2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER wheels
[x] Cancel search: wheelsPage 2107 of 2585

TIRE CHAINS
Refer to the owners manual supplied with the vehi-
cle to determine whether the use of tire chains is per-
mitted on this vehicle.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, ride
quality and decrease rolling resistance. Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of four
and under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. It is recommended that tires from dif-
ferent manufacturers NOT be mixed. They may be
mixed with a temporary spare tire when necessary. A
maximum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph) is recom-
mended while a temporary spare is in use. Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
WARNING: IN ORDER TO MAINTAIN THE SPEED
CAPABILITY OF THE VEHICLE, REPLACEMENT
TIRES MUST HAVE SPEED RATINGS EQUAL TO OR
HIGHER THAN THOSE FITTED TO THE VEHICLE AS
ORIGINAL EQUIPMENT. IF TIRES WITH LOWER
SPEED RATINGS ARE FITTED, THE VEHICLE'S
HANDLING MAY BE AFFECTED AND THE SPEED
CAPABILITY OF THE VEHICLE MAY BE LOWERED
TO THE MAXIMUM SPEED CAPABILITY OF THE
REPLACEMENT TIRES. TO AVOID AN ACCIDENT
RESULTING IN SEVERE OR FATAL INJURY, CON-
SULT THE TIRE MANUFACTURER IN REGARDS TO
MAXIMUM SPEED RATINGS. It is recommended that tires equivalent to the orig-
inal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed. Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehi-
cle. The original equipment tires provide a proper com-
bination of many characteristics such as: ² Ride
² Noise
² Handling
² Durability
² Tread life
² Traction
² Rolling resistance
² Speed capability
The use of tires smaller than the minimum tire
size approved for the vehicle can result in tire over-
loading and failure. Use tires that have the approved load rating for
the vehicle and never overload them. Failure to equip
the vehicle with tires having adequate speed capabil-
ity can result in sudden tire failure and loss of vehi-
cle control. The use of oversize tires may cause interference
with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspen-
sion and steering travel, interference with vehicle
components may cause tire damage.
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)
The temporary (convenience) spare tire is designed
for emergency use only. The original tire should be
repaired and reinstalled, or replaced with a new, at
the first opportunity. The temporary (convenience) spare tire should be
inflated to the pressure listed on its sidewall. Do not
exceed speeds of 80 km/h (50 mph) when the tempo-
rary spare tire is in use on the vehicle. Refer to the
Owner's Manual for more details.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE
Unusual tire noise can be associated with tire and
wheel vibration or irregular tire wear. For vibration,
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For irregular tire wear, (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS/TIRES - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE
LEAD
Use the following Vehicle Lead Diagnosis And Cor-
rection Chart to diagnose and correct a vehicle lead
or drift problem.
Fig. 1 Tire Aspect Ratio
1 - SECTIONAL WIDTH
2 - SECTIONAL HEIGHT
22s - 6 TIRESRS
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2110 of 2585
pressures may increase from 2 to 6 pounds per
square inch (psi) (14 to 41 kPa) during operation. Do
not reduce this normal pressure buildup.Improper inflation can cause:
² Uneven wear patterns
² Reduced tread life
² Reduced fuel economy
² Unsatisfactory ride
² The vehicle to drift.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES CAN
AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN FAIL
SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
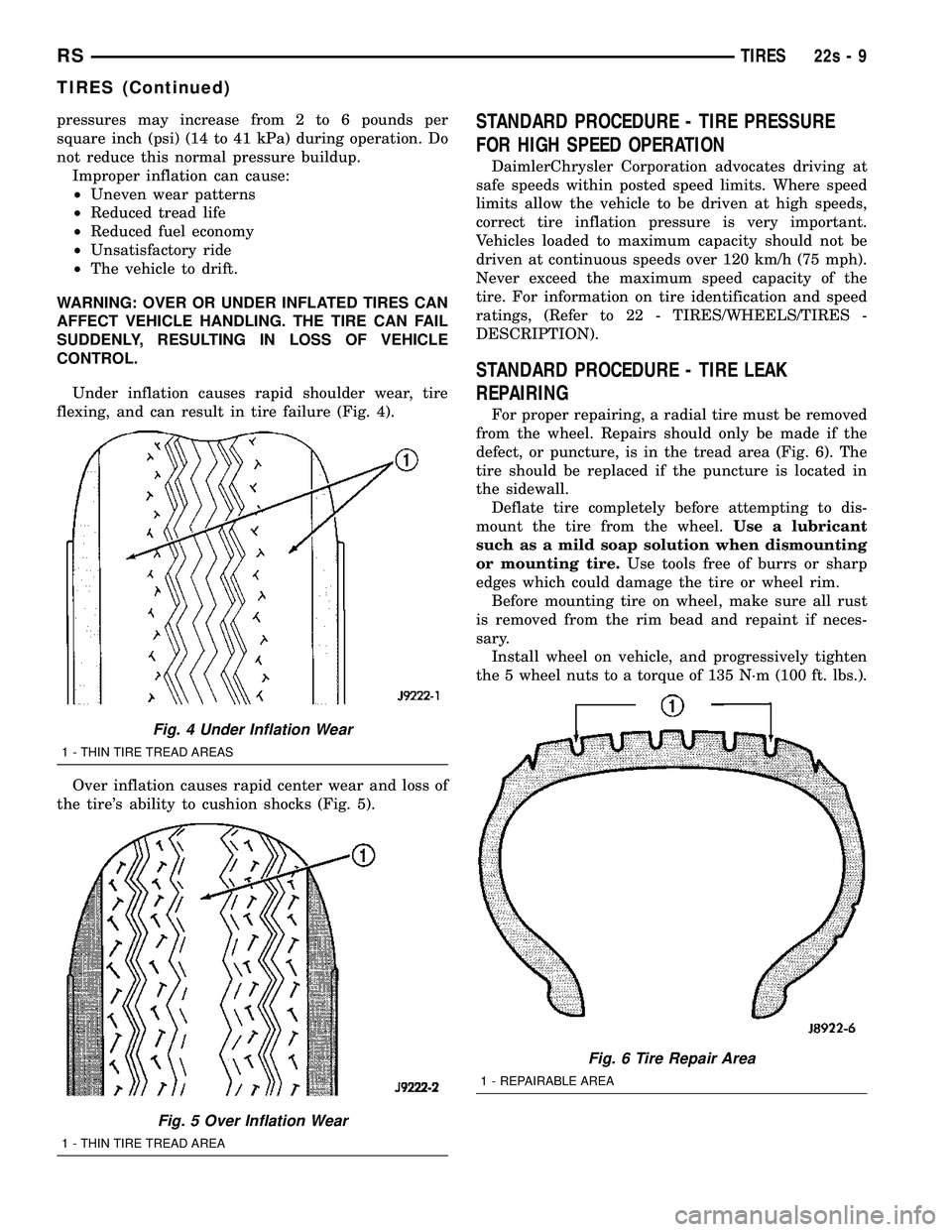
CONTROL. Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and can result in tire failure (Fig. 4).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 5).STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
FOR HIGH SPEED OPERATION
DaimlerChrysler Corporation advocates driving at
safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed
limits allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds,
correct tire inflation pressure is very important.
Vehicles loaded to maximum capacity should not be
driven at continuous speeds over 120 km/h (75 mph).
Never exceed the maximum speed capacity of the
tire. For information on tire identification and speed
ratings, (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/TIRES -
DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE LEAK
REPAIRING
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 6). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall. Deflate tire completely before attempting to dis-
mount the tire from the wheel. Use a lubricant
such as a mild soap solution when dismounting
or mounting tire. Use tools free of burrs or sharp
edges which could damage the tire or wheel rim. Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary. Install wheel on vehicle, and progressively tighten
the 5 wheel nuts to a torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 4 Under Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE TREAD AREAS
Fig. 5 Over Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE TREAD AREA
Fig. 6 Tire Repair Area
1 - REPAIRABLE AREA
RS TIRES22s-9
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2116 of 2585
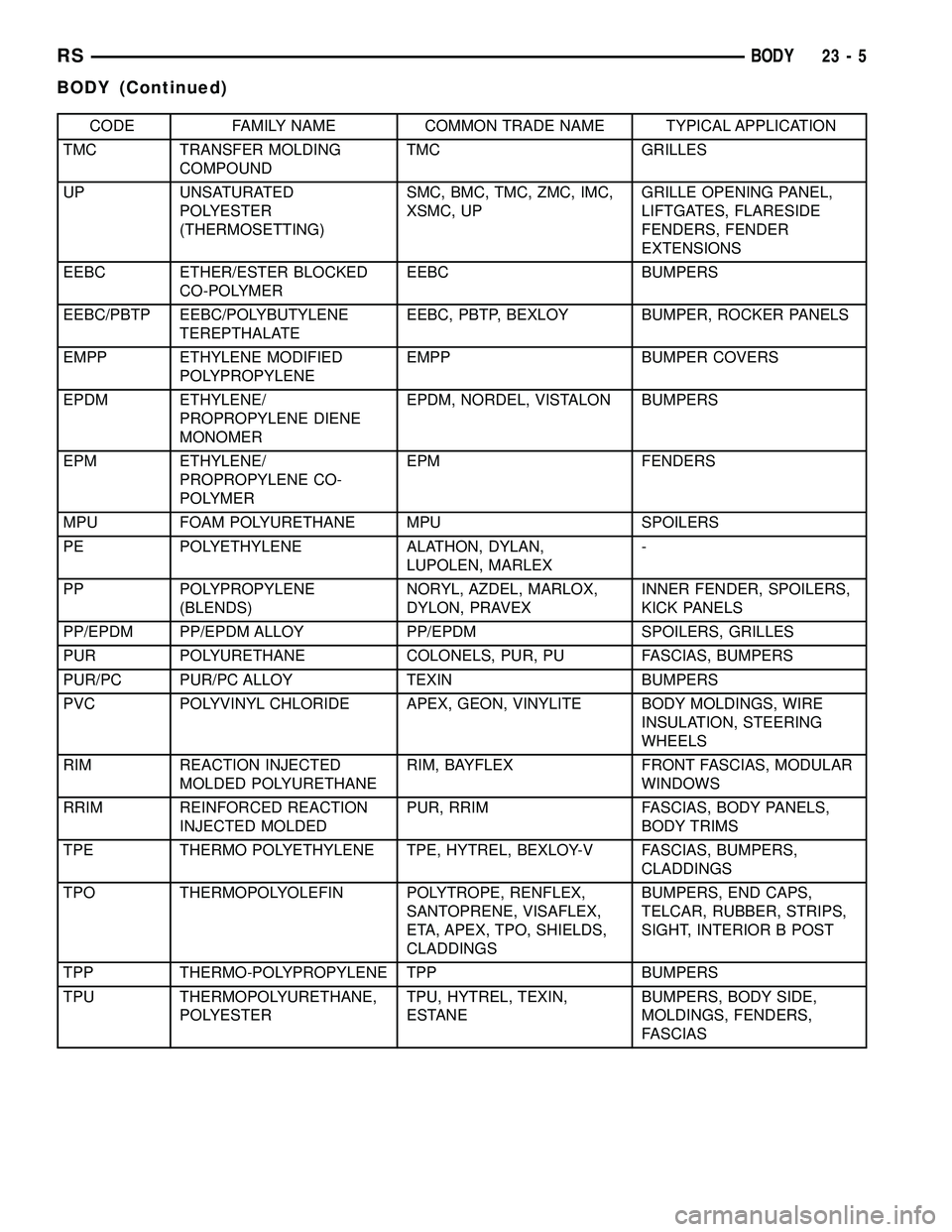
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
UP UNSATURATED
POLYESTER
(THERMOSETTING)SMC, BMC, TMC, ZMC, IMC,
XSMC, UPGRILLE OPENING PANEL,
LIFTGATES, FLARESIDE
FENDERS, FENDER
EXTENSIONS
EEBC ETHER/ESTER BLOCKED
CO-POLYMEREEBC BUMPERS
EEBC/PBTP EEBC/POLYBUTYLENE
TEREPTHALATEEEBC, PBTP, BEXLOY BUMPER, ROCKER PANELS
EMPP ETHYLENE MODIFIED
POLYPROPYLENEEMPP BUMPER COVERS
EPDM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE DIENE
MONOMEREPDM, NORDEL, VISTALON BUMPERS
EPM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE CO-
POLYMEREPM FENDERS
MPU FOAM POLYURETHANE MPU SPOILERS
PE POLYETHYLENE ALATHON, DYLAN,
LUPOLEN, MARLEX-
PP POLYPROPYLENE
(BLENDS)NORYL, AZDEL, MARLOX,
DYLON, PRAVEXINNER FENDER, SPOILERS,
KICK PANELS
PP/EPDM PP/EPDM ALLOY PP/EPDM SPOILERS, GRILLES
PUR POLYURETHANE COLONELS, PUR, PU FASCIAS, BUMPERS
PUR/PC PUR/PC ALLOY TEXIN BUMPERS
PVC POLYVINYL CHLORIDE APEX, GEON, VINYLITE BODY MOLDINGS, WIRE
INSULATION, STEERING
WHEELS
RIM REACTION INJECTED
MOLDED POLYURETHANERIM, BAYFLEX FRONT FASCIAS, MODULAR
WINDOWS
RRIM REINFORCED REACTION
INJECTED MOLDEDPUR, RRIM FASCIAS, BODY PANELS,
BODY TRIMS
TPE THERMO POLYETHYLENE TPE, HYTREL, BEXLOY-V FASCIAS, BUMPERS,
CLADDINGS
TPO THERMOPOLYOLEFIN POLYTROPE, RENFLEX,
SANTOPRENE, VISAFLEX,
ETA, APEX, TPO, SHIELDS,
CLADDINGSBUMPERS, END CAPS,
TELCAR, RUBBER, STRIPS,
SIGHT, INTERIOR B POST
TPP THERMO-POLYPROPYLENE TPP BUMPERS
TPU THERMOPOLYURETHANE,
POLYESTERTPU, HYTREL, TEXIN,
ESTANEBUMPERS, BODY SIDE,
MOLDINGS, FENDERS,
FASCIAS
RSBODY23-5
BODY (Continued)
Page 2410 of 2585
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/
COIL
DESCRIPTION
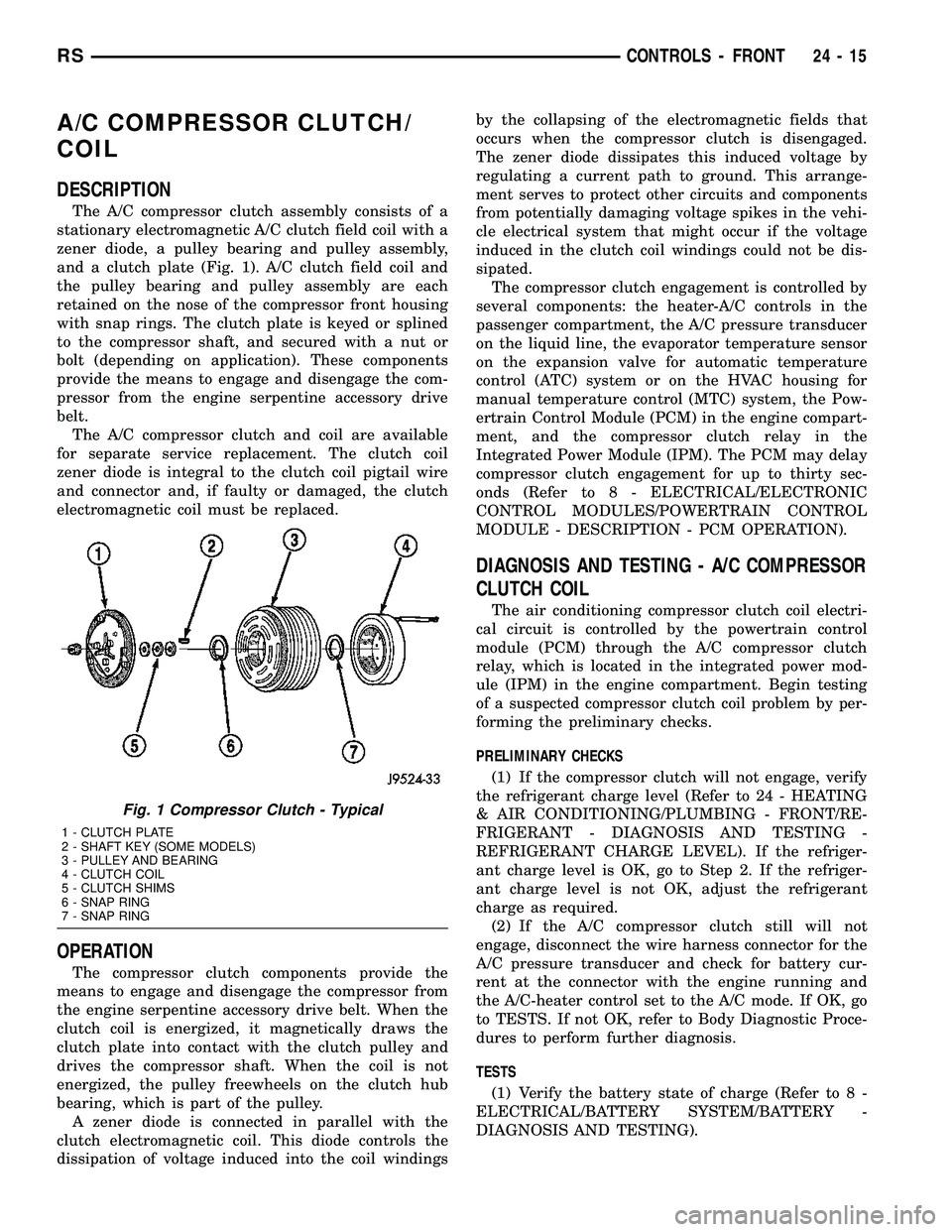
The A/C compressor clutch assembly consists of a
stationary electromagnetic A/C clutch field coil with a
zener diode, a pulley bearing and pulley assembly,
and a clutch plate (Fig. 1). A/C clutch field coil and
the pulley bearing and pulley assembly are each
retained on the nose of the compressor front housing
with snap rings. The clutch plate is keyed or splined
to the compressor shaft, and secured with a nut or
bolt (depending on application). These components
provide the means to engage and disengage the com-
pressor from the engine serpentine accessory drive
belt.
The A/C compressor clutch and coil are available
for separate service replacement. The clutch coil
zener diode is integral to the clutch coil pigtail wire
and connector and, if faulty or damaged, the clutch
electromagnetic coil must be replaced.
OPERATION
The compressor clutch components provide the
means to engage and disengage the compressor from
the engine serpentine accessory drive belt. When the
clutch coil is energized, it magnetically draws the
clutch plate into contact with the clutch pulley and
drives the compressor shaft. When the coil is not
energized, the pulley freewheels on the clutch hub
bearing, which is part of the pulley.
A zener diode is connected in parallel with the
clutch electromagnetic coil. This diode controls the
dissipation of voltage induced into the coil windingsby the collapsing of the electromagnetic fields that
occurs when the compressor clutch is disengaged.
The zener diode dissipates this induced voltage by
regulating a current path to ground. This arrange-
ment serves to protect other circuits and components
from potentially damaging voltage spikes in the vehi-
cle electrical system that might occur if the voltage
induced in the clutch coil windings could not be dis-
sipated.
The compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the heater-A/C controls in the
passenger compartment, the A/C pressure transducer
on the liquid line, the evaporator temperature sensor
on the expansion valve for automatic temperature
control (ATC) system or on the HVAC housing for
manual temperature control (MTC) system, the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) in the engine compart-
ment, and the compressor clutch relay in the
Integrated Power Module (IPM). The PCM may delay
compressor clutch engagement for up to thirty sec-
onds (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE - DESCRIPTION - PCM OPERATION).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
The air conditioning compressor clutch coil electri-
cal circuit is controlled by the powertrain control
module (PCM) through the A/C compressor clutch
relay, which is located in the integrated power mod-
ule (IPM) in the engine compartment. Begin testing
of a suspected compressor clutch coil problem by per-
forming the preliminary checks.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
(1) If the compressor clutch will not engage, verify
the refrigerant charge level (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - FRONT/RE-
FRIGERANT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
REFRIGERANT CHARGE LEVEL). If the refriger-
ant charge level is OK, go to Step 2. If the refriger-
ant charge level is not OK, adjust the refrigerant
charge as required.
(2) If the A/C compressor clutch still will not
engage, disconnect the wire harness connector for the
A/C pressure transducer and check for battery cur-
rent at the connector with the engine running and
the A/C-heater control set to the A/C mode. If OK, go
to TESTS. If not OK, refer to Body Diagnostic Proce-
dures to perform further diagnosis.
TESTS
(1) Verify the battery state of charge (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fig. 1 Compressor Clutch - Typical
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SHAFT KEY (SOME MODELS)
3 - PULLEY AND BEARING
4 - CLUTCH COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-15
Page 2532 of 2585
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV SYSTEM
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST
OR ADJUSTMENT WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
(1) With engine idling, remove the hose from the
PCV valve. If the valve is not plugged, a hissing
noise will be heard as air passes through the valve. A
strong vacuum should also be felt when a finger is
placed over the valve inlet.
(2) Install hose on PCV valve. Remove the
make-up air hose from the air plenum at the rear of
the engine. Hold a piece of stiff paper (parts tag)
loosely over the end of the make-up air hose.
(3) After allowing approximately one minute for
crankcase pressure to reduce, the paper should draw
up against the hose with noticeable force. If the
engine does not draw the paper against the grommet
after installing a new valve, replace the PCV valve
hose.
(4) Turn the engine off. Remove the PCV valve
from intake manifold. The valve should rattle when
shaken.
(5) Replace the PCV valve and retest the system if
it does not operate as described in the preceding
tests.Do not attempt to clean the old PCV valve.
If the valve rattles, apply a light coating of Loctitet
Pipe Sealant With Teflon to the threads. Thread the
PCV valve into the manifold plenum and tighten to 7
N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 10 PCV VALVE 2.4L
1 - PCV Valve
Fig. 11 PCV VALVE 3.3/3.8L
Fig. 12 Engine Off or Engine Backfire No Vapor
Flow
Fig. 13 High Intake Manifold Vacuum Minimal Vapor
Flow
Fig. 14 Moderate Intake Manifold Vacuum Maximum
Vapor Flow
RSEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS25-17
PCV VALVE (Continued)