2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 1531 of 2585
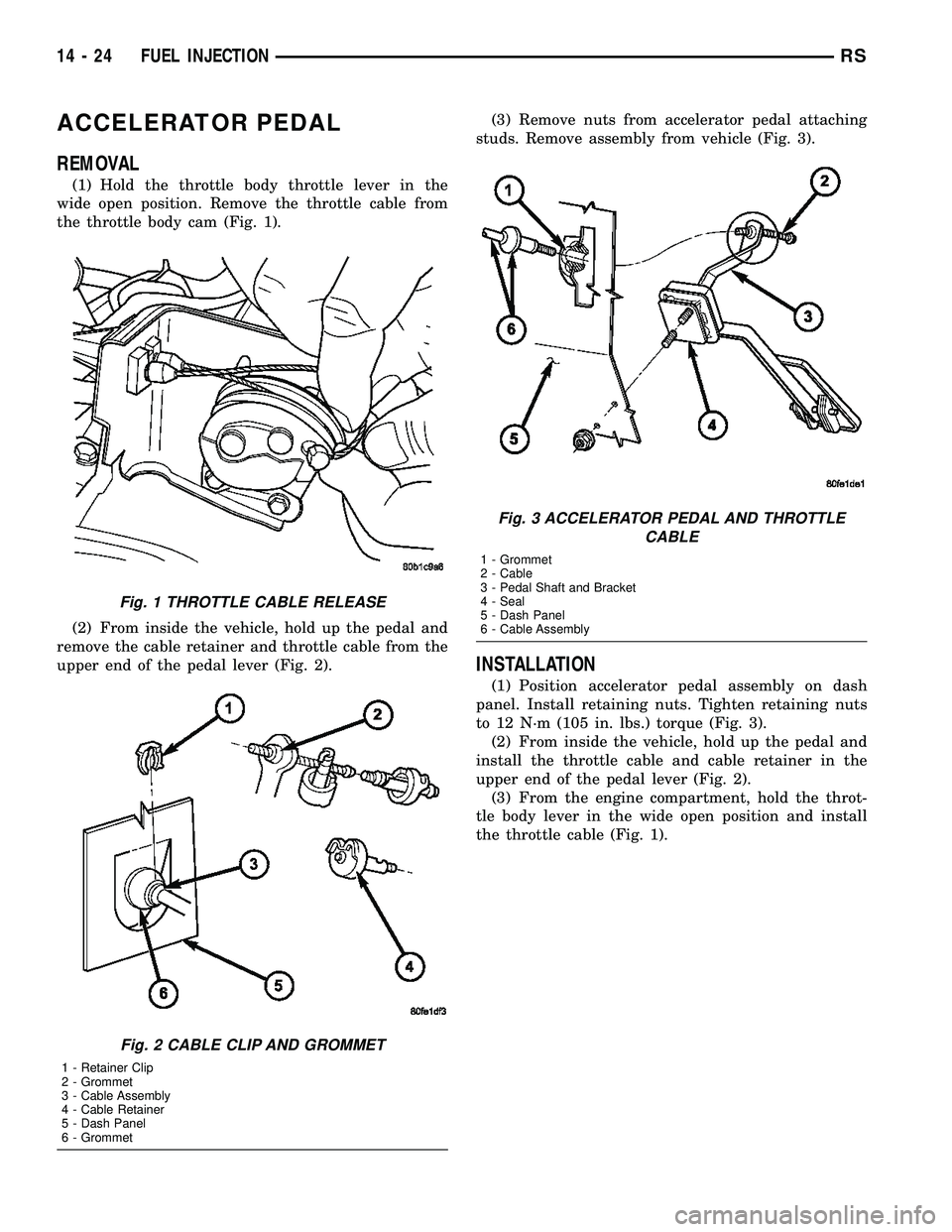
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL
(1) Hold the throttle body throttle lever in the
wide open position. Remove the throttle cable from
the throttle body cam (Fig. 1).
(2) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
remove the cable retainer and throttle cable from the
upper end of the pedal lever (Fig. 2).(3) Remove nuts from accelerator pedal attaching
studs. Remove assembly from vehicle (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position accelerator pedal assembly on dash
panel. Install retaining nuts. Tighten retaining nuts
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 3).
(2) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
install the throttle cable and cable retainer in the
upper end of the pedal lever (Fig. 2).
(3) From the engine compartment, hold the throt-
tle body lever in the wide open position and install
the throttle cable (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 THROTTLE CABLE RELEASE
Fig. 2 CABLE CLIP AND GROMMET
1 - Retainer Clip
2 - Grommet
3 - Cable Assembly
4 - Cable Retainer
5 - Dash Panel
6 - Grommet
Fig. 3 ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE
CABLE
1 - Grommet
2 - Cable
3 - Pedal Shaft and Bracket
4 - Seal
5 - Dash Panel
6 - Cable Assembly
14 - 24 FUEL INJECTIONRS
Page 1533 of 2585

INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install the crankshaft sensor.
(2) Install crankshaft sensor bolt and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector (Fig. 8).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The PCM receives a signal from the TCM to indi-
cate vehicle speed on automatic transmission cars.
On 4 cylinder Manual transmission cars (if equipped)
vehicle, a dedicated vehicle speed sensor is connectedto the PCM.On V-6 Manual transmission cars (if
equipped) vehicle, the ABS module provides the sig-
nal to the PCM for vehicle speed.
OPERATION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) supplies
the road speed and distance traveled inputs to the
PCM. From these inputs and the throttle position
sensor input, the PCM determines when a decelera-
tion condition occurs.
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
or cylinder head with the nozzle ends directly above
the intake valve port (Fig. 10).
OPERATION
The fuel injectors are 12 volt electrical solenoids
(Fig. 11). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone or two streams. The spraying action
atomizes the fuel, adding it to the air entering the
combustion chamber. Fuel injectors are not inter-
changeable between engines.
The PCM provides battery voltage to each injector
through the ASD relay. Injector operation is con-
trolled by a ground path provided for each injector by
the PCM. Injector on-time (pulse-width) is variable,
Fig. 7 Timing Slots
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER DRIVE PLATE
2 - SLOTS
Fig. 8 CRANKSHAFT SENSOR 2.4L
Fig. 9 CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR LOCATION
2.4L
14 - 26 FUEL INJECTIONRS
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1537 of 2585
the O-RINGS ONLY (Fig. 18)to aid assembly. Use
care when removing hoses to prevent damage to hose
or hose nipple.
(1) Carefully place idle air control motor into
throttle body.
(2) Install mounting screw. Tighten screw to 7 N´m
(62 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to idle air control
motor.
(4) Connect negative cable to battery.
INLET AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The IAT Sensor is a Negative Temperature Coeffi-
cient (NTC) Sensor that provides information to the
PCM regarding the temperature of the air entering
the intake manifold (Fig. 19).
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The MAP sensor (Fig. 20) or (Fig. 21) mounts to
the intake manifold. The sensor is connects electri-
cally to the PCM.
OPERATION
The MAP serves as a PCM input, using a silicon
based sensing unit, to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When MAP equals Barometric pressure, the pulse
width will be at maximum.
Also like the cam and crank sensors, a 5 volt ref-
erence is supplied from the PCM and returns a volt-age signal to the PCM that reflects manifold
pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V and full
scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of0Ð15psithe
voltage changes 4.0V. The sensor is supplied a regu-
lated 4.8 to 5.1 volts to operate the sensor. Like the
cam and crank sensors ground is provided through
the sensor return circuit.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to pulse width. The most important function of
the MAP sensor is to determine barometric pressure.
The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is at sea level
or is it in Denver at 5000 feet above sea level,
because the air density changes with altitude. It will
also help to correct for varying weather conditions. If
a hurricane was coming through the pressure would
be very, very low or there could be a real fair
Fig. 18 O-RINGS
1 - O-rings
Fig. 19 3.3/3.8L IAT SENSOR
Fig. 20 MAP SENSOR - 2.4L
14 - 30 FUEL INJECTIONRS
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1542 of 2585
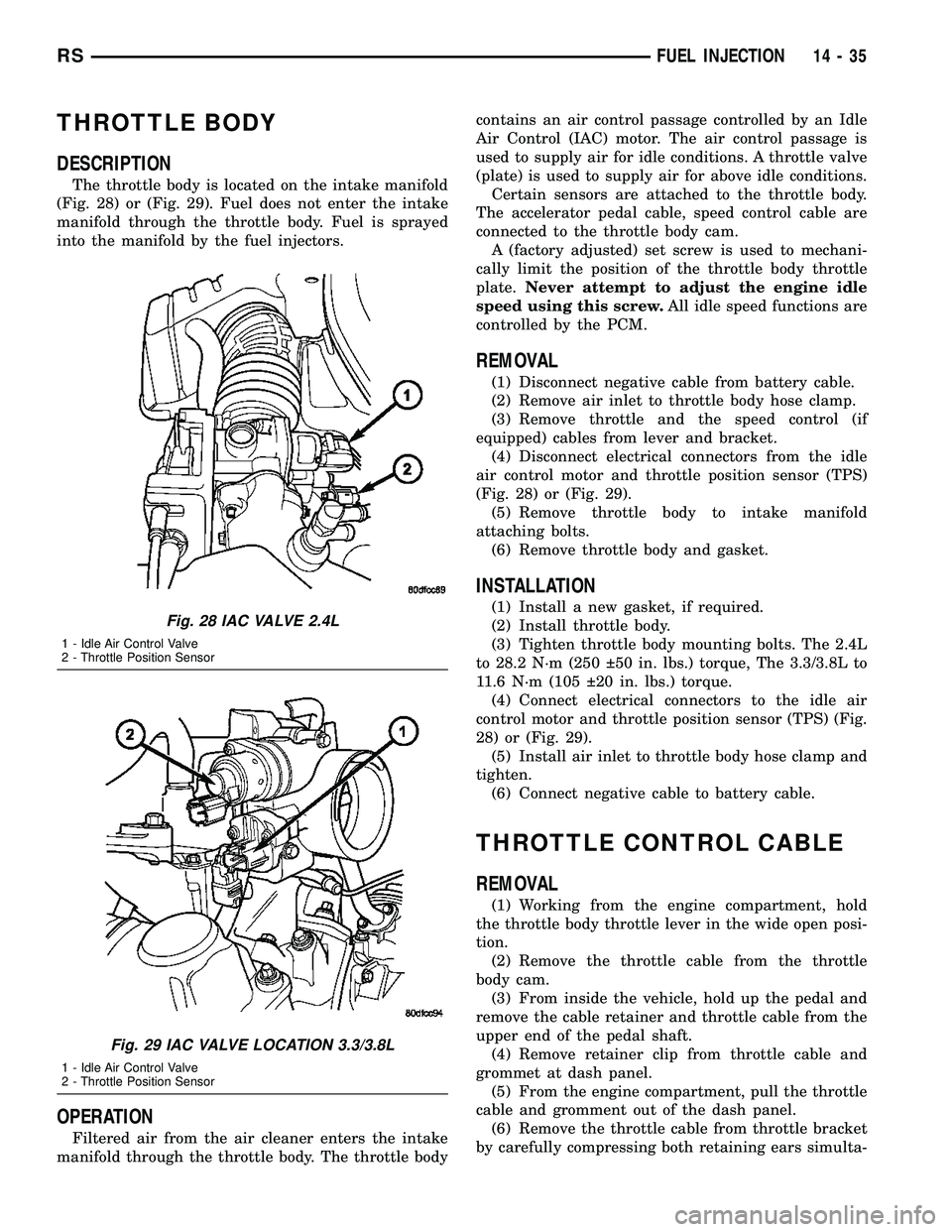
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The throttle body is located on the intake manifold
(Fig. 28) or (Fig. 29). Fuel does not enter the intake
manifold through the throttle body. Fuel is sprayed
into the manifold by the fuel injectors.
OPERATION
Filtered air from the air cleaner enters the intake
manifold through the throttle body. The throttle bodycontains an air control passage controlled by an Idle
Air Control (IAC) motor. The air control passage is
used to supply air for idle conditions. A throttle valve
(plate) is used to supply air for above idle conditions.
Certain sensors are attached to the throttle body.
The accelerator pedal cable, speed control cable are
connected to the throttle body cam.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the PCM.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery cable.
(2) Remove air inlet to throttle body hose clamp.
(3) Remove throttle and the speed control (if
equipped) cables from lever and bracket.
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors from the idle
air control motor and throttle position sensor (TPS)
(Fig. 28) or (Fig. 29).
(5) Remove throttle body to intake manifold
attaching bolts.
(6) Remove throttle body and gasket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new gasket, if required.
(2) Install throttle body.
(3) Tighten throttle body mounting bolts. The 2.4L
to 28.2 N´m (250 50 in. lbs.) torque, The 3.3/3.8L to
11.6 N´m (105 20 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect electrical connectors to the idle air
control motor and throttle position sensor (TPS) (Fig.
28) or (Fig. 29).
(5) Install air inlet to throttle body hose clamp and
tighten.
(6) Connect negative cable to battery cable.
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Working from the engine compartment, hold
the throttle body throttle lever in the wide open posi-
tion.
(2) Remove the throttle cable from the throttle
body cam.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
remove the cable retainer and throttle cable from the
upper end of the pedal shaft.
(4) Remove retainer clip from throttle cable and
grommet at dash panel.
(5) From the engine compartment, pull the throttle
cable and gromment out of the dash panel.
(6) Remove the throttle cable from throttle bracket
by carefully compressing both retaining ears simulta-
Fig. 28 IAC VALVE 2.4L
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
Fig. 29 IAC VALVE LOCATION 3.3/3.8L
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
RSFUEL INJECTION14-35
Page 1546 of 2585

STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STEERING
DESCRIPTION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM . . 1
OPERATION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM . . . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING SYSTEM FLOW AND
PRESSURE TEST......................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS............3SPECIFICATIONS
POWER STEERING FASTENER TORQUE . . . 9
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING....................9
COLUMN..............................10
GEAR.................................26
PUMP.................................36
STEERING
DESCRIPTION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
This vehicle comes with power steering as stan-
dard equipment. The power steering system consists
of these major components:
²POWER STEERING PUMP
²POWER STEERING GEAR
²POWER STEERING FLUID
²POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
²POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
²POWER STEERING FLUID SUPPLY HOSE
²POWER STEERING FLUID PRESSURE HOSE
²POWER STEERING FLUID RETURN HOSE
For information on the first two components, refer
to their respective sections within this service man-
ual group. Information on all other components can
be found in POWER STEERING PUMP.
OPERATION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear (side-to-side) travel through the meshing of the
helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth within the
steering gear. The lateral travel pushes and pulls the
tie rods to change the direction of the vehicle's front
wheels.
Power assist steering is provided by a belt driven
rotary type pump. It directs fluid through power
steering fluid hoses to the power steering gear where
it is used to assist the driver's turning effort.
Manual steering control of the vehicle can be main-
tained if power steering assist is lost. However,
under this condition, steering effort is significantly
increased.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING
SYSTEM FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
ALL ENGINES
The following procedure is to be used to test the
operation of the power steering system on this vehi-
cle. This test will provide the flow rate of the power
steering pump along with the maximum relief pres-
sure. This test is to be performed to determine if the
power steering pump or power steering gear is not
functioning properly. The following flow and pressure
test is performed using the Power Steering Analyzer
Kit, Special Tool 6815 (Fig. 1), hoses, Special Tools
6905 and 6959, and fittings from adapter kit, Special
Tool 6893.
Fig. 1 Power Steering Analyzer With Hoses Installed
1 - OUTLET
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6815
3 - INLET
RSSTEERING19-1
Page 1548 of 2585

(6) Start engine and let idle just long enough to
circulate power steering fluid through the analyzer
and hoses. Shut off engine.
(7) Check power steering fluid level and add fluid
as necessary. Start engine again and let idle until the
air is out of the fluid.
(8) Gauge should read below 300 psi (2068 kPa). If
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the range
of 100-275 psi (689-1896 kPa) depending on fluid
temperature. The flow meter should read above 1.5
GPM.
CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than four seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
NOTE:
Power steering pump maximum pressure for
2.4L engines is 1,200 ± 1,350 psi (8,274 ± 9,308 kPa).
Power steering pump maximum pressure for all other
engines is 1,400 ± 1,500 psi (9,653 ± 10,342 kPa).
(9) Close analyzer valve fully three times and
record highest pressure indicated each time. All three
readings must be within specifications. If any of the
three power steering pump pressures are above orbelow specifications, replace pump. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - REMOVAL)
CAUTION: Do not force the steering to operate
against the stops for more than 4 seconds at a time
because pump damage can result.
(10) Once the pump has been verified as working
correctly, completely open the valve on the Power
Steering Analyzer. Turn the steering wheel to the
extreme left until the stop in the steering gear is
met. Hold it there for 2±4 seconds, then release it.
Now turn the steering wheel to the right until the
right stop is met. Hold it there for 2±4 seconds, then
release it. Record the stabilized pressure at each
position. Compare the recorded readings to the spec-
ifications. If the output pressures are not within 100
psi (689 kPa) of one another against either stop or
are below specifications, the steering gear is leaking
internally and must be replaced. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/GEAR - REMOVAL)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
NOTE: There are three diagnosis charts following
that cover POWER STEERING NOISE, STEERING
WHEEL FEEL, and POWER STEERING FLUID.
POWER STEERING NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONABLE HISS
OR WHISTLE*1. Damaged or mispositioned
steering column shaft/coupling dash
panel seal.1. Reposition or replace steering column
shaft/coupling dash panel seal.
2. Noisy valve in power steering
gear.2. Replace power steering gear.
3. Mis-routed power steering hose. 3. Check routing of power steering
hoses. Ensure hoses do not come in
unwanted contact with other components
and objects.
RATTLE OR EXCESSIVE
CLUNK**1. Power steering gear loose on front
suspension crossmember.1. Inspect power steering gear mounting
bolts. Replace as necessary. Tighten to
the specified torque.
2. Front suspension crossmember
mounting fasteners loose at frame.2. Tighten the front suspension
crossmember mounting fasteners to the
specified torque.
3. Loose tie rod (outer or inner). 3. Check tie rod pivot points for wear.
Replace worn/loose parts as required.
4. Loose lower control arm mounting
bolts at front suspension
crossmember.4. Tighten control arm mounting bolts to
the specified torques.
RSSTEERING19-3
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1549 of 2585
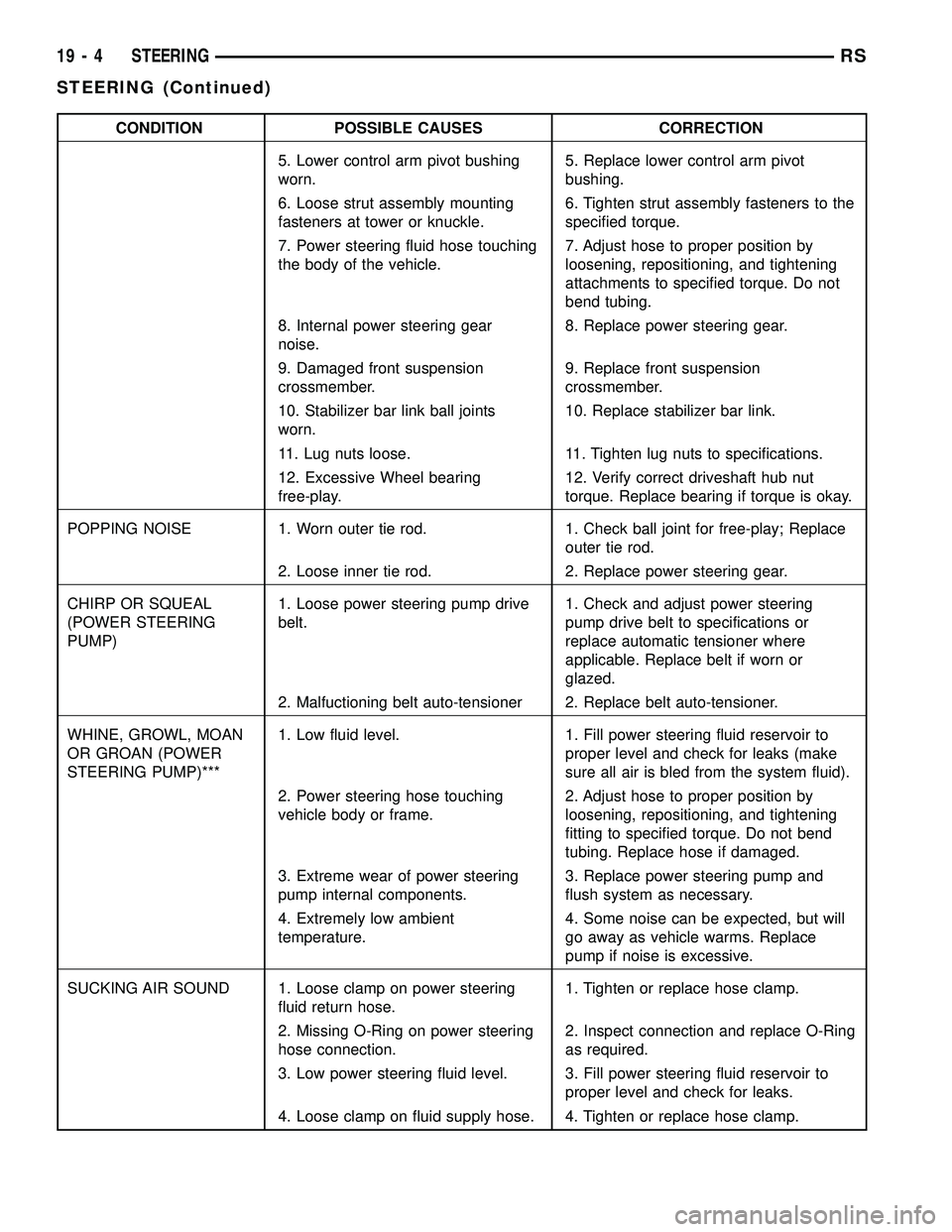
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
5. Lower control arm pivot bushing
worn.5. Replace lower control arm pivot
bushing.
6. Loose strut assembly mounting
fasteners at tower or knuckle.6. Tighten strut assembly fasteners to the
specified torque.
7. Power steering fluid hose touching
the body of the vehicle.7. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
attachments to specified torque. Do not
bend tubing.
8. Internal power steering gear
noise.8. Replace power steering gear.
9. Damaged front suspension
crossmember.9. Replace front suspension
crossmember.
10. Stabilizer bar link ball joints
worn.10. Replace stabilizer bar link.
11. Lug nuts loose. 11. Tighten lug nuts to specifications.
12. Excessive Wheel bearing
free-play.12. Verify correct driveshaft hub nut
torque. Replace bearing if torque is okay.
POPPING NOISE 1. Worn outer tie rod. 1. Check ball joint for free-play; Replace
outer tie rod.
2. Loose inner tie rod. 2. Replace power steering gear.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL
(POWER STEERING
PUMP)1. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.1. Check and adjust power steering
pump drive belt to specifications or
replace automatic tensioner where
applicable. Replace belt if worn or
glazed.
2. Malfuctioning belt auto-tensioner 2. Replace belt auto-tensioner.
WHINE, GROWL, MOAN
OR GROAN (POWER
STEERING PUMP)***1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks (make
sure all air is bled from the system fluid).
2. Power steering hose touching
vehicle body or frame.2. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
fitting to specified torque. Do not bend
tubing. Replace hose if damaged.
3. Extreme wear of power steering
pump internal components.3. Replace power steering pump and
flush system as necessary.
4. Extremely low ambient
temperature.4. Some noise can be expected, but will
go away as vehicle warms. Replace
pump if noise is excessive.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose clamp on power steering
fluid return hose.1. Tighten or replace hose clamp.
2. Missing O-Ring on power steering
hose connection.2. Inspect connection and replace O-Ring
as required.
3. Low power steering fluid level. 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks.
4. Loose clamp on fluid supply hose. 4. Tighten or replace hose clamp.
19 - 4 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1550 of 2585

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SQUEAK OR RUBBING
SOUND1. Steering column shroud rubbing. 1. Realign shrouds as necessary.
2. Steering column shaft rubbing. 2. Move or realign item rubbing shaft.
3. Clockspring noisy. 3. Remove clockspring. Reinstall wheel.
If noise is gone, replace clockspring.
4. Seal lubrication inadequate. 4. Lube seal (if external).
5. Steering gear internally noisy. 5. Replace steering gear (if no other
cause can be found).
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING NOISE.1. Incorrect tire or wheel size. 1. Replace incorrect size tire or wheel
with size used as original equipment.
2. Interference between steering
gear and other vehicle components.2. Check for bent or misaligned
components and correct as necessary.
3. Steering gear internal stops worn
excessively allowing tires to be
steered excessively far.3. Replace steering gear.
NOTE: * There is some noise in all power steering
systems. One of the most common is a hissing
sound evident when turning the steering wheel
when at a standstill or when parking and the steer-
ing wheel is at the end of its travel. Hiss is a very
high frequency noise similar to that experienced
while slowly closing a water tap. The noise is
present in every valve and results when high veloc-
ity fluid passes valve orifice edges. There is no
relationship between this noise and the perfor-
mance of the steering system.NOTE: ** A light clunk may be felt or heard during
steering wheel reversal while vehicle is stationary.
This results from internal steering gear rack move-
ment at the bushings and in no way affects the per-
formance of the steering system. This movement
may be felt in the steering components during
steering wheel reversal.
NOTE: *** Power steering pump growl/moan/groan
results from the development of high pressure fluid
flow. Normally this noise level should not be high
enough to be objectionable.
STEERING WHEEL FEEL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STEERING WHEEL/
COLUMN CLICKING,
CLUNKING OR RATTLING.1. Loose steering coupling pinch
bolt.1. Replace pinch bolt and torque to
specifications.
2. Steering column bearings. 2. Replace steering column.
3. Excessive intermediate shaft
coupling free-play.3. Replace intermediate shaft.
STEERING WHEEL HAS
FORE AND AFT
LOOSENESS.1. Steering wheel retaining nut not
properly tightened and torqued.1. Tighten the steering wheel retaining nut
to its specified torque.
2. Steering column lower bearing
spring retainer slipped on steering
column shaft.2. Replace steering column.
3. Loose steering column to
instrument panel fasteners.3. Tighten fasteners to specified torque.
RSSTEERING19-5
STEERING (Continued)