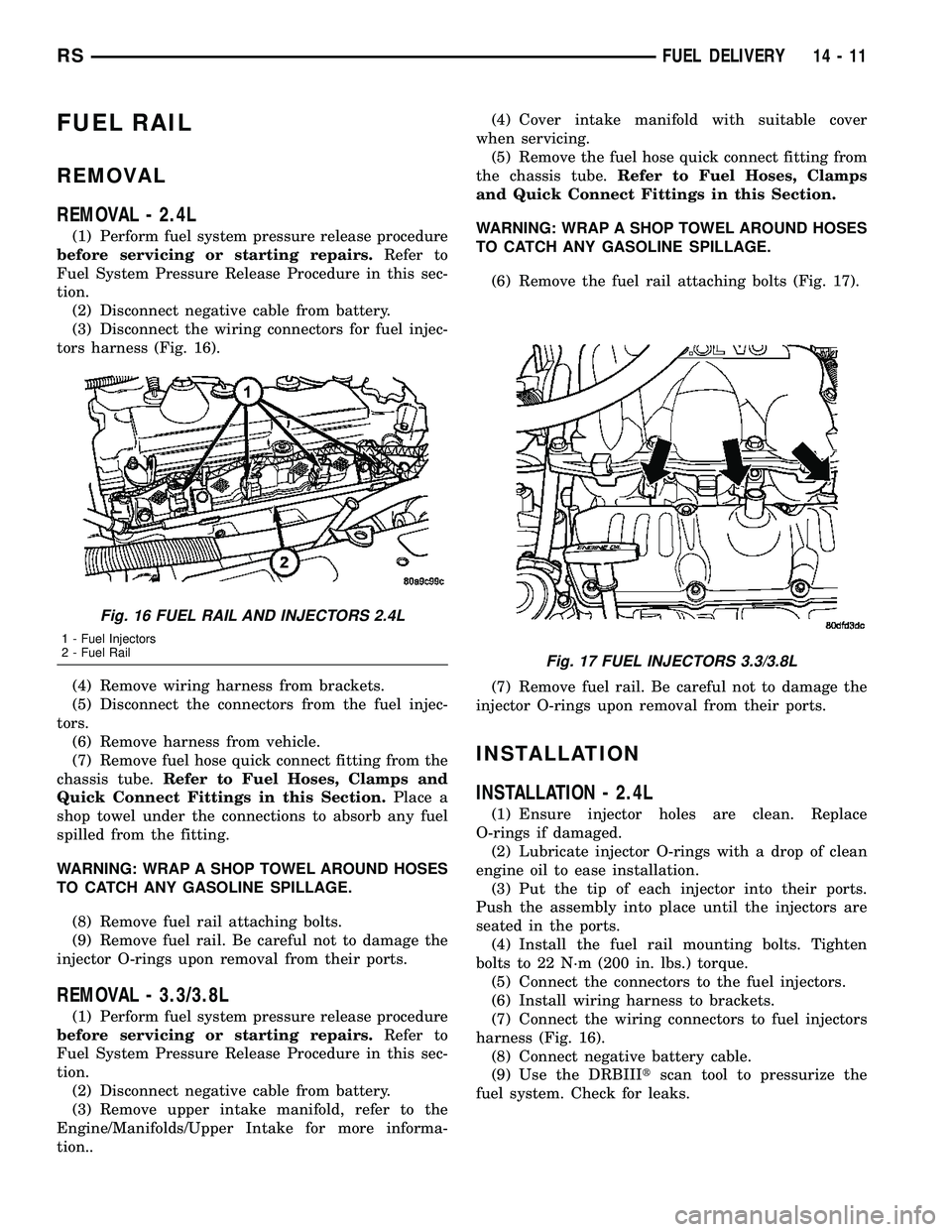
FUEL RAIL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before servicing or starting repairs.Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this sec-
tion.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Disconnect the wiring connectors for fuel injec-
tors harness (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove wiring harness from brackets.
(5) Disconnect the connectors from the fuel injec-
tors.
(6) Remove harness from vehicle.
(7) Remove fuel hose quick connect fitting from the
chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Place a
shop towel under the connections to absorb any fuel
spilled from the fitting.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(8) Remove fuel rail attaching bolts.
(9) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before servicing or starting repairs.Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this sec-
tion.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper intake manifold, refer to the
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more informa-
tion..(4) Cover intake manifold with suitable cover
when servicing.
(5) Remove the fuel hose quick connect fitting from
the chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps
and Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(6) Remove the fuel rail attaching bolts (Fig. 17).
(7) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect the connectors to the fuel injectors.
(6) Install wiring harness to brackets.
(7) Connect the wiring connectors to fuel injectors
harness (Fig. 16).
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
Fig. 16 FUEL RAIL AND INJECTORS 2.4L
1 - Fuel Injectors
2 - Fuel Rail
Fig. 17 FUEL INJECTORS 3.3/3.8L
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-11
Page 1377 of 2339

INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surface.
(6) Install the Upper Intake Manifold, refer to
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more information.
(7) Install fuel hose quick connector fitting to chas-
sis tubes.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Push the
fitting onto the chassis tube until it clicks into place.
Pull on the fitting to ensure complete insertion.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module. The tank is made
from High density Polyethylene (HDPE) material.If
equipped with ORVR (Onboard Refueling Vapor
Recovery) it has been added to the fuel tank to con-
trol refueling vapor emissions.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with either one or two
check valves mounted into the top of the fuel tank (or
pump module).
An evaporation control system is connected to the
check valve(s)/control valve(Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/
ORVR - OPERATION) to reduce emissions of fuel
vapors into the atmosphere, when the tank is vented
due to vapor expansion in the tank. When fuel evap-
orates from the fuel tank, vapors pass through vent
hoses or tubes to a charcoal canister where they are
temporarily held. When the engine is running, the
vapors are drawn into the intake manifold. In addi-
tion, fuel vapors produced during vehicle refueling
are allowed to pass through the vent hoses/tubes to
the charcoal canister(s) for temporary storage (priorto being drawn into the intake manifold). All models
are equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) or Natural Vacuum
Leak Detection (NVLD). Refer to the Emission Con-
trol System for additional information.
INLET CHECK VALVE
All vehicles have an inlet check valve on the inside
of the fuel tank at the filler inlet
The valve prevents fuel from splashing back on
customer during vehicle refueling. The valve is a
non-serviceable item.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure (Fig. 18).
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(6) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(7) Lower tank slightly.
(8) Disconnect the fuel filler vent tube. Squeeze
tabs and pull apart (Fig. 19).
Fig. 18 Fuel Tank
1 - ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL FILLER INLET
3 - ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
14 - 12 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1383 of 2339
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE. THIS MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
(1) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery or aux-
iliary jumper terminal.
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Make sure that the o-ring in installed in
fitting. Never install a quick-connect fitting without
the retainer being either on the fuel tube or already
in the quick-connect fitting. In either case, ensure
the retainer locks securely into the quick-connect
fitting by firmly push-pulling-push on fuel tube and
fitting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean engine oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
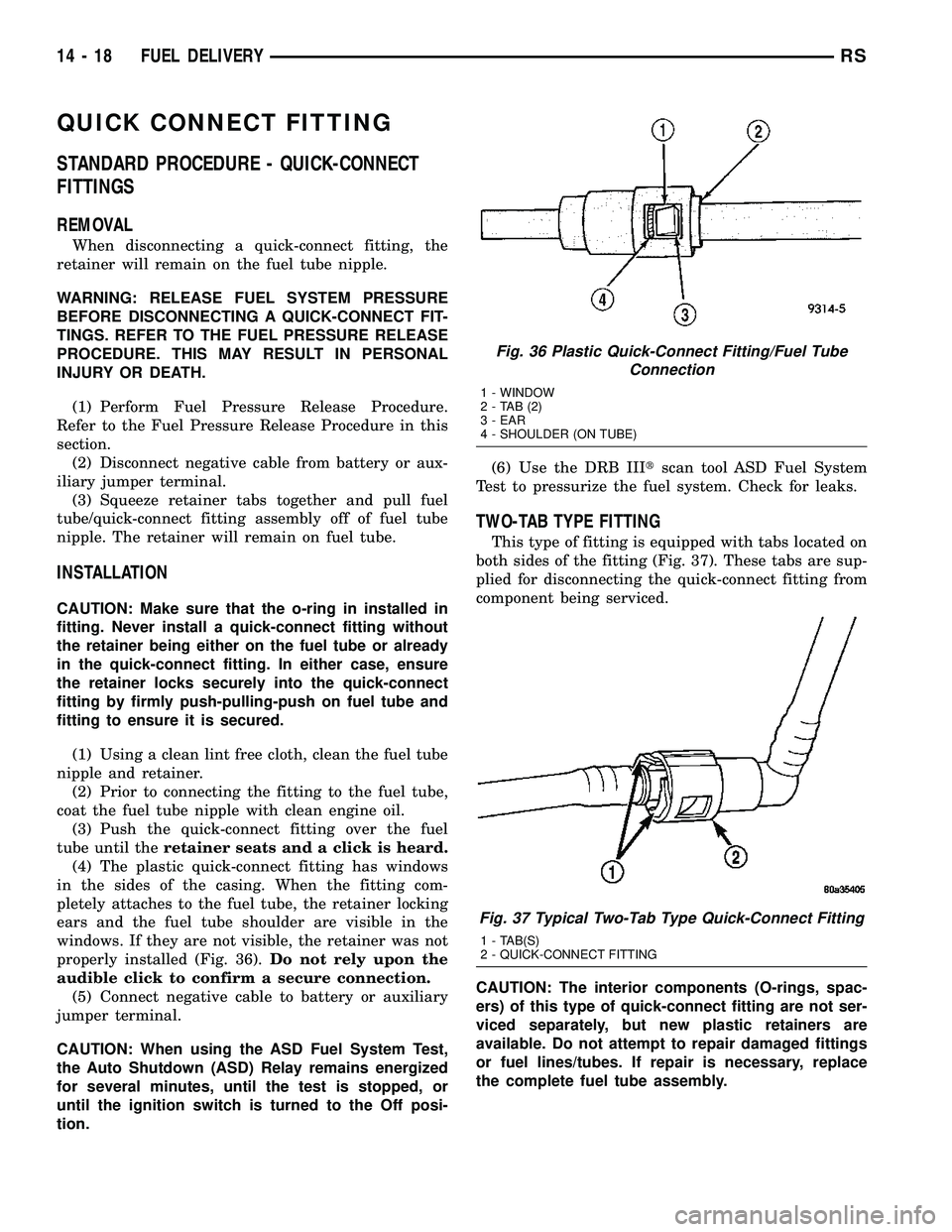
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
properly installed (Fig. 36).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for several minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.(6) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
TWO-TAB TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting is equipped with tabs located on
both sides of the fitting (Fig. 37). These tabs are sup-
plied for disconnecting the quick-connect fitting from
component being serviced.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new plastic retainers are
available. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings
or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace
the complete fuel tube assembly.
Fig. 36 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
1 - WINDOW
2-TAB(2)
3 - EAR
4 - SHOULDER (ON TUBE)
Fig. 37 Typical Two-Tab Type Quick-Connect Fitting
1 - TAB(S)
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
14 - 18 FUEL DELIVERYRS
Page 1384 of 2339
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP. THIS MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
OR DEATH.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To disconnect quick-connect fitting, squeeze
plastic retainer tabs (Fig. 37) against sides of quick-
connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is not
required for removal and may damage plastic
retainer. Pull fitting from fuel system component
being serviced. The plastic retainer will remain on
component being serviced after fitting is discon-
nected. The O-rings and spacer will remain in quick-
connect fitting connector body.
(5) Inspect quick-connect fitting body and compo-
nent for damage. Replace as necessary.
CAUTION: When the quick-connect fitting was dis-
connected, the plastic retainer will remain on the
component being serviced. If this retainer must be
removed, very carefully release the retainer from
the component with two small screwdrivers. After
removal, inspect the retainer for cracks or any dam-
age.
(6) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert quick-connect fitting to component being
serviced and into plastic retainer. When a connection
is made, a click will be heard.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly push-pull-
ing-push on fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(10) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
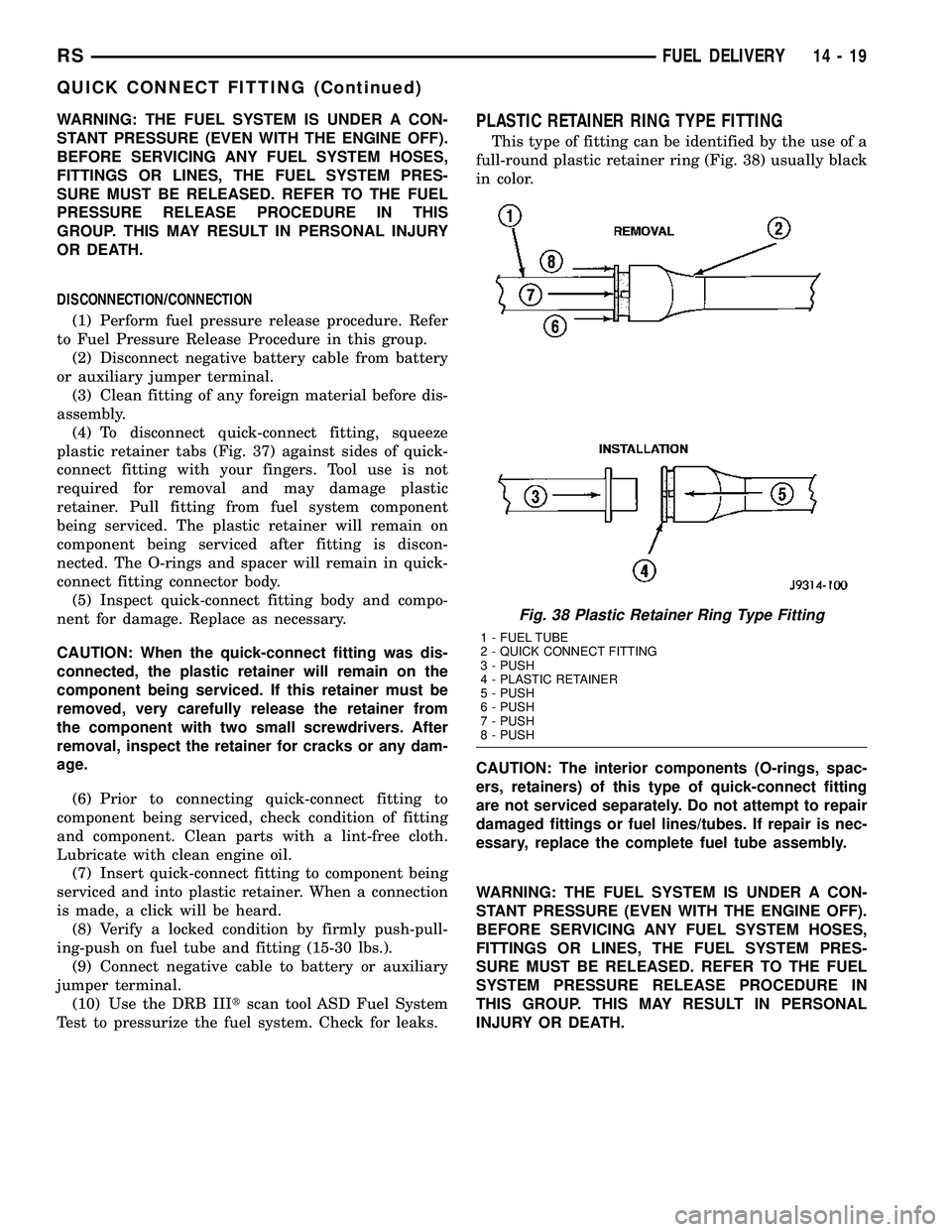
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 38) usually black
in color.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP. THIS MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
Fig. 38 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 - FUEL TUBE
2 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 - PUSH
4 - PLASTIC RETAINER
5 - PUSH
6 - PUSH
7 - PUSH
8 - PUSH
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-19
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)