2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock diagram
[x] Cancel search: lock diagramPage 1535 of 2585

(3) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor.
(4) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel
injectors are easily accessible (Fig. 13).
(5) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector.
(6) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is dam-
aged.
(7) Repeat for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The fuel rail must be removed first. Refer to Fuel
Injector Rail Removal in this section.
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.
(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip.
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 14).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Connect fuel injector wiring.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation.(2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into the
top slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup
will slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 13).
(3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during installa-
tion (Fig. 13).
(4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install fuel rail, refer to Fuel Rail in the Fuel
Delivery section.
(6) Connect fuel injector wiring.
(7) Install the Intake Manifold, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
OPERATION
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. A buss bar in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) supplies voltage to the solenoid side and
contact side of the relay. The fuel pump relay power
circuit contains a fuse between the buss bar in the
PDC and the relay. The fuse is located in the PDC.
Refer to the Wiring Diagrams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-
gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The idle air control valve is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control valve
(Fig. 15) or (Fig. 16).
OPERATION
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control valve to compensate for engine load,
coolant temperature or barometric pressure changes.
The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine during closed throttle idle.
The idle air control valve regulates air flow through
the bypass passage.
Fig. 14 SERVICING FUEL INJECTOR TYPICAL
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - LOCKING SLOT
3 - FUEL RAIL RECEIVER CUP
14 - 28 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1559 of 2585
(10) Install the coupling onto the intermediate
shaft and install the pinch bolt. Tighten the pinch
bolt to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Install the cable from the bracket on the col-
umn, then install the pinch side clips.
(12) Reconnect the shift cable at the lever.
(13) Reconnect the wiring harness connectors to
the clockspring, multi-function switch, halo lamp,
SKIM module, ignition switch and BTSI solenoid.
(14) Install the steering wheel (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/STEERING WHEEL -
INSTALLATION).
(15) Install the vibration damper weight.
(16) Install the steering wheel retaining nut.
Tighten the nut to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
(17) Install the airbag (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the knee blocker reinforcement (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/KNEE
BLOCKER - INSTALLATION).
(19) Install the parking brake handle link.
(20) Install the knee blocker (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN
OPENING COVER - INSTALLATION).
(21) Install the cluster trim bezel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/CLUSTER BEZEL -
INSTALLATION).
(22) Install the upper shroud (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER SHROUD - INSTAL-
LATION).
(23) Install the traction off switch.
(24) Install the lower shroud.
SPECIFICATIONS
COLUMN TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Driver Airbag Attaching Bolts 10 Ð 90
Steering Column Coupling
Pinch Bolt28 Ð 250
Steering Column Mounting
Nuts12 Ð 105
Steering Wheel Retaining
Nut61 45 Ð
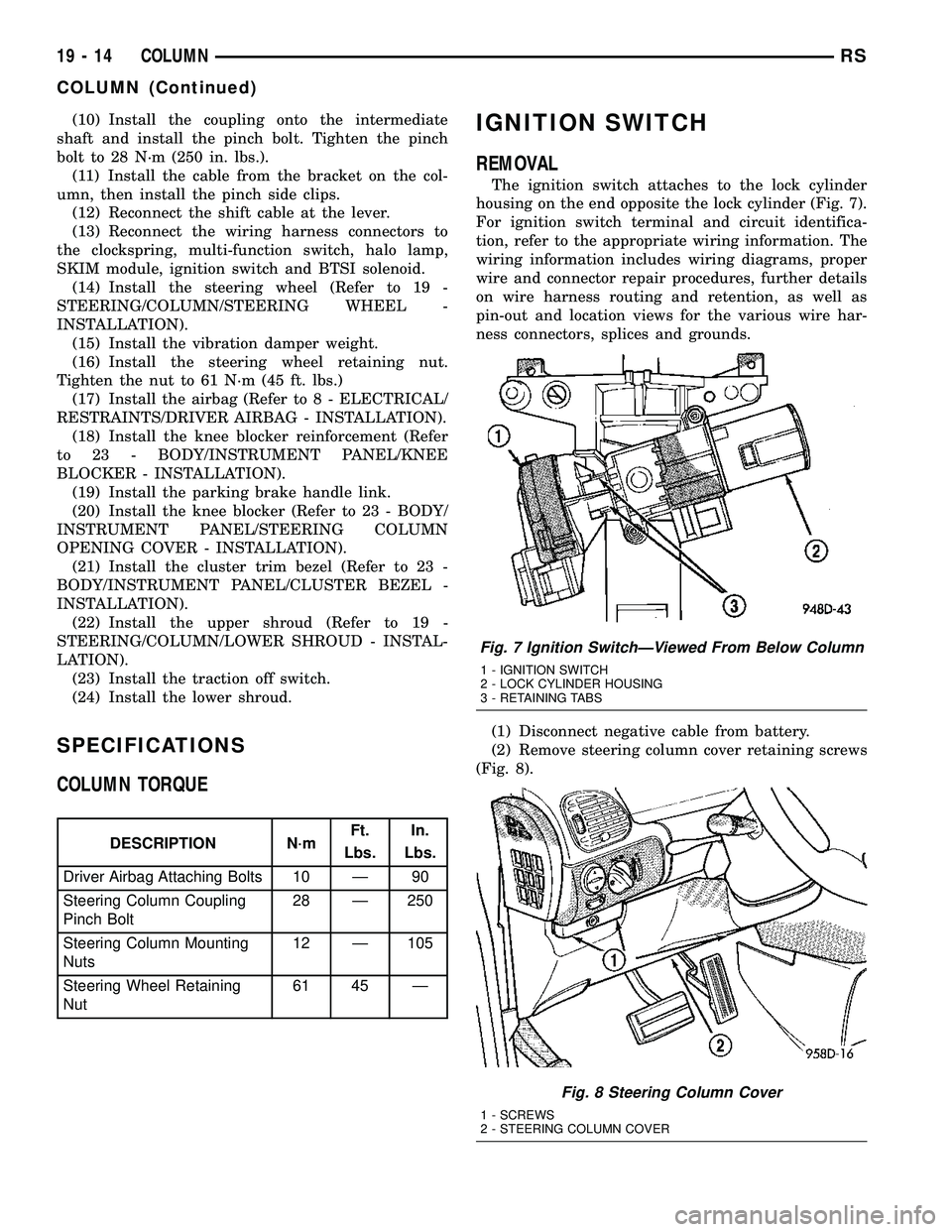
IGNITION SWITCH
REMOVAL
The ignition switch attaches to the lock cylinder
housing on the end opposite the lock cylinder (Fig. 7).
For ignition switch terminal and circuit identifica-
tion, refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove steering column cover retaining screws
(Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Ignition SwitchÐViewed From Below Column
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
3 - RETAINING TABS
Fig. 8 Steering Column Cover
1 - SCREWS
2 - STEERING COLUMN COVER
19 - 14 COLUMNRS
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1561 of 2585
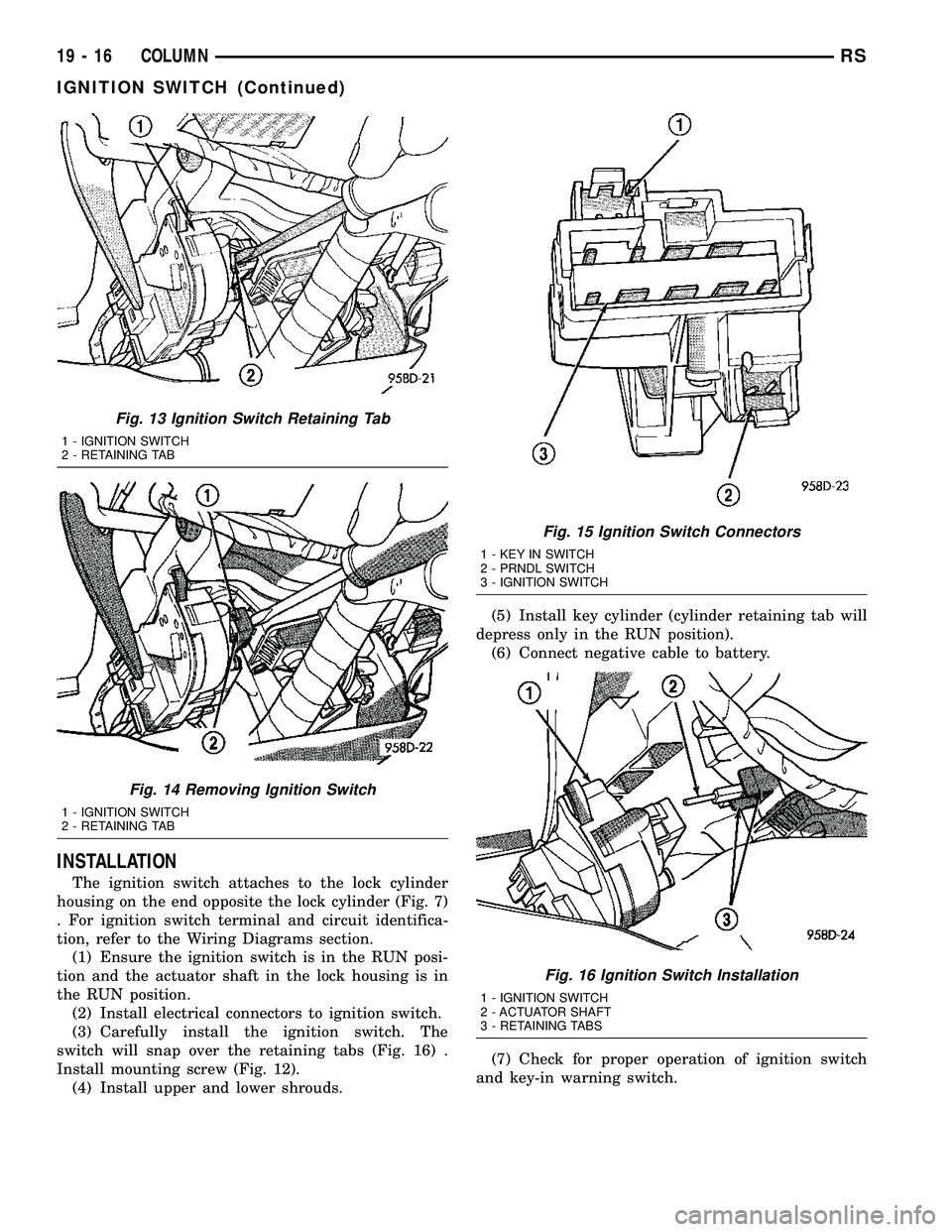
INSTALLATION
The ignition switch attaches to the lock cylinder
housing on the end opposite the lock cylinder (Fig. 7)
. For ignition switch terminal and circuit identifica-
tion, refer to the Wiring Diagrams section.
(1) Ensure the ignition switch is in the RUN posi-
tion and the actuator shaft in the lock housing is in
the RUN position.
(2) Install electrical connectors to ignition switch.
(3) Carefully install the ignition switch. The
switch will snap over the retaining tabs (Fig. 16) .
Install mounting screw (Fig. 12).
(4) Install upper and lower shrouds.(5) Install key cylinder (cylinder retaining tab will
depress only in the RUN position).
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
(7) Check for proper operation of ignition switch
and key-in warning switch.
Fig. 13 Ignition Switch Retaining Tab
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - RETAINING TAB
Fig. 14 Removing Ignition Switch
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - RETAINING TAB
Fig. 15 Ignition Switch Connectors
1 - KEY IN SWITCH
2 - PRNDL SWITCH
3 - IGNITION SWITCH
Fig. 16 Ignition Switch Installation
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - ACTUATOR SHAFT
3 - RETAINING TABS
19 - 16 COLUMNRS
IGNITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1713 of 2585

41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION........................117
OPERATION..........................119
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 41TE
TRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS......119
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST . . 119
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS...................120
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS...................122
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE . . 123
REMOVAL............................124
DISASSEMBLY........................125
ASSEMBLY...........................144
INSTALLATION........................166
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
41TE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC
SCHEMATICS.......................169
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE......181
SPECIAL TOOLS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.........183
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION........................188
OPERATION..........................189
AUTOSTICK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................189
OPERATION..........................189
DRIVING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................190
OPERATION..........................190
FINAL DRIVE
DISASSEMBLY........................190
ASSEMBLY...........................195
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
PRELOAD..........................199
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK . . . 201
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER SERVICE.....................203
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................204
INSTALLATION........................205
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT.......206HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................207
OPERATION..........................207
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY........................208
ASSEMBLY...........................216
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................230
OPERATION..........................230
DISASSEMBLY........................230
ASSEMBLY...........................232
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................232
OPERATION..........................232
SEAL - OIL PUMP
REMOVAL............................232
INSTALLATION........................233
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................233
OPERATION..........................233
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID..........................235
REMOVAL............................235
INSTALLATION........................236
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY
DESCRIPTION........................237
OPERATION..........................237
REMOVAL............................238
INSTALLATION........................239
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION........................239
OPERATION..........................240
REMOVAL............................240
INSTALLATION........................240
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION........................241
OPERATION..........................241
REMOVAL............................241
INSTALLATION........................242
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................242
OPERATION..........................245
REMOVAL............................247
INSTALLATION........................247
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................247
OPERATION..........................248
21 - 116 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1885 of 2585

40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTION .........................25
OPERATION ...........................27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTETRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS .......27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST . . . 27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS ....................28
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS ....................30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE . . . 31
REMOVAL .............................31
DISASSEMBLY .........................34
ASSEMBLY ............................51
INSTALLATION .........................73
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS 4XTE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULICSCHEMATICS ........................75
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE .......87
SPECIAL TOOLS .......................89
ACCUMULATOR DESCRIPTION .........................94
OPERATION ...........................94
DRIVING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................95
FINAL DRIVE DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................96
DISASSEMBLY .........................96
ASSEMBLY ............................99
ADJUSTMENTS DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOADMEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT ......100
FLUID STANDARD PROCEDURE FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK . . . 102
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID ANDFILTER SERVICE .....................104
GEAR SHIFT CABLE REMOVAL ............................105
HOLDING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION ........................106
OPERATION ..........................106
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY DISASSEMBLY ........................107
ASSEMBLY ...........................116 OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION ........................131
OPERATION ..........................131
DISASSEMBLY ........................131
ASSEMBLY ...........................132
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN DESCRIPTION ........................132
OPERATION ..........................132
SEAL - OIL PUMP REMOVAL ............................133
INSTALLATION ........................133
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID DESCRIPTION ........................133
OPERATION ..........................134
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/ TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID ..........................135
REMOVAL ............................135
INSTALLATION ........................136
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY DESCRIPTION ........................137
OPERATION ..........................137
REMOVAL ............................138
INSTALLATION ........................139
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT DESCRIPTION ........................140
OPERATION ..........................140
REMOVAL ............................141
INSTALLATION ........................141
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT DESCRIPTION ........................142
OPERATION ..........................142
REMOVAL ............................143
INSTALLATION ........................143
TORQUE CONVERTER DESCRIPTION ........................144
OPERATION ..........................148
REMOVAL ............................149
INSTALLATION ........................149
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................150
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................151
REMOVAL ............................151
INSTALLATION ........................152
VALVE BODY DESCRIPTION ........................152
21s - 24 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 2227 of 2585

SUNROOF
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
SUNROOF
DESCRIPTION........................116
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUNROOF.....116
DRAIN TUBE
REMOVAL............................119
INSTALLATION........................120
GLASS PANEL
REMOVAL............................120
INSTALLATION........................120
ADJUSTMENTS
SUNROOF GLASS PANEL ADJUSTMENT . . 120
SUNROOF ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL............................120
INSTALLATION........................120
SUNSHADE
REMOVAL............................120INSTALLATION........................121
WIND DEFLECTOR
REMOVAL............................121
INSTALLATION........................121
WATER CHANNEL
REMOVAL............................121
INSTALLATION........................121
SUNROOF MOTOR
REMOVAL............................121
INSTALLATION........................121
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT.......................122
SUNROOF SWITCH
REMOVAL............................123
INSTALLATION........................123
SUNROOF
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Keep fingers and other body parts out
of sunroof opening at all times.
The sun roof features consists of: (Fig. 1)
²Sun roof glass
²Sun roof sun shade
The sunroof power sliding glass panel and sun-
shade can be positioned anywhere along its travel,
rearward of glass panel front edge.
The sunroof is electrically operated from a switch
located in the overhead console. To operate the sun-
roof the ignition switch must be in the Accessory or
On/Run position. Both switchs are a rocker style
design that open or close the sunroof. When pressing
and releasing the open button once, the sunroof will
express open to the comfort stop and the wind deflec-
tor will raise. If the button is pressed a second time,
the sunroof will continue to open to full travel unless
the button is released, at which time it will stop in
that position. Pressing and holding the close button
will close the sunroof. If the close button is released
before the glass fully closes, the sunroof will stop in
that position. The vent switch operates in a similar
manor. The sunroof will also operate for up to fifteenminutes after the ignition key is turned off for cus-
tomer comfort and convenance while parking.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUNROOF
Refer to Sunroof Diagnostic Chart for possible
causes. Before beginning sunroof diagnostics verify
that all other power accessories are in proper operat-
ing condition. If not, a common electrical problem
may exist. Refer to Wiring Diagrams, in this publica-
tion for circuit, splice and component descriptions.
Check the condition of the circuit protection (20 amp
circuit breaker in the Junction Block). Inspect all
wiring connector pins for proper engagement and
continuity. Check for battery voltage at the power
sunroof controller, refer to Wiring Diagrams, for cir-
cuit information. If battery voltage of more than 10
volts is detected at the controller, proceed with the
following tests (the controller will not operate at less
than 10 volts).
Before beginning diagnosis for wind noise or water
leaks, verify that the problem was not caused by
releasing the control switch before the sunroof was
fully closed. The sunroof module has a water-man-
agement system. If however, the sunroof glass is in a
partial closed position, high pressure water may be
forced beyond the water management system bound-
aries and onto the headlining.
23 - 116 SUNROOFRS
Page 2421 of 2585

BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
A blower motor resistor is used on this model when
it is equipped with the manual heater-A/C system.
Models equipped with the optional Automatic Tem-
perature Control (ATC) system use a blower power
module, instead of the blower motor resistor block
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
CONTROLS/POWER MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
The blower motor resistor block is mounted to the
rear of the HVAC housing, directly behind the glove
box opening in the instrument panel. The resistor
block consists of a molded plastic mounting plate
with two integral connector receptacles. Concealed
behind the mounting plate are four coiled resistor
wires contained within a protective stamped steel
cage. The blower motor resistor block is accessed for
service by removing the glove box from the instru-
ment panel.
OPERATION
The blower motor resistor block is connected to the
vehicle electrical system through a dedicated take
out and connector of the instrument panel wire har-
ness. A second connector receptacle receives the pig-
tail wire connector from the blower motor. The
blower motor resistor has multiple resistor wires,
each of which will reduce the current flow through
the blower motor to change the blower motor speed.
The blower motor switch in the manual heater-A/C
system directs the ground path for the blower motor
through the correct resistor wire to obtain the
selected speed.
With the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, the ground path for the motor is applied
through all of the resistor wires. Each higher speed
selected with the blower motor switch applies the
blower motor ground path through fewer of the resis-
tor wires, increasing the blower motor speed.
The blower motor resistor cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
RESISTOR BLOCK
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, further details on wire
harness routing and retention, as well as pin-out and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the glove box from the instrument
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
GLOVE BOX - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the two wire harness connectors
from the blower motor resistor block.
(4) Check for continuity between each of the
blower motor switch input terminals of the resistor
and the resistor output terminal. In each case there
should be continuity. If OK, repair the wire harness
circuits between the blower motor switch and the
blower motor resistor, blower motor or blower motor
relay as required. If not OK, replace the faulty
blower motor resistor block.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WARNING: THE BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK MAY GET VERY HOT DURING NORMAL
OPERATION. IF THE BLOWER MOTOR WAS
TURNED ON PRIOR TO SERVICING THE BLOWER
MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK, WAIT FIVE MINUTES
TO ALLOW THE BLOWER MOTOR RESISTORS TO
COOL BEFORE PERFORMING DIAGNOSIS OR SER-
VICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THIS PRECAUTION CAN
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
24 - 26 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
Page 2433 of 2585
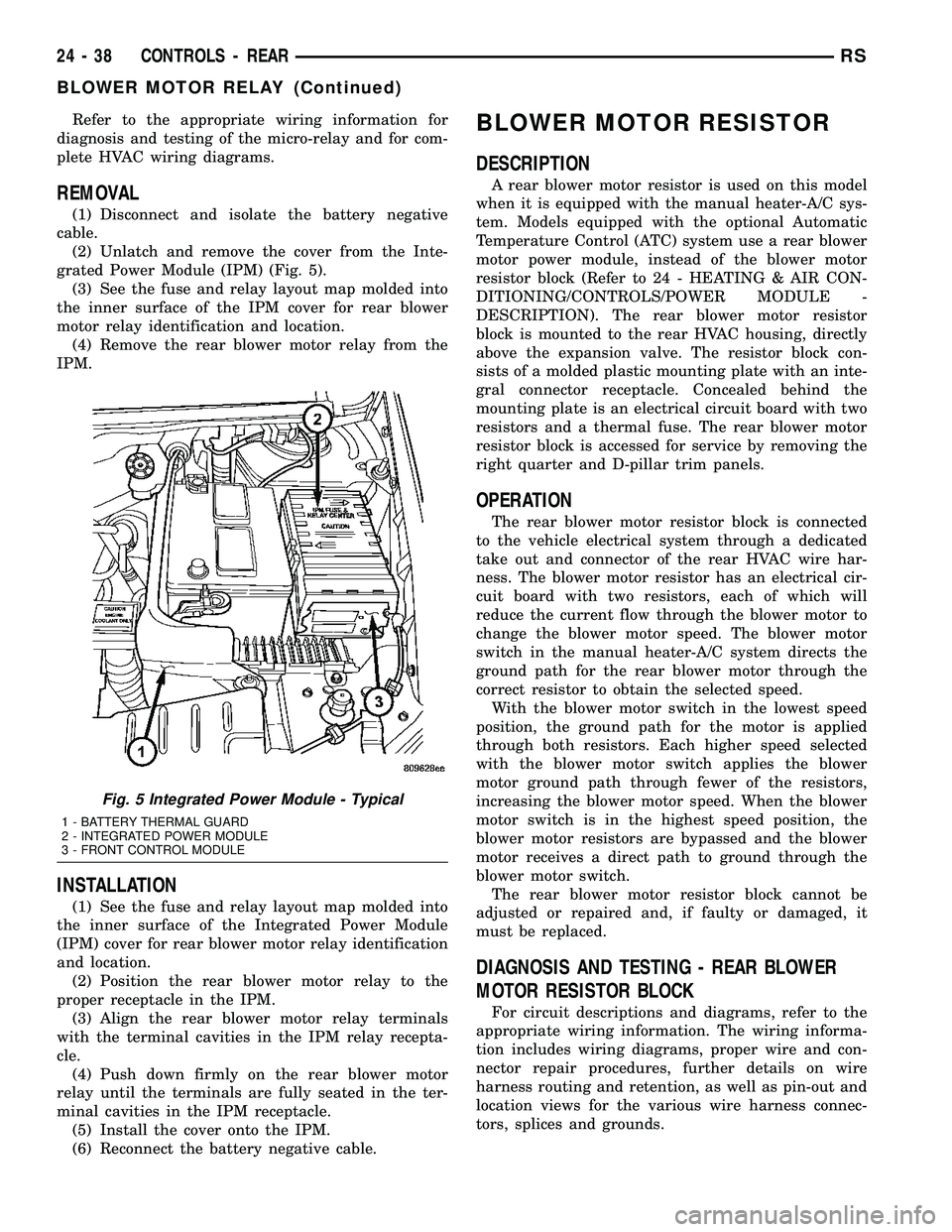
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unlatch and remove the cover from the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM) (Fig. 5).
(3) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the IPM cover for rear blower
motor relay identification and location.
(4) Remove the rear blower motor relay from the
IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the Integrated Power Module
(IPM) cover for rear blower motor relay identification
and location.
(2) Position the rear blower motor relay to the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the rear blower motor relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the IPM relay recepta-
cle.
(4) Push down firmly on the rear blower motor
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
DESCRIPTION
A rear blower motor resistor is used on this model
when it is equipped with the manual heater-A/C sys-
tem. Models equipped with the optional Automatic
Temperature Control (ATC) system use a rear blower
motor power module, instead of the blower motor
resistor block (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/CONTROLS/POWER MODULE -
DESCRIPTION). The rear blower motor resistor
block is mounted to the rear HVAC housing, directly
above the expansion valve. The resistor block con-
sists of a molded plastic mounting plate with an inte-
gral connector receptacle. Concealed behind the
mounting plate is an electrical circuit board with two
resistors and a thermal fuse. The rear blower motor
resistor block is accessed for service by removing the
right quarter and D-pillar trim panels.
OPERATION
The rear blower motor resistor block is connected
to the vehicle electrical system through a dedicated
take out and connector of the rear HVAC wire har-
ness. The blower motor resistor has an electrical cir-
cuit board with two resistors, each of which will
reduce the current flow through the blower motor to
change the blower motor speed. The blower motor
switch in the manual heater-A/C system directs the
ground path for the rear blower motor through the
correct resistor to obtain the selected speed.
With the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, the ground path for the motor is applied
through both resistors. Each higher speed selected
with the blower motor switch applies the blower
motor ground path through fewer of the resistors,
increasing the blower motor speed. When the blower
motor switch is in the highest speed position, the
blower motor resistors are bypassed and the blower
motor receives a direct path to ground through the
blower motor switch.
The rear blower motor resistor block cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it
must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR BLOWER
MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, further details on wire
harness routing and retention, as well as pin-out and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 5 Integrated Power Module - Typical
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
24 - 38 CONTROLS - REARRS
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)