2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA service indicator
[x] Cancel search: service indicatorPage 1042 of 2643

MASTER CYLINDER 4B – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
MASTER CYLINDER
The master cylinder is designed for use in a diagonal–split
system. One front and one diagonally opposite rear brake
are served by the primary piston. The opposite front and
rear brakes are served by the secondary piston. The mas-
ter cylinder incorporates the functions of the standard dual
master cylinder, plus a low fluid level indicator and the pro-
portioning valves in the non–antilock braking system. The
proportioning valves limit the outlet pressure to the rear
brakes after a predetermined master cylinder pressure
has been reached.
Important :
S Replace all the components included in the repair
kits used to service this master cylinder.S Lubricate rubber parts with clean brake fluid to ease
assembly.
S Do not use lubricated shop air on brake parts, as
this may damage rubber components.
S If any hydraulic component is removed or discon-
nected, it may be necessary to bleed all or part of
the brake system.
S The torque values specified are for dry, unlubri-
cated fasteners.
S Perform all service operations on a clean bench,
free from all traces of mineral oil.
FLUID LEVEL SENSOR
The master cylinder is equipped with a fluid level sensor.
This sensor will activate the BRAKE light if a low fluid level
condition is detected. Once the fluid level is corrected, the
BRAKE light will go out.
Page 1082 of 2643

SECTION : 4F
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS4F–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 4F–2. . . . . . . . . .
SPECIAL TOOLS4F–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Tools Table 4F–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SCHEMATIC AND ROUTING DIAGRAMS4F–3 . . . . .
Abs System Circuit (I) 4F–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abs System Circuit (II) 4F–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ebcm Connector Face View 4F–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
COMPONENT LOCATOR4F–6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS/EBD System Drive 4F–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSIS4F–7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Circuit Check 4F–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS Indicator Lamp Inoperative 4F–9. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Supply to Control Module,
No DTCs Stored 4F–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS Indicator Lamp Illuminated Continuously,
No DTCs Stored 4F–16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Brake–Force Distribution (EBD)
System Indicator Lamp Inoperative 4F–18. . . . . . . .
SELF–DIAGNOSTICS 4F–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DISPLAYING DTCs 4F–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CLEARING DTCs 4F–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
INTERMITTENTS AND POOR
CONNECTIONS 4F–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0035 Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Circuit Malfunction 4F–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0040 Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Circuit Malfunction 4F–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0045 Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Circuit Malfunction 4F–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0050 Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Circuit Malfunction 4F–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0060/C0065 Left Front Inlet and
Outlet Valve Solenoid Fault 4F–35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0070/C0075 Right Front Inlet and
Outlet Valve Solenoid Fault 4F–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DTC C0080/C0085 Left Rear Inlet and
Outlet Valve Solenoid Fault 4F–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0090/C0095 Right Rear Inlet and
Outlet Valve Solenoid Fault 4F–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0110 Pump Motor Circuit Malfunction 4F–43. .
DTC C0121 Valve Relay Circuit Malfunction 4F–45. .
DTC C0161 ABS Brake Switch Circuit
Malfunction 4F–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0245 Wheel Speed Sensor Frequency
Error 4F–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0550 ABS Control Module Internal
Fault 4F–54. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0800 Low Voltage Fault 4F–56. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC C0931 Overheated 4F–59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR4F–60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE 4F–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Service Precautions 4F–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bleeding System 4F–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS 5.3 Assembly 4F–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Wheel Speed Sensor 4F–62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Jumper Harness 4F–63.
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor 4F–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION4F–65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Knowledge Required 4F–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS System Components 4F–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Base Braking Mode 4F–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antilock Braking Mode 4F–66. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EBD System 4F–69. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Brake–Force Distribution (EBD) Failure
Matrix 4F–70. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tires and ABS/EBD 4F–71. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Brake Control Module (EBCM) 4F–71. . . .
Front Wheel Speed Sensors 4F–71. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Wheel Speed Sensor Rings 4F–71. . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Wheel Speed Sensors and Rings 4F–71. . . . . .
Valve Relay and Pump Motor Relay 4F–71. . . . . . . . .
Page 1146 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 65
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have a ba-
sic knowledge of the following items. Without this knowl-
edge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic procedures
contained in this section.
S Basic Electrical Circuits : You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the mean-
ing of voltage, current (amps), and resistance
(ohms). You should understand what happens in a
circuit with an open or shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram.
S Use of Circuit Testing Tools : You should know how
to use a test light and how to bypass components
to test circuits using fused jumper wires. You should
be familiar with a digital multimeter. You should be
able to measure voltage, resistance, and current,
and be familiar with the controls and how to use
them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists of
a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock com-
ponents. The conventional brake system includes a vacu-
um booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes, rear lead-
ing/trailing drum brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake
pipes and hoses, brake fluid level sensor and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator (which
is connected to the parking lamp) and the rear disk brakes.
See “ABS Component Locator” in this section for the gen-
eral layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located be-
tween the surge tank and the fire wall on the left side of the
vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hydraulic
check valves, two solenoid valves for each wheel, a hy-
draulic pump, two accumulators, and two damper. The hy-
draulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front calipers
and rear wheel cylinders by modulating hydraulic pressure
to prevent wheel lockup.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit with at-
tached EBCM must be replaced. For more information, re-
fer to ”Base Braking Mode” and ”Antilock Braking Mode”
in this section.
BASE BRAKING MODE
The baseline braking mode of the ABS 5.3 system used
in this vehicle is a diagonal split system. In this system,
one master cylinder circuit supplies pressure to the right
front and the left rear brakes; the other circuit supplies
pressure to the left front and the right rear brakes. All
valves in the hydraulic modulator are in their normal, non–
energized positions as shown in the drawings found in
”ABS System Components” in this section.
Page 1152 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 71
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TIRES AND ABS/EBD
Replacement Tires
Tire size is important for proper performance of the ABS
system. Replacement tires should be the same size, load
range, and construction as the original tires. Replace tires
in axle sets and only with tires of the same tire perfor-
mance criteria (TPC) specification number. Use of any
other size or type may seriously affect the ABS operation.
TIRES AND ABS/EBD
Notice : There is no serviceable or removable EEPROM.
The EBCM must be replaced as an assembly.
The EBCM is attached to the hydraulic unit in the engine
compartment. The controlling element of ABS 5.3 is a mi-
croprocessor–based EBCM. Inputs to the system include
the four wheel speed sensors, the stoplamp switch, the
ignition switch, and the unswitched battery voltage. There
is an output to a bi–directional serial data link, located in
pin K of Data Link Connector (DLC) for service diagnostic
tools and assembly plant testing.
The EBCM monitors the speed of each wheel. If any wheel
begins to approach lockup and the brake switch is closed
(brake pedal depressed), the EBCM controls the sole-
noids to reduce brake pressure to the wheel approaching
lockup. Once the wheel regains traction, brake pressure
is increased until the wheel again begins to approach lock-
up. This cycle repeats until either the vehicle comes to a
stop, the brake pedal is released, or no wheels approach
lockup.
Additionally, the EBCM monitors itself, each input (except
the serial data link), and each output for proper operation.
If it detects any system malfunction, the EBCM will store
a DTC in nonvolatile memory (EEPROM) (DTCs will not
disappear if the battery is disconnected). Refer to ”Self
Diagnostics” in this section for more detailed information.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
The front wheel speed sensors are of a variable reluctance
type. Each sensor is attached to the steering knuckle,
close to a toothed ring. The result, as teeth pass by the
sensor, is an AC voltage with a frequency proportional to
the speed of the wheel. The magnitude of the voltage and
frequency increase with increasing speed. The sensor is
not repairable, nor is the air gap adjustable.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
RINGS
The toothed ring mentioned above is pressed onto the
wheel–side (outer) constant velocity joint. Each ring con-
tains 47 equally spaced teeth. Exercise care during ser-
vice procedures to avoid prying or contacting this ring. Ex-cessive contact may cause damage to one or more teeth.
If the ring is damaged, the wheel–side constant velocity
joint must be replaced.
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR AND
RINGS
The rear wheel speed sensors operate in the same man-
ner as the front wheel speed sensors. They incorporate a
length of flexible harness with the connector attached to
the end of the harness. The rear wheel speed rings are in-
corporated into the hub assemblies and cannot be re-
placed separately, but require replacement of the rear
hub/bearing assembly.
VALUE RELAY AND PUMP MOTOR
RELAY
The valve relay and the motor pump relay are located in-
side the electronic brake control module (EBCM) and are
not replaceable. If one should fail, replace the EBCM.
WIRING HARNESS
The wiring harness is the mechanism by which the elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM) is electrically con-
nected to power and to ground, to the wheel speed sen-
sors, the fuses, the switches, the indicators, and the serial
communications port. The components, considered part
of the wiring harness, are the wires that provide electrical
interconnection, and connectors (terminals, pins, con-
tacts, or lugs) that provide an electrical/mechanical inter-
face from the wire to a system component.
INDICATORS
The electronic brake control module (EBCM) continuously
monitors itself and the other ABS components. If the
EBCM detects a problem with the system, the amber ABS
indicator will light continuously to alert the driver to the
problem. An illuminated ABS indicator indicates that the
ABS system has detected a problem that affects the op-
eration of ABS. No antilock braking will be available. Nor-
mal, non–antilock brake performance will remain. In order
to regain ABS braking ability, the ABS must be serviced.
The red BRAKE indicator will be illuminated when the sys-
tem detects a low brake fluid level in the master cylinder
or when the parking brake switch is closed (the parking
brake is engaged) or EBD system is diabled.
WARNING : EBD INDICATOR LAMP WIRING IS CON-
NECTED TO THE PARKING BRAKE LAMP. IF THE
PARKING BRAKE LAMP IS TURNED ON WHEN YOU
DRIVING, CHECKING ON WHETHER THE PARKING
BRAKE LEVER IS ENAGED OR THE BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL IS LOW. IF THE SYSTEM HAS NO PROBLEM,
THE EBD SYSTEM IS WORKING IMPROPERLY. THE
EBD SYSTEM MUST BE SERVICED.
Page 1904 of 2643

POWER STEERING SYSTEM 6A – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE
BLEEDING THE POWER STEERING
SYSTEM
If the power steering hydraulic system has been serviced,
an accurate fluid level reading cannot be obtained until the
air is bled from the system. Follow these steps to bleed the
air from the system.
1. Turn the wheels all the way to the left and add the
power steering fluid to the MIN mark on the fluid
level indicator.
Notice : When adding fluid or making a complete fluid
change, always use DEXRON®–II or III power steering
fluid. Failure to use the proper fluid will cause hose and
seal damage and fluid leaks.
2. Start the engine. With the engine running at fast
idle, recheck the fluid level. If necessary, add fluid
to bring the level up to the MIN mark.
3. Bleed the system by turning the wheels from side to
side without reaching the stop at either end. Keep
the fluid level at the MIN mark. The air must be
eliminated from the fluid before normal steering ac-
tion can be obtained.
4. Return the wheels to the center position. Continue
running the engine for 2 to 3 minutes.
5. Road test the car to be sure the steering functions
normally and is free from noise.
6. Recheck the fluid level as described in steps 1 and
2. Make sure the fluid level is at the MAX mark af-
ter the system has stabilized at its normal operating
temperature. Add fluid as needed.
CHECKING AND ADDING FLUID
Notice : When adding fluid or making a complete fluid
change, always use DEXRON®–II or III power steering
fluid. Failure to use the proper fluid will cause hose and
seal damage and fluid leaks.
1. The power steering fluid level is indicated either by
marks on a see–through fluid reservoir or by marks
on a fluid level indicator on the fluid reservoir cap.
2. If the fluid is warmed up to 66°C (150°F), the fluid
level should be between the MAX and MIN marks.
Add fluid as needed.
3. If the fluid is cool, 21°C (70°F), the fluid level
should be at the MIN mark. Add fluid as needed.
Page 2022 of 2643

7B – 20IMANUAL CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Dip new O–rings in clean polyalkaline glycol refrig-
erant oil before installation.
MAINTAINING CHEMICAL STABILITY
IN THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
The efficient operation and the life of the air conditioning
(A/C) system is dependent upon the chemical stability of
the refrigeration system. When foreign materials, such as
dirt, air, or moisture, contaminate the refrigeration system,
they will change the stability of the refrigerant and the poly-
alkaline glycol (PAG) compressor oil. They will also affect
the pressure–temperature relationship, reduce efficient
operation, and can possibly cause interior corrosion and
abnormal wear of moving parts.
Observe the following practices to ensure chemical stabil-
ity in the system:
S Wipe away dirt or oil at and near any connection
before opening that connection. This will reduce the
chance of dirt entering the system.
S Cap, plug, or tape both sides of a connection as
soon as possible after opening the connection. This
will prevent the entry of dirt, foreign material, and
moisture.
S Keep all tools clean and dry, including the manifold
gauge set and all replacement parts.
S Use a clean and dry transfer device and container
to add polyalkaline glycol refrigerant oil. This will
ensure that the oil remains as moisture–free as
possible. Refer to ”Discharging, Adding Oil, Eva-
cuating, and Charging Procedures for A/C System”
in this section.
S Have everything you need ready to allow you to
perform all operations quickly when opening an A/C
system. Do not leave the A/C system open any lon-
ger than necessary.
S Evacuate and recharge any A/C system that has
been opened. Refer to ”Discharging, Adding Oil,
Evacuating, and Charging Procedures for A/C Sys-
tem” in this section for the instructions to perform
this procedure properly.
All service parts are dehydrated and sealed before ship-
ping. They should remain sealed until just before making
connections. All the parts should be at room temperature
before uncapping. This prevents condensation of mois-
ture from the air from entering the system. Reseal all parts
as soon as possible.
DISCHARGING, ADDING OIL,
EVACUATING, AND CHARGING
PROCEDURES FOR A/C SYSTEM
CAUTION : Use only refillable refrigerant tanks that
are authorized for the charging station being used.
The use of other tanks may cause personal injury or
void the warranty. Refer to the manufacturer’s in-
structions for the charging station.CAUTION : To avoid personal injury, always wear
goggles and gloves when performing work that in-
volves opening the refrigeration system.
A charging station discharges, evacuates, and recharges
an air–conditioning (A/C) system with one hookup. Filter-
ing the refrigerant during the recovery cycle together with
filtering during the evacuation cycle ensures a supply of
clean, dry refrigerant for A/C system charging.
S Never use the R–134a charging station on a sys-
tem charged with R–12. The refrigerants and the
oils from each system are not compatible with
those from the other system and must never be
mixed, even in the smallest amount. Mixing refriger-
ant residue will damage the equipment.
S Never use adapters which convert from one size
fitting to another. Such use allows contamination,
which may cause system failure.
Charging Station Setup and Maintenance
There are many charging stations available. All perform
the various tasks required to discharge the system and re-
cover refrigerant, evacuate the system, add a measured
amount of oil, and recharge an A/C system with a mea-
sured amount of refrigerant. Refer to the manufacturer’s
instructions for all initial setup procedures and all mainte-
nance procedures.
Control Panel Functions
A charging station will have controls and indicators to allow
the operator to control and monitor the operation in prog-
ress. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for details.
These can be expected to include the following:
1. Main Power Switch
S Supplies electrical power to the control panel.
2. Display
S Shows the time programmed for vacuum.
S Shows the weight of the refrigerant programmed
for recharging.
S Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for de-
tailed programming information.
3. Low–Side Manifold Gauge
S Shows the system’s low–side pressure.
4. High–Side Manifold Gauge
S Shows the system’s high–side pressure.
5. Controls Panel
S Controls the various operating functions.
6. Low–Side Valve
S Connects the low side of the A/C system to the
unit.
7. Moisture Indicator
S Shows whether the refrigerant is wet or dry.
8. High–Side Valve
S Connects the high side of the A/C system to the
unit.
Page 2112 of 2643
8B – 8ISUPPLEMENTAL INFLATABLE RESTRAINTS (SIR)
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SIR DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM CHECK
Notice : If the vehicle interior has been exposed to exten-
sive water intrusion such as water leaks, driving through
high water, flooding, or other causes, the sensing and
diagnostic module(SDM) and SDM connector may need
to be replaced. With ignition OFF, inspect the area around
the SDM, including the carpet. If any significant soaking or
evidence of previous soaking is detected, the water must
be removed, water damage repaired, and the SDM and
the SDM connector must be replaced. Before attempting
any of these repairs, the supplemental inflatable re-
straints(SIR) must be disabled. Refer to ”Disabling the
SIR” and ”Sensing and Diagnostic Module(SDM)” in this
section for instructions on how to disable the SIR and re-
place the SDM.
The SIR Diagnostic System Check must always be the
starting point for any SIR diagnosis. The Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check reveals diagnostic trouble codes(DTCs)
through the use of scan tool. The diagnostic procedures
used in this section are designed to find any repair SIR
conditions. To get the best results, it is important to use the
diagnostic charts and follow the sequence listed below.
1. Perform the SIR Diagnostic System Check, which
reveal diagnostic trouble codes(DTCs) through theuse of scan tool.. It also checks for proper airbag
indicator operation.
2. Refer to the proper diagnostic chart as directed by
SIR Diagnostic System Check. Bypassing these
procedures may result in extended diagnostic time,
incorrect diagnosis, and incorrect parts replace-
ment.
3. Repeat the SIR Diagnostic System Check after any
repair or diagnostic procedures have been per-
formed to ensure that the repair has been made
correctly and that no other malfunction exists.
Circiut Description
When the ignition switch is first turned to ON, ignition volt-
age is supplied from airbag fuse to find the SDM at input
terminal A1. The SDM responds by flashing the airbag in-
dicator seven times and then turning it off while the SDM
performs tests on the SIR.
Diagnostic Aids
The order in which DTCs are diagnosed is very important.
Failure to diagnose the DTCs in the order specified may
result in extended diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis,
and incorrect parts replacement.
SIR Diagnostic System Check
CAUTION : The sensing and the diagnosis module
(SDM) can maintain surfficient voltage to deploy the
airbags and pretensioners for 1 minute after the igni-
tion is OFF and the fuse has been removed. If the air-
bags and pretensioners are not disconnected, do not
begin service until one minute has been passed after
disconnecting power to the SDM. Otherwise, injury
could result.
CAUTION : During service procedure, be very careful
when handling the SDM. Never strike or jar the SDM.Never power the supplemental inflatable re-
straints(SIR) when the SDM is not rigidly attached to
the vehicle. All SDM mounting bolts must be carefully
tightened , and the arrow on the SDM must be point
toward the front of the vehicle to ensure proper op-
eration of the SIR. The SDM could be activated if it is
powered when it is not rigidly attached to the vehicle,
resulting in unexpected deployment and possible in-
jury.
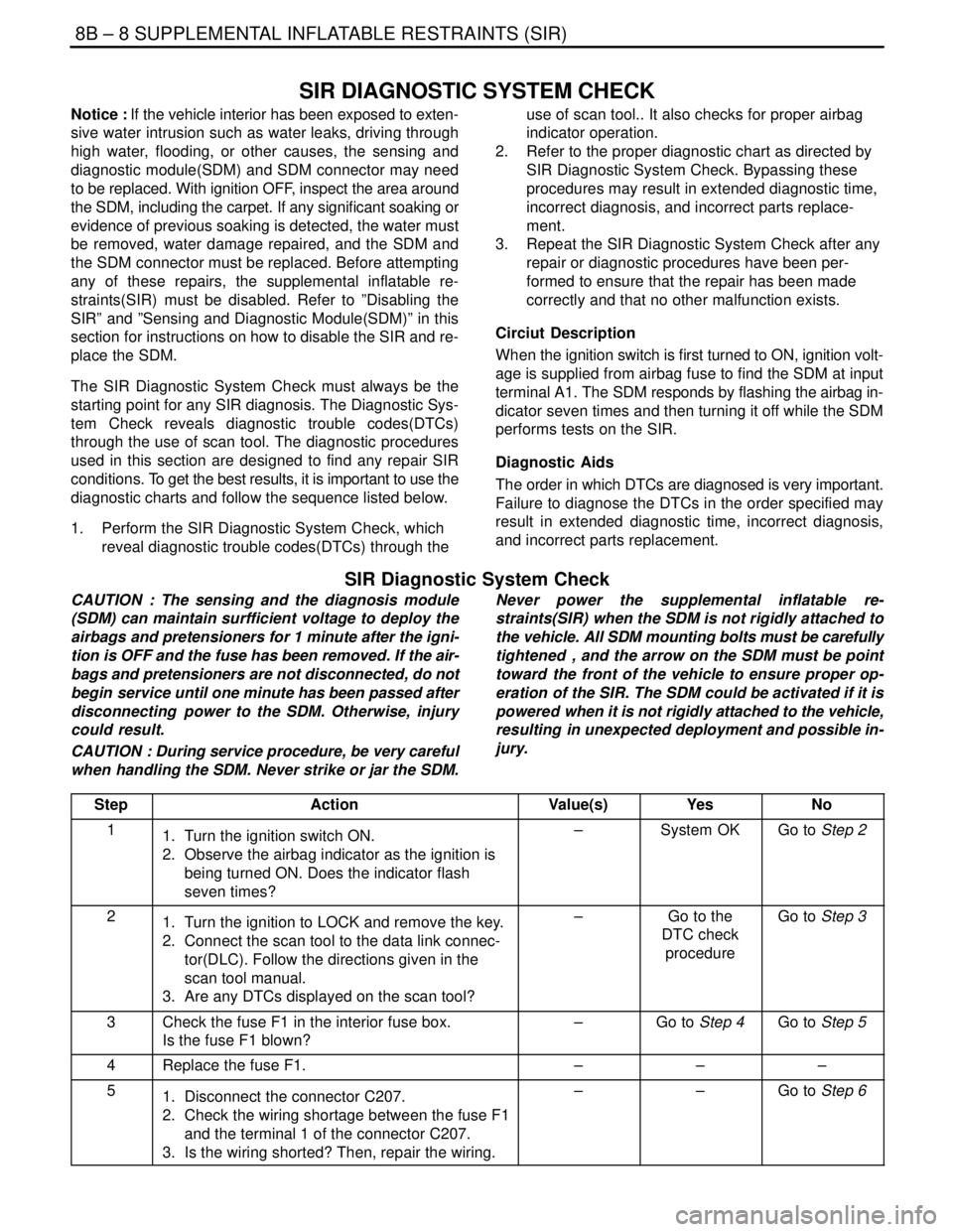
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition switch ON.
2. Observe the airbag indicator as the ignition is
being turned ON. Does the indicator flash
seven times?–System OKGo to Step 2
21. Turn the ignition to LOCK and remove the key.
2. Connect the scan tool to the data link connec-
tor(DLC). Follow the directions given in the
scan tool manual.
3. Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool?–Go to the
DTC check
procedureGo to Step 3
3Check the fuse F1 in the interior fuse box.
Is the fuse F1 blown?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Replace the fuse F1.–––
51. Disconnect the connector C207.
2. Check the wiring shortage between the fuse F1
and the terminal 1 of the connector C207.
3. Is the wiring shorted? Then, repair the wiring.––Go to Step 6
Page 2114 of 2643
8B – 10ISUPPLEMENTAL INFLATABLE RESTRAINTS (SIR)
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SENSING AND DIAGNOSTIC MODULE (SDM) INTEGRITY
CHECK
The following diagnostic chart must be used when all cir-
cuitry outside the sensing and diagnostic module (SDM)
has been found to operate properly, as indicated by follow-
ing the appropriate diagnostic trouble code(DTC) chart.
The chart verifies the need for SDM replacement.
Circuit Description
When the SDM recognizes ignition voltage greater than 9
volts at terminal A1 of the SDM, the airbag indicator
flashes seven times to verify operation. At this time the
SDM performs turn–on tests followed by resistance mea-surement tests and continuous monitoring tests.
When malfunction is detected, the SDM sets current DTC
and illuminates the airbag indicator.
When the malfuncation is no longer detected and/or the
ignition switch is cycled, the SDM will clear current DTCs
and move them to a history file, except for the DTCs 51
and sometimes 71. DTCs 51 will not be cleared by scan
tool because these codes require replacement of SDM.
The SDM must be replaced only after the malfunction that
set the DTC has been repaired.
Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM) Integrity Check
CAUTION : The sensing and diagnostic module
(SDM) can maimtain sufficient voltage to deploy the
airbags and pretensioners for 1 minute after the igni-
tion is OFF and the fuse has been removed. If the air-
bags and pretensioners are not disconnected, do not
begin service until one minute has passed after dis-
connecting the power to the SDM. Otherwise, injury
could result.
CAUTION : During service procedure, be very careful
when handling the SDM. Never strike or jar the SDM.Never power the supplemental inflatable re-
straints(SIR) when the SDM is not rigidlyattached to
the vehile. All SDM mounting bolts must be carefully
tightened , and the arrow on the SDM must be point
toward the front of the vehicle to ensure proper op-
eration of the SIR. The SDM could be activated if it is
powered when it is not rigidly attached to the vehicle,
resulting in unexpected deployment and possible in-
jury.
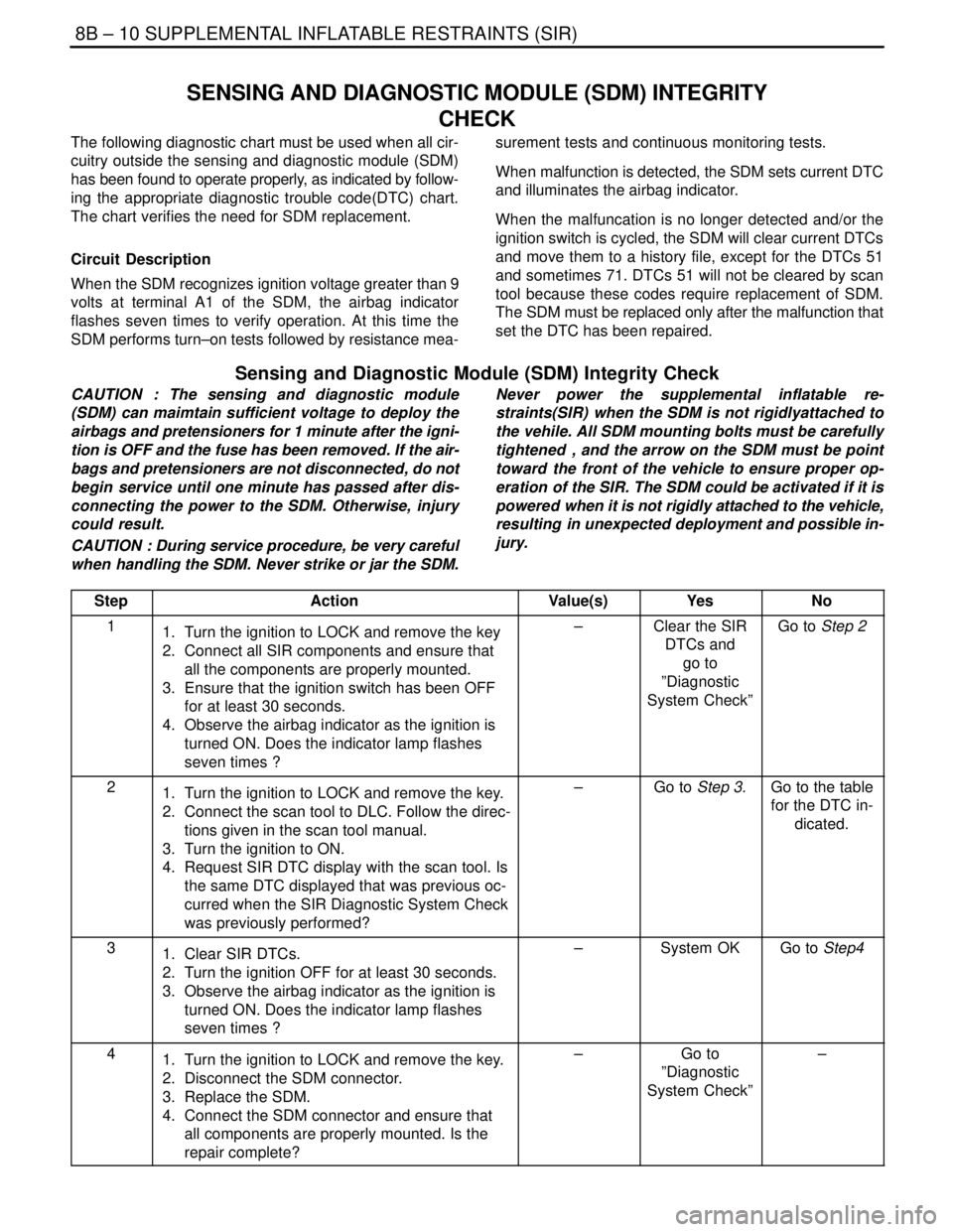
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition to LOCK and remove the key
2. Connect all SIR components and ensure that
all the components are properly mounted.
3. Ensure that the ignition switch has been OFF
for at least 30 seconds.
4. Observe the airbag indicator as the ignition is
turned ON. Does the indicator lamp flashes
seven times ?–Clear the SIR
DTCs and
go to
”Diagnostic
System Check”Go to Step 2
21. Turn the ignition to LOCK and remove the key.
2. Connect the scan tool to DLC. Follow the direc-
tions given in the scan tool manual.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Request SIR DTC display with the scan tool. Is
the same DTC displayed that was previous oc-
curred when the SIR Diagnostic System Check
was previously performed?–Go to Step 3.Go to the table
for the DTC in-
dicated.
31. Clear SIR DTCs.
2. Turn the ignition OFF for at least 30 seconds.
3. Observe the airbag indicator as the ignition is
turned ON. Does the indicator lamp flashes
seven times ?–System OKGo to Step4
41. Turn the ignition to LOCK and remove the key.
2. Disconnect the SDM connector.
3. Replace the SDM.
4. Connect the SDM connector and ensure that
all components are properly mounted. Is the
repair complete?–Go to
”Diagnostic
System Check”–