2003 NISSAN ALMERA N16 ecm
[x] Cancel search: ecmPage 1063 of 3189

SEF348N
When measuring ECM signals with a circuit tester, never
allow the two tester probes to contact.
Accidental contact of probes will cause a short circuit and
damage the ECM power transistor.
Do not use ECM ground terminals when measuring input/
output voltage. Doing so may result in damage to the
ECM’s transistor. Use a ground other than ECM terminals,
such as the ground.
Install the break-out box between ECM and ECM harness
connectors when measuring ECM input/output voltage.
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble DiagnosisNJEC0604When you read Wiring diagrams, refer to the following:
GI-12, “HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS”
EL-12, “POWER SUPPLY ROUTING” for power distribution circuit
When you perform trouble diagnosis, refer to the following:
GI-33, “HOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUPS IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES”
GI-22, “HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT”
GI
MA
EM
LC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
PRECAUTIONSYD
Precautions (Cont’d)
EC-9
Page 1070 of 3189
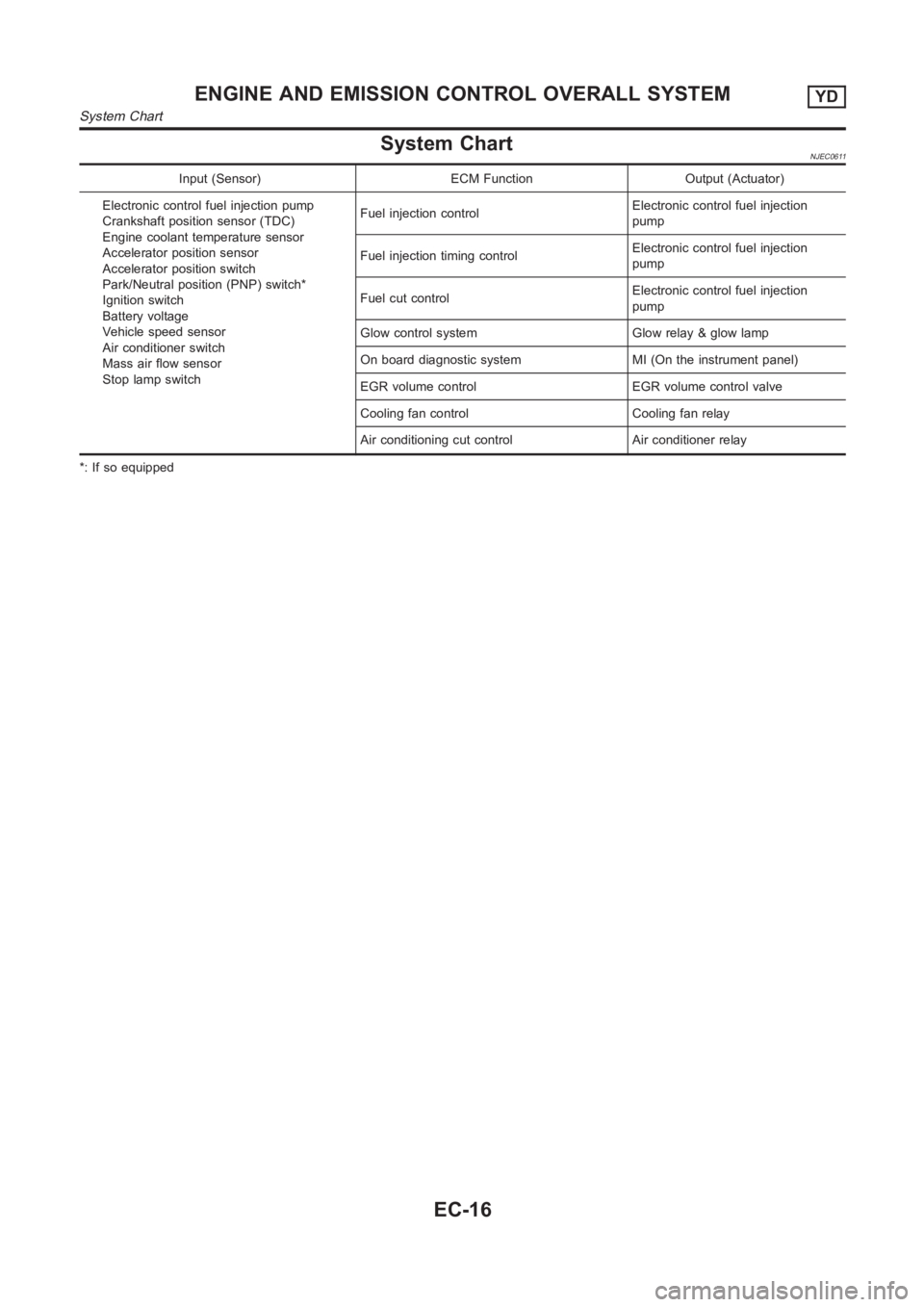
System ChartNJEC0611
Input (Sensor) ECM Function Output (Actuator)
Electronic control fuel injection pump
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Accelerator position sensor
Accelerator position switch
Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch*
Ignition switch
Battery voltage
Vehicle speed sensor
Air conditioner switch
Mass air flow sensor
Stop lamp switchFuel injection controlElectronic control fuel injection
pump
Fuel injection timing controlElectronic control fuel injection
pump
Fuel cut controlElectronic control fuel injection
pump
Glow control system Glow relay & glow lamp
On board diagnostic system MI (On the instrument panel)
EGR volume control EGR volume control valve
Cooling fan control Cooling fan relay
Air conditioning cut control Air conditioner relay
*: If so equipped
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMYD
System Chart
EC-16
Page 1071 of 3189

Fuel Injection Control System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0612System DescriptionNJEC0612S01Three types of fuel injection control are provided to accommodate engine operating conditions; normal control,
idle control and start control. The ECM determines the appropriate fuel injection control. Under each control,
the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance.
Pulse signals are exchanged between ECM and electronic control fuel injection pump (control unit is built-in).
The fuel injection pump control unit performs duty control on the spill valve (built into the fuel injection pump)
according to the input signals to compensate the amount of fuel injected tothe preset value.
Start ControlNJEC0612S02Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0201
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection
control (start
control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Ignition switch Start signal
SEF648S
When the ECM receives a start signal from the ignition switch, the ECM adapts the fuel injection system for
the start control. The amount of fuel injected at engine starting is a preset program value in the ECM. The
program is determined by the engine speed and engine coolant temperature.
For better startability under cool engine conditions, the lower the coolant temperature becomes, the greater
the amount of fuel injected. The ECM ends the start control when the engine speed reaches the specific value,
and shifts the control to the normal or idle control.
Idle ControlNJEC0612S03Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0301
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection
control (Idle con-
trol)Electronic control fuel
injection pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Battery Battery voltage
Accelerator position switch Idle position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner signal
When the ECM determines that the engine speed is at idle, the fuel injectionsystem is adapted for the idle
control. The ECM regulates the amount of fuel injected corresponding to changes in load applied to the engine
to keep engine speed constant. The ECM also provides the system with a fast idle control in response to the
engine coolant temperature signal.
GI
MA
EM
LC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Fuel Injection Control System
EC-17
Page 1072 of 3189

Normal ControlNJEC0612S04Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0401
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speedFuel injection
control (Normal
control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump
Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
SEF649S
The amount of fuel injected under normal driving conditions is determinedaccording to sensor signals. The
crankshaft position sensor (TDC) detects engine speed and the accelerator position sensor detects accelera-
tor position. These sensors send signals to the ECM.
The fuel injection data, predetermined by correlation between various engine speeds and accelerator positions,
are stored in the ECM memory, forming a map. The ECM determines the optimal amount of fuel to be injected
using the sensor signals in comparison with the map.
Maximum Amount ControlNJEC0612S05Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0501
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Fuel injection
control (Maxi-
mum amount
control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump Engine coolnat temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
The maximum injection amount is controlled to an optimum by the engine speed, intake air amount, engine
coolant temperature, and accelerator opening in accordance with the driving conditions.
This prevents the oversupply of the injection amount caused by decreased air density at a high altitude or
during a system failure.
Deceleration ControlNJEC0612S06Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0601
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Accelerator position switch Accelerator positionFuel injection
control (Decel-
eration control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
The ECM sends a fuel cut signal to the electronic control fuel injection pump during deceleration for better
fuel efficiency. The ECM determines the time of deceleration according tosignals from the accelerator posi-
tion switch and crankshaft position sensor (TDC).
Fuel Injection Timing Control System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0613The target fuel injection timing in accordance with the engine speed and the fuel injection amount are recorded
as a map in the ECM beforehand. The ECM and the injection pump control unit exchange signals and per-
form feedback control for optimum injection timing in accordance with themap.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Fuel Injection Control System (Cont’d)
EC-18
Page 1073 of 3189

Air Conditioning Cut Control
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0614Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0614S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner “ON” signal
Air conditioner
cut controlAir conditioner relay Accelerator position sensor Accelerator valve opening angle
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
System DescriptionNJEC0614S02This system improves acceleration when the air conditioner is used.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the air conditioner is turned off for a few seconds.
When engine coolant temperature becomes excessively high, the air conditioner is turned off. This continues
until the engine coolant temperature returns to normal.
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed)
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0615Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0615S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Fuel cut controlElectronic control fuel
injection pump Accelerator position switch Accelerator position
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
If the engine speed is above 2,800 rpm with no load (for example, in neutral and engine speed over 2,800
rpm) fuel will be cut off after some time. The exact time when the fuel is cut off varies based on engine speed.
Fuel cut will operate until the engine speed reaches 1,500 rpm, then fuel cut is cancelled.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control listed under “Fuel Injection Control System”, EC-17.
SEF440Z
Crankcase Ventilation System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0616In this system, blow-by gas is sucked into the air duct after oil
separation by oil separator in the rocker cover.
GI
MA
EM
LC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Air Conditioning Cut Control
EC-19
Page 1088 of 3189

DTC and MI Detection LogicNJEC0626When a malfunction is detected, the malfunction (DTC) is stored in the ECM memory.
The MI will light up each time the ECM detects malfunction. For diagnostic items causing the MI to light up,
refer to “TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INDEX”, EC-4.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)NJEC0627HOW TO READ DTCNJEC0627S01The DTC can be read by the following methods.
Without CONSULT-II
ECM displays the DTC by a set of four digit numbers with MI illumination in the diagnostic test mode II (Self-
diagnostic results). Example: 0103, 0807, 1002, etc.
With CONSULT-II
CONSULT-II displays the DTC in “SELF-DIAG RESULTS” mode. Examples: P0115, P0571, P1202, etc.
These DTCs are prescribed by ISO15031-6.
(CONSULT-II also displays the malfunctioning component or system.)
Output of the trouble code means that the indicated circuit has a malfunction. However, in the Mode
II it does not indicate whether the malfunction is still occurring or occurred in the past and returned
to normal.
CONSULT-II can identify them. Therefore, using CONSULT-II (if available) is recommended.
HOW TO ERASE DTCNJEC0627S02How to Erase DTC (With CONSULT-II)NJEC0627S02011. If the ignition switch stays “ON” after repair work, be sure to turn ignition switch “OFF” once. Wait at least
5 seconds and then turn it “ON” (engine stopped) again.
2. Touch “ENGINE”.
3. Touch “SELF-DIAG RESULTS”.
4. Touch “ERASE”. (The DTC in the ECM will be erased.)
SEF246Z
The emission related diagnostic information in the ECM can be erased by selecting “ERASE” in the “SELF-
DIAG RESULTS” mode with CONSULT-II.
How to Erase DTC (Without CONSULT-II)NJEC0627S02021. If the ignition switch stays “ON” after repair work, be sure to turn ignition switch “OFF” once. Wait at least
5 seconds and then turn it “ON” (engine stopped) again.
2. Change the diagnostic test mode from Mode II to Mode I by using the data link connector. (See EC-36.)
The emission related diagnostic information in the ECM can be erased by changing the diagnostic test mode.
If the battery is disconnected, the emission-related diagnostic information will be lost after approx.
24 hours.
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
DTC and MI Detection Logic
EC-34
Page 1089 of 3189

Erasing the emission-related diagnostic information using CONSULT-II is easier and quicker than
switching the diagnostic test mode using the data link connector.
Malfunction Indicator (MI)
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0628
SAT652J
The MI is located on the instrument panel.
1. The MI will light up when the ignition switch is turned ON without the engine running. This is a bulb check.
If the MI does not light up, refer to EL-129, EL-129, “WARNING LAMPS” or see EC-213.
2. When the engine is started, the MI should go off.
If the MI remains on, the on board diagnostic system has detected an engine system malfunction.
If MI illuminates or blinks irregularly after starting engine, water may have accumulated in fuel filter.
Drain water from fuel filter. Refer to “WATER DRAINING”, EC-32.
On Board Diagnostic System FunctionNJEC0628S01The on board diagnostic system has the following three functions.
Diagnostic Test
ModeKEY and ENG.
StatusFunction Explanation of Function
Mode I Ignition switch in
ON position
Engine stopped
BULB CHECK This function checks the MI bulb for damage (blown,
open circuit, etc.).
If the MI does not come on, check MI circuit. (See
EC-213.)
Engine running
MALFUNCTION
WARNINGThis is a usual driving condition. When ECM detects a
malfunction, the MI will light up to inform the driver that
a malfunction has been detected.
Mode II Ignition switch in
ON position
Engine stopped
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULTS This function allows DTCs to be read.
GI
MA
EM
LC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) (Cont’d)
EC-35
Page 1091 of 3189

Diagnostic Test Mode I — Bulb CheckNJEC0628S03In this mode, the MI on the instrument panel should stay ON. If it remains OFF, check the bulb. Refer to EL-129,
EL-129, “WARNING LAMPS” or see EC-213.
Diagnostic Test Mode I — Malfunction WarningNJEC0628S04
MI Condition
ON When the malfunction is detected or the ECM’s CPU is malfunctioning.
OFF No malfunction.
Diagnostic Test Mode II — Self-diagnostic ResultsNJEC0628S05In this mode, DTC is indicated by the number of blinks of the MI as shown below.
SEF298QA
SEF162PB
Long (0.6 second) blinking indicates the two LH digits of number and short (0.3 second) blinking indicates the
two RH digits of number. For example, the MI blinks 10 times for 6 seconds (0.6 sec x 10 times) and then it
blinks three times for about 1 second (0.3 sec x 3 times). This indicates theDTC “1003”.
In this way, all the detected malfunctions are classified by their DTC numbers. The DTC “0505” refers to no
malfunction. (See TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INDEX, EC-4.)
How to Erase Diagnostic Test Mode II (Self-diagnostic results)NJEC0628S06The DTC can be erased from the backup memory in the ECM when the diagnostic test mode is changed from
Diagnostic Test Mode II to Diagnostic Test Mode I. (Refer to “How to Switch Diagnostic Test Modes”, EC-36.)
If the battery terminal is disconnected, the DTC will be lost from the backup memory within 24
hours.
Be careful not to erase the stored memory before starting trouble diagnoses.
GI
MA
EM
LC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Malfunction Indicator (MI) (Cont’d)
EC-37