2005 CHEVROLET AVEO service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 224 of 316
Replacement Bulbs
Exterior Lamp Bulb Number
Back-Up 94535571
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp
(CHMSL)94535587
Headlamps 94535548
Fog 96535557
Front Parking/Turn Signal 94535574
Sidemarker, Front and Rear 94535587
Side Turn Signal 94535587
Stoplamp/Taillamps 94535574
Turn Signal Lamps 94535572
For replacement bulbs not listed here, contact your
dealer.
Windshield Wiper Blade
Replacement
Windshield wiper blades should be inspected for
wear or cracking. See “Wiper Blade Check” under
Part B: Owner Checks and Services on page 6-18
for more information.Replacement blades come in different types and are
removed in different ways.
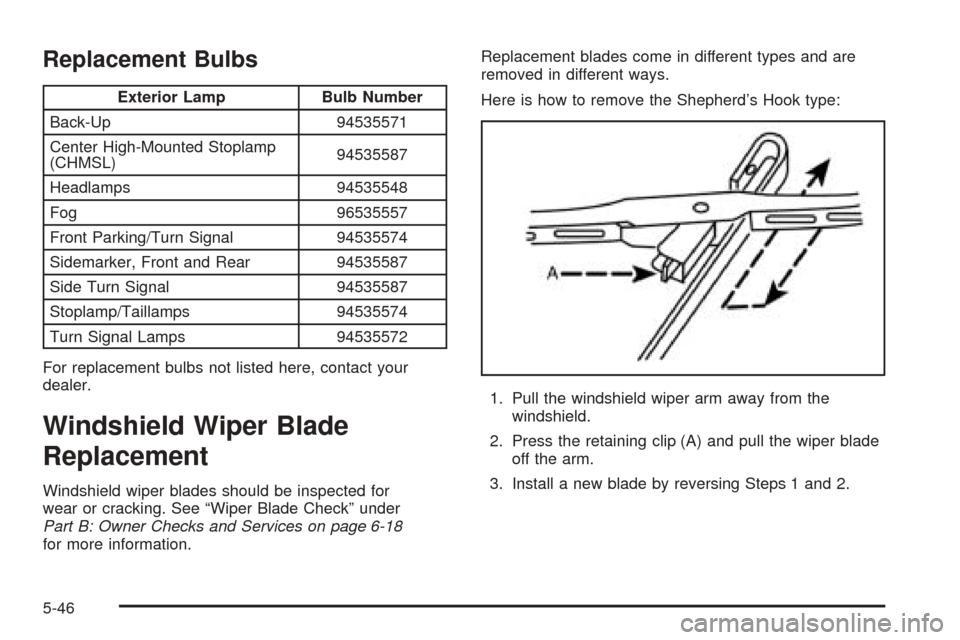
Here is how to remove the Shepherd’s Hook type:
1. Pull the windshield wiper arm away from the
windshield.
2. Press the retaining clip (A) and pull the wiper blade
off the arm.
3. Install a new blade by reversing Steps 1 and 2.
5-46
Page 225 of 316

Tires
Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by
a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions
about your tire warranty and where to obtain service,
see your GM Warranty booklet for details. For additional
information refer to the tire manufacturer’s booklet
included with your vehicle’s Owner Manual.{CAUTION:
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires are
dangerous.
Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result of too much friction.
You could have an air-out and a serious
accident. SeeLoading Your Vehicle on
page 4-28.
Underin�ated tires pose the same danger
as overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked
when your tires are cold. SeeInflation - Tire
Pressure on page 5-53.
Overin�ated tires are more likely to be
cut, punctured or broken by a sudden
impact — such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
Worn, old tires can cause accidents. If your
tread is badly worn, or if your tires have
been damaged, replace them.
5-47
Page 226 of 316

Tire Sidewall Labelling
Useful information about a tire is molded into its
sidewall. The examples below show a typical passenger
car tire and a compact spare tire sidewall.
(A) Tire Size:The tire size is a combination of letters
and numbers used to define a particular tire’s width,
height, aspect ratio, construction type and service
description. See the “Tire Size” illustration later in this
section for more detail.(B) DOT (Department of Transportation):The
Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that
the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
(C) Tire Identi�cation Number (TIN):The letters and
numbers following DOT code are the Tire Identification
Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer
and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of
the tire, although only one side may have the date
of manufacture.
(D) Tire Ply Material:The type of cord and number of
plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(E) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG):Tire
manufacturers are required to grade tires based on
three performance factors: treadwear, traction and
temperature resistance. For more information see
Uniform Tire Quality Grading on page 5-56.
(F) Maximum Cold In�ation Load Limit:Maximum
load that can be carried and the maximum pressure
needed to support that load. For information on
recommended tire pressure seeInflation - Tire Pressure
on page 5-53andLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-28. Passenger Car Tire Example
5-48
Page 227 of 316

(A) Temporary Use Only:The compact spare tire or
temporary use tire has a tread life of approximately
3,000 miles (5 000 km) and should not be driven
at speeds over 65 mph (105 km/h). The compact spare
tire is for emergency use when a regular road tire
has lost air and gone flat. SeeCompact Spare Tire on
page 5-68andIf a Tire Goes Flat on page 5-60.(B) Tire Ply Material:The type of cord and number
of plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(C) Tire Identi�cation Number (TIN):The Tire
Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the
tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto
both sides of the tire, although only one side may have
the date of manufacture.
(D) Maximum Cold In�ation Load Limit:Maximum
load that can be carried and the maximum pressure
needed to support that load. SeeCompact Spare Tire
on page 5-68andLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-28.
(E) Tire In�ation:The temporary use tire or compact
spare tire should be inflated to 60 psi (420 kPa).
For more information on tire pressure and inflation see
Inflation - Tire Pressure on page 5-53.
(F) Tire Size:A combination of letters and numbers
define a tire’s width, height, aspect ratio, construction
type and service description. The letter T as the
first character in the tire size means the tire is for
temporary use only. Compact Spare Tire Example
5-49
Page 228 of 316

Tire Size
The following illustration shows an example of a typical
passenger car tire size.
(A) Passenger (P-Metric) Tire:The United States
version of a metric tire sizing system. The letter P as
the first character in the tire size means a passenger
vehicle tire engineered to standards set by the U. S. Tire
and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width:The three-digit number indicates the
tire section width in millimeters from sidewall to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio:A two-digit number that indicates
the tire height-to-width measurements. For example, if
the tire size aspect ratio is 70, as shown in item C of
the illustration, it would mean that the tire’s sidewall
is 70% as high as it is wide.(D) Construction Code:A letter code is used to
indicate the type of ply construction in the tire. The
letter R means radial ply construction; the letter D means
diagonal or bias ply construction; and the letter B means
belted-bias ply construction.
(E) Rim Diameter:Diameter of the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description:These characters represent
the load range and the speed rating of a tire. The
load range represents the load carry capacity a tire is
certified to carry. The speed rating is the maximum
speed a tire is certified to carry a load. Speed ratings
range from A to Z.
Tire Terminology and De�nitions
Air Pressure:The amount of air inside the tire pressing
outward on each square inch of the tire. Air pressure
is expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or
kilopascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight:This means the combined weight
of optional accessories. Some examples of optional
accessories are, automatic transmission, power steering,
power brakes, power windows, power seats, and air
conditioning.
Aspect Ratio:The relationship of a tire’s height to
its width.
5-50
Page 232 of 316

Remove the valve cap from the tire valve stem. Press
the tire gage firmly onto the valve to get a pressure
measurement. If the cold tire inflation pressure matches
the recommended pressure on the Tire and Loading
Information label, no further adjustment is necessary.
If the inflation pressure is low, add air until you reach the
recommended amount.
If you overfill the tire, release air by pushing on the
metal stem in the center of the tire valve. Re-check the
tire pressure with the tire gage.
Be sure to put the valve caps back on the valve stems.
They help prevent leaks by keeping out dirt and
moisture.
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be rotated every 5,000 to 8,000 miles
(8 000 to 13 000 km).
Any time you notice unusual wear, rotate your tires as
soon as possible and check wheel alignment. Also
check for damaged tires or wheels. SeeWhen It Is Time
for New Tires on page 5-55andWheel Replacement
on page 5-58for more information.The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first rotation
is the most important. SeePart A: Scheduled
Maintenance Services on page 6-4.
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Do not include the compact spare tire in the tire
rotation.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown on the tire and loading
information label. SeeLoading Your Vehicle on
page 4-28for an example of the tire and loading
information label and where it is located on your vehicle.
5-54
Page 235 of 316

While the tires available on General Motors passenger
cars and light trucks may vary with respect to these
grades, they must also conform to federal safety
requirements.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on
the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified government test course.
For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and
a half (1
1⁄2) times as well on the government course as
a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires
depends upon the actual conditions of their use,
however, and may depart significantly from the norm
due to variations in driving habits, service practices and
differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction — AA, A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are AA, A,
B, and C. Those grades represent the tire’s ability
to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor
traction performance. Warning: The traction grade
assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking
traction tests, and does not include acceleration,
cornering, hydroplaning, or peak traction characteristics.
Temperature — A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C,
representing the tire’s resistance to the generation
of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested
under controlled conditions on a specified indoor
laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can
cause the material of the tire to degenerate and
reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a
level of performance which all passenger car tires must
meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of
performance on the laboratory test wheel than the
minimum required by law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination,
can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
5-57
Page 254 of 316

Vehicle Identi�cation
Vehicle Identi�cation Number (VIN)
This is the legal identifier for your vehicle. It appears on
a plate in the front corner of the instrument panel, on
the driver’s side. You can see it if you look through the
windshield from outside your vehicle. The VIN also
appears on the Vehicle Certification and Service Parts
labels and the certificates of title and registration.
Engine Identi�cation
The eighth character in your VIN is the engine
code. This code will help you identify your engine,
specifications and replacement parts.
Service Parts Identi�cation Label
You will find this label on the inside of the glove box.
It is very helpful if you ever need to order parts.
On this label, you will find the following:
•VIN
•Model designation
•Paint information
•Production options and special equipment
Be sure that this label is not removed from the vehicle.
Electrical System
Add-On Electrical Equipment
Notice:Don’t add anything electrical to your vehicle
unless you check with your dealer �rst. Some
electrical equipment can damage your vehicle and
the damage wouldn’t be covered by your warranty.
Some add-on electrical equipment can keep other
components from working as they should.
Your vehicle has an airbag system. Before attempting to
add anything electrical to your vehicle, seeServicing
Your Airbag-Equipped Vehicle on page 1-52.
5-76