Page 3471 of 4179
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
ATC-75
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
AT C
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
Mode Door Motor
The mode door motor is attached to the heater & cooling unit. It
rotates so that air is discharged from the outlet set by the auto amp.
Motor rotation is conveyed to a link which activates the mode door.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FOR MODE DOOR MOTOR
SYMPTOM: Mode door motor does not operate normally.
Perform diagnostic procedure. Refer to AT C - 6 9 , "
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FOR LAN CIRCUIT" .
RJIA0513E
RJIA0514E
Page 3474 of 4179
ATC-78
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
Air Mix Door Motor
The air mix door motor is attached to the heater & cooling unit. It
rotates so that the air mix door is opened or closed to a position set
by the auto amp. The air mix door position is fed back to the auto
amp. by PBR built-in air mix door motor.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FOR AIR MIX DOOR MOTOR
SYMPTOM: Discharge air temperature does not change.
Perform diagnostic procedure. Refer to AT C - 6 9 , "
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FOR LAN CIRCUIT" .
RJIA0516E
RJIA0517E
Page 3492 of 4179
ATC-96
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Insufficient CoolingEJS004H2
SYMPTOM: Insufficient cooling
INSPECTION FLOW
*1ATC-65, "Operational Check".*2ATC-59, "FUNCTION CONFIRMA-
TION PROCEDURE", see No. 1.*3AT C - 5 9 , "
FUNCTION CONFIRMA-
TION PROCEDURE", see No. 5 to 7.
*4 QR engine; EM-13, "
Checking Drive
Belts" or YD engine; EM-131,
"Checking Drive Belts" .*5ATC-76, "
Air Mix Door Motor Circuit".*6ATC-100, "Test Reading (QR
Engine)" or ATC-101, "Test Reading
(YD Engine)" .
*7ATC-63, "
AUXILIARY MECHA-
NISM: TEMPERATURE SETTING
TRIMMER".*8ATC-59, "
FUNCTION CONFIRMA-
TION PROCEDURE", see No. 9.*9AT C - 6 9 , "
LAN System Circuit".
SJIA0408E
Page 3498 of 4179
ATC-102
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS FOR UNUSUAL PRESSURE
Whenever system’s high and/or low side pressure(s) is/are unusual, diagnose using a manifold gauge. The
marker above the gauge scale in the following tables indicates the standard (usual) pressure range. Since the
standard (usual) pressure, however, differs from vehicle to vehicle, refer to above table (Ambient air tempera-
ture-to-operating pressure table).
Both High- and Low-pressure Sides are Too High
High-pressure Side is Too High and Low-pressure Side is Too Low
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Both high- and low-pressure
sides are too high.Pressure is reduced soon after
water is splashed on con-
denser.Excessive refrigerant charge in
refrigeration cycleReduce refrigerant until speci-
fied pressure is obtained.
Air suction by cooling fan is
insufficient.Insufficient condenser cooling
performance
↓
1. Condenser fins are clogged.
2. Improper fan rotation of cool-
ing fan
�Clean condenser.
�Check and repair cooling fan
as necessary.
�Low-pressure pipe is not
cold.
�When compressor is stopped
high-pressure value quickly
drops by approximately 196
kPa (1.96 bar, 2 kg/cm
2 , 28
psi). It then decreases gradu-
ally thereafter.Poor heat exchange in con-
denser
(After compressor operation
stops, high-pressure decreases
too slowly.)
↓
Air in refrigeration cycleEvacuate repeatedly and
recharge system.
Engine tends to overheat.Engine cooling systems mal-
function.Check and repair each engine
cooling system.
�An area of the low-pressure
pipe is colder than areas
near the evaporator outlet.
�Plates are sometimes cov-
ered with frost.
�Excessive liquid refrigerant
on low-pressure side
�Excessive refrigerant dis-
charge flow
�Expansion valve is open a lit-
tle compared with the specifi-
cation.
↓
Improper expansion valve
adjustmentReplace expansion valve.
AC359A
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
High-pressure side is too high and
low-pressure side is too low.
Upper side of condenser and
high-pressure side are hot,
however, liquid tank is not so
hot.High-pressure tube or parts
located between compressor
and condenser are clogged or
crushed.
�Check and repair or replace
malfunctioning parts.
�Check lubricant for contami-
nation.
AC360A
Page 3500 of 4179
ATC-104
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Low-pressure Side Sometimes Becomes Negative
Low-pressure Side Becomes Negative
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Low-pressure side sometimes
becomes negative.
�Air conditioning system
does not function and does
not cyclically cool the com-
partment air.
�The system constantly func-
tions for a certain period of
time after compressor is
stopped and restarted.Refrigerant does not dis-
charge cyclically.
↓
Moisture is frozen at expan-
sion valve outlet and inlet.
↓
Water is mixed with refriger-
ant.
�Drain water from refrigerant
or replace refrigerant.
�Replace liquid tank.
AC354A
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Low-pressure side becomes nega-
tive.
Liquid tank or front/rear side of
expansion valve′s pipe is
frosted or dewed.High-pressure side is closed
and refrigerant does not flow.
↓
Expansion valve or liquid tank
is frosted.Leave the system at rest until
no frost is present. Start it
again to check whether or not
the malfunction is caused by
water or foreign particles.
�If water is the cause, initially
cooling is okay. Then the
water freezes causing a
blockage. Drain water from
refrigerant or replace refrig-
erant.
�If due to foreign particles,
remove expansion valve
and remove the particles
with dry and compressed air
(not shop air).
�If either of the above meth-
ods cannot correct the mal-
function, replace expansion
valve.
�Replace liquid tank.
�Check lubricant for contami-
nation.
AC362A
Page 3507 of 4179
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
ATC-111
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
AT C
COMPONENT INSPECTION
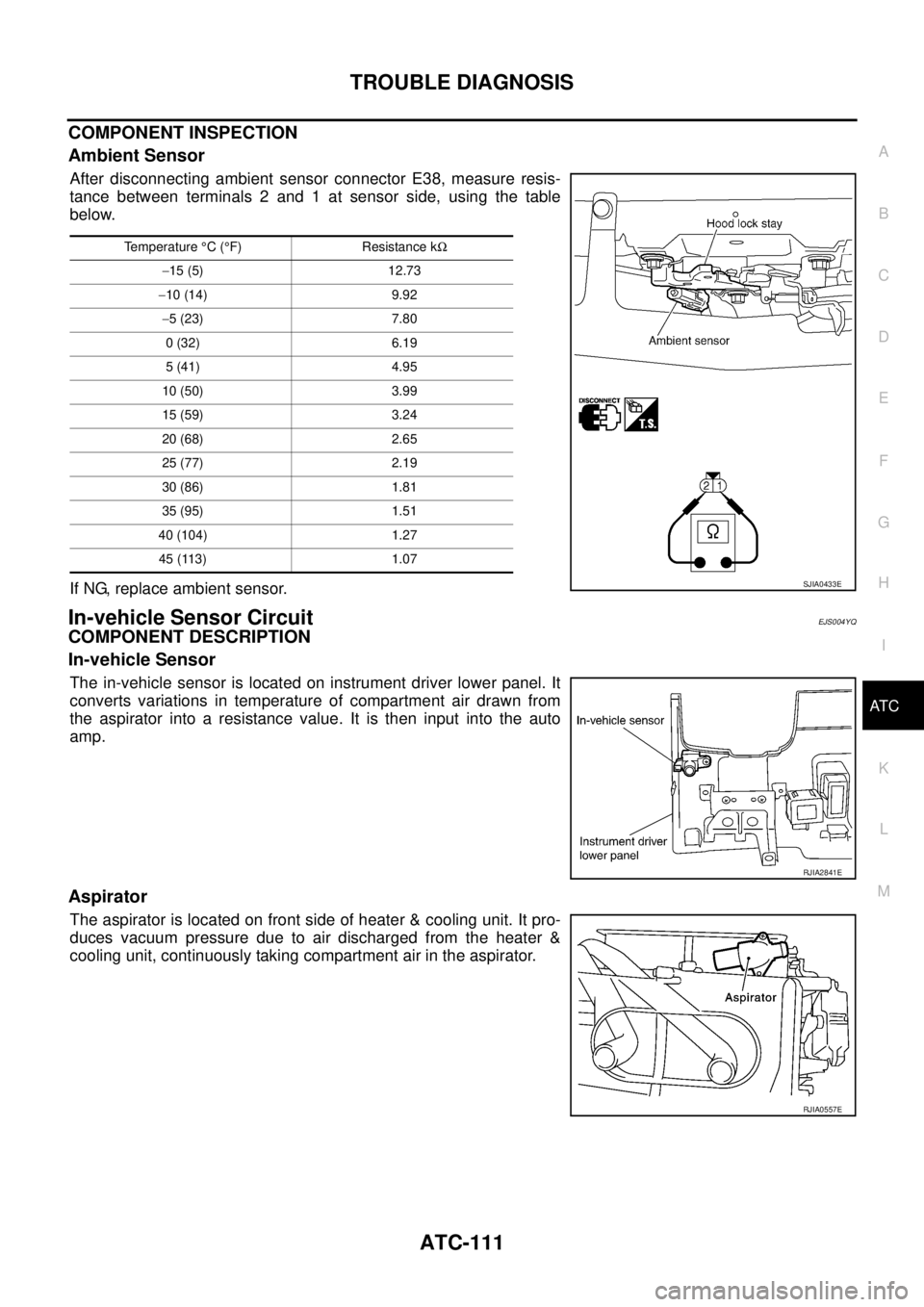
Ambient Sensor
After disconnecting ambient sensor connector E38, measure resis-
tance between terminals 2 and 1 at sensor side, using the table
below.
If NG, replace ambient sensor.
In-vehicle Sensor CircuitEJS004YQ
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
In-vehicle Sensor
The in-vehicle sensor is located on instrument driver lower panel. It
converts variations in temperature of compartment air drawn from
the aspirator into a resistance value. It is then input into the auto
amp.
Aspirator
The aspirator is located on front side of heater & cooling unit. It pro-
duces vacuum pressure due to air discharged from the heater &
cooling unit, continuously taking compartment air in the aspirator.
Temperature °C (°F) Resistance kΩ
−15 (5) 12.73
−10 (14) 9.92
−5 (23) 7.80
0 (32) 6.19
5 (41) 4.95
10 (50) 3.99
15 (59) 3.24
20 (68) 2.65
25 (77) 2.19
30 (86) 1.81
35 (95) 1.51
40 (104) 1.27
45 (113) 1.07
SJIA0433E
RJIA2841E
RJIA0557E
Page 3513 of 4179
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
ATC-117
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
AT C
Intake Sensor CircuitEJS004L6
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
Intake Sensor
The intake sensor is located on the heater & cooling unit. It converts
temperature of air after it passes through the evaporator into a resis-
tance value which is then input to the auto amp.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FOR INTAKE SENSOR
SYMPTOM: Intake sensor circuit is open or shorted.
LED of A/C switch does not illuminate as a result of performing self-
diagnosis STEP-2.
1. CHECK VOLTAGE BETWEEN INTAKE SENSOR AND GROUND
1. Disconnect intake sensor connector.
2. Turn ignition switch ON.
3. Check voltage between intake sensor harness connector M68 (Gasoline engine) or M69 (Diesel engine)
terminal 1 (BR/Y) and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> GO TO 4.
RJIA0051E
RJIA0567E
1 – Ground : Approx. 5V
RJIA0568E
Page 3522 of 4179
ATC-126
BLOWER UNIT
Disassembly and AssemblyEJS000UM
NOTE:
This illustration is for RHD models. The layout for LHD models is symmetrically opposite.
CAUTION:
If retaining tabs are damaged while disassembling blower unit,
use 9 screws (27111-2Y000) to assemble blower unit.
1. Fan control amplifier 2. Screw 3. Cooling hose
4. Blower motor assembly 5. Washer 6. Blower fan
7. Nut 8. Screw 9. Bell mouth
10. Intake door lever 2 11. Intake door lever 1 12. Intake door link
13. Intake door motor 14. Screw 15. Upper case 2
16. Intake door 2 17. Intake door 1 18. Upper case 1
19. Screw 20. Ventilation air filter 21. Filter cover
RJIA0053J
RJIA0097E