2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER wheels
[x] Cancel search: wheelsPage 1627 of 2585
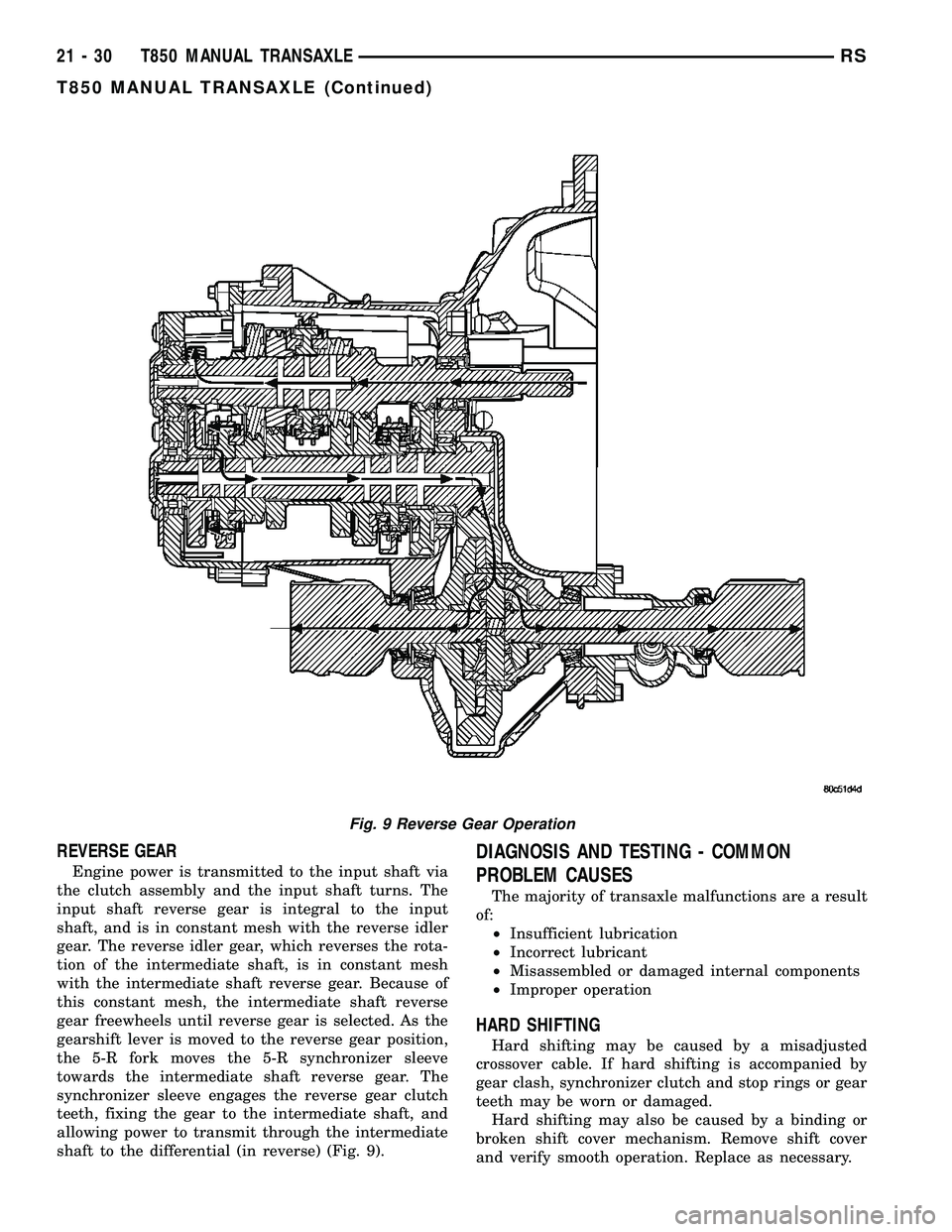
REVERSE GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft reverse gear is integral to the input
shaft, and is in constant mesh with the reverse idler
gear. The reverse idler gear, which reverses the rota-
tion of the intermediate shaft, is in constant mesh
with the intermediate shaft reverse gear. Because of
this constant mesh, the intermediate shaft reverse
gear freewheels until reverse gear is selected. As the
gearshift lever is moved to the reverse gear position,
the 5-R fork moves the 5-R synchronizer sleeve
towards the intermediate shaft reverse gear. The
synchronizer sleeve engages the reverse gear clutch
teeth, fixing the gear to the intermediate shaft, and
allowing power to transmit through the intermediate
shaft to the differential (in reverse) (Fig. 9).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMMON
PROBLEM CAUSES
The majority of transaxle malfunctions are a result
of:
²Insufficient lubrication
²Incorrect lubricant
²Misassembled or damaged internal components
²Improper operation
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting may be caused by a misadjusted
crossover cable. If hard shifting is accompanied by
gear clash, synchronizer clutch and stop rings or gear
teeth may be worn or damaged.
Hard shifting may also be caused by a binding or
broken shift cover mechanism. Remove shift cover
and verify smooth operation. Replace as necessary.
Fig. 9 Reverse Gear Operation
21 - 30 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERS
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1659 of 2585
BACK-UP LAMP SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Disconnect back-up lamp switch connector.
(3) Remove back-up lamp switch (Fig. 95).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install back-up lamp switch (Fig. 95) and
torque to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.) using Tool 8827.
(2) Connect back-up lamp switch connector.
(3) Lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
DESCRIPTION
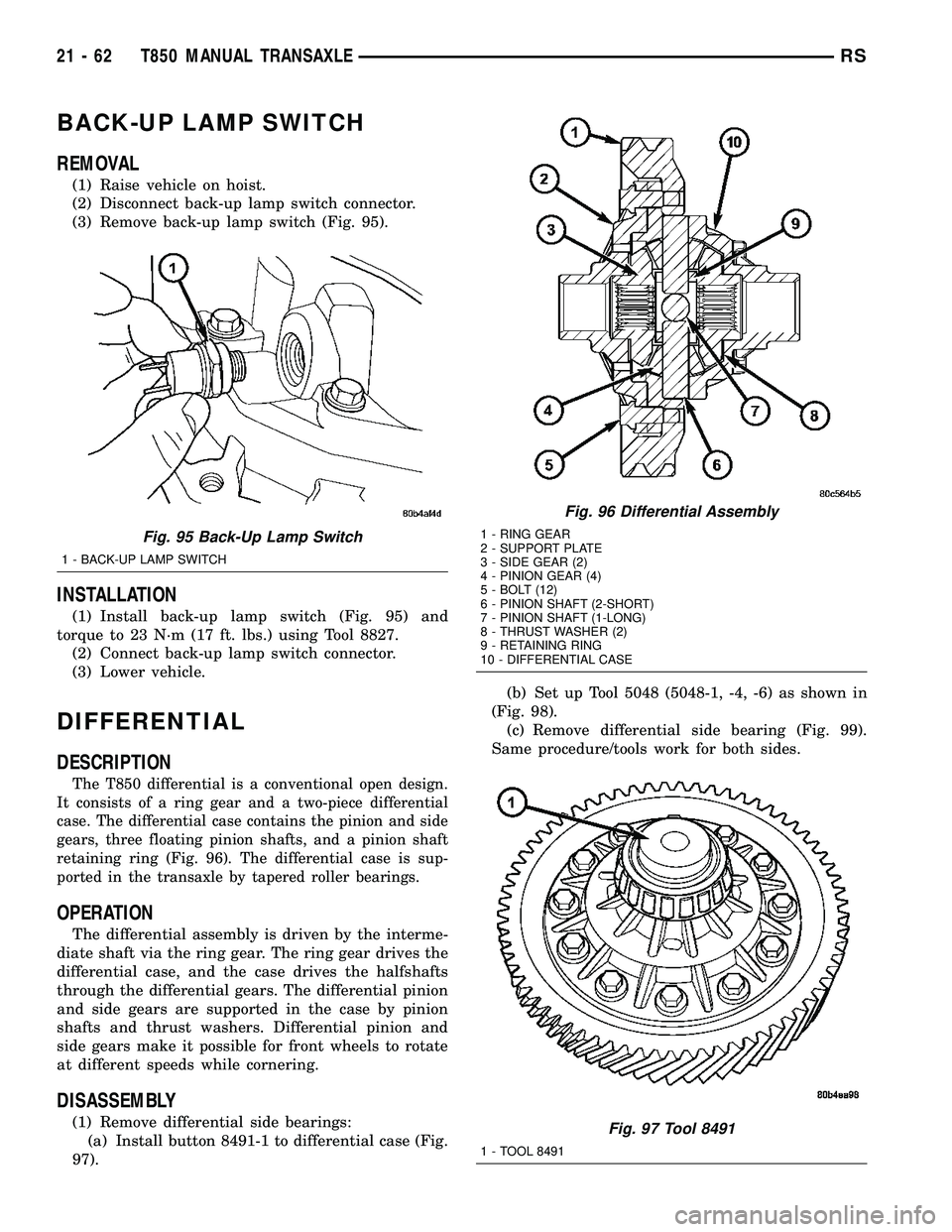
The T850 differential is a conventional open design.
It consists of a ring gear and a two-piece differential
case. The differential case contains the pinion and side
gears, three floating pinion shafts, and a pinion shaft
retaining ring (Fig. 96). The differential case is sup-
ported in the transaxle by tapered roller bearings.
OPERATION
The differential assembly is driven by the interme-
diate shaft via the ring gear. The ring gear drives the
differential case, and the case drives the halfshafts
through the differential gears. The differential pinion
and side gears are supported in the case by pinion
shafts and thrust washers. Differential pinion and
side gears make it possible for front wheels to rotate
at different speeds while cornering.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove differential side bearings:
(a) Install button 8491-1 to differential case (Fig.
97).(b) Set up Tool 5048 (5048-1, -4, -6) as shown in
(Fig. 98).
(c) Remove differential side bearing (Fig. 99).
Same procedure/tools work for both sides.
Fig. 95 Back-Up Lamp Switch
1 - BACK-UP LAMP SWITCH
Fig. 96 Differential Assembly
1 - RING GEAR
2 - SUPPORT PLATE
3 - SIDE GEAR (2)
4 - PINION GEAR (4)
5 - BOLT (12)
6 - PINION SHAFT (2-SHORT)
7 - PINION SHAFT (1-LONG)
8 - THRUST WASHER (2)
9 - RETAINING RING
10 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 97 Tool 8491
1 - TOOL 8491
21 - 62 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERS
Page 1717 of 2585
replacement of the torque converter and thorough
transaxle cleaning.
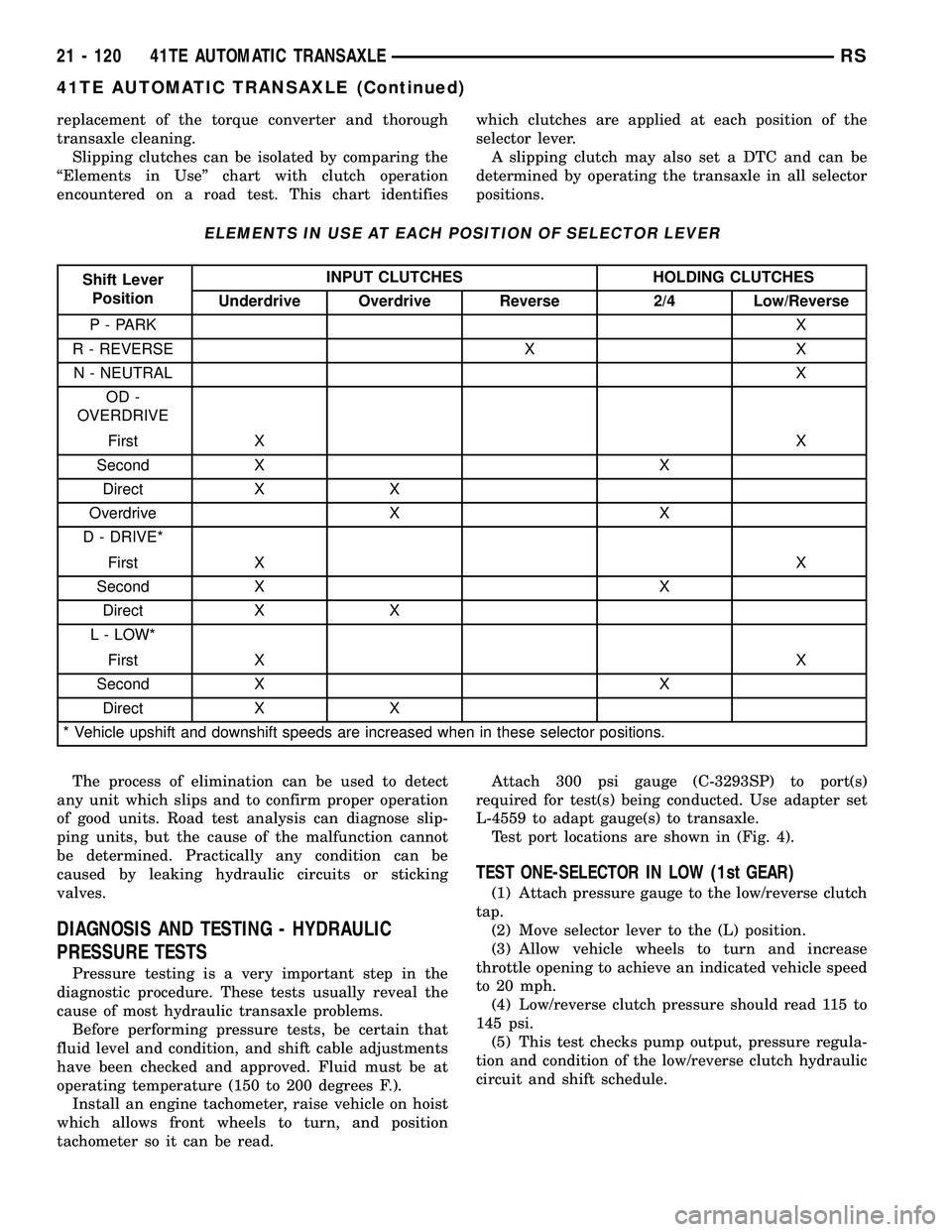
Slipping clutches can be isolated by comparing the
ªElements in Useº chart with clutch operation
encountered on a road test. This chart identifieswhich clutches are applied at each position of the
selector lever.
A slipping clutch may also set a DTC and can be
determined by operating the transaxle in all selector
positions.
ELEMENTS IN USE AT EACH POSITION OF SELECTOR LEVER
Shift Lever
PositionINPUT CLUTCHES HOLDING CLUTCHES
Underdrive Overdrive Reverse 2/4 Low/Reverse
P - PARKX
R - REVERSE X X
N - NEUTRALX
OD -
OVERDRIVE
First XX
Second X X
Direct X X
Overdrive X X
D - DRIVE*
First XX
Second X X
Direct X X
L - LOW*
First XX
Second X X
Direct X X
* Vehicle upshift and downshift speeds are increased when in these selector positions.
The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road test analysis can diagnose slip-
ping units, but the cause of the malfunction cannot
be determined. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most hydraulic transaxle problems.
Before performing pressure tests, be certain that
fluid level and condition, and shift cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. Fluid must be at
operating temperature (150 to 200 degrees F.).
Install an engine tachometer, raise vehicle on hoist
which allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read.Attach 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP) to port(s)
required for test(s) being conducted. Use adapter set
L-4559 to adapt gauge(s) to transaxle.
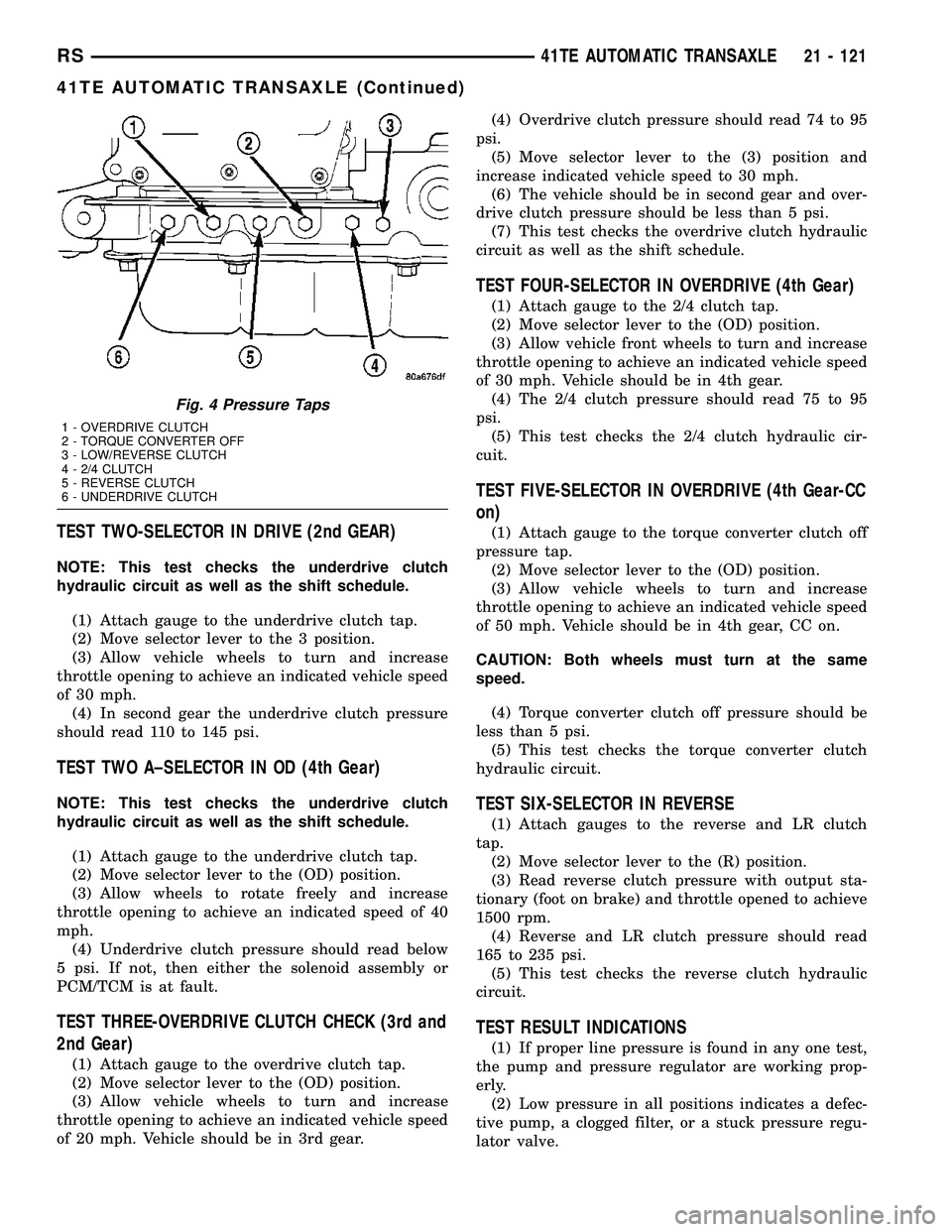
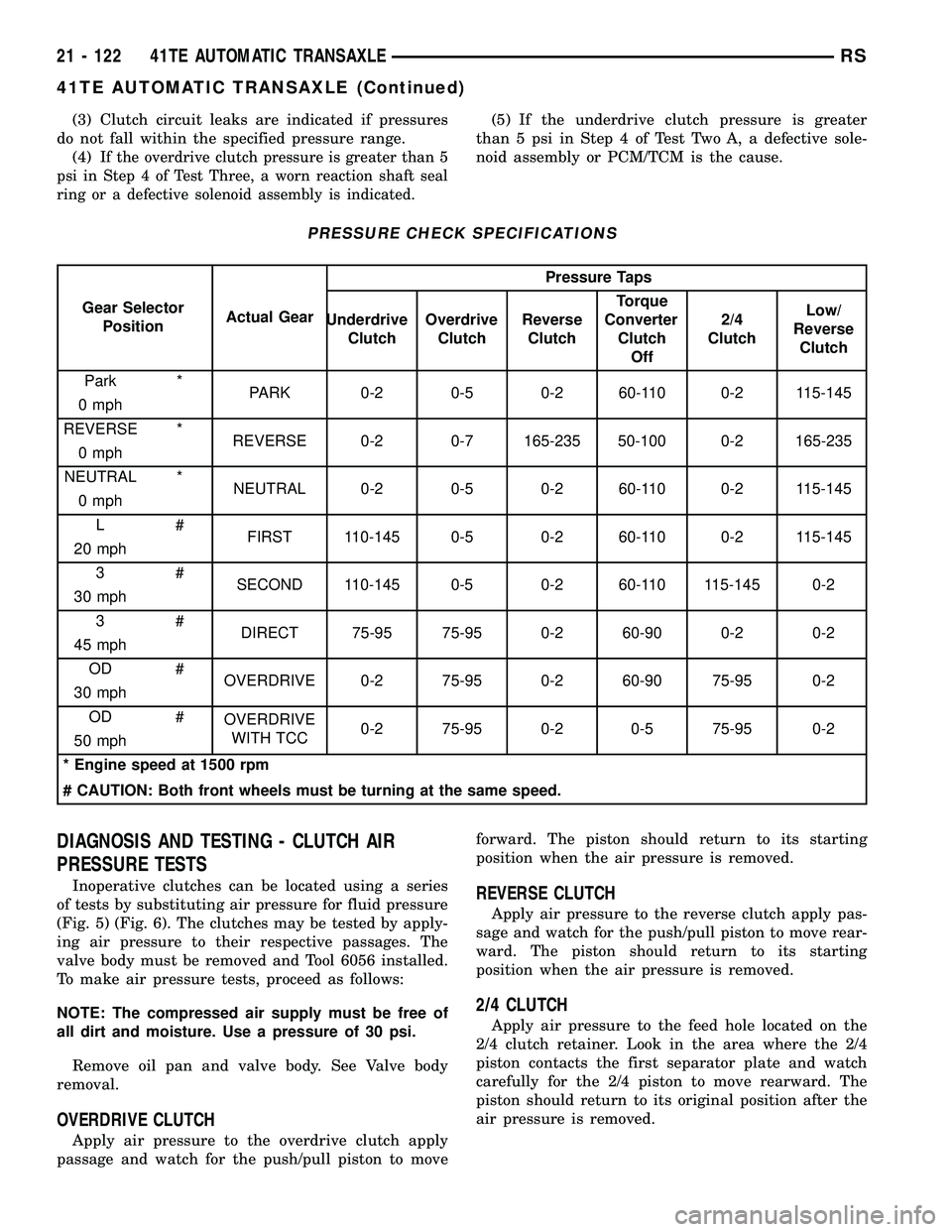
Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 4).
TEST ONE-SELECTOR IN LOW (1st GEAR)
(1) Attach pressure gauge to the low/reverse clutch
tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (L) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
to 20 mph.
(4) Low/reverse clutch pressure should read 115 to
145 psi.
(5) This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion and condition of the low/reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit and shift schedule.
21 - 120 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1718 of 2585
TEST TWO-SELECTOR IN DRIVE (2nd GEAR)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the 3 position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph.
(4) In second gear the underdrive clutch pressure
should read 110 to 145 psi.
TEST TWO A±SELECTOR IN OD (4th Gear)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow wheels to rotate freely and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated speed of 40
mph.
(4) Underdrive clutch pressure should read below
5 psi. If not, then either the solenoid assembly or
PCM/TCM is at fault.
TEST THREE-OVERDRIVE CLUTCH CHECK (3rd and
2nd Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the overdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 20 mph. Vehicle should be in 3rd gear.(4) Overdrive clutch pressure should read 74 to 95
psi.
(5) Move selector lever to the (3) position and
increase indicated vehicle speed to 30 mph.
(6) The vehicle should be in second gear and over-
drive clutch pressure should be less than 5 psi.
(7) This test checks the overdrive clutch hydraulic
circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST FOUR-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the 2/4 clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle front wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear.
(4) The 2/4 clutch pressure should read 75 to 95
psi.
(5) This test checks the 2/4 clutch hydraulic cir-
cuit.
TEST FIVE-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear-CC
on)
(1) Attach gauge to the torque converter clutch off
pressure tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 50 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear, CC on.
CAUTION: Both wheels must turn at the same
speed.
(4) Torque converter clutch off pressure should be
less than 5 psi.
(5) This test checks the torque converter clutch
hydraulic circuit.
TEST SIX-SELECTOR IN REVERSE
(1) Attach gauges to the reverse and LR clutch
tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (R) position.
(3) Read reverse clutch pressure with output sta-
tionary (foot on brake) and throttle opened to achieve
1500 rpm.
(4) Reverse and LR clutch pressure should read
165 to 235 psi.
(5) This test checks the reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure is found in any one test,
the pump and pressure regulator are working prop-
erly.
(2) Low pressure in all positions indicates a defec-
tive pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure regu-
lator valve.
Fig. 4 Pressure Taps
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER OFF
3 - LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
4 - 2/4 CLUTCH
5 - REVERSE CLUTCH
6 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 121
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1719 of 2585
(3) Clutch circuit leaks are indicated if pressures
do not fall within the specified pressure range.
(4)
If the overdrive clutch pressure is greater than 5
psi in Step 4 of Test Three, a worn reaction shaft seal
ring or a defective solenoid assembly is indicated.
(5) If the underdrive clutch pressure is greater
than 5 psi in Step 4 of Test Two A, a defective sole-
noid assembly or PCM/TCM is the cause.
PRESSURE CHECK SPECIFICATIONS
Gear Selector
PositionActual GearPressure Taps
Underdrive
ClutchOverdrive
ClutchReverse
ClutchTorque
Converter
Clutch
Off2/4
ClutchLow/
Reverse
Clutch
Park *
PARK 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
REVERSE *
REVERSE 0-2 0-7 165-235 50-100 0-2 165-235
0 mph
NEUTRAL *
NEUTRAL 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
L#
FIRST 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
20 mph
3#
SECOND 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 115-145 0-2
30 mph
3#
DIRECT 75-95 75-95 0-2 60-90 0-2 0-2
45 mph
OD #
OVERDRIVE 0-2 75-95 0-2 60-90 75-95 0-2
30 mph
OD #
OVERDRIVE
WITH TCC0-2 75-95 0-2 0-5 75-95 0-2
50 mph
* Engine speed at 1500 rpm
# CAUTION: Both front wheels must be turning at the same speed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS
Inoperative clutches can be located using a series
of tests by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Fig. 5) (Fig. 6). The clutches may be tested by apply-
ing air pressure to their respective passages. The
valve body must be removed and Tool 6056 installed.
To make air pressure tests, proceed as follows:
NOTE: The compressed air supply must be free of
all dirt and moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi.
Remove oil pan and valve body. See Valve body
removal.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the overdrive clutch apply
passage and watch for the push/pull piston to moveforward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the reverse clutch apply pas-
sage and watch for the push/pull piston to move rear-
ward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
2/4 CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the feed hole located on the
2/4 clutch retainer. Look in the area where the 2/4
piston contacts the first separator plate and watch
carefully for the 2/4 piston to move rearward. The
piston should return to its original position after the
air pressure is removed.
21 - 122 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1889 of 2585
The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road test analysis can diagnose slip-
ping units, but the cause of the malfunction cannot
be determined. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most hydraulic transaxle problems. Before performing pressure tests, be certain that
fluid level and condition, and shift cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. Fluid must be at
operating temperature (150 to 200 degrees F.). Install an engine tachometer, raise vehicle on hoist
which allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read. Attach 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP) to port(s)
required for test(s) being conducted. Use adapter set
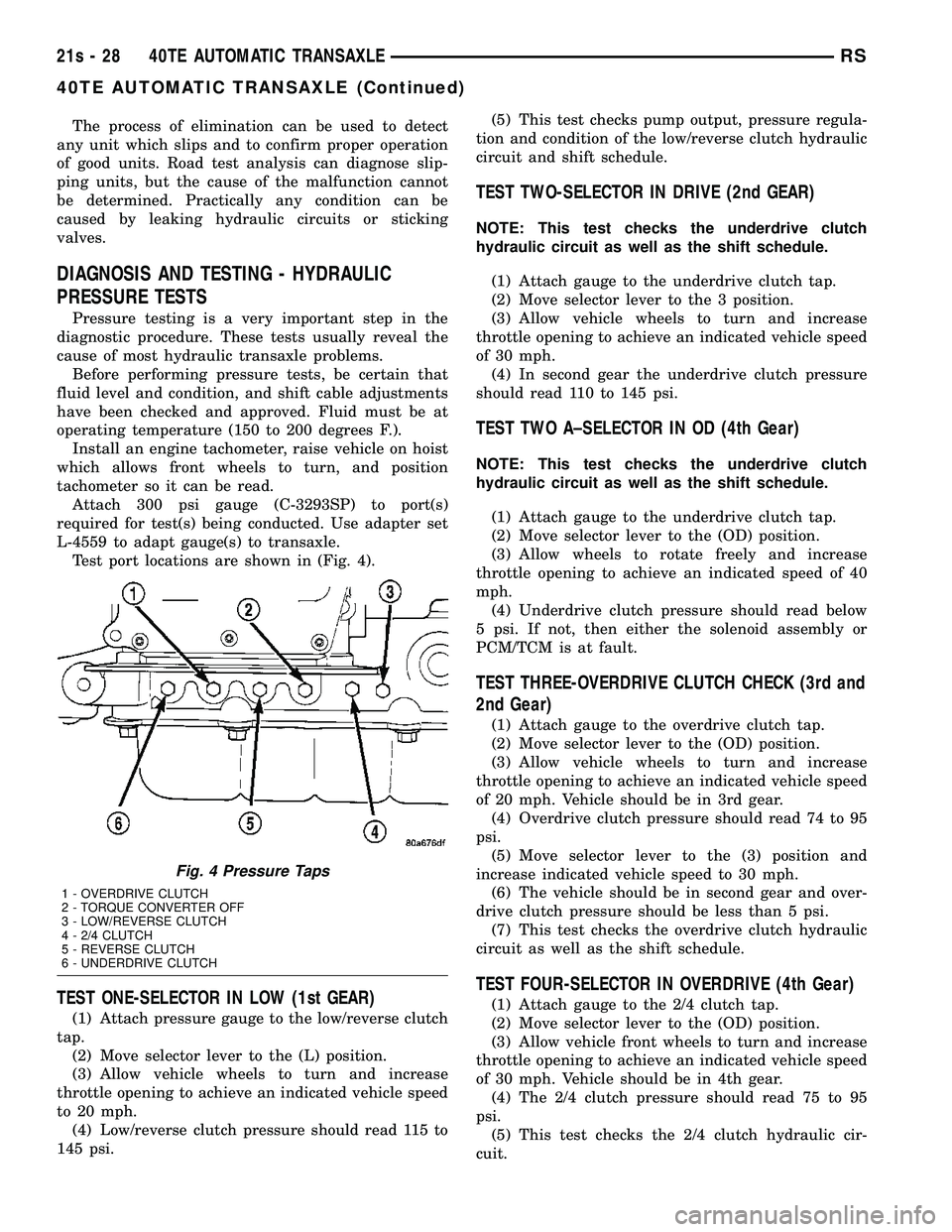
L-4559 to adapt gauge(s) to transaxle. Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 4).
TEST ONE-SELECTOR IN LOW (1st GEAR)
(1) Attach pressure gauge to the low/reverse clutch
tap. (2) Move selector lever to the (L) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
to 20 mph. (4) Low/reverse clutch pressure should read 115 to
145 psi. (5) This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion and condition of the low/reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit and shift schedule.
TEST TWO-SELECTOR IN DRIVE (2nd GEAR)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the 3 position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph. (4) In second gear the underdrive clutch pressure
should read 110 to 145 psi.
TEST TWO A±SELECTOR IN OD (4th Gear)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow wheels to rotate freely and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated speed of 40
mph. (4) Underdrive clutch pressure should read below
5 psi. If not, then either the solenoid assembly or
PCM/TCM is at fault.
TEST THREE-OVERDRIVE CLUTCH CHECK (3rd and
2nd Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the overdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 20 mph. Vehicle should be in 3rd gear. (4) Overdrive clutch pressure should read 74 to 95
psi. (5) Move selector lever to the (3) position and
increase indicated vehicle speed to 30 mph. (6) The vehicle should be in second gear and over-
drive clutch pressure should be less than 5 psi. (7) This test checks the overdrive clutch hydraulic
circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST FOUR-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the 2/4 clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle front wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear. (4) The 2/4 clutch pressure should read 75 to 95
psi. (5) This test checks the 2/4 clutch hydraulic cir-
cuit.
Fig. 4 Pressure Taps
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER OFF
3 - LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
4 - 2/4 CLUTCH
5 - REVERSE CLUTCH
6 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
21s - 28 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1890 of 2585
TEST FIVE-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear-CC
on)
(1) Attach gauge to the torque converter clutch off
pressure tap. (2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 50 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear, CC on.
CAUTION: Both wheels must turn at the same
speed.
(4) Torque converter clutch off pressure should be
less than 5 psi. (5) This test checks the torque converter clutch
hydraulic circuit.
TEST SIX-SELECTOR IN REVERSE
(1) Attach gauges to the reverse and LR clutch
tap. (2) Move selector lever to the (R) position.
(3) Read reverse clutch pressure with output sta-
tionary (foot on brake) and throttle opened to achieve
1500 rpm. (4) Reverse and LR clutch pressure should read
165 to 235 psi. (5) This test checks the reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure is found in any one test,
the pump and pressure regulator are working prop-
erly. (2) Low pressure in all positions indicates a defec-
tive pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure regu-
lator valve. (3) Clutch circuit leaks are indicated if pressures
do not fall within the specified pressure range. (4) If the overdrive clutch pressure is greater than
5 psi in Step 4 of Test Three, a worn reaction shaft
seal ring or a defective solenoid assembly is indi-
cated. (5) If the underdrive clutch pressure is greater
than 5 psi in Step 4 of Test Two A, a defective sole-
noid assembly or PCM/TCM is the cause.
PRESSURE CHECK SPECIFICATIONS
Pressure Taps
Gear
Selector
Position Actual Gear
Underdrive
Clutch Overdrive
Clutch Reverse
Clutch Torque
Converter
Clutch Off 2/4 Clutch Low/
Reverse Clutch
Park * PARK 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
REVERSE * REVERSE 0-2 0-7 165-235 50-100 0-2 165-235
0 mph
NEUTRAL * NEUTRAL 0-2 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
0 mph
L# FIRST 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 0-2 115-145
20 mph
3# SECOND 110-145 0-5 0-2 60-110 115-145 0-2
30 mph
3# DIRECT 75-95 75-95 0-2 60-90 0-2 0-2
45 mph
OD # OVERDRIVE 0-2 75-95 0-2 60-90 75-95 0-2
30 mph
OD # OVERDRIVE
WITH TCC 0-2 75-95 0-2 0-5 75-95 0-2
50 mph
* Engine speed at 1500 rpm
# CAUTION: Both front wheels must be turning at the same speed.
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s-29
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 2080 of 2585

TIRES/WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND
WHEEL VIBRATION.....................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL BALANCE......................5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING..............7
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL ROTATION.....................7
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(ALUMINUM WHEEL)....................7
REMOVAL - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(STEEL WHEEL).......................8
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - TIRE AND WHEEL
ASSEMBLY (ALUMINUM WHEEL)..........8
INSTALLATION - TIRE AND WHEEL
ASSEMBLY (STEEL WHEEL)..............8
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
SENSOR - TPM
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
CAUTION.............................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR............................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR RETRAIN....................10
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRE..................13
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES.......14DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES....14
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE
(TEMPORARY).......................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE . . . 14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE
LEAD...............................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS..........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS.........................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE INFLATION
PRESSURES.........................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE
PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION.........................17
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE LEAK
REPAIRING..........................17
CLEANING - TIRES.....................17
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL..................18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION.........................18
CLEANING - ALUMINUM WHEEL CARE......18
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL.............................19
WHEEL COVER
DESCRIPTION.........................19
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - FRONT
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - REAR
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................22
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND WHEEL
VIBRATION
Tire and wheel imbalance, runout and force varia-
tion can cause vehicles to exhibit steering wheel
vibration.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Visual inspection of the vehicle is recommended
prior to road testing or performing any other proce-
dure. Raise vehicle on a suitable hoist. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Inspect for the following:
²Verify correct (OEM) wheel and tire, as well as
correct wheel weights. Aluminum wheels require
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-1