2005 CHEVROLET CORVETTE weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 261 of 400
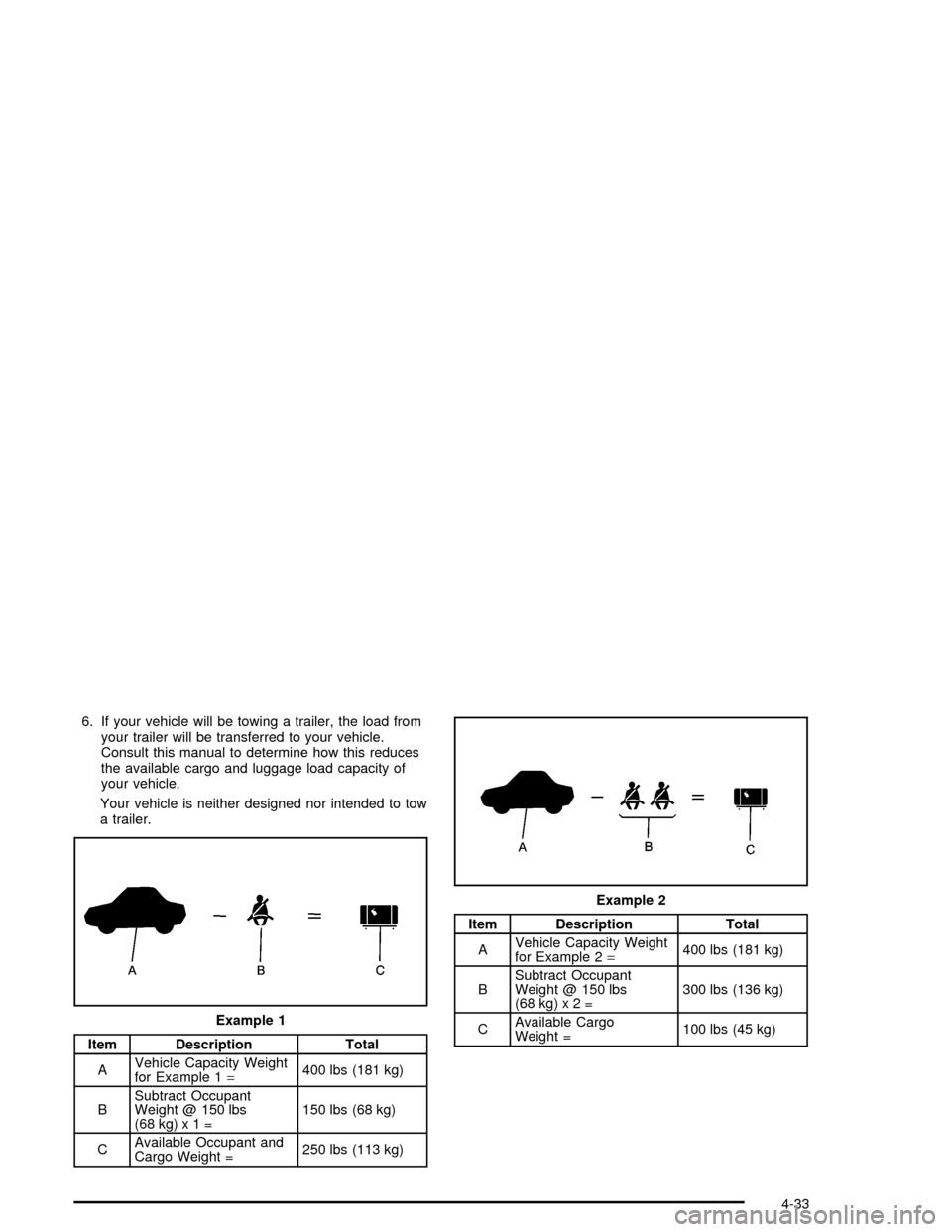
6. If your vehicle will be towing a trailer, the load from
your trailer will be transferred to your vehicle.
Consult this manual to determine how this reduces
the available cargo and luggage load capacity of
your vehicle.
Your vehicle is neither designed nor intended to tow
a trailer.
Item Description Total
AVehicle Capacity Weight
for Example 1=400 lbs (181 kg)
BSubtract Occupant
Weight @ 150 lbs
(68kg)x1=150 lbs (68 kg)
CAvailable Occupant and
Cargo Weight =250 lbs (113 kg)
Item Description Total
AVehicle Capacity Weight
for Example 2=400 lbs (181 kg)
BSubtract Occupant
Weight @ 150 lbs
(68kg)x2=300 lbs (136 kg)
CAvailable Cargo
Weight =100 lbs (45 kg) Example 1
Example 2
4-33
Page 262 of 400

Item Description Total
AVehicle Capacity Weight
for Example 3=400 lbs (181 kg)
BSubtract Occupant
Weight @ 200 lbs
(91kg)x2=400 lbs (181 kg)
CAvailable Cargo
Weight =0 lbs (0 kg)
Refer to your vehicle’s tire and loading information label
for speci�c information about your vehicle’s capacity
weight and seating positions. The combined weight of
the driver, passengers and cargo should never
exceed your vehicle’s capacity weight.
Certi�cation Label
A vehicle speci�c Certi�cation label is attached to the
rear edge of the driver’s door. It tells you the gross
weight capacity of your vehicle, called the Gross Vehicle
Weight Rating (GVWR). The GVWR includes the
weight of the vehicle, all occupants, fuel and cargo.
Never exceed the GVWR for your vehicle, or the Gross
Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) for either the front or
rear axle. Example 3
4-34
Page 263 of 400

And, if you do have a heavy load, you should spread it
out. Do not carry more than 100 lbs (45 kg) in the
rear area of your vehicle.
{CAUTION:
Do not load your vehicle any heavier than the
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR), or either
the maximum front or rear Gross Axle Weight
Rating (GAWR). If you do, parts on your
vehicle can break, and it can change the way
your vehicle handles. These could cause you
to lose control and crash. Also, overloading
can shorten the life of your vehicle.
Notice:Overloading your vehicle may cause
damage. Repairs would not be covered by your
warranty. Do not overload your vehicle.If you put things inside your vehicle — like suitcases,
tools, packages or anything else — they will go as fast
as the vehicle goes. If you have to stop or turn
quickly, or if there is a crash, they will keep going.
{CAUTION:
Things you put inside your vehicle can strike
and injure people in a sudden stop or turn, or
in a crash.
Put things in the rear area of your vehicle.
Try to spread the weight evenly.
Never stack heavier things, like suitcases,
inside the vehicle so that some of them
are above the tops of the seats.
Do not leave an unsecured child restraint
in your vehicle.
When you carry something inside the
vehicle, secure it whenever you can.
4-35
Page 318 of 400

(D) Construction Code:A letter code is used to
indicate the type of ply construction in the tire. The letter
R means radial ply construction; the letter D means
diagonal or bias ply construction; and the letter B means
belted-bias ply construction.
(E) Rim Diameter:Diameter of the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description:These characters represent
the load range and speed rating of the tire. The load
index represents the load carry capacity a tire is certi�ed
to carry. The load index can range from 1 to 279. The
speed rating is the maximum speed a tire is certi�ed
to carry a load. Speed ratings range from A to Z.
Tire Terminology and De�nitions
Air Pressure:The amount of air inside the tire pressing
outward on each square inch of the tire. Air pressure
is expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or
kilopascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight:This means the combined weight
of optional accessories. Some examples of optional
accessories are, automatic transmission, power steering,
power brakes, power windows, power seats, and air
conditioning.
Aspect Ratio:The relationship of a tire’s height to
its width.Belt:A rubber coated layer of cords that is located
between the plies and the tread. Cords may be made
from steel or other reinforcing materials.
Bead:The tire bead contains steel wires wrapped by
steel cords that hold the tire onto the rim.
Bias Ply Tire:A pneumatic tire in which the plies are
laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees to the
centerline of the tread.
Cold In�ation Pressure:The amount of air pressure in
a tire, measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or
kilopascals (kPa) before a tire has built up heat
from driving. SeeIn�ation - Tire Pressure on page 5-58.
Curb Weight:This means the weight of a motor
vehicle with standard and optional equipment including
the maximum capacity of fuel, oil and coolant, but
without passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings:A code molded into the sidewall of a
tire signifying that the tire is in compliance with the U.S.
Department of Transportation (DOT) motor vehicle
safety standards. The DOT code includes the Tire
Identi�cation Number (TIN), an alphanumeric designator
which can also identify the tire manufacturer, production
plant, brand and date of production.
GVWR:Gross Vehicle Weight Rating, seeLoading
Your Vehicle on page 4-31.
5-54
Page 319 of 400

GAWR FRT:Gross Axle Weight Rating for the front
axle, seeLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-31.
GAWR RR:Gross Axle Weight Rating for the rear axle,
seeLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-31.
Intended Outboard Sidewall:The side of an
asymmetrical tire, that must always face outward when
mounted on a vehicle.
Kilopascal (kPa):The metric unit for air pressure.
Light Truck (LT-Metric) Tire:A tire used on light duty
trucks and some multipurpose passenger vehicles.
Load Index:An assigned number ranging
from 1 to 279 that corresponds to the load carrying
capacity of a tire.
Maximum In�ation Pressure:The maximum air
pressure to which a cold tire may be in�ated. The
maximum air pressure is molded onto the sidewall.
Maximum Load Rating:The load rating for a tire at the
maximum permissible in�ation pressure for that tire.
Maximum Loaded Vehicle Weight:The sum of curb
weight; accessory weight; vehicle capacity weight;
and production options weight.
Normal Occupant Weight:The number of occupants a
vehicle is designed to seat multiplied by 150 lbs (68 kg).
SeeLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-31.Occupant Distribution:Designated seating positions.
Outward Facing Sidewall:The side of an
asymmetrical tire that has a particular side that faces
outward when mounted on a vehicle. The side of the tire
that contains a whitewall, bears white lettering or
bears manufacturer, brand, and/or model name molding
that is higher or deeper than the same moldings on
the other sidewall of the tire.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire:A tire used on passenger
cars and some light duty trucks and multipurpose
vehicles.
Recommended In�ation Pressure:Vehicle
manufacturer’s recommended tire in�ation pressure and
shown on the tire placard. SeeIn�ation - Tire Pressure
on page 5-58andLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-31.
Radial Ply Tire:A pneumatic tire in which the ply cords
that extend to the beads are laid at 90 degrees to the
centerline of the tread.
Rim:A metal support for a tire and upon which the tire
beads are seated.
Sidewall:The portion of a tire between the tread and
the bead.
Speed Rating:An alphanumeric code assigned to a
tire indicating the maximum speed at which a tire
can operate.
5-55
Page 320 of 400

Traction:The friction between the tire and the road
surface. The amount of grip provided.
Tread:The portion of a tire that comes into contact
with the road.
Treadwear Indicators:Narrow bands, sometimes
called “wear bars,” that show across the tread of a tire
when only 1/16 inch (1.6 mm) of tread remains. See
When It Is Time for New Tires on page 5-62.
UTQGS (Uniform Tire Quality Grading Standards):A
tire information system that provides consumers with
ratings for a tire’s traction, temperature, and treadwear.
Ratings are determined by tire manufacturers using
government testing procedures. The ratings are molded
into the sidewall of the tire. SeeUniform Tire Quality
Grading on page 5-64.
Vehicle Capacity Weight:The number of designated
seating positions multiplied by 150 lbs (68 kg) plus
the rated cargo load. SeeLoading Your Vehicle
on page 4-31.
Vehicle Maximum Load on the Tire:Load on an
individual tire due to curb weight, accessory weight,
occupant weight, and cargo weight.Vehicle Placard:A label permanently attached to a
vehicle showing the vehicle’s capacity weight and
the original equipment tire size and recommended
in�ation pressure. See “Tire and Loading Information
Label” underLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-31.
Extended Mobility Tires
Your vehicle, when new, had Goodyear Extended
Mobility Tires (EMT). There’s no spare tire, no tire
changing equipment and no place to store a tire in the
vehicle. Extended Mobility Tires perform so well
without any air that a Tire Pressure Monitor (TPM) is
used to alert you if a tire has lost pressure.
If a tire goes �at, you won’t need to stop on the side of
the road to change the tire. You can just keep on
driving. The shorter the distance you drive and the
slower the speed, the greater the chance that the tire will
not have to be replaced. If you drive on a de�ated
EMT for 25 miles (80 km) or less and at speeds
of 55 mph (90 km/h) or less, there is a good chance that
the tire can be repaired. The tire can operate effectively
with no air pressure for up to 100 miles (320 km) at
speeds up to 55 mph (90 km/h), but the tire would then
have to be replaced. When a tire is �lled with air, it
provides a cushion between the road and the wheel.
Because you won’t have this cushion when driving on a
de�ated tire, try to avoid potholes that could damage
your wheel and require replacement of it.
5-56
Page 322 of 400

In�ation - Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount of air pressure to operate
effectively.
Notice:Do not let anyone tell you that
under-in�ation or over-in�ation is all right. It is not.
If your tires do not have enough air (under-in�ation),
you can get the following:
Too much �exing
Too much heat
Tire overloading
Premature or irregular wear
Poor handling
Reduced fuel economy
If your tires have too much air (over-in�ation), you
can get the following:
Unusual wear
Poor handling
Rough ride
Needless damage from road hazardsA Tire and Loading Information label is attached to the
vehicle’s b-pillar. This label lists your vehicle’s original
equipment tires and shows the correct in�ation
pressures for your tires when they are cold. The
recommended cold tire in�ation pressure, shown on the
label, is the minimum amount of air pressure needed
to support your vehicle’s maximum load carrying
capacity.
For additional information regarding how much weight
your vehicle can carry, and an example of the tire
and loading information label, seeLoading Your Vehicle
on page 4-31. How you load your vehicle affects
vehicle handling and ride comfort, never load your
vehicle with more weight than it was designed to carry.
When to Check
Check your tires once a month or more.
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure. You cannot tell if your tires are properly in�ated
simply by looking at them. Radial tires may look properly
in�ated even when they’re under-in�ated. Check the tire’s
in�ation pressure when the tires are cold. Cold means
your vehicle has been sitting for at least three hours or
driven no more than 1 mile (1.6 km).
5-58