2004 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 1306 of 2585

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-9
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1307 of 2585
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
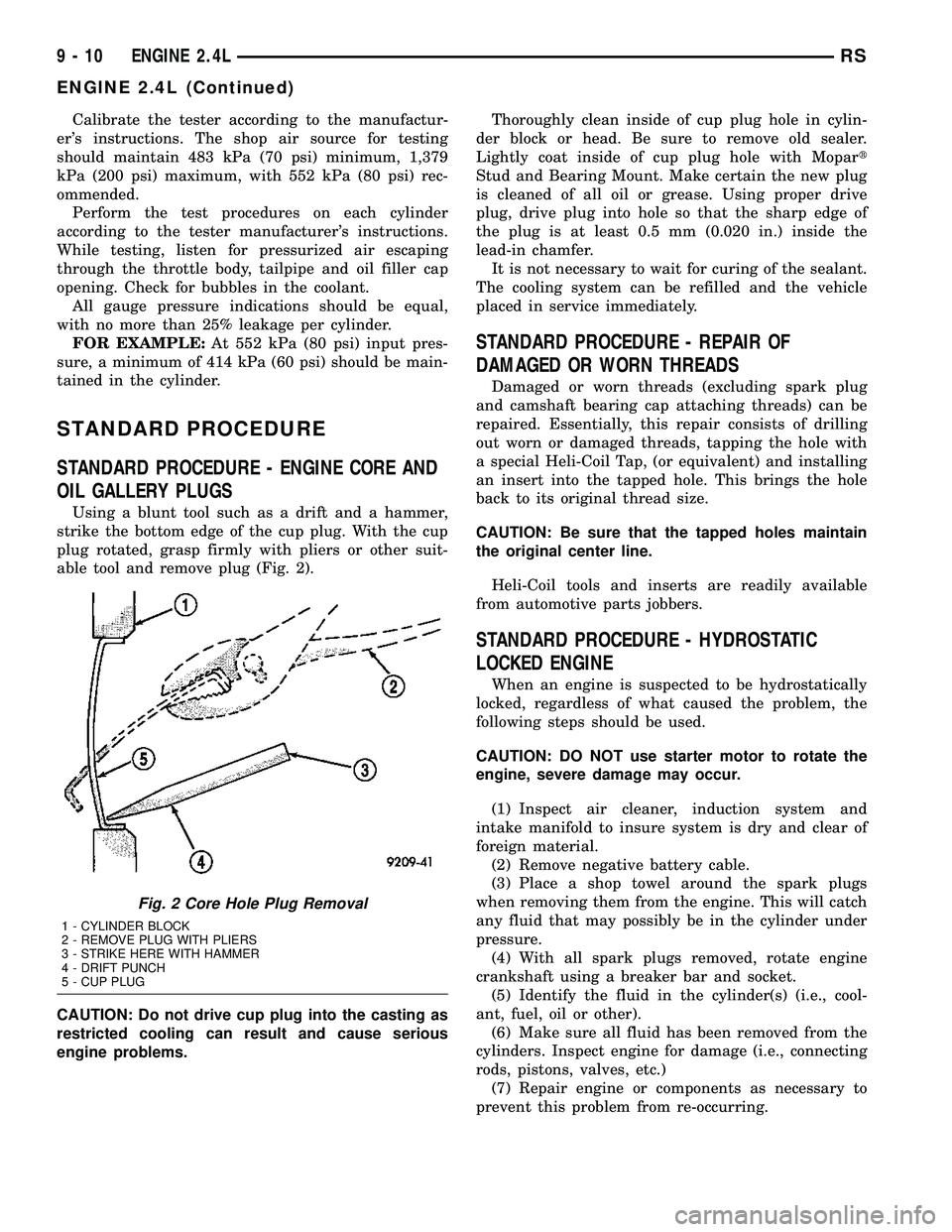
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
Fig. 2 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
9 - 10 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1309 of 2585

NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 3)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocŸ Bristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 3)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 4). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Compare clearance measurements to specs found in
engine specifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).Plastigage generally is accompa-
nied by two scales. One scale is in inches, the
other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
(4) Install the proper crankshaft bearings to
achieve the specified bearing clearances.
Fig. 3 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCŸ BRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
Fig. 4 Plastigage Placed in Lower ShellÐTypical
1 - PLASTIGAGE
9 - 12 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1310 of 2585
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Remove air cleaner housing and inlet tube.
(4) Disconnect the fuel line from fuel rail. (Refer to
14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(5) Disconnect all vacuum hoses.
(6) Drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(7) Remove radiator fans. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL)
(8) Remove radiator upper and lower hoses.
NOTE: When the transaxle cooler lines are removed
from the rolled-groove type fittings at the transaxle,
damage to the inner wall of the hose will occur. To
prevent prevent potential leakage, the cooler hoses
must be cut off flush at the transaxle fitting, and a
service cooler hose splice kit must be installed
upon reassembly.(9) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug cooler
lines and fittings to prevent debris from entering
transaxle or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be
installed upon reassembly.
(10) Disconnect transmission shift linkage and
electrical connectors.
(11) Disconnect throttle body linkage.
(12) Disconnect engine wiring harness.
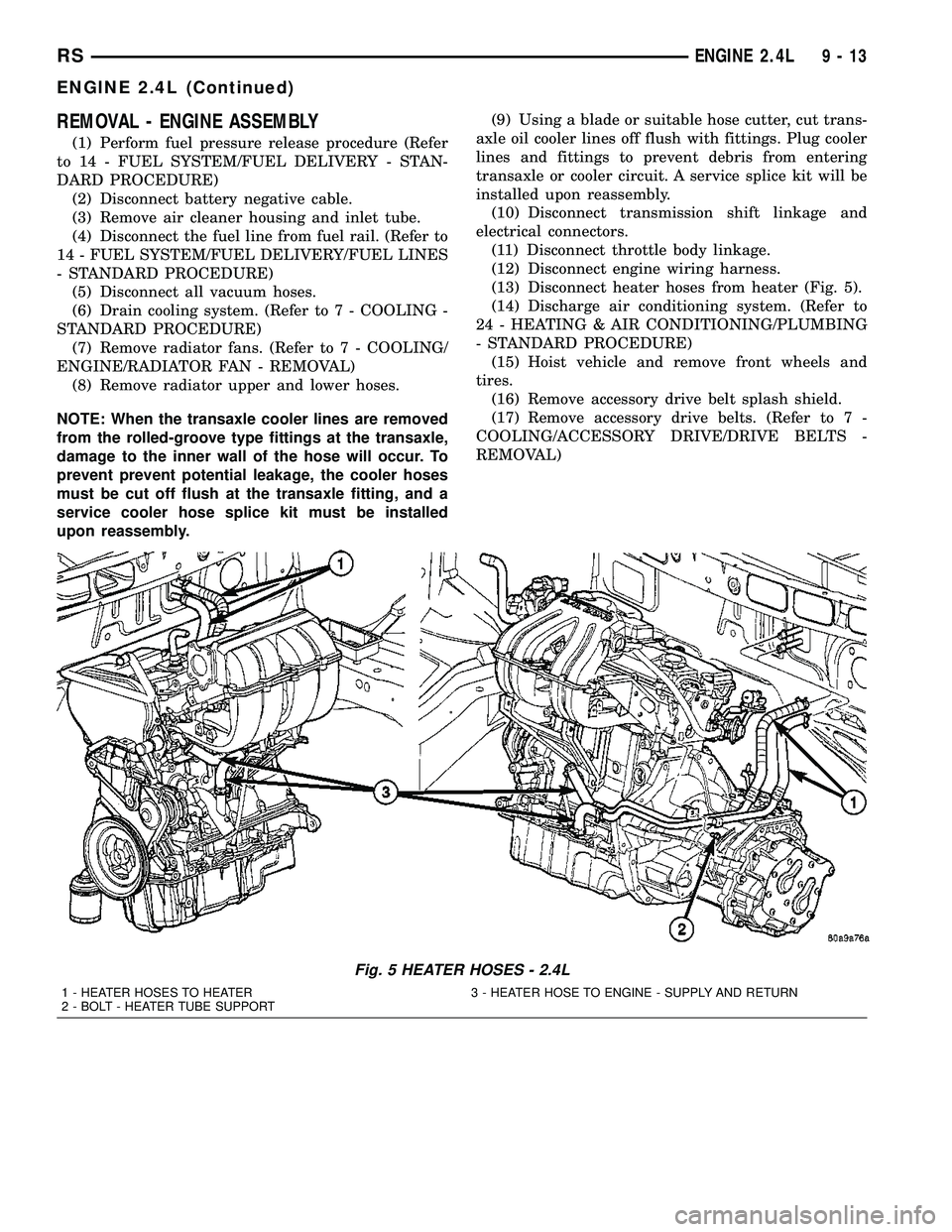
(13) Disconnect heater hoses from heater (Fig. 5).
(14) Discharge air conditioning system. (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(15) Hoist vehicle and remove front wheels and
tires.
(16) Remove accessory drive belt splash shield.
(17) Remove accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL)
Fig. 5 HEATER HOSES - 2.4L
1 - HEATER HOSES TO HEATER 3 - HEATER HOSE TO ENGINE - SUPPLY AND RETURN
2 - BOLT - HEATER TUBE SUPPORT
RSENGINE 2.4L9-13
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1311 of 2585
(18) Remove axle shafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(19) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
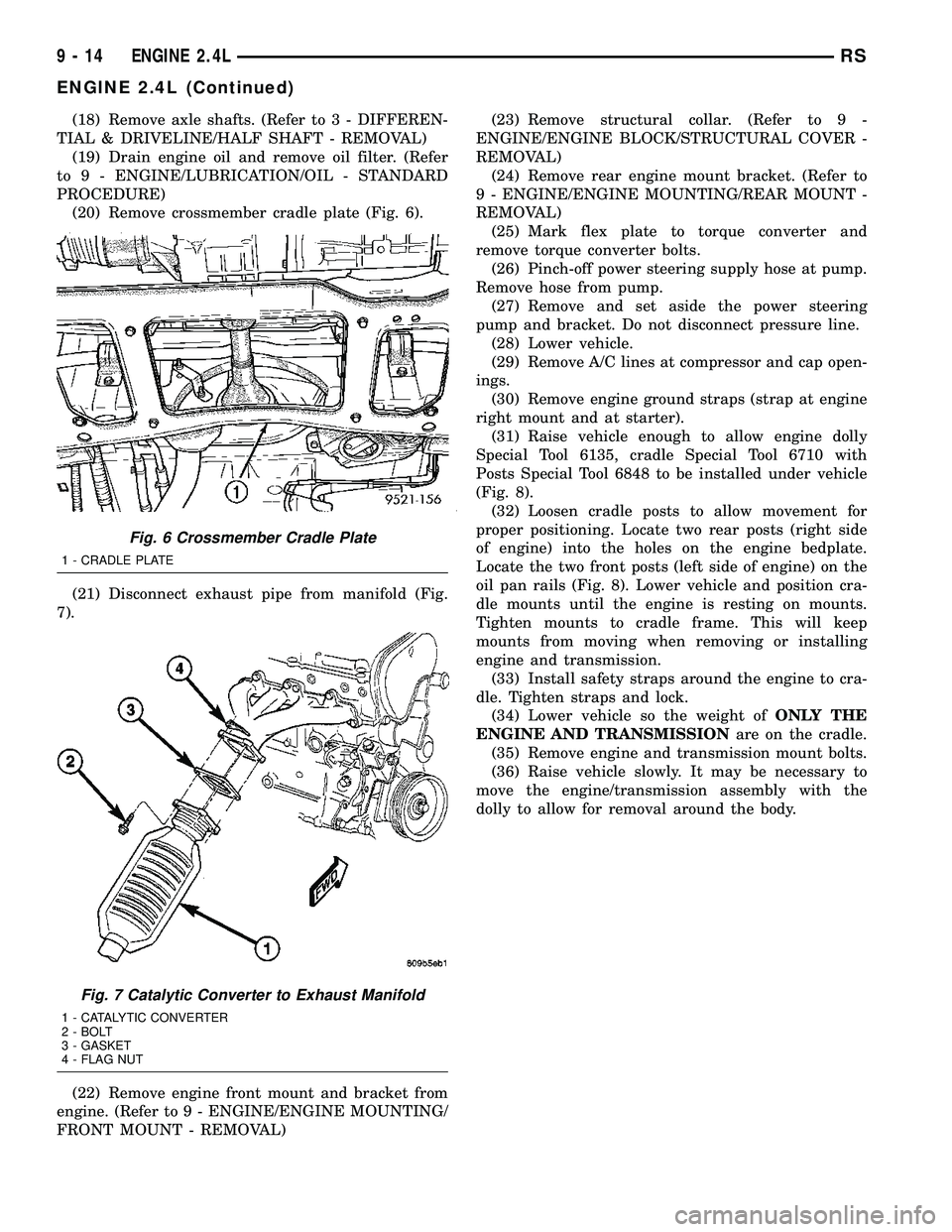
(20) Remove crossmember cradle plate (Fig. 6).
(21) Disconnect exhaust pipe from manifold (Fig.
7).
(22) Remove engine front mount and bracket from
engine. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/
FRONT MOUNT - REMOVAL)(23) Remove structural collar. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER -
REMOVAL)
(24) Remove rear engine mount bracket. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/REAR MOUNT -
REMOVAL)
(25) Mark flex plate to torque converter and
remove torque converter bolts.
(26) Pinch-off power steering supply hose at pump.
Remove hose from pump.
(27) Remove and set aside the power steering
pump and bracket. Do not disconnect pressure line.
(28) Lower vehicle.
(29) Remove A/C lines at compressor and cap open-
ings.
(30) Remove engine ground straps (strap at engine
right mount and at starter).
(31) Raise vehicle enough to allow engine dolly
Special Tool 6135, cradle Special Tool 6710 with
Posts Special Tool 6848 to be installed under vehicle
(Fig. 8).
(32) Loosen cradle posts to allow movement for
proper positioning. Locate two rear posts (right side
of engine) into the holes on the engine bedplate.
Locate the two front posts (left side of engine) on the
oil pan rails (Fig. 8). Lower vehicle and position cra-
dle mounts until the engine is resting on mounts.
Tighten mounts to cradle frame. This will keep
mounts from moving when removing or installing
engine and transmission.
(33) Install safety straps around the engine to cra-
dle. Tighten straps and lock.
(34) Lower vehicle so the weight ofONLY THE
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSIONare on the cradle.
(35) Remove engine and transmission mount bolts.
(36) Raise vehicle slowly. It may be necessary to
move the engine/transmission assembly with the
dolly to allow for removal around the body.
Fig. 6 Crossmember Cradle Plate
1 - CRADLE PLATE
Fig. 7 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - BOLT
3 - GASKET
4 - FLAG NUT
9 - 14 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1316 of 2585
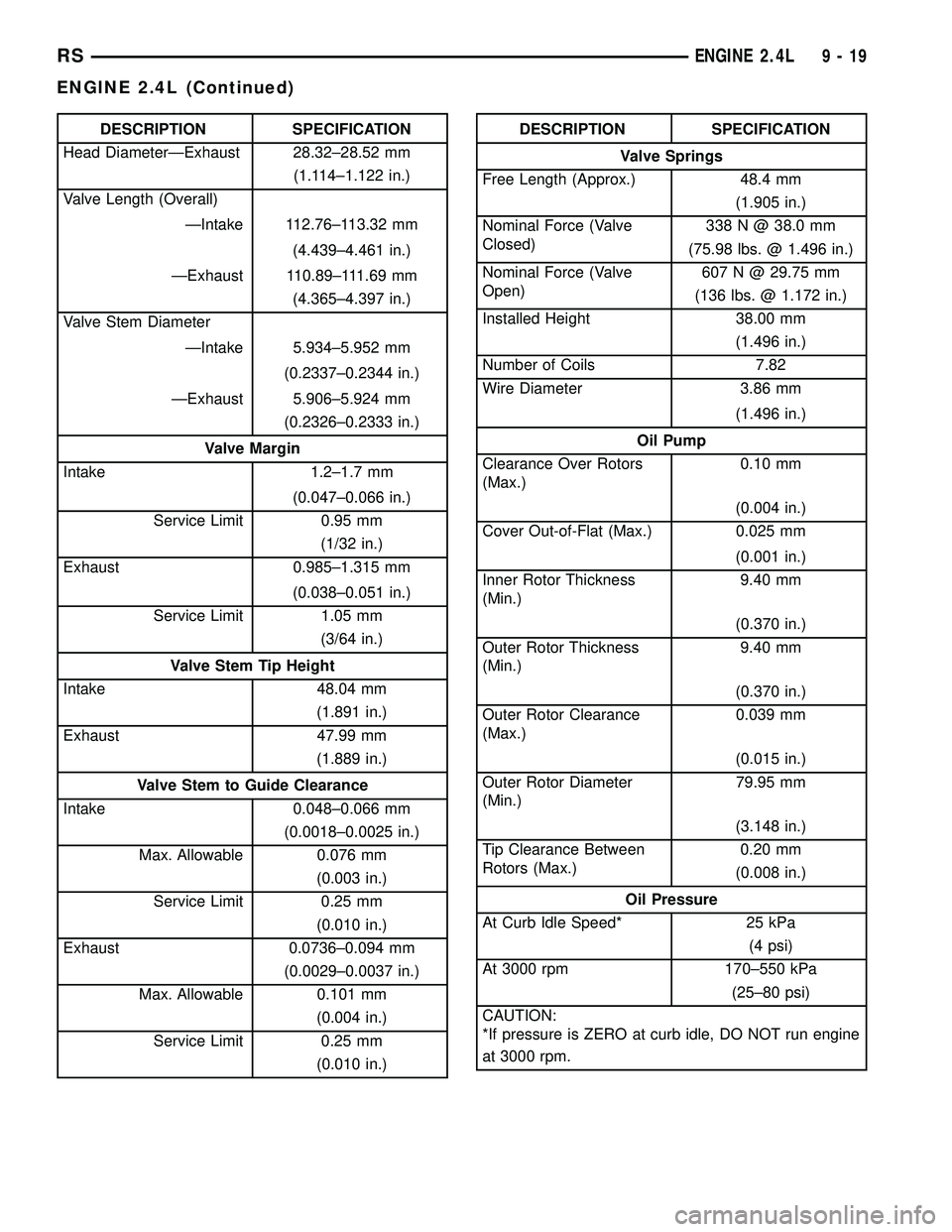
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Head DiameterÐExhaust 28.32±28.52 mm
(1.114±1.122 in.)
Valve Length (Overall)
ÐIntake 112.76±113.32 mm
(4.439±4.461 in.)
ÐExhaust 110.89±111.69 mm
(4.365±4.397 in.)
Valve Stem Diameter
ÐIntake 5.934±5.952 mm
(0.2337±0.2344 in.)
ÐExhaust 5.906±5.924 mm
(0.2326±0.2333 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake 1.2±1.7 mm
(0.047±0.066 in.)
Service Limit 0.95 mm
(1/32 in.)
Exhaust 0.985±1.315 mm
(0.038±0.051 in.)
Service Limit 1.05 mm
(3/64 in.)
Valve Stem Tip Height
Intake 48.04 mm
(1.891 in.)
Exhaust 47.99 mm
(1.889 in.)
Valve Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake 0.048±0.066 mm
(0.0018±0.0025 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.076 mm
(0.003 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
Exhaust 0.0736±0.094 mm
(0.0029±0.0037 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.101 mm
(0.004 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Valve Springs
Free Length (Approx.) 48.4 mm
(1.905 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Closed)338 N @ 38.0 mm
(75.98 lbs. @ 1.496 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Open)607 N @ 29.75 mm
(136 lbs. @ 1.172 in.)
Installed Height 38.00 mm
(1.496 in.)
Number of Coils 7.82
Wire Diameter 3.86 mm
(1.496 in.)
Oil Pump
Clearance Over Rotors
(Max.)0.10 mm
(0.004 in.)
Cover Out-of-Flat (Max.) 0.025 mm
(0.001 in.)
Inner Rotor Thickness
(Min.)9.40 mm
(0.370 in.)
Outer Rotor Thickness
(Min.)9.40 mm
(0.370 in.)
Outer Rotor Clearance
(Max.)0.039 mm
(0.015 in.)
Outer Rotor Diameter
(Min.)79.95 mm
(3.148 in.)
Tip Clearance Between
Rotors (Max.)0.20 mm
(0.008 in.)
Oil Pressure
At Curb Idle Speed* 25 kPa
(4 psi)
At 3000 rpm 170±550 kPa
(25±80 psi)
CAUTION:
*If pressure is ZERO at curb idle, DO NOT run engine
at 3000 rpm.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-19
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1317 of 2585
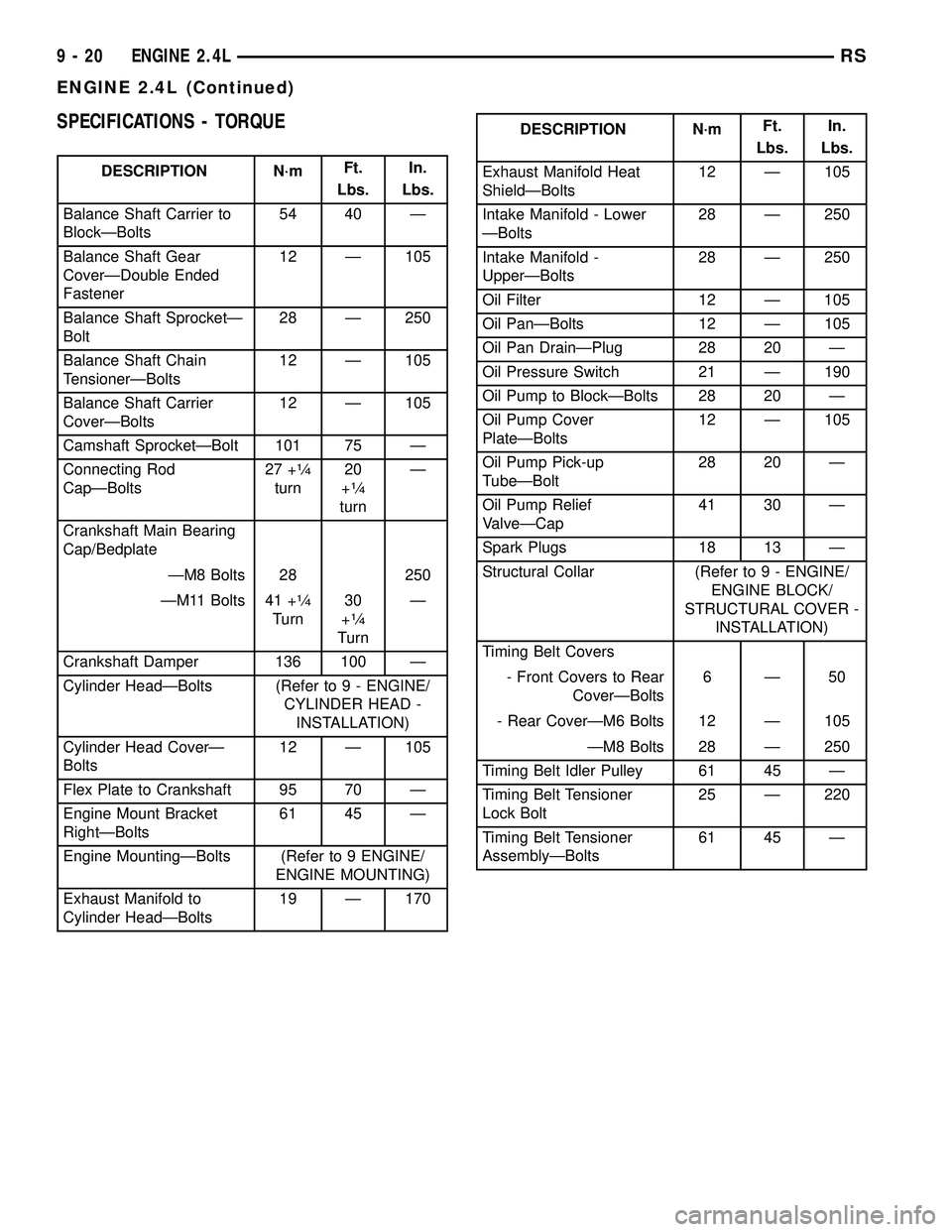
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Balance Shaft Carrier to
BlockÐBolts54 40 Ð
Balance Shaft Gear
CoverÐDouble Ended
Fastener12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft SprocketÐ
Bolt28 Ð 250
Balance Shaft Chain
TensionerÐBolts12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft Carrier
CoverÐBolts12 Ð 105
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 101 75 Ð
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts27 +
1¤4
turn20
+1¤4
turnÐ
Crankshaft Main Bearing
Cap/Bedplate
ÐM8 Bolts 28 250
ÐM11 Bolts 41 +
1¤4
Turn30
+1¤4
TurnÐ
Crankshaft Damper 136 100 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION)
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts12 Ð 105
Flex Plate to Crankshaft 95 70 Ð
Engine Mount Bracket
RightÐBolts61 45 Ð
Engine MountingÐBolts (Refer to 9 ENGINE/
ENGINE MOUNTING)
Exhaust Manifold to
Cylinder HeadÐBolts19 Ð 170
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Exhaust Manifold Heat
ShieldÐBolts12 Ð 105
Intake Manifold - Lower
ÐBolts28 Ð 250
Intake Manifold -
UpperÐBolts28 Ð 250
Oil Filter 12 Ð 105
Oil PanÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Pan DrainÐPlug 28 20 Ð
Oil Pressure Switch 21 Ð 190
Oil Pump to BlockÐBolts 28 20 Ð
Oil Pump Cover
PlateÐBolts12 Ð 105
Oil Pump Pick-up
TubeÐBolt28 20 Ð
Oil Pump Relief
ValveÐCap41 30 Ð
Spark Plugs 18 13 Ð
Structural Collar (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/
STRUCTURAL COVER -
INSTALLATION)
Timing Belt Covers
- Front Covers to Rear
CoverÐBolts6Ð50
- Rear CoverÐM6 Bolts 12 Ð 105
ÐM8 Bolts 28 Ð 250
Timing Belt Idler Pulley 61 45 Ð
Timing Belt Tensioner
Lock Bolt25 Ð 220
Timing Belt Tensioner
AssemblyÐBolts61 45 Ð
9 - 20 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1322 of 2585
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.(Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - SPECIFICA-
TIONS)
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(4) Remove air filter housing and inlet tube.
(5) Remove upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove heater tube support bracket from cyl-
inder head.
(7) Disconnect radiator upper and heater supply
hoses from intake manifold water outlet connections.
(8) Remove accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL)
(9) Raise vehicle and remove exhaust pipe from
manifold.
(10) Remove power steering pump reservoir and
line support bracket from lower intake manifold and
set aside. Do not disconnect lines.
(11) Remove ignition coil and wires from engine.
(12) Disconnect cam sensor and fuel injector wir-
ing connectors.
(13) Remove timing belt and camshaft sprockets.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)
(14) Remove timing belt idler pulley and rear tim-
ing belt cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIM-
ING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) -
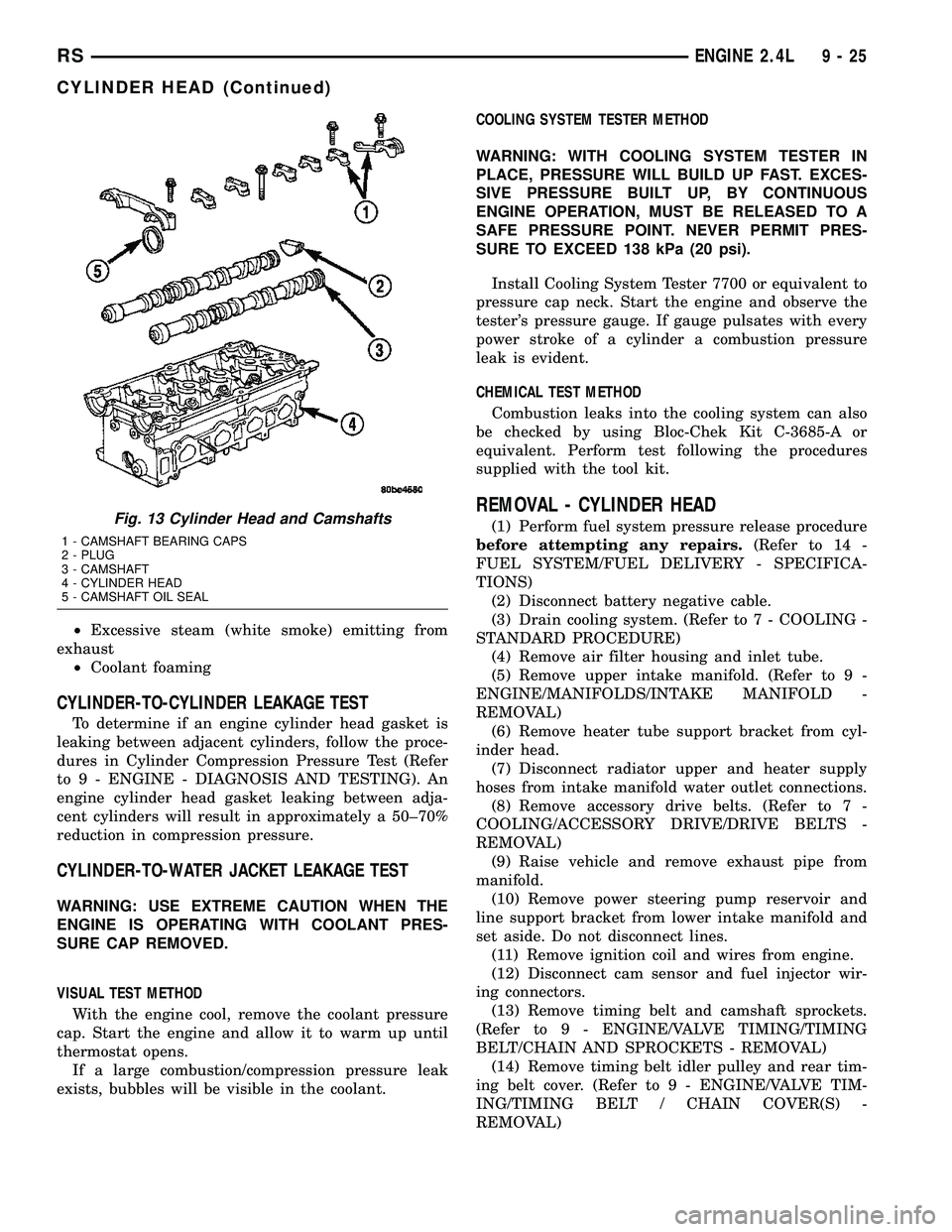
REMOVAL)Fig. 13 Cylinder Head and Camshafts
1 - CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS
2 - PLUG
3 - CAMSHAFT
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5 - CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL
RSENGINE 2.4L9-25
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)