2003 OLDSMOBILE AURORA steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 141 of 387

Move the control between the rear outlets up to direct
airflow through the upper outlets. Move the control down
to direct airflow through the floor outlets. Adjust the
direction of the airflow with the levers located in
the center of each rear outlet.
Operation Tips
Clear away any ice, snow or leaves from the air
inlets at the base of the windshield that may
block the flow of air into your vehicle.
Use of non-GM approved hood deflectors may
adversely affect the performance of the system.
Keep the path under the front seats clear of objects
to help circulate the air inside
of your vehicle more
effectively.
Steering Wheel Climate Controls
With this feature some
heating and cooling
controls can be adjusted at
the steering wheel.
3-28
ProCarManuals.com
Page 187 of 387

Audio Steering Wheel Controls
With this feature, you can
control certain radio
functions using the buttons
on your steering wheel.
A VOL (Volume) v : Press the up or the down arrow
to increase or to decrease volume.
A SEEK: Press this button to seek to the next radio
station. When playing a cassette tape or compact disc,
press this button to hear the next selection. There
must be at least a three-second gap between selections
on a cassette tape.
PROG (Program): Press this button to tune to the next
preset radio station. When playing a cassette tape,
press this button
to hear the other side of a tape that is
playing. When listening to a disc in the
CD changer,
press this button to select the next loaded disc.
Understanding Radio Reception
AM
The range for most AM stations is greater than for FM,
especially at night. The longer range, however, can
cause stations
to interfere with each other. AM can pick
up noise from things like storms and power lines.
Try
reducing the treble to reduce this noise if you ever get it.
FM
FM stereo will give you the best sound, but FM signals
will reach only about
10 to 40 miles (1 6 to 65 km).
Tall buildings or hills can interfere with
FM signals,
causing the sound to come and go.
Care of Your Cassette Tape Player
A tape player that is not cleaned regularly can cause
reduced sound quality, ruined cassettes or a damaged
mechanism. Cassette tapes should be stored in their
cases away from contaminants, direct sunlight and
extreme heat.
If they aren’t, they may not operate
properly or may cause failure of the tape player.
3-74
ProCarManuals.com
Page 197 of 387
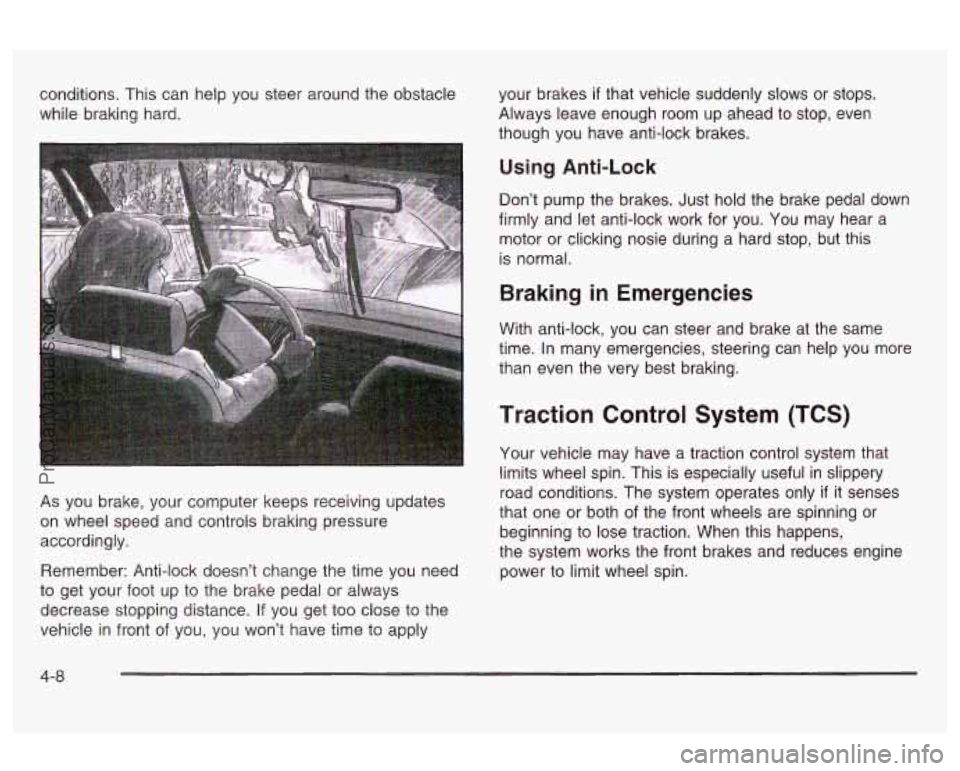
conditions. This can help you steer around the obstacle
while braking hard.
As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates
on wheel speed and controls braking pressure
accordingly.
Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal or always
decrease stopping distance.
If you get too close to the
vehicle
in front of you, you won’t have time to apply your
brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops.
Always leave enough room up ahead to stop, even
though you have anti-lock brakes.
Using Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
firmly and let anti-lock work for you. You may hear a
motor or clicking nosie during a hard stop, but this
is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
With anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the same
time. In many emergencies, steering can help you more
than even the very best braking.
Traction Control System (TCS)
Your vehicle may have a traction control system that
limits wheel spin. This is especially useful in slippery
road conditions. The system operates only
if it senses
that one or both of the front wheels are spinning
or
beginning to lose traction. When this happens,
the system works the front brakes and reduces engine
power to limit wheel spin.
4-8
ProCarManuals.com
Page 199 of 387

To turn the system off,
press the TC button on the
center console.
The traction control system warning light will come on
and stay on. If the system is limiting wheel spin
when you press the button, the warning light will come
on
- but the system won’t turn off right away. It will
wait until there’s no longer a current need
to limit
wheel spin.
You can turn the system back on at any time by
pressing the button again. The traction control system
warning light should go
off.
Steering
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine
stops or the system is not functioning, you can steer but
it will take much more effort.
Magnetic-Speed Variable Assist
Steering
Your vehicle is equipped with a steering system that
continuously adjusts the effort you feel when steering at
all vehicle speeds. It provides ease when parking,
yet
a firm, solid feel at highway speeds.
4-1 0
ProCarManuals.com
Page 200 of 387

Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves.
The traction of the tires against the road surface makes
it possible for the vehicle to change its path when
you turn the front wheels. If there’s no traction, inertia
will keep the vehicle going in the same direction. If
you’ve ever tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll
understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While
you’re in a curve, speed is the one factor you can
control.
Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then
~II slddenly accelerate. Both control systems -
steering and acceleration - have to do their work where
the tires meet the road. Adding the sudden acceleration
can demand too much of those places. You can lose
control. See
Traction Control System (TCS) on page 4-8.
What should you do if this ever happens? Ease up on
the accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way you
want
it to go, and slow down.
If you have Stabilitrak@, you may see the STABILITY
ACTIVE message on the Driver Information Center. See
“Stability Active Message” under
DIC Warnings and
Wlessages on page
3-50.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds
are based on good weather and road conditions. Under
less favorable conditions you’ll want to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed
so you can “drive” through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait to
accelerate until you are out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
4-1 1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 201 of 387

Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective
than braking. For example, you come over a hill and find
a truck stopped
in your lane, or a car suddenly pulls
out from nowhere, or a child darts out from between
parked cars and stops right in front of you.
You
can avoid these problems by braking - if you can stop
in time. But sometimes you can’t; there isn’t room.
That’s the time for evasive action
- steering around the
problem.
Your vehicle can perform very well in emergencies like
these. First apply your brakes.
See
Braking on page 4-6. It is better to remove as much
speed as you can from a possible collision. Then
steer around the problem, to the left or right depending
on the space available. An emergency
like this requires close attention and a
quick decision. If you are holding the steering wheel at
the recommended
9 and 3 o’clock positions, you
can turn it a full
180 degrees very quickly without
removing either hand. But you have
to act fast, steer
quickly, and just as quickly straighten the wheel
once you have avoided the object.
The fact that such emergency situations are always
possible is a good reason to practice defensive driving
at all times and wear safety belts properly.
4-1 2
ProCarManuals.com
Page 202 of 387

Off-Road Recovery
You may find that your right wheels have dropped off
the edge of a road onto the shoulder while you’re
driving. If
the level of the shoulder is only slightly below the
pavement, recovery should be fairly easy. Ease off the
accelerator and then, if there is nothing in the way,
steer
so that your vehicle straddles the edge of
the pavement. You can turn the steering wheel up to
one-quarter turn until the right front tire contacts
the pavement edge. Then turr! your steering wheel to
go
straight down the roadway.
Passing
The driver of a vehicle about to pass another on a
two-lane highway waits for just the right moment,
accelerates, moves around the vehicle ahead, then
goes back into the right lane again.
A simple maneuver?
Not necessarily! Passing another vehicle on a two-lane
highway is a potentially dangerous move, since the
passing vehicle occupies the same lane as oncoming
traffic for several seconds.
A miscalculation, an error in
judgment, or a brief surrender to frustration or anger
can suddenly put the passing driver face to face with the
worst of all traffic accidents
- the head-on collision.
4-1 3
ProCarManuals.com
Page 204 of 387

e e
e Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time 011
two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not flashing, it
may be slowing down or starting to turn.
If you’re being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little to the right.
LOSS of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes,
steering and acceleration) don’t have enough friction
where the tires meet the road to do what the driver has
asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to steer
and constantly seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited
to existing conditions, and by not
“overdriving” those conditions. But skids are always
possible.
The three types of skids correspond
to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling. In the steering or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip
and lose cornering force. And in the acceleration
skid, too much throttle causes the driving wheels
to spin.
A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.
Remember: Any traction control system helps avoid only
the acceleration skid. If your traction control system is
off, then an acceleration skid is also best handled
by easing your foot
off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot
off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go.
If you start steering quickly enough,
your vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid
if it occurs.
4-1 5
ProCarManuals.com