2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER volt
[x] Cancel search: voltPage 1837 of 2585
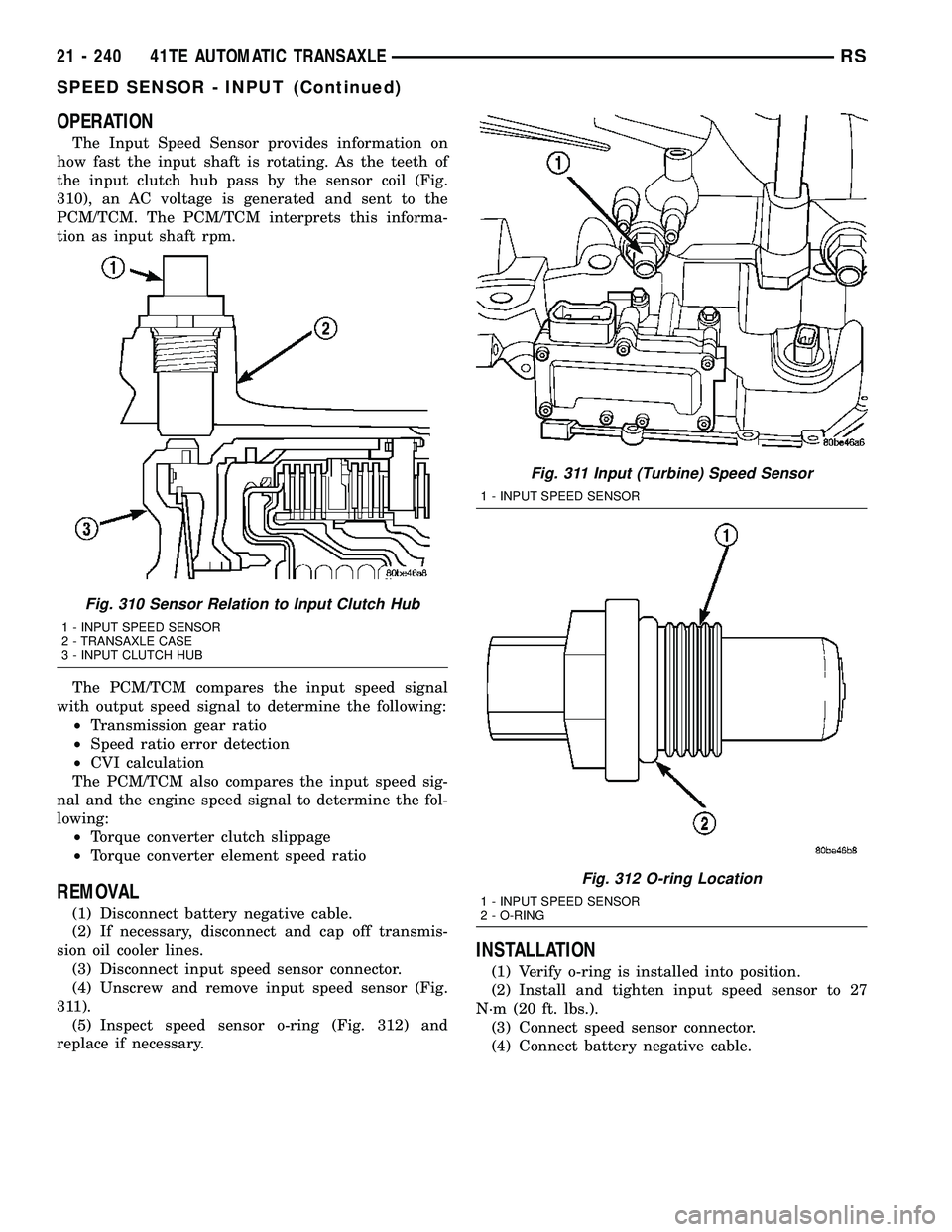
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil (Fig.
310), an AC voltage is generated and sent to the
PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this informa-
tion as input shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input speed signal
with output speed signal to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The PCM/TCM also compares the input speed sig-
nal and the engine speed signal to determine the fol-
lowing:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) If necessary, disconnect and cap off transmis-
sion oil cooler lines.
(3) Disconnect input speed sensor connector.
(4) Unscrew and remove input speed sensor (Fig.
311).
(5) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 312) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position.
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector.
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 310 Sensor Relation to Input Clutch Hub
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - TRANSAXLE CASE
3 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB
Fig. 311 Input (Turbine) Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 312 O-ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
21 - 240 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT (Continued)
Page 1838 of 2585
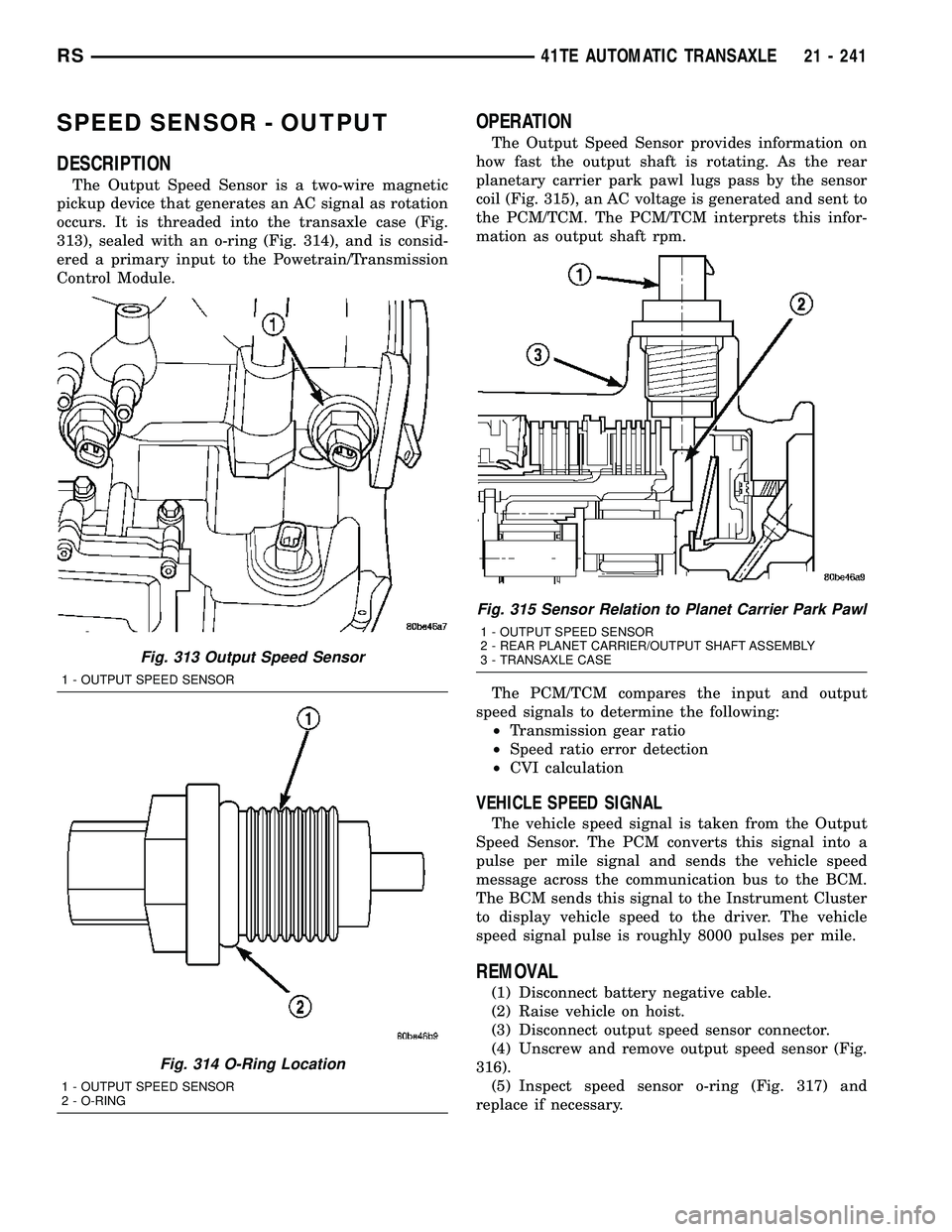
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Output Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates an AC signal as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
313), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 314), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powetrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Output Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the output shaft is rotating. As the rear
planetary carrier park pawl lugs pass by the sensor
coil (Fig. 315), an AC voltage is generated and sent to
the PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this infor-
mation as output shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input and output
speed signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
The vehicle speed signal is taken from the Output
Speed Sensor. The PCM converts this signal into a
pulse per mile signal and sends the vehicle speed
message across the communication bus to the BCM.
The BCM sends this signal to the Instrument Cluster
to display vehicle speed to the driver. The vehicle
speed signal pulse is roughly 8000 pulses per mile.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect output speed sensor connector.
(4) Unscrew and remove output speed sensor (Fig.
316).
(5) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 317) and
replace if necessary.
Fig. 313 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 314 O-Ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 315 Sensor Relation to Planet Carrier Park Pawl
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - REAR PLANET CARRIER/OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - TRANSAXLE CASE
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 241
Page 1845 of 2585
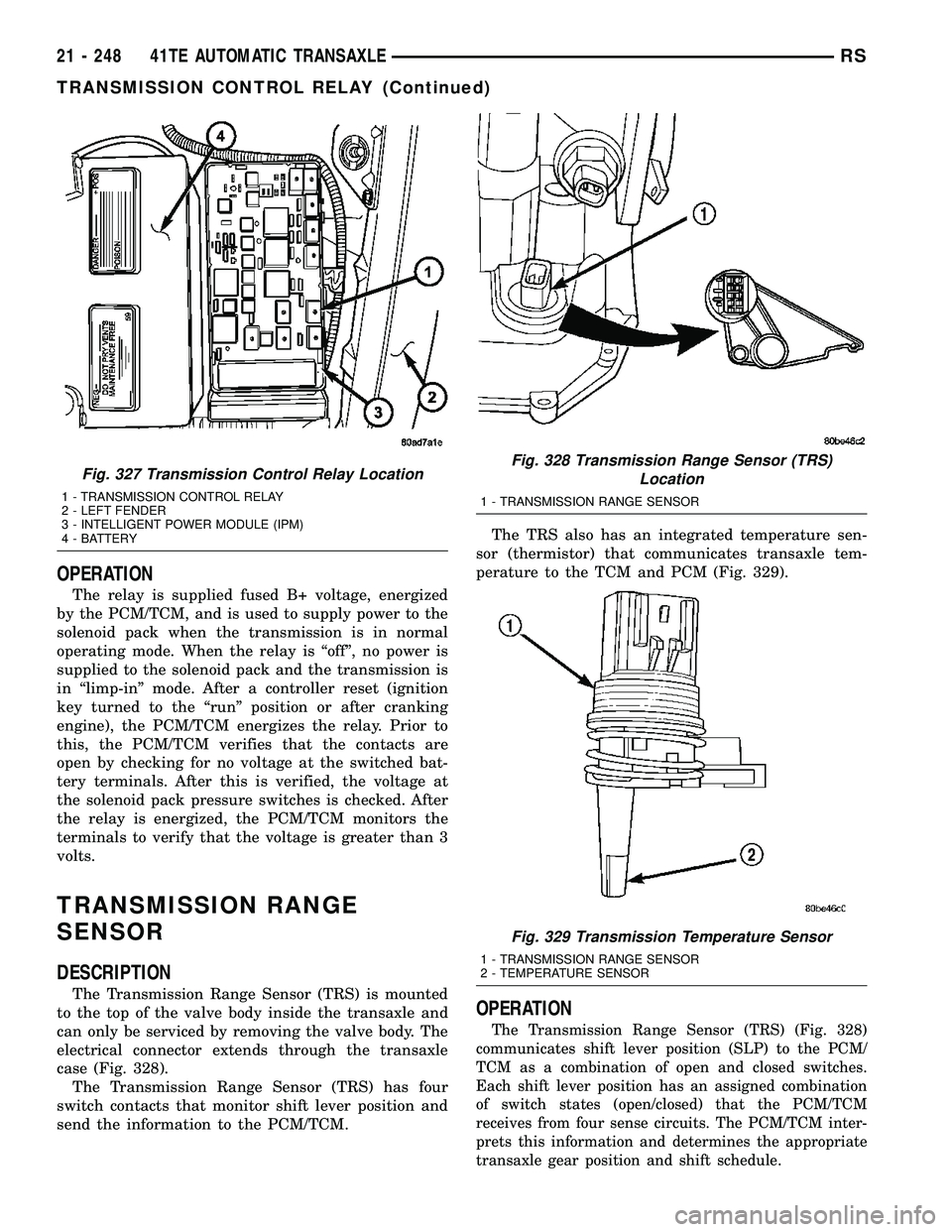
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the PCM/TCM, and is used to supply power to the
solenoid pack when the transmission is in normal
operating mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is
supplied to the solenoid pack and the transmission is
in ªlimp-inº mode. After a controller reset (ignition
key turned to the ªrunº position or after cranking
engine), the PCM/TCM energizes the relay. Prior to
this, the PCM/TCM verifies that the contacts are
open by checking for no voltage at the switched bat-
tery terminals. After this is verified, the voltage at
the solenoid pack pressure switches is checked. After
the relay is energized, the PCM/TCM monitors the
terminals to verify that the voltage is greater than 3
volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle and
can only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 328).
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the PCM/TCM.The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 329).
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 328)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the PCM/
TCM as a combination of open and closed switches.
Each shift lever position has an assigned combination
of switch states (open/closed) that the PCM/TCM
receives from four sense circuits. The PCM/TCM inter-
prets this information and determines the appropriate
transaxle gear position and shift schedule.
Fig. 327 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERY
Fig. 328 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 329 Transmission Temperature Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - TEMPERATURE SENSOR
21 - 248 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY (Continued)
Page 1846 of 2585
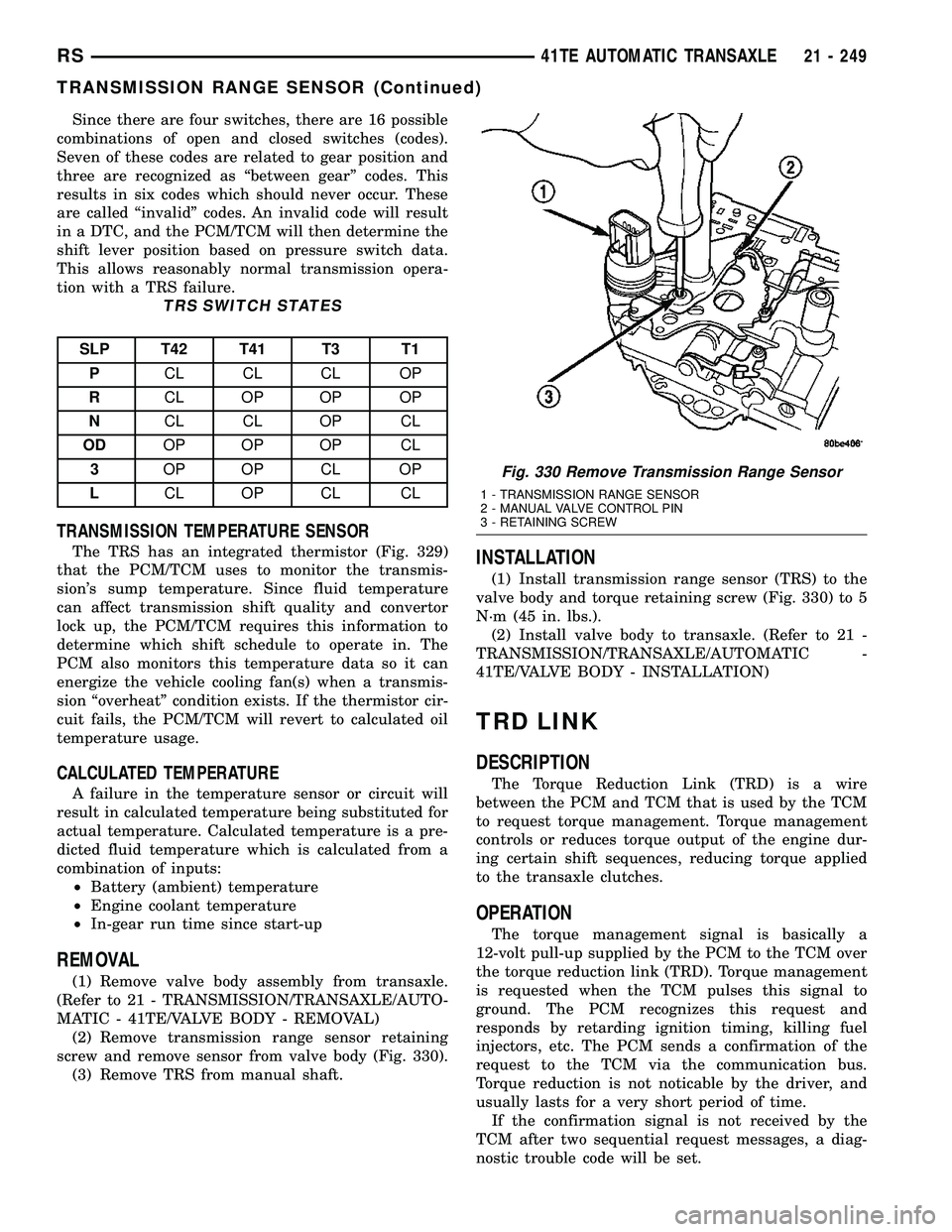
Since there are four switches, there are 16 possible
combinations of open and closed switches (codes).
Seven of these codes are related to gear position and
three are recognized as ªbetween gearº codes. This
results in six codes which should never occur. These
are called ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result
in a DTC, and the PCM/TCM will then determine the
shift lever position based on pressure switch data.
This allows reasonably normal transmission opera-
tion with a TRS failure.
TRS SWITCH STATES
SLP T42 T41 T3 T1
PCL CL CL OP
RCL OP OP OP
NCL CL OP CL
ODOP OP OP CL
3OP OP CL OP
LCL OP CL CL
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The TRS has an integrated thermistor (Fig. 329)
that the PCM/TCM uses to monitor the transmis-
sion's sump temperature. Since fluid temperature
can affect transmission shift quality and convertor
lock up, the PCM/TCM requires this information to
determine which shift schedule to operate in. The
PCM also monitors this temperature data so it can
energize the vehicle cooling fan(s) when a transmis-
sion ªoverheatº condition exists. If the thermistor cir-
cuit fails, the PCM/TCM will revert to calculated oil
temperature usage.
CALCULATED TEMPERATURE
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body assembly from transaxle.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove transmission range sensor retaining
screw and remove sensor from valve body (Fig. 330).
(3) Remove TRS from manual shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transmission range sensor (TRS) to the
valve body and torque retaining screw (Fig. 330) to 5
N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(2) Install valve body to transaxle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
41TE/VALVE BODY - INSTALLATION)
TRD LINK
DESCRIPTION
The Torque Reduction Link (TRD) is a wire
between the PCM and TCM that is used by the TCM
to request torque management. Torque management
controls or reduces torque output of the engine dur-
ing certain shift sequences, reducing torque applied
to the transaxle clutches.
OPERATION
The torque management signal is basically a
12-volt pull-up supplied by the PCM to the TCM over
the torque reduction link (TRD). Torque management
is requested when the TCM pulses this signal to
ground. The PCM recognizes this request and
responds by retarding ignition timing, killing fuel
injectors, etc. The PCM sends a confirmation of the
request to the TCM via the communication bus.
Torque reduction is not noticable by the driver, and
usually lasts for a very short period of time.
If the confirmation signal is not received by the
TCM after two sequential request messages, a diag-
nostic trouble code will be set.
Fig. 330 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 249
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1995 of 2585
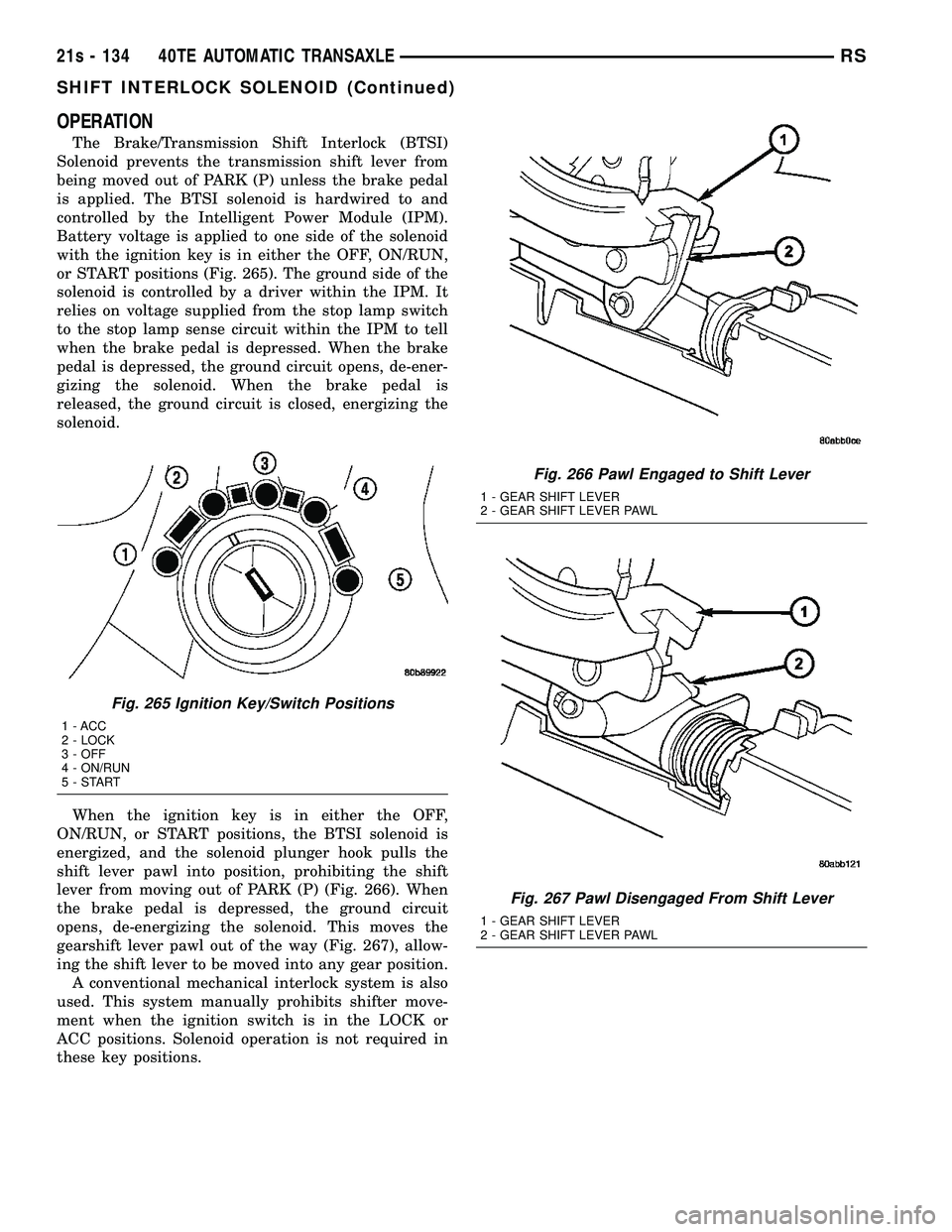
OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the OFF, ON/RUN,
or START positions (Fig. 265). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 266). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 267), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position. A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
Fig. 265 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 266 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 267 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
21s - 134 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 2001 of 2585
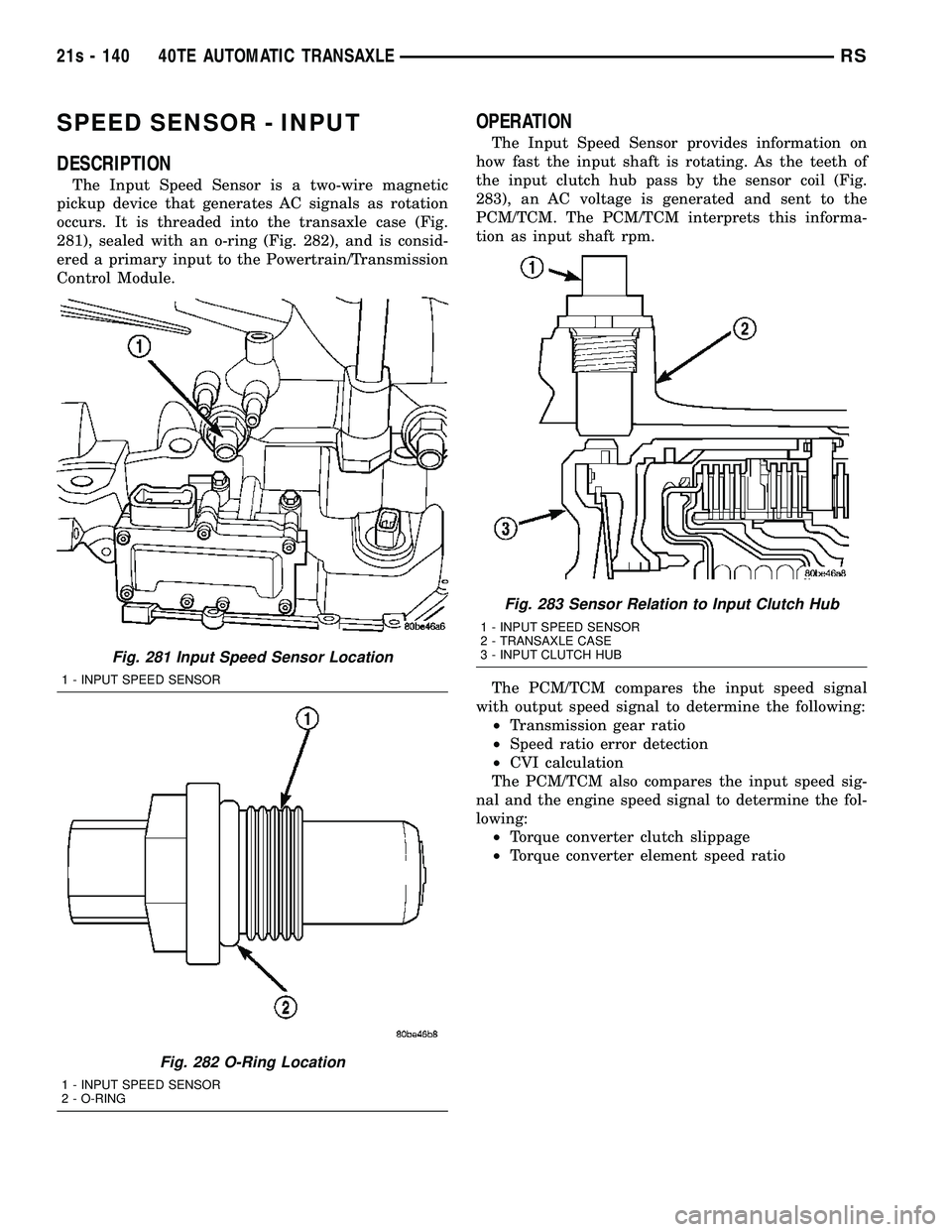
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Input Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates AC signals as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
281), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 282), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powertrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil (Fig.
283), an AC voltage is generated and sent to the
PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this informa-
tion as input shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input speed signal
with output speed signal to determine the following: ² Transmission gear ratio
² Speed ratio error detection
² CVI calculation
The PCM/TCM also compares the input speed sig-
nal and the engine speed signal to determine the fol-
lowing: ² Torque converter clutch slippage
² Torque converter element speed ratio
Fig. 281 Input Speed Sensor Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 282 O-Ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 283 Sensor Relation to Input Clutch Hub
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - TRANSAXLE CASE
3 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB
21s - 140 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 2003 of 2585
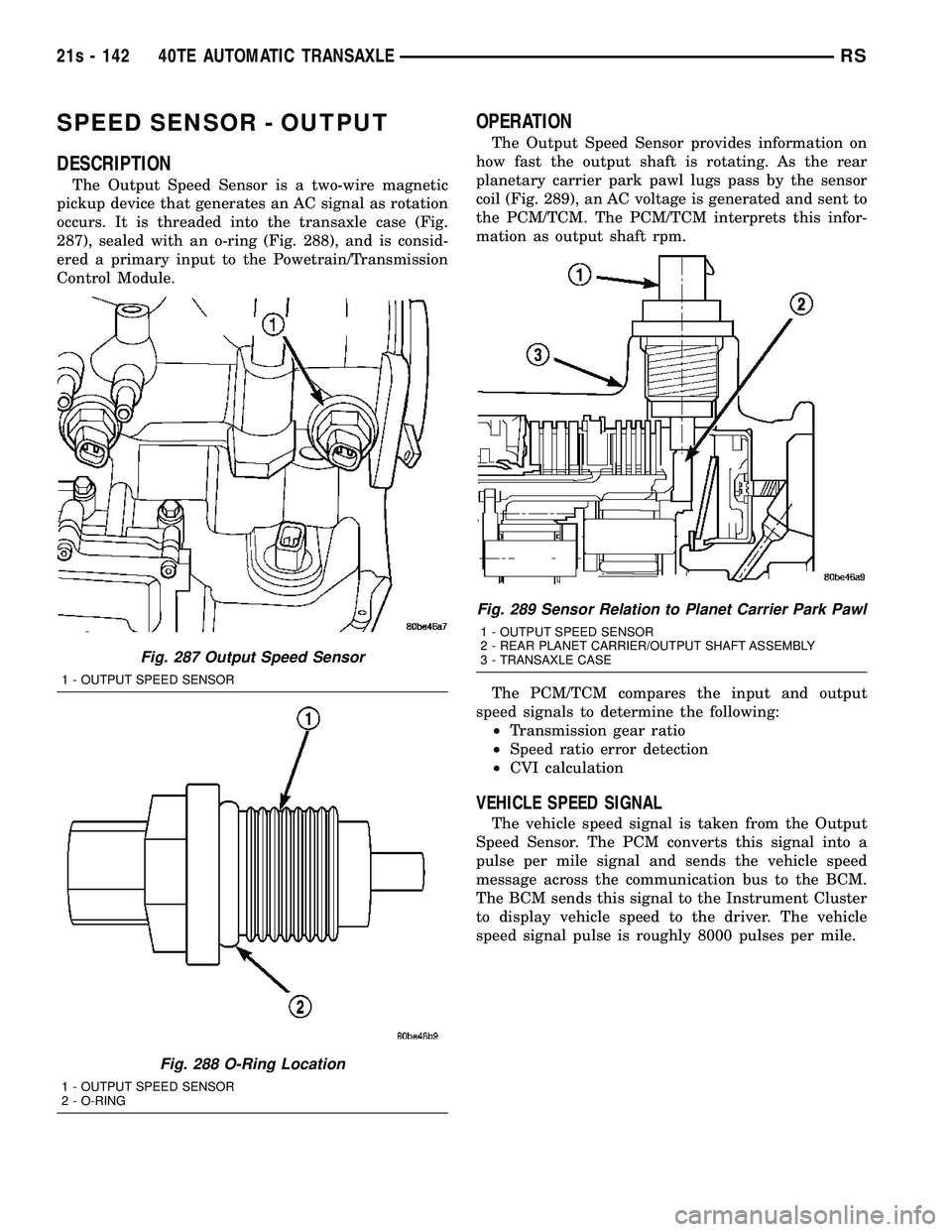
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Output Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates an AC signal as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
287), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 288), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powetrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Output Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the output shaft is rotating. As the rear
planetary carrier park pawl lugs pass by the sensor
coil (Fig. 289), an AC voltage is generated and sent to
the PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this infor-
mation as output shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input and output
speed signals to determine the following: ² Transmission gear ratio
² Speed ratio error detection
² CVI calculation
VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
The vehicle speed signal is taken from the Output
Speed Sensor. The PCM converts this signal into a
pulse per mile signal and sends the vehicle speed
message across the communication bus to the BCM.
The BCM sends this signal to the Instrument Cluster
to display vehicle speed to the driver. The vehicle
speed signal pulse is roughly 8000 pulses per mile.
Fig. 287 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 288 O-Ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 289 Sensor Relation to Planet Carrier Park Pawl
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - REAR PLANET CARRIER/OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - TRANSAXLE CASE
21s - 142 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 2011 of 2585
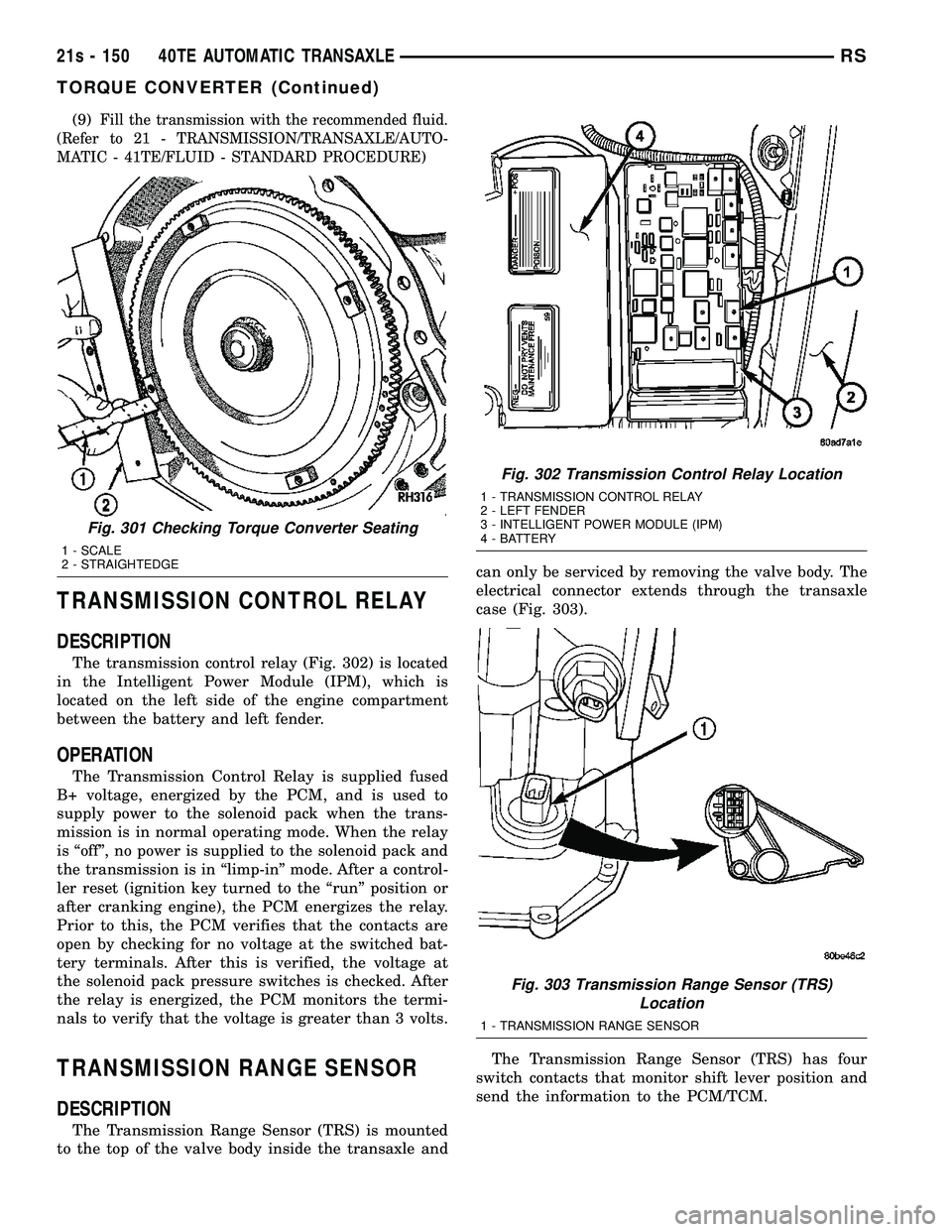
(9)Fill the transmission with the recommended fluid.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission control relay (Fig. 302) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
OPERATION
The Transmission Control Relay is supplied fused
B+ voltage, energized by the PCM, and is used to
supply power to the solenoid pack when the trans-
mission is in normal operating mode. When the relay
is ªoffº, no power is supplied to the solenoid pack and
the transmission is in ªlimp-inº mode. After a control-
ler reset (ignition key turned to the ªrunº position or
after cranking engine), the PCM energizes the relay.
Prior to this, the PCM verifies that the contacts are
open by checking for no voltage at the switched bat-
tery terminals. After this is verified, the voltage at
the solenoid pack pressure switches is checked. After
the relay is energized, the PCM monitors the termi-
nals to verify that the voltage is greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle and can only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 303).
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the PCM/TCM.
Fig. 301 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
Fig. 302 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERY
Fig. 303 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
21s - 150 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)