2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 2398 of 2585

REAR CONTROL PANEL
The rear A/C-heater control centrally mounted in
the headliner allows intermediate seat passengers to
adjust rear air distribution, temperature and blower
motor speed when the center knob on the front A/C-
heater control is set to the Rear position. The rear
A/C-heater control contains:
²a rotary adjustment knob for temperature.
²a rotary adjustment for fan speed control.
DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC THREE ZONE
The automatic temperature control (ATC), three
zone, front and rear heating and air conditioning sys-
tem allows both the driver and front occupants and
the rear intermediate occupants to select individual
comfort temperatures.
NOTE: Individual comfort temperatures are the per-
ceived temperature level at the individual seating
areas, NOT the actual passenger compartment air
temperature.
The ATC system includes a particulate air filter.
The filter element is the same size as the air condi-
tioning evaporator to ensure ample capacity. A door
at the base of the HVAC housing below the glove box
provides easy access to the filter element.
The ATC computer utilizes integrated circuitry and
information carried on the programmable communi-
cations interface (PCI) data bus network to monitor
many sensors and switch inputs throughout the vehi-
cle. In response to those inputs, the internal circuitry
and programming of the ATC computer allow it to
control electronic functions and features of the ATC
system. The inputs to the ATC computer are:
²Vehicle Speed/Engine RPM± The ATC com-
puter monitors engine rpm, vehicle speed and mani-
fold absolute pressure information from the
powertrain control module (PCM).
²Coolant Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors coolant temperature received from the PCM and
converts it to degrees Fahrenheit.
²Ambient Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors ambient temperature from the compass mini trip
computer (CMTC) and converts it to degrees Fahren-
heit.
²Engine Miscellaneous Sensor Status±ATC
computer monitors A/C disable information from the
PCM.
²Refrigerant Pressure± ATC computer moni-
tors barometric pressure, intake air temperature,
high side pressure and methanol content as broad-
cast by the PCM.
²Door Ajar Status± The ATC computer moni-
tors driver front door, passenger front door, left rear
door, right rear door and liftgate ajar information, asidentified by the body control module (BCM), to
determine if all in-car temperatures should be main-
tained.
²Dimming± The ATC computer monitors dim-
ming status from the BCM to determine the required
level of brightness and will dim accordingly.
²Vehicle Odometer± The ATC computer moni-
tors the vehicle odometer information from the BCM
to prevent flashing the vacuum-flourescent (VF) dig-
ital display icons if the manual motor calibration or
manual cool down tests have failed. Flashing of the
display icons will cease when the vehicle odometer is
greater than 3 miles.
²English/Metric± The ATC computer monitors
the English/Metric information broadcast by the
CMTC. The set temp displays for both the front and
rear control heads will be set accordingly.
²Vehicle Identification Number± The ATC
computer monitors the last eight characters of the
VIN broadcast by the PCM and compares it to the
information stored in EEPROM. If it is different, the
new number will be stored over the old one and a
motor calibration shall be initiated.
²A/C System Information± The ATC computer
will send a message for evaporator temperature too
low, fan blower relay status, evaporator sensor fail-
ure, rear window defogger relay and A/C select.
FRONT CONTROL PANEL
The front A/C-heater control and integral computer
is mounted in the instrument panel and contains:
²a power button which allows the system to be
completely turned off. The display is blank when the
system is off.
²a rocker switch that selects a cool-down rate.
LO-AUTO or HI-AUTO are displayed when the sys-
tem is in automatic operation.
²three rocker switches that select comfort temper-
atures from 15É to 30É C (59É to 85É F), which are
shown in the VF digital display. If the set temp is 15É
C (59É F) and the down button is pressed, the set
temp value will become 13É C (55É F) but the display
will show LO. If the set temp is 29É C (85É F) and the
up button is pressed, the set temp value will become
32É C (90É F) but the display will show HIGH. Tem-
peratures can be displayed in either metric or Fahr-
enheit, which is controlled from the overhead console.
²an air conditioning button that allows the com-
pressor to be turned off. A Snowflake symbol is illu-
minated when air conditioning is on, whether under
manual or automatic control.
²an air recirculation button. A Recirculation sym-
bol appears in the display when the button is
pressed, or when the system exceeds 80 percent cir-
culated air under automatic control due to high air
conditioning demand.
RSHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24-3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2438 of 2585

DISTRIBUTION - FRONT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AIR FILTER
DESCRIPTION.........................43
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................44
AIR OUTLETS
DESCRIPTION.........................44
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CENTER BEZEL OUTLETS....44
REMOVAL - DEMISTER OUTLET..........45
REMOVAL - INSTRUMENT PANEL OUTLET . 45
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CENTER BEZEL OUTLETS . 45
INSTALLATION - DEMISTER OUTLET......46
INSTALLATION - INSTRUMENT PANEL
OUTLET............................46
BLOWER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER
MOTOR .............................47
REMOVAL.............................47INSTALLATION.........................49
DEFROSTER DUCT
REMOVAL.............................50
INSTALLATION.........................50
FLOOR DISTRIBUTION DUCTS
REMOVAL.............................50
INSTALLATION.........................50
HVAC HOUSING
REMOVAL
REMOVAL...........................51
DISSASEMBLY.......................51
INSTALLATION
ASSEMBLY..........................53
INSTALLATION.......................54
INSTRUMENT PANEL DEMISTER DUCTS
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................55
INSTRUMENT PANEL DUCTS
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................55
AIR FILTER
DESCRIPTION
A dust and odor air filter is standard equipment on
models equipped with the three zone temperature
control systems (Fig. 1). The filter element is the
same size as the front air conditioner evaporator to
ensure ample filtering capacity. A removable door on
the bottom of the front HVAC housing below the
glove box provides easy access to the filter element
for replacement. The filter should be checked and
replaced at least once every 24,000 km (15,000 miles)
and checked if heater-A/C system performance seems
lower than expected.
REMOVAL
(1) Locate the air filter door on the bottom of the
lower HVAC housing just outboard of the passenger
side of the instrument panel center stack (Fig. 2).
(2) Slide the air filter door latch toward the rear of
the vehicle until it engages the opened stop on the
door.
(3) Pull the air filter door straight downward to
disengage it from the air filter opening of the lower
HVAC housing.(4) Use your fingers to reach through the air filter
opening of the lower HVAC housing far enough to
grasp the air filter.Fig. 1 Air Filter - LHD Shown, RHD Typical
1 - LOWER HVAC HOUSING
2 - LOWER EDGE OF INSTRUMENT PANEL
3 - AIR FILTER (IF EQUIPPED)
4 - CENTER FLOOR BRACKET COVER
5 - FILTER SEALING EDGES (IF EQUIPPED)
6 - AIR FILTER OPENING (IF EQUIPPED)
RSDISTRIBUTION - FRONT24-43
Page 2439 of 2585

(5) Pull the air filter straight down and out of the
HVAC housing (Fig. 2).
INSTALLATION
(1) Note the ªAirflowº directional arrow imprinted
on the foam seal around the frame of the air filter.
This arrow should always be oriented towards the
center of the vehicle.
(2) With the air filter ªAirflowº arrow properly ori-
ented, carefully slide the filter fully upward into the
HVAC housing through the air filter opening.
(3) With the latch still positioned against its
opened stop, reinstall the air filter door onto the
lower HVAC housing air filter opening.
(4) Slide the air filter door latch toward the front
of the vehicle until it hits the closed stop on the door.
AIR OUTLETS
DESCRIPTION
Based upon the system mode selected, conditioned
air can exit the front HVAC housing through one or a
combination of the four main housing outlets: defrost,
demist, panel, or floor. Once the conditioned air exits
the unit housing, it is directed through molded plas-
tic ducts to the various outlets in the vehicle interior.
These outlets and their locations are as follows:
²Defroster Outlet- A single, centrally mounted
outlet delivers air for defrosting the large windshield.
Because outlet vanes are not needed to direct flow, a
simple, integral grid is molded into the center of the
instrument panel top cover to prevent objects from
falling into the duct. If the defroster outlet is faultyor damaged, the instrument panel top cover must be
replaced.
²Demister Outlets- There are two side window
demisters that aid in defogging and defrosting the
front door windows. One demister outlet is located at
each outboard end of the instrument panel top pad,
near the belt line at the A-pillars. The demister out-
lets can be removed from the top pad individually for
service replacement.
²Instrument Panel Outlets- There are five
panel outlets in the instrument panel, one located
near each outboard end of the instrument panel fac-
ing the rear of the vehicle, and three located near the
top of the instrument panel center bezel. On models
with manual temperature control, all five of these
outlets are fully adjustable. On models with Auto-
matic Temperature Control (ATC) system, the center
outlet in the center bezel has fixed vanes because it
also houses the remote infrared temperature sensors
for the front seat positions. The outboard outlets can
be removed individually for service replacement. The
center bezel outlets are serviced as a gang of three
outlets and, on models with ATC, also includes the
infrared sensors.
²Front Door Rear Outlets- A fully adjustable
outlet located at the rear of each front door trim
panel supplies only cooled air to the intermediate
seat passengers. Air is supplied to these outlets from
the instrument panel through ducts in the doors that
use molded seals at the instrument panel to prevent
air leakage. The door ducts are integral to the front
door trim panels. These outlets also incorporate a red
reflector to improve the safety and visibility of an
opened front door to traffic approaching the vehicle
from the rear at night. These outlets can be removed
from the door trim panels for service replacement.
²Front Floor Outlets- There are two front floor
outlets, one located above each side of the floor panel
center tunnel below the instrument panel. These out-
lets are integral to the front HVAC distribution hous-
ing.
²Rear Floor Outlets- Wide rear floor outlets
located under each front seat have integral, fixed
directional dividers to distribute heated air across
the floor for intermediate seat passengers. These out-
lets are integral to the floor distribution ducts routed
under the front floor carpet from an outlet nozzle on
the bottom of the front HVAC distribution housing.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CENTER BEZEL OUTLETS
The three outlets located near the top of the
instrument panel center bezel are serviced only as a
set of all three outlets. If the vehicle is equipped with
the optional automatic temperature control (ATC)
Fig. 2 Air Filter Door - Typical
1 - AIR FILTER DOOR
2-LATCH
3 - CLOSED STOP
4 - LOWER HVAC HOUSING
5 - OPENED STOP
24 - 44 DISTRIBUTION - FRONTRS
AIR FILTER (Continued)
Page 2469 of 2585

The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
NOISE DIAGNOSIS
Excessive noise while the air conditioning compres-
sor is operating can be caused by loose compressor
mounts, a loose compressor clutch, or high operating
pressures in the refrigerant system. Verify compres-
sor drive belt condition, proper compressor mounting,
correct refrigerant charge level, and compressor head
pressure before compressor repair is performed.
With the close tolerances within the compressor, it
is possible to experience a temporary lockup. The
longer the compressor is inactive, the more likely the
condition is to occur. This condition is the result of
normal refrigerant migration within the refrigerant
system caused by ambient temperature changes. The
refrigerant migration may wash the refrigerant oil
out of the compressor.
NOTE: Prior to a vehicle being removed from ser-
vice or stored for more than two weeks, the com-
pressor should be operated to ensure adequate
refrigerant oil distribution throughout the system
components. Turn on the air conditioner for a min-
imum of five minutes with outside air and the high-
est blower speed selected.
BELT NOISE
If the compressor drive belt slips at initial start-up,
it does not necessarily mean the compressor has
failed. The following procedure can be used to iden-
tify a compressor drive belt noise problem.
A. Start the vehicle and run at idle.
B. Turn the air conditioner On and listen for belt
squeal.
C. If belt squeal is heard, turn the air conditioner
Off immediately.
If the belt squeal stops when the air conditioner is
turned Off, perform the following repair procedures.
(1) Using an appropriate sized oil filter wrench or
a strap wrench, grasp the outer diameter of the com-
pressor clutch hub. While facing the compressor,
rotate the hub clockwise, then counterclockwise. If
the hub rotates, proceed to the next step. If the hub
will not rotate, the compressor is internally damaged,
and must be replaced.
(2) Turn the hub clockwise five complete revolu-
tions and remove the tool.
(3) Start the vehicle and run at idle.(4) Turn the air conditioner On. Observe the com-
pressor and the system for normal operation, noting
cooling performance and noise levels. Operate for five
minutes before turning the air conditioner Off. If
acceptable cooling performance is observed during
compressor operation, the compressor does not need
to be replaced.
(5) Inspect the drive belt for wear, damage, and
proper tension. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY
DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - COMPRESSOR
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING) and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY).
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the nut that secures the suction line
fitting to the top of the compressor.
(4) Disconnect the suction line fitting from the
compressor suction port.
(5) Remove the O-ring seal and gasket from the
suction line fitting and discard.
(6) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened suc-
tion line fitting and the compressor suction port.
(7) Remove the nut that secures the discharge line
fitting to the top of the compressor.
(8) Disconnect the discharge line fitting from the
compressor discharge port.
(9) Remove the O-ring seal and gasket from the
discharge line fitting and discard.
(10) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened dis-
charge line fitting and the compressor discharge port.
(11) Raise and support the vehicle.
(12) Remove the serpentine accessory drive belt
from the front of the engine (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS).
(13) Disconnect the engine wire harness connector
from the compressor clutch coil pigtail wire connector
on the top of the compressor (Fig. 5) or (Fig. 6).
(14) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines,
disengage the retainer on the engine wire harness
24 - 74 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2470 of 2585
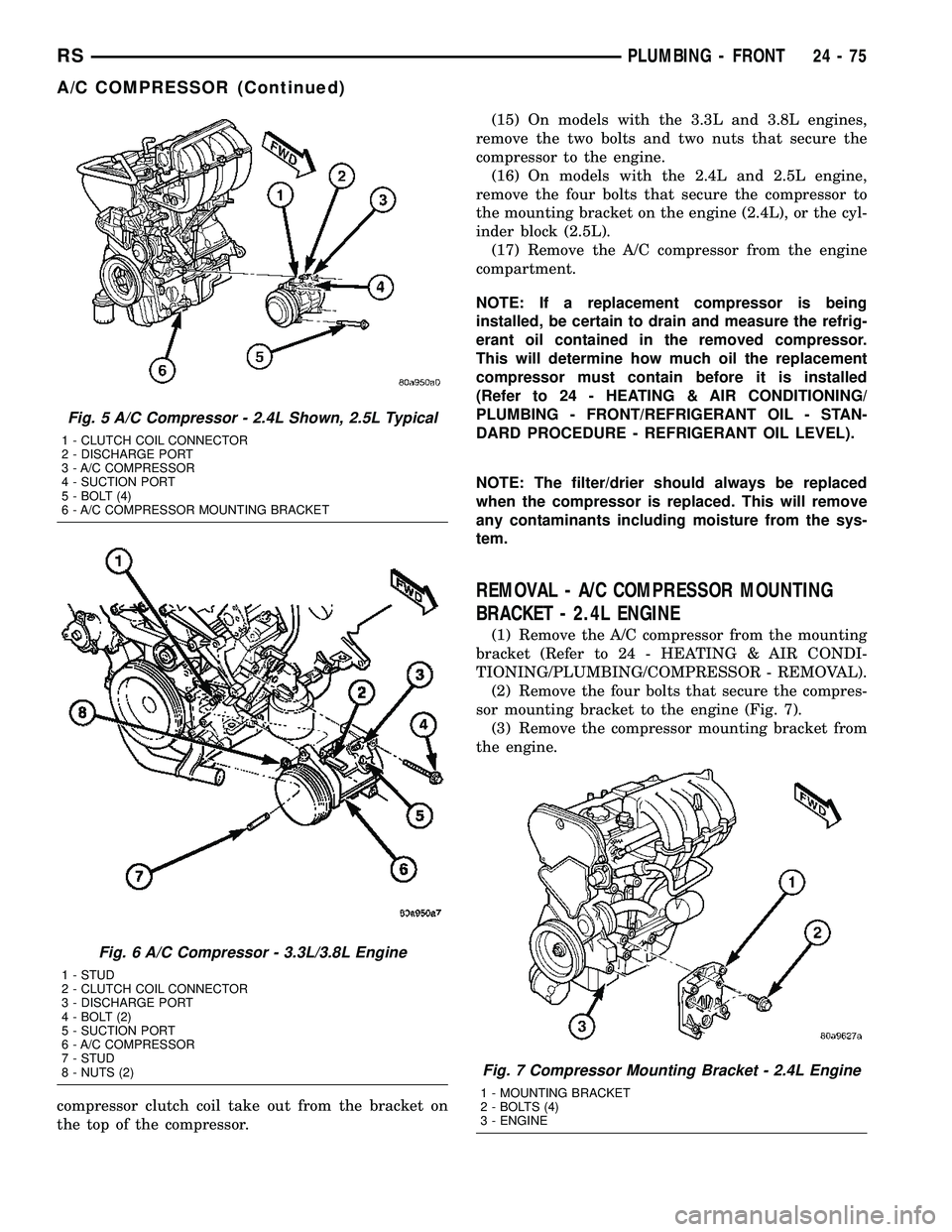
compressor clutch coil take out from the bracket on
the top of the compressor.(15) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines,
remove the two bolts and two nuts that secure the
compressor to the engine.
(16) On models with the 2.4L and 2.5L engine,
remove the four bolts that secure the compressor to
the mounting bracket on the engine (2.4L), or the cyl-
inder block (2.5L).
(17) Remove the A/C compressor from the engine
compartment.
NOTE: If a replacement compressor is being
installed, be certain to drain and measure the refrig-
erant oil contained in the removed compressor.
This will determine how much oil the replacement
compressor must contain before it is installed
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT OIL - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL).
NOTE: The filter/drier should always be replaced
when the compressor is replaced. This will remove
any contaminants including moisture from the sys-
tem.
REMOVAL - A/C COMPRESSOR MOUNTING
BRACKET - 2.4L ENGINE
(1) Remove the A/C compressor from the mounting
bracket (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the four bolts that secure the compres-
sor mounting bracket to the engine (Fig. 7).
(3) Remove the compressor mounting bracket from
the engine.
Fig. 5 A/C Compressor - 2.4L Shown, 2.5L Typical
1 - CLUTCH COIL CONNECTOR
2 - DISCHARGE PORT
3 - A/C COMPRESSOR
4 - SUCTION PORT
5 - BOLT (4)
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR MOUNTING BRACKET
Fig. 6 A/C Compressor - 3.3L/3.8L Engine
1 - STUD
2 - CLUTCH COIL CONNECTOR
3 - DISCHARGE PORT
4 - BOLT (2)
5 - SUCTION PORT
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR
7 - STUD
8 - NUTS (2)
Fig. 7 Compressor Mounting Bracket - 2.4L Engine
1 - MOUNTING BRACKET
2 - BOLTS (4)
3 - ENGINE
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-75
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2471 of 2585

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If a replacement A/C compressor is being
installed, be certain to check the refrigerant oil level
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT OIL - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL).
Use only refrigerant oil of the type recommended
for the compressor in the vehicle.
NOTE: The filter/drier should always be replaced
when the compressor is replaced. This will remove
any contaminants including moisture from the sys-
tem.
(1) Position the A/C compressor into the engine
compartment.
(2) On models with the 2.4L and 2.5L engine,
loosely install the four bolts that secure the compres-
sor to the mounting bracket on the engine (2.4L), or
the cylinder block (2.5L). Tighten the bolts to 28 N´m
(21 ft. lbs.).
(3) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines,
loosely install the two bolts and two nuts that secure
the compressor to the engine. Tighten each of the fas-
teners using the following sequence to 54 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.).
²The upper nut at the front of the compressor.
²The lower nut at the front of the compressor.
²The upper bolt at the rear of the compressor.
²The lower bolt at the rear of the compressor.
(4) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines,
engage the retainer on the engine wire harness com-
pressor clutch coil take out to the bracket on the top
of the compressor.
(5) Connect the engine wire harness connector to
the compressor clutch coil pigtail wire connector on
the top of the compressor.
(6) Reinstall the serpentine accessory drive belt
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE
BELTS).
(7) Lower the vehicle.
(8) Remove the tape or plugs from the compressor
discharge port and the discharge line fitting.
(9) Lubricate a new rubber O-ring seal with clean
refrigerant oil and install it on the discharge line fit-
ting.
(10) Install a new gasket and reconnect the dis-
charge line fitting to the compressor discharge port.
(11) Install the nut that secures the discharge line
fitting to the compressor. Tighten the nut to 23 N´m
(17 ft. lbs.).
(12) Remove the tape or plugs from the compressor
suction port and the suction line fitting.(13) Lubricate a new rubber O-ring seal with clean
refrigerant oil and install it on the suction line fit-
ting.
(14) Install a new gasket and reconnect the suc-
tion line fitting to the compressor suction port.
(15) Install the nut that secures the suction line
fitting to the compressor. Tighten the nut to 23 N´m
(17 ft. lbs.).
(16) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(17) Evacuate the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE).
(18) Charge the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE).
INSTALLATION - A/C COMPRESSOR
MOUNTING BRACKET - 2.4L ENGINE
(1) Position the compressor mounting bracket onto
the engine.
(2) Install the four bolts that secure the compres-
sor mounting bracket to the engine. Tighten the bolts
to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(3) Reinstall the A/C compressor onto the mount-
ing bracket (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/COMPRESSOR -
INSTALLATION).
A/C CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION
The A/C condenser is integral to a cooling module
which includes the radiator, the electric cooling fan,
the fan shroud, air seals and an automatic transmis-
sion oil cooler. The cooling module is located in the
air flow in the front of the engine compartment
behind the radiator grille. The A/C condenser is a
heat exchanger that allows the high-pressure refrig-
erant gas being discharged from the compressor to
give up its heat to the air passing over the condenser
fins. The A/C condenser may be removed from the
cooling module for service without removing the cool-
ing module from the vehicle.
OPERATION
When the refrigerant gas gives up its heat, it con-
denses. When the refrigerant leaves the condenser, it
has become a high-pressure liquid refrigerant. The
volume of air flowing over the condenser fins is crit-
ical to the proper cooling performance of the air con-
ditioning system. Therefore, it is important that
there are no objects placed in front of the radiator
grille openings in the front of the vehicle or foreign
24 - 76 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2486 of 2585
(21) Install a new tie strap just forward of the con-
nections between the underbody plumbing and the
engine compartment plumbing for the rear heater
and air conditioner.
(22) Lower the vehicle.
(23) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
(24) Evacuate the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE).
(25) Charge the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE).
RECEIVER / DRIER
DESCRIPTION
The receiver/drier is mounted in a bracket secured
to the right front strut tower in the engine compart-
ment. The receiver/drier is connected between the
front and rear sections of the liquid line between the
condenser outlet and the evaporator inlet. The receiv-
er/drier cannot be repaired. If the receiver/drier is
faulty or damaged, or if the refrigerant system has
been contaminated or left open to the atmosphere for
an indeterminable period or if the A/C compressor
has failed, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The receiver/drier performs a filtering action to
prevent foreign material in the refrigerant from con-
taminating the expansion valve. Desiccant inside the
receiver/drier canister absorbs any moisture which
may have entered and become trapped within the
refrigerant system. In addition, during periods of
high demand air conditioner operation, the receiver/
drier acts as a reservoir to store surplus refrigerant.
Refrigerant enters the receiver/drier as a high-pres-
sure, low temperature liquid.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING) and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY).(2) Remove the air cleaner housing from the right
side of the engine compartment.
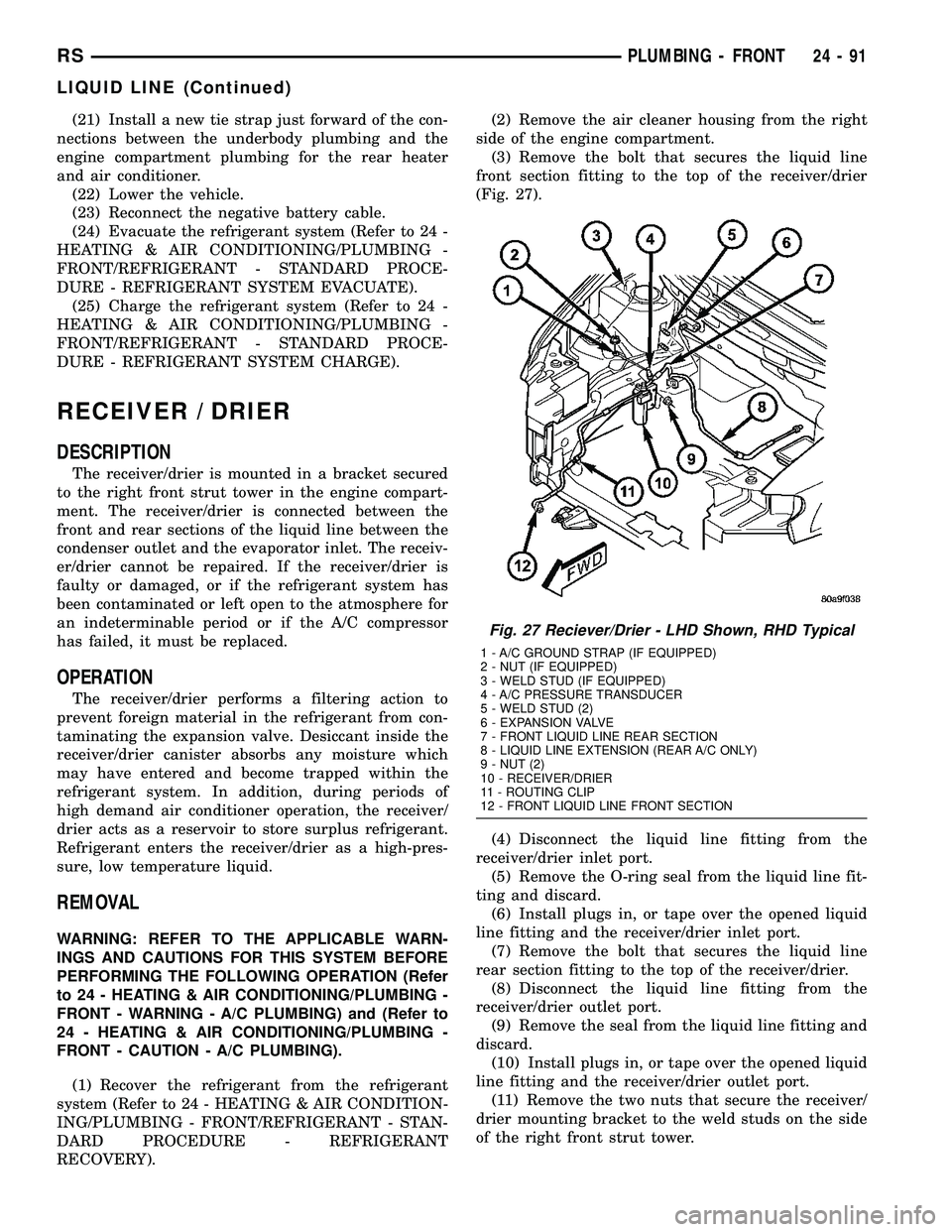
(3) Remove the bolt that secures the liquid line
front section fitting to the top of the receiver/drier
(Fig. 27).
(4) Disconnect the liquid line fitting from the
receiver/drier inlet port.
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the liquid line fit-
ting and discard.
(6) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened liquid
line fitting and the receiver/drier inlet port.
(7) Remove the bolt that secures the liquid line
rear section fitting to the top of the receiver/drier.
(8) Disconnect the liquid line fitting from the
receiver/drier outlet port.
(9) Remove the seal from the liquid line fitting and
discard.
(10) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened liquid
line fitting and the receiver/drier outlet port.
(11) Remove the two nuts that secure the receiver/
drier mounting bracket to the weld studs on the side
of the right front strut tower.
Fig. 27 Reciever/Drier - LHD Shown, RHD Typical
1 - A/C GROUND STRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - NUT (IF EQUIPPED)
3 - WELD STUD (IF EQUIPPED)
4 - A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
5 - WELD STUD (2)
6 - EXPANSION VALVE
7 - FRONT LIQUID LINE REAR SECTION
8 - LIQUID LINE EXTENSION (REAR A/C ONLY)
9 - NUT (2)
10 - RECEIVER/DRIER
11 - ROUTING CLIP
12 - FRONT LIQUID LINE FRONT SECTION
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-91
LIQUID LINE (Continued)
Page 2520 of 2585

period the switch ratio reaches a predetermined
value, a counter is incremented by one. The monitor
is enabled to run another test during that trip. When
the test fails 6 times, the counter increments to 3, a
malfunction is entered, and a Freeze Frame is stored,
the code is matured and the MIL is illuminated. If
the first test passes, no further testing is conducted
during that trip.
The MIL is extinguished after three consecutive
good trips. The good trip criteria for the catalyst
monitor is more stringent than the failure criteria. In
order to pass the test and increment one good trip,
the downstream sensor switch rate must be less than
45% of the upstream rate. The failure percentages
are 59% respectively.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met before the PCM runs the cat-
alyst monitor. Specific times for each parameter may
be different from engine to engine.
²Accumulated drive time
²Enable time
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure
²Catalyst warm-up counter
²Engine coolant temperature
²Vehicle speed
²MAP
²RPM
²Engine in closed loop
²Fuel level
Pending ConditionsÐ
²Misfire DTC
²Front Oxygen Sensor Response
²Front Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Rationality (middle check)
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Fuel System Monitor
²All TPS faults
²All MAP faults
²All ECT sensor faults
²Purge flow solenoid functionality
²Purge flow solenoid electrical
²All PCM self test faults
²All CMP and CKP sensor faults
²All injector and ignition electrical faults
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor functionality
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Brake switch (auto trans only)
²Intake air temperature
ConflictÐThe catalyst monitor does not run if any
of the following are conditions are present:
²EGR Monitor in progress (if equipped)
²Fuel system rich intrusive test in progress
²EVAP Monitor in progress²Time since start is less than 60 seconds
²Low fuel level-less than 15 %
²Low ambient air temperature
²Ethanol content learn is taking place and the
ethanol used once flag is set
SuspendÐThe Task Manager does not mature a
catalyst fault if any of the following are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Priority 1
²Oxygen Sensor Heater, Priority 1
²EGR Monitor, Priority 1 (if equipped)
²EVAP Monitor, Priority 1
²Fuel System Monitor, Priority 2
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor all circuits, systems
and conditions that could have malfunctions causing
driveability problems. However, problems with these
systems may cause the PCM to store diagnostic trou-
ble codes for other systems or components. For exam-
ple, a fuel pressure problem will not register a fault
directly, but could cause a rich/lean condition or mis-
fire. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor or misfire diagnostic trouble code.
The major non-monitored circuits are listed below
along with examples of failures modes that do not
directly cause the PCM to set a DTC, but for a sys-
tem that is monitored.
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor, fuel system, or mis-
fire diagnostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables. The misfire will however,
increase the oxygen content in the exhaust, deceiving
the PCM in to thinking the fuel system is too lean.
Also see misfire detection.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression. Low compression lowers O2
content in the exhaust. Leading to fuel system, oxy-
gen sensor, or misfire detection fault.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system. It may set a EGR (if
equipped) or Fuel system or O2S fault.
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-5
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)