2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 1317 of 2585
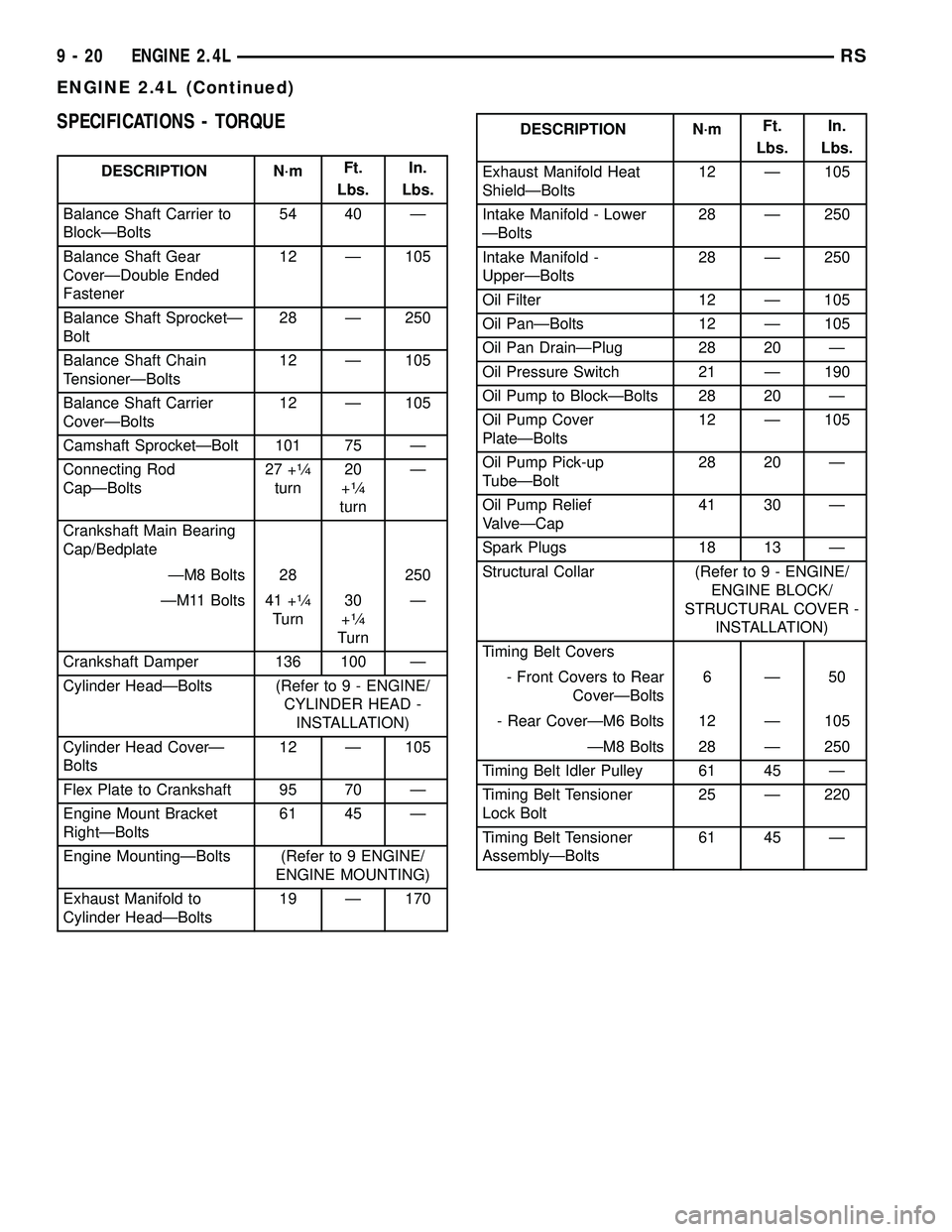
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Balance Shaft Carrier to
BlockÐBolts54 40 Ð
Balance Shaft Gear
CoverÐDouble Ended
Fastener12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft SprocketÐ
Bolt28 Ð 250
Balance Shaft Chain
TensionerÐBolts12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft Carrier
CoverÐBolts12 Ð 105
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 101 75 Ð
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts27 +
1¤4
turn20
+1¤4
turnÐ
Crankshaft Main Bearing
Cap/Bedplate
ÐM8 Bolts 28 250
ÐM11 Bolts 41 +
1¤4
Turn30
+1¤4
TurnÐ
Crankshaft Damper 136 100 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION)
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts12 Ð 105
Flex Plate to Crankshaft 95 70 Ð
Engine Mount Bracket
RightÐBolts61 45 Ð
Engine MountingÐBolts (Refer to 9 ENGINE/
ENGINE MOUNTING)
Exhaust Manifold to
Cylinder HeadÐBolts19 Ð 170
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Exhaust Manifold Heat
ShieldÐBolts12 Ð 105
Intake Manifold - Lower
ÐBolts28 Ð 250
Intake Manifold -
UpperÐBolts28 Ð 250
Oil Filter 12 Ð 105
Oil PanÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Pan DrainÐPlug 28 20 Ð
Oil Pressure Switch 21 Ð 190
Oil Pump to BlockÐBolts 28 20 Ð
Oil Pump Cover
PlateÐBolts12 Ð 105
Oil Pump Pick-up
TubeÐBolt28 20 Ð
Oil Pump Relief
ValveÐCap41 30 Ð
Spark Plugs 18 13 Ð
Structural Collar (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/
STRUCTURAL COVER -
INSTALLATION)
Timing Belt Covers
- Front Covers to Rear
CoverÐBolts6Ð50
- Rear CoverÐM6 Bolts 12 Ð 105
ÐM8 Bolts 28 Ð 250
Timing Belt Idler Pulley 61 45 Ð
Timing Belt Tensioner
Lock Bolt25 Ð 220
Timing Belt Tensioner
AssemblyÐBolts61 45 Ð
9 - 20 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1321 of 2585

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Unsnap 2 clips.
(2) Lift cover and pull toward the engine and
remove cover tabs from air box.
(3) Lift cover and remove the element (Fig. 11).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the air filter element into air box (Fig.
11).
(2) Move cover so that the tabs insert into the air
box.
(3) Push cover down and snap the 2 clips.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect the inlet air temperature sensor
(Fig. 12).
(3) Remove the inlet hose to throttle body (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the bolt for air box at upper radiator
cross member.
(5) Pull air box up and off over the single locating
pin.
(6) Remove air box from vehicle
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air box into vehicle and onto the locat-
ing pin.(2) Install bolt to hold air box to the upper radia-
tor cross member.
(3) Install the inlet hose to the throttle body.
(4) Connect the inlet air temperature sensor (Fig.
12).
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cross flow designed, aluminum cylinder head
contains dual over-head camshafts with four valves
per cylinder (Fig. 13). The valves are arranged in two
in-line banks. The intake valves face toward the
front of the vehicle. The exhaust valves face the dash
panel. The cylinder head incorporates powdered
metal valve guides and seats. The cylinder head is
sealed to the block using a multi-layer steel head
gasket and retaining bolts.
Integral oil galleries provide lubrication passages
to the hydraulic lash adjusters, camshafts, and valve
mechanisms.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
Fig. 11 AIR BOX COVER
Fig. 12 IAT SENSOR 2.4L
9 - 24 ENGINE 2.4LRS
Page 1323 of 2585
(15) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(16) Remove camshafts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Identify rocker arm position to ensure cor-
rect re-installation in original position, if reused.
(17) Remove rocker arms. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - REMOVAL)
(18) Remove cylinder head bolts in REVERSE
sequence of tightening (Fig. 19).
(19) Remove cylinder head from engine block.
(20) Inspect and clean cylinder head. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSPECTION) (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - CLEANING)
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE). Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
Clean all engine oil passages.
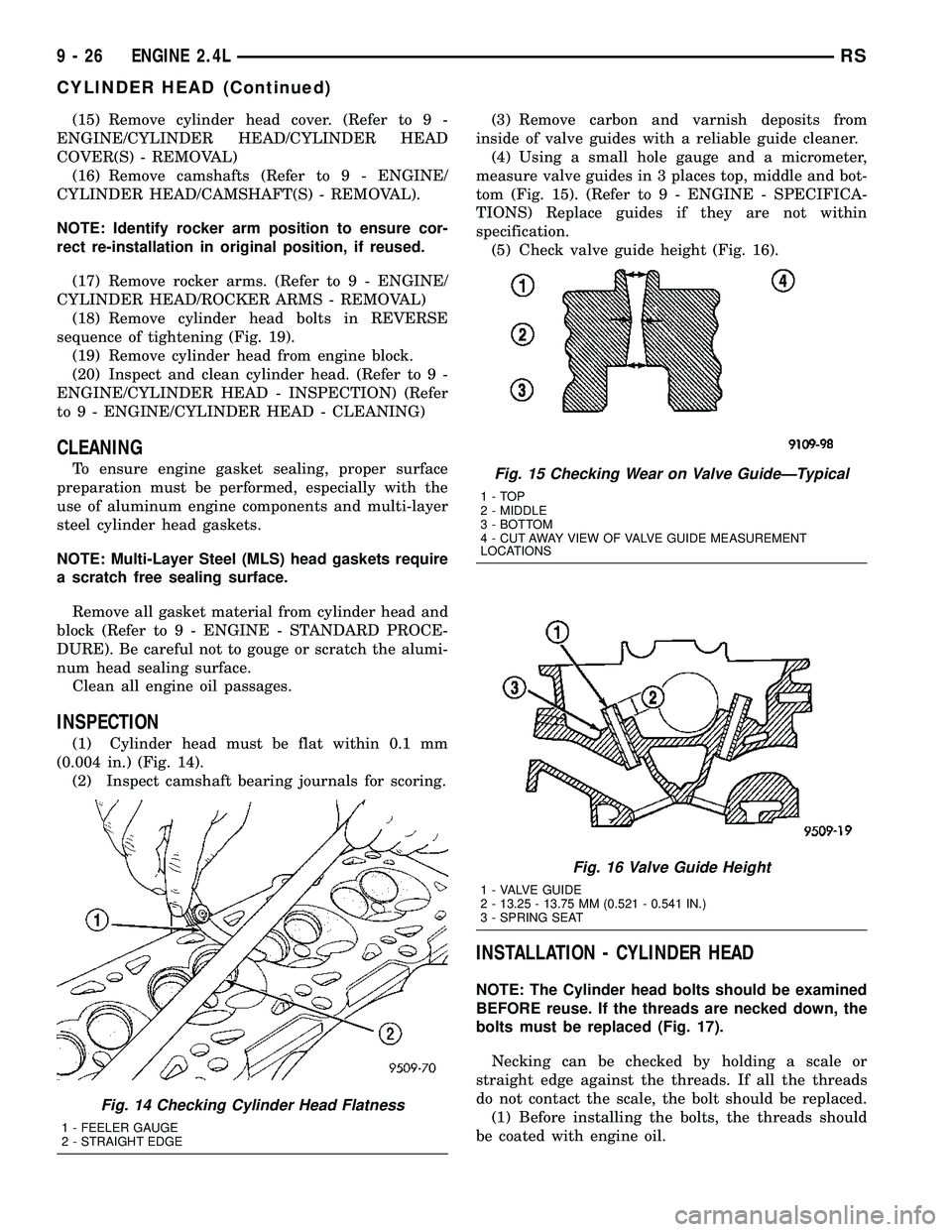
INSPECTION
(1) Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm
(0.004 in.) (Fig. 14).
(2) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for scoring.(3) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(4) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 15). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS) Replace guides if they are not within
specification.
(5) Check valve guide height (Fig. 16).
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD
NOTE: The Cylinder head bolts should be examined
BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked down, the
bolts must be replaced (Fig. 17).
Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale, the bolt should be replaced.
(1) Before installing the bolts, the threads should
be coated with engine oil.
Fig. 14 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - STRAIGHT EDGE
Fig. 15 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
1-TOP
2 - MIDDLE
3 - BOTTOM
4 - CUT AWAY VIEW OF VALVE GUIDE MEASUREMENT
LOCATIONS
Fig. 16 Valve Guide Height
1 - VALVE GUIDE
2 - 13.25 - 13.75 MM (0.521 - 0.541 IN.)
3 - SPRING SEAT
9 - 26 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1324 of 2585
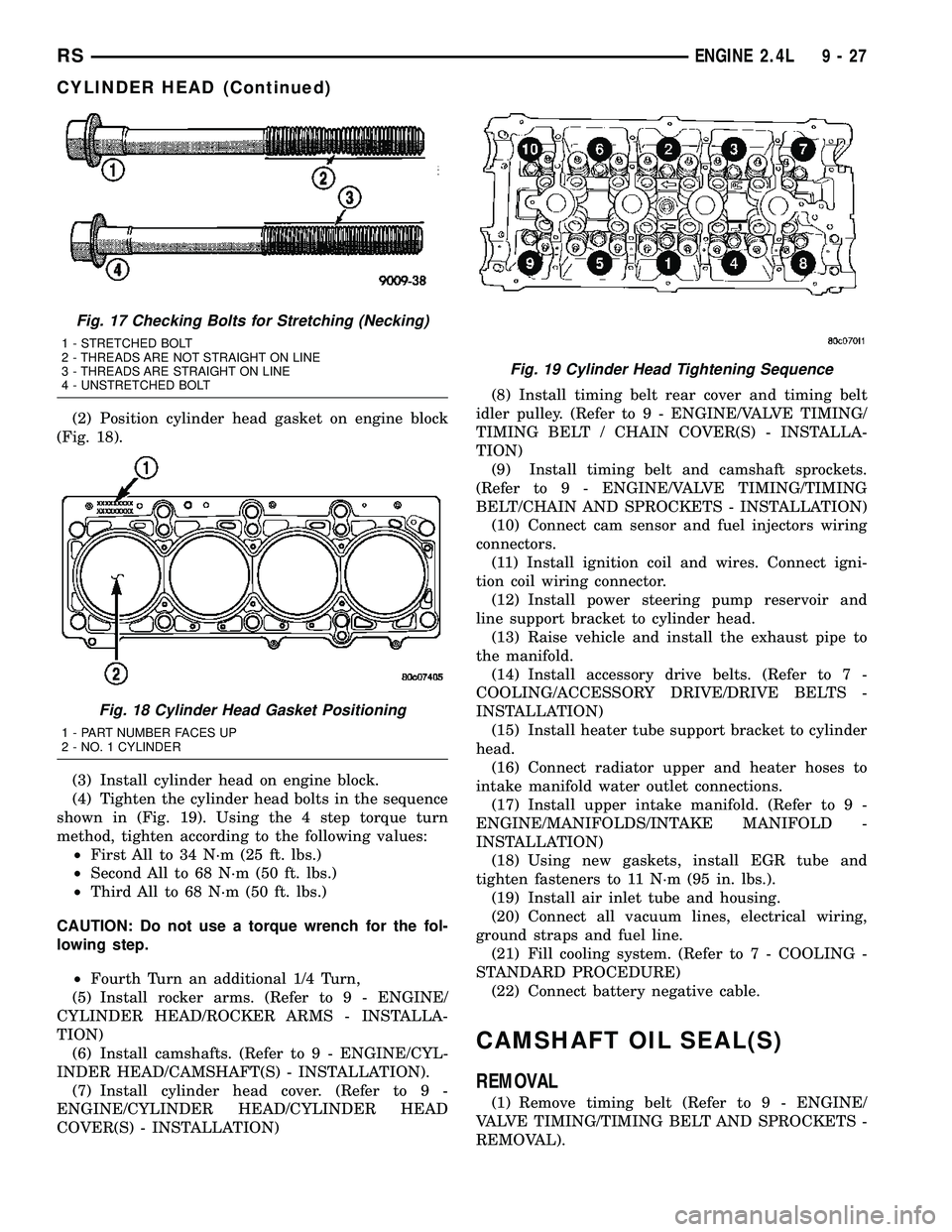
(2) Position cylinder head gasket on engine block
(Fig. 18).
(3) Install cylinder head on engine block.
(4) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in the sequence
shown in (Fig. 19). Using the 4 step torque turn
method, tighten according to the following values:
²First All to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
²Second All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
²Third All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
CAUTION: Do not use a torque wrench for the fol-
lowing step.
²Fourth Turn an additional 1/4 Turn,
(5) Install rocker arms. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - INSTALLA-
TION)
(6) Install camshafts. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)(8) Install timing belt rear cover and timing belt
idler pulley. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION)
(9) Install timing belt and camshaft sprockets.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION)
(10) Connect cam sensor and fuel injectors wiring
connectors.
(11) Install ignition coil and wires. Connect igni-
tion coil wiring connector.
(12) Install power steering pump reservoir and
line support bracket to cylinder head.
(13) Raise vehicle and install the exhaust pipe to
the manifold.
(14) Install accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION)
(15) Install heater tube support bracket to cylinder
head.
(16) Connect radiator upper and heater hoses to
intake manifold water outlet connections.
(17) Install upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(18) Using new gaskets, install EGR tube and
tighten fasteners to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.).
(19) Install air inlet tube and housing.
(20) Connect all vacuum lines, electrical wiring,
ground straps and fuel line.
(21) Fill cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(22) Connect battery negative cable.
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT AND SPROCKETS -
REMOVAL).
Fig. 17 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 18 Cylinder Head Gasket Positioning
1 - PART NUMBER FACES UP
2 - NO. 1 CYLINDER
Fig. 19 Cylinder Head Tightening Sequence
RSENGINE 2.4L9-27
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1329 of 2585
(6) If the PCV valve was removed, apply Mopart
Thread Sealant with Teflon to threads and install
valve to cylinder head cover. Tighten PCV valve to 8
N´m (70 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect PCV and make-up air hoses to cylin-
der head cover.
(8) Install upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel. They
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Viton
rubber valve stem seals are integral with the spring
seats. The valves have three-bead lock keepers to
retain springs and to promote valve rotation.
CLEANING
(1) Clean all valves thoroughly and discard
burned, warped and cracked valves.
VALVE SPRINGS & SEALS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Remove cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove camshafts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
(3) Rotate crankshaft until piston is at TDC on
compression.
(4) With air hose attached to adapter tool installed
in spark plug hole, apply 90-120 psi air pressure.(5) Using Special Tool MD-998772-A with adapter
6779 (Fig. 33), compress valve springs and remove
valve locks.
(6) Remove valve spring(s).
(7) Remove valve stem seal(s) by a using valve
stem seal tool (Fig. 35).
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) With cylinder head removed from cylinder
block, compress valve springs using a universal valve
spring compressor.
(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves, locks and
retainers to insure installation in original location.
(4) Inspect the valves. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - INSPECTION)
INSPECTION
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspec-
tion, reconditioning or replacement, valve springs
should be tested for correct tension. Discard the
springs that do not meet specifications. The following
specifications apply to both intake and exhaust
valves springs:
²Valve Closed Nominal TensionÐ76 lbs. @ 38.0
mm (1.50 in.)
²Valve Open Nominal TensionÐ136 lbs. @ 29.75
mm (1.17 in.)
(2) Inspect each valve spring for squareness with a
steel square and surface plate, test springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 inch)
out of square, install a new spring.
Fig. 32 Cylinder Head Cover Tightening Sequence
(Typical Cover Shown)
Fig. 33 Valve Spring - Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE SPRING COMPRESSOR MD 998772A
2 - AIR HOSE
9 - 32 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CYLINDER HEAD COVER (Continued)
Page 1330 of 2585
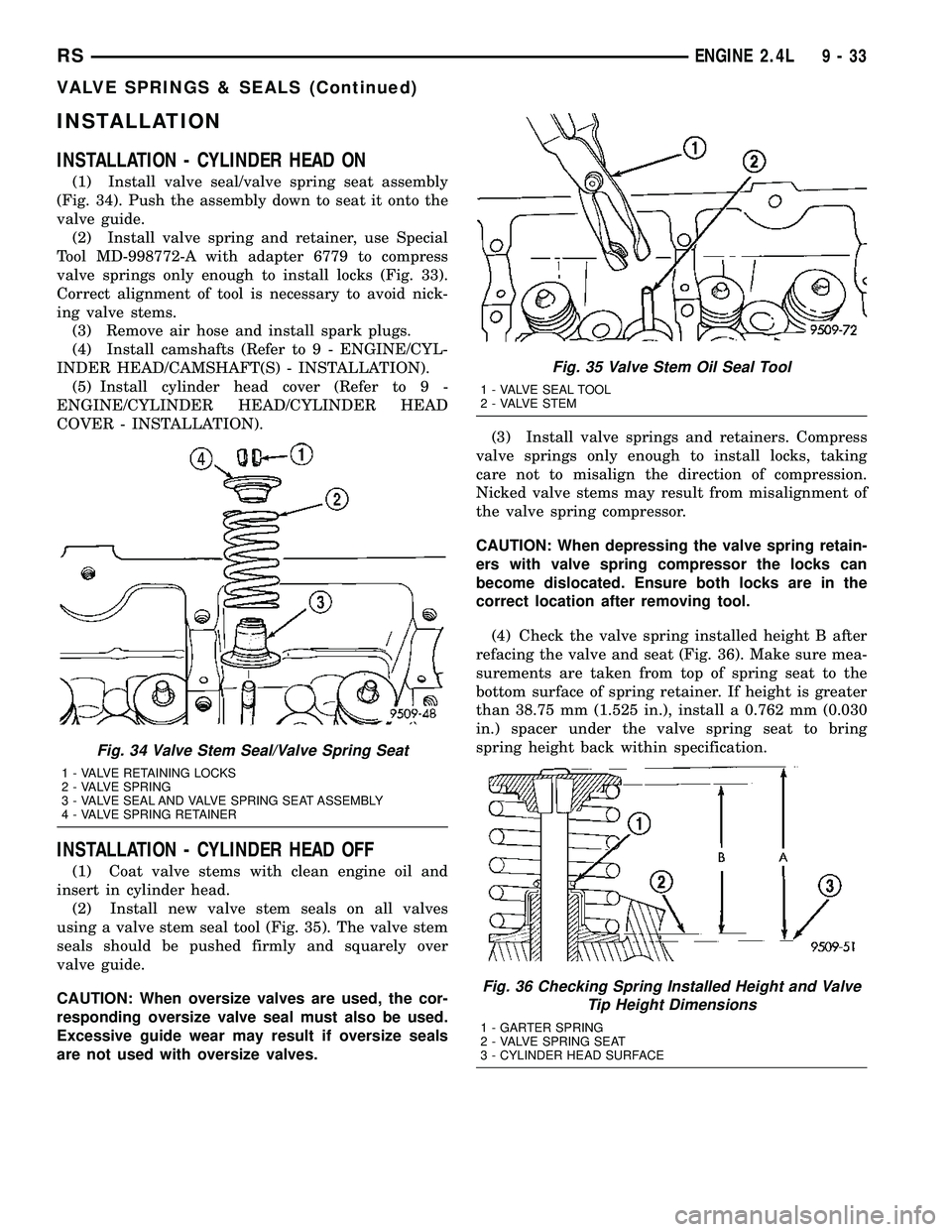
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Install valve seal/valve spring seat assembly
(Fig. 34). Push the assembly down to seat it onto the
valve guide.
(2) Install valve spring and retainer, use Special
Tool MD-998772-A with adapter 6779 to compress
valve springs only enough to install locks (Fig. 33).
Correct alignment of tool is necessary to avoid nick-
ing valve stems.
(3) Remove air hose and install spark plugs.
(4) Install camshafts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER - INSTALLATION).
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves
using a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 35). The valve stem
seals should be pushed firmly and squarely over
valve guide.
CAUTION: When oversize valves are used, the cor-
responding oversize valve seal must also be used.
Excessive guide wear may result if oversize seals
are not used with oversize valves.(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring retain-
ers with valve spring compressor the locks can
become dislocated. Ensure both locks are in the
correct location after removing tool.
(4) Check the valve spring installed height B after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 36). Make sure mea-
surements are taken from top of spring seat to the
bottom surface of spring retainer. If height is greater
than 38.75 mm (1.525 in.), install a 0.762 mm (0.030
in.) spacer under the valve spring seat to bring
spring height back within specification.
Fig. 34 Valve Stem Seal/Valve Spring Seat
1 - VALVE RETAINING LOCKS
2 - VALVE SPRING
3 - VALVE SEAL AND VALVE SPRING SEAT ASSEMBLY
4 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER
Fig. 35 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
1 - VALVE SEAL TOOL
2 - VALVE STEM
Fig. 36 Checking Spring Installed Height and Valve
Tip Height Dimensions
1 - GARTER SPRING
2 - VALVE SPRING SEAT
3 - CYLINDER HEAD SURFACE
RSENGINE 2.4L9-33
VALVE SPRINGS & SEALS (Continued)
Page 1332 of 2585
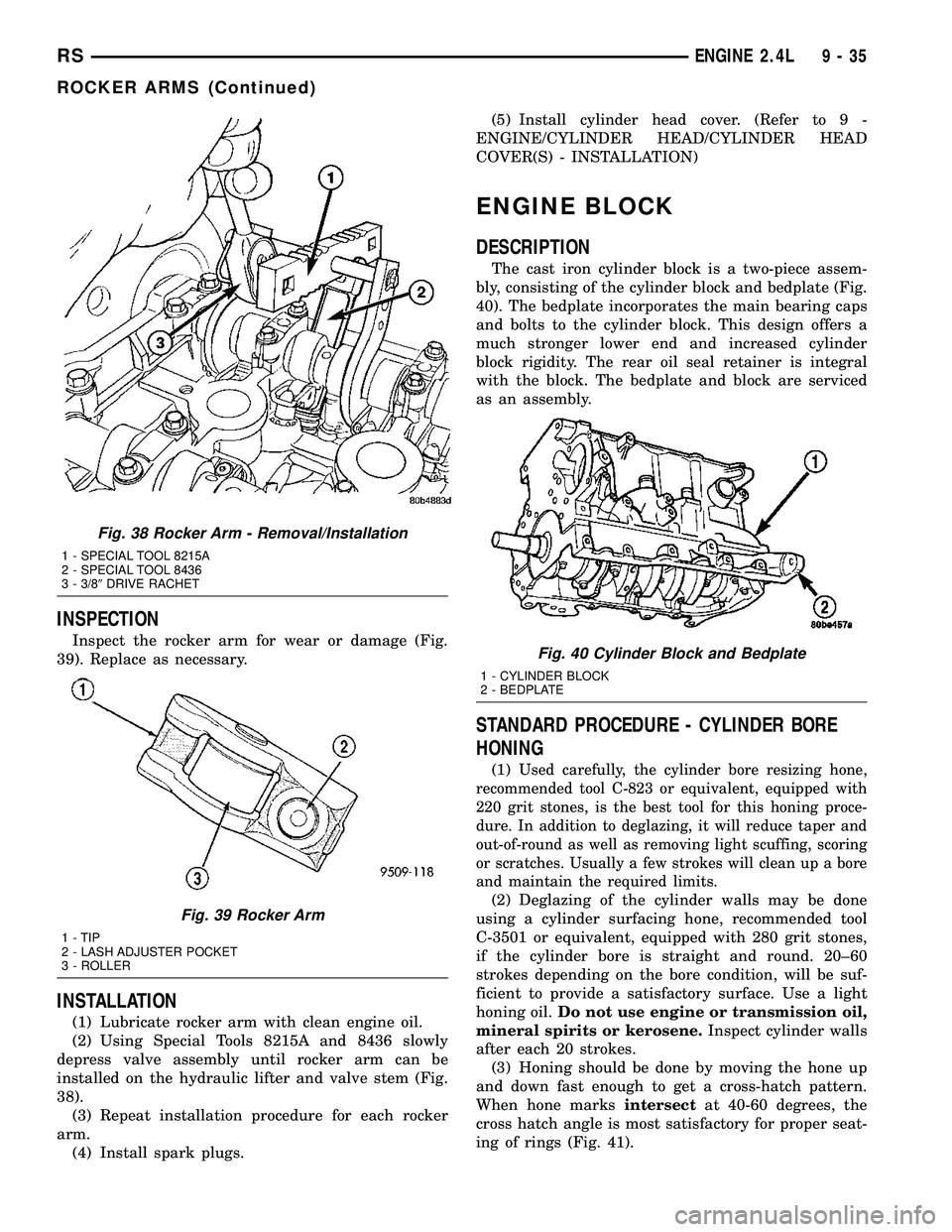
INSPECTION
Inspect the rocker arm for wear or damage (Fig.
39). Replace as necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate rocker arm with clean engine oil.
(2) Using Special Tools 8215A and 8436 slowly
depress valve assembly until rocker arm can be
installed on the hydraulic lifter and valve stem (Fig.
38).
(3) Repeat installation procedure for each rocker
arm.
(4) Install spark plugs.(5) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The cast iron cylinder block is a two-piece assem-
bly, consisting of the cylinder block and bedplate (Fig.
40). The bedplate incorporates the main bearing caps
and bolts to the cylinder block. This design offers a
much stronger lower end and increased cylinder
block rigidity. The rear oil seal retainer is integral
with the block. The bedplate and block are serviced
as an assembly.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
(1)Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone,
recommended tool C-823 or equivalent, equipped with
220 grit stones, is the best tool for this honing proce-
dure. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce taper and
out-of-round as well as removing light scuffing, scoring
or scratches. Usually a few strokes will clean up a bore
and maintain the required limits.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, recommended tool
C-3501 or equivalent, equipped with 280 grit stones,
if the cylinder bore is straight and round. 20±60
strokes depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Use a light
honing oil.Do not use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.Inspect cylinder walls
after each 20 strokes.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 40-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 41).
Fig. 38 Rocker Arm - Removal/Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8215A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8436
3 - 3/89DRIVE RACHET
Fig. 39 Rocker Arm
1 - TIP
2 - LASH ADJUSTER POCKET
3 - ROLLER
Fig. 40 Cylinder Block and Bedplate
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - BEDPLATE
RSENGINE 2.4L9-35
ROCKER ARMS (Continued)
Page 1333 of 2585
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly using a suitable
cleaning solvent.
INSPECTION
ENGINE BLOCK
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
(2) If new core plugs are to be installed, (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
CORE AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS).
(3) Examine block and cylinder bores for cracks or
fractures.(4) Check block deck surfaces for flatness. Deck
surface must be within service limit of 0.1 mm (0.004
in.).
CYLINDER BORE
NOTE: The cylinder bores should be measured at
normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C119 or equivalent (Fig.
42) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). If
the cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the
cylinder block should be replaced, and new pistons
and rings fitted.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 42). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 in.) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 in.) up from bottom of bore.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
CRANKSHAFT
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT END
PLAY
(1) Using Dial Indicator C-3339 and Mounting
Post L-4438, attach to front of engine, locating probe
perpendicular on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 43).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
Fig. 41 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
1 - CROSS-HATCH PATTERN
2 - 40ɱ60É
Fig. 42 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
9 - 36 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)