2004 CHEVROLET TRACKER tires
[x] Cancel search: tiresPage 207 of 374

Weight of the Trailer Tongue
The tongue load (A) of any trailer is an important weight
to measure because it affects the total or gross weight
of your vehicle. The Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW)
includes the curb weight of the vehicle, any cargo you
may carry in it, and the people who will be riding in
the vehicle. And if you will tow a trailer, you must add
the tongue load to the GVW because your vehicle will be
carrying that weight, too. See
Loading Your Vehicle
on page 4-51for more information about your vehicle's
maximum load capacity.If you're using a weight-carrying or a weight-distributing
hitch, the trailer tongue weight (A) should be 10 percent
to 15 percent of the total loaded trailer weight (B).
Do not exceed the maximum allowable tongue weight
for your vehicle.
After you've loaded your trailer, weigh the trailer and
then the tongue, separately, to see if the weights
are proper. If they aren't, you may be able to get them
right simply by moving some items around in the
trailer.
Total Weight on Your Vehicle's Tires
Be sure your vehicle's tires are in¯ated to the upper limit
for cold tires. You'll ®nd these numbers on the Tire
and Loading Information label. See
Tires on page 5-55.
Then be sure you don't go over the GVW limit for
your vehicle, including the weight of the trailer tongue.
4-59
Page 209 of 374

Driving with a Trailer
Towing a trailer requires a certain amount of experience.
Before setting out for the open road, you'll want to get
to know your rig. Acquaint yourself with the feel of
handling and braking with the added weight of the trailer.
And always keep in mind that the vehicle you are
driving is now a good deal longer and not nearly as
responsive as your vehicle is by itself.
Before you start, check the trailer hitch and platform
(and attachments), safety chains, electrical connector,
lamps, tires and mirror adjustment. If the trailer has
electric brakes, start your vehicle and trailer moving and
then apply the trailer brake controller by hand to be
sure the brakes are working. This lets you check your
electrical connection at the same time.
During your trip, check occasionally to be sure that the
load is secure, and that the lamps and any trailer
brakes are still working.
Following Distance
Stay at least twice as far behind the vehicle ahead as
you would when driving your vehicle without a trailer.
This can help you avoid situations that require
heavy braking and sudden turns.
Passing
You'll need more passing distance up ahead when
you're towing a trailer. And, because you're a good deal
longer, you'll need to go much farther beyond the
passed vehicle before you can return to your lane.
Backing Up
Hold the bottom of the steering wheel with one hand.
Then, to move the trailer to the left, just move that hand
to the left. To move the trailer to the right, move your
hand to the right. Always back up slowly and, if possible,
have someone guide you.
4-61
Page 213 of 374

Service............................................................5-3
Doing Your Own Service Work.........................5-3
Adding Equipment to the Outside of Your
Vehicle......................................................5-4
Fuel................................................................5-4
Gasoline Octane............................................5-4
Gasoline Speci®cations....................................5-4
California Fuel...............................................5-5
Additives.......................................................5-6
Fuels in Foreign Countries...............................5-6
Filling Your Tank............................................5-7
Filling a Portable Fuel Container.......................5-9
Checking Things Under the Hood....................5-10
Hood Release..............................................5-10
Engine Compartment Overview.......................5-12
Engine Oil...................................................5-13
Engine Air Cleaner/Filter................................5-18
Automatic Transmission Fluid.........................5-20
Manual Transmission Fluid.............................5-23
Hydraulic Clutch...........................................5-24
Engine Coolant.............................................5-25
Radiator Pressure Cap..................................5-28
Engine Overheating.......................................5-28
Cooling System............................................5-31
Power Steering Fluid.....................................5-37Windshield Washer Fluid................................5-37
Brakes........................................................5-39
Battery........................................................5-42
Jump Starting...............................................5-43
Rear Axle.......................................................5-48
Four-Wheel Drive............................................5-49
Bulb Replacement..........................................5-51
Halogen Bulbs..............................................5-51
Headlamps..................................................5-51
Front Turn Signal and Parking Lamps..............5-53
Sidemarker Lamps........................................5-53
Rear Combination Lamps...............................5-54
Replacement Bulbs.......................................5-55
Tires..............................................................5-55
In¯ation - Tire Pressure.................................5-63
Tire Inspection and Rotation...........................5-64
When It Is Time for New Tires.......................5-66
Buying New Tires.........................................5-67
Uniform Tire Quality Grading..........................5-68
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance..................5-69
Wheel Replacement......................................5-70
Tire Chains..................................................5-71
If a Tire Goes Flat........................................5-72
Changing a Flat Tire.....................................5-72
Section 5 Service and Appearance Care
5-1
Page 253 of 374

Brake Wear
Your vehicle has front disc brakes and rear drum
brakes.
Disc brake pads have built-in wear indicators that make
a high-pitched warning sound when the brake pads
are worn and new pads are needed. The sound
may come and go or be heard all the time your vehicle
is moving (except when you are pushing on the
brake pedal ®rmly).
{CAUTION:
The brake wear warning sound means that
soon your brakes will not work well. That
could lead to an accident. When you hear the
brake wear warning sound, have your vehicle
serviced.
Notice:Continuing to drive with worn-out brake
pads could result in costly brake repair.
Some driving conditions or climates may cause a brake
squeal when the brakes are ®rst applied or lightly
applied. This does not mean something is wrong with
your brakes.Properly torqued wheel nuts are necessary to help
prevent brake pulsation. When tires are rotated, inspect
brake pads for wear and evenly tighten wheel nuts in
the proper sequence to GM torque speci®cations.
Your rear drum brakes do not have wear indicators, but
if you ever hear a rear brake rubbing noise, have the
rear brake linings inspected immediately. Also, the rear
brake drums should be removed and inspected each
time the tires are removed for rotation or changing.
When you have the front brake pads replaced, have the
rear brakes inspected, too.
Brake linings should always be replaced as complete
axle sets.
See
Brake System Inspection on page 6-29.
Brake Pedal Travel
See your dealer if the brake pedal does not return to
normal height, or if there is a rapid increase in
pedal travel. This could be a sign of brake trouble.
Brake Adjustment
Every time you make a brake stop, your disc brakes
adjust for wear.
5-41
Page 267 of 374
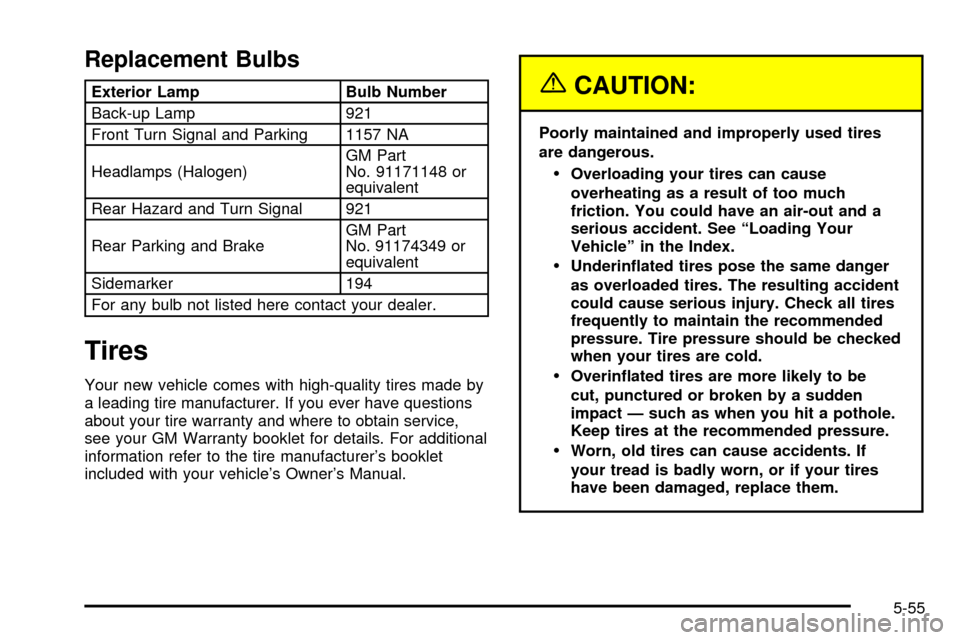
Replacement Bulbs
Exterior Lamp Bulb Number
Back-up Lamp 921
Front Turn Signal and Parking 1157 NA
Headlamps (Halogen)GM Part
No. 91171148 or
equivalent
Rear Hazard and Turn Signal 921
Rear Parking and BrakeGM Part
No. 91174349 or
equivalent
Sidemarker 194
For any bulb not listed here contact your dealer.
Tires
Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by
a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions
about your tire warranty and where to obtain service,
see your GM Warranty booklet for details. For additional
information refer to the tire manufacturer's booklet
included with your vehicle's Owner's Manual.
{CAUTION:
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
·Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result of too much
friction. You could have an air-out and a
serious accident. See ªLoading Your
Vehicleº in the Index.
·Underin¯ated tires pose the same danger
as overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked
when your tires are cold.
·Overin¯ated tires are more likely to be
cut, punctured or broken by a sudden
impact Ð such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
·Worn, old tires can cause accidents. If
your tread is badly worn, or if your tires
have been damaged, replace them.
5-55
Page 269 of 374

(A) Tire Size Code:The tire size code is a combination
of letters and numbers used to de®ne a particular
tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type and
service description. See the ªTire Size Codeº illustration
later in this section for more detail.
(B) Tire Performance Criteria Speci®cation (TPC
Spec):Original equipment tires designed to GM's
speci®c tire performance criteria have a TPC
speci®cation code molded onto the sidewall. GM's TPC
speci®cations meet or exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
(C) Department of Transportation (DOT):The
Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that
the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.(D) Tire Identi®cation Number (TIN):The letters and
numbers following DOT code are the Tire Identi®cation
Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer
and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may have the date of
manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material:The type of cord and number of
plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG):Tire
manufacturers are required to grade tires based on three
performance factors: treadwear, traction and
temperature resistance. For more information, see
Uniform Tire Quality Grading on page 5-68.
(G) Maximum Cold In¯ation Load Limit:Maximum
load that can be carried and the maximum pressure
needed to support that load. For information on
recommended tire pressure see
In¯ation - Tire Pressure
on page 5-63andLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-51.
5-57
Page 270 of 374

(A) Tire Size:The tire size code is a combination of
letters and numbers used to de®ne a particular
tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type and
service description. See the ªTire Sizeº illustration
later in this section for more detail.
(B) Tire Performance Criteria Speci®cation (TPC
Spec):Original equipment tires designed to GM's
speci®c tire performance criteria have a TPC speci®cation
code molded onto the sidewall. GM's TPC speci®cations
meet or exceed all federal safety guidelines.
(C) Dual Tire Maximum Load:Maximum load that can
be carried and the maximum pressure needed to
support that load when used in a dual con®guration. For
information on recommended tire pressure see
In¯ation - Tire Pressure on page 5-63andLoading Your
Vehicle on page 4-51.
(D) Department of Transportation (DOT):The
Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that
the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
(E) Tire Identi®cation Number (TIN):The letters and
numbers following DOT code are the Tire Identi®cation
Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer
and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may have the date of
manufacture.
LT-Metric Tire
5-58
Page 274 of 374

Normal Occupant Weight:The number of occupants a
vehicle is designed to seat multiplied by 150 pounds
(68 kg). See
Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-51.
Occupant Distribution:Designated seating positions.
Outward Facing Sidewall:The side of a asymmetrical
tire that has a particular side that faces outward
when mounted on a vehicle. The side of the tire that
contains a whitewall, bears white lettering or bears
manufacturer, brand and or model name molding that is
higher or deeper than the same moldings on the
other sidewall of the tire.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire:A tire used on passenger
cars and some light duty trucks and multipurpose
vehicles.
Recommended In¯ation Pressure:Vehicle
manufacturer's recommended tire in¯ation pressure and
shown on the tire placard. See
In¯ation - Tire Pressure
on page 5-63andLoading Your Vehicle on page 4-51.
Radial Ply tire:A pneumatic tire in which the ply cords
that extend to the beads are laid at 90 degrees to the
centerline of the tread.
Rim:A metal support for a tire and upon which the tire
beads are seated.
Sidewall:The portion of a tire between the tread and
the bead.Speed Rating:An alphanumeric code assigned to a
tire indicating the maximum speed at which a tire
can operate.
Traction:The friction between the tire and the road
surface. The amount of grip provided.
Tread:The portion of a tire that comes into contact
with the road.
Treadwear Indicators:Narrow bands, sometimes
called ªwear bars,º that show across the tread of a tire
when only 2/32 inch of tread remains. See
When It
Is Time for New Tires on page 5-66.
UTQGS:Uniform Tire Quality Grading Standards, a tire
information system that provides consumers with
ratings for a tire's traction, temperature and treadwear.
Ratings are determined by tire manufacturers using
government testing procedures. The ratings are molded
into the sidewall of the tire. See
Uniform Tire Quality
Grading on page 5-68.
Vehicle Capacity Weight:The number of designated
seating positions multiplied by 150 lbs. (68 kg) plus
the rated cargo load. See
Loading Your Vehicle
on page 4-51.
Vehicle Maximum Load on the Tire:Load on an
individual tire due to curb weight, accessory weight,
occupant weight and cargo weight.
5-62