2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Drivetrain
[x] Cancel search: DrivetrainPage 17 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - ENGINE OIL - DIESEL
ENGINES
Use only Diesel Engine Oil meeting standardMIL-
2104Cor API ClassificationCD or higherorCCML
D4, D5.
SAE VISCOSITY GRADE
CAUTION: Low viscosity oils must have the proper
API quality or the CCMC G5 designation.
To assure of properly formulated engine oils, it is
recommended that SAE Grade 10W-40 engine oils
that meet Chrysler material standard MS-6395, be
used. European Grade 10W-40 oils are also accept-
able.
Oils of the SAE 5W-40 or 8W-80 grade number are
preferred when minimum temperatures consistently
fall below -12ÉC.
OPERATION - AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID
The automatic transmission fluid is selected based
upon several qualities. The fluid must provide a high
level of protection for the internal components by
providing a lubricating film between adjacent metal
components. The fluid must also be thermally stable
so that it can maintain a consistent viscosity through
a large temperature range. If the viscosity stays con-
stant through the temperature range of operation,
transmission operation and shift feel will remain con-
sistent. Transmission fluid must also be a good con-
ductor of heat. The fluid must absorb heat from the
internal transmission components and transfer that
heat to the transmission case.
FLUID FILL/CHECK
LOCATIONS
INSPECTION - FLUID FILL/CHECK LOCATIONS
The fluid fill/check locations and lubrication points
are located in each applicable group.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
DESCRIPTION
9Maintenance Schedule Information not included in
this section, is located in the appropriate Owner's
Manual.9
LIFT POINTS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOISTING AND
JACKING RECOMMENDATIONS
FLOOR JACK
When properly positioned, a floor jack can be used
to lift a WJ vehicle (Fig. 7). Support the vehicle in
the raised position with jack stands at the front and
rear ends of the frame rails.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to lift a vehicle with a
floor jack positioned under:
²An axle tube.
²Aluminum differential.
²A body side sill.
²A steering linkage component.
²A drive shaft.
²The engine or transmission oil pan.
²The fuel tank.
²A front suspension arm.
HOIST
A vehicle can be lifted with:
²A single-post, frame-contact hoist.
²A twin-post, chassis hoist.
²A ramp-type, drive-on hoist.
NOTE: When a frame-contact type hoist is used,
verify that the lifting pads are positioned properly
(Fig. 7).
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN A CHASSIS OR DRIVETRAIN COMPO-
NENT IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE
CENTER OF GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME
HOISTING CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY
SUPPORT OR SECURE VEHICLE TO HOISTING
DEVICE WHEN THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEWJ
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
Page 51 of 2199

PROPELLER SHAFT - FRONT
REMOVAL
NOTE: Different length propeller shafts are used for
different drivetrain applications. Ensure that the
correct propeller shaft is used.
(1) Place vehicle on floor or drive-on hoist with full
weight of vehicle on suspension.
(2) Shift the transmission and transfer case, if nec-
essary, into the Neutral position.
(3) Measure the distance from the face of the C/V
joint cup to the end of the C/V joint boot (Fig. 8).
(4) The correct length is 142.7 mm (5.61 in.).
NOTE: If the measurement is not correct, the wrong
shaft may have been installed or a mating compo-
nent (front axle or transfer case) may be installed
incorrectly. Investigate and correct as necessary.
(5) Mark a line across the companion flange at the
transfer case and C/V joint at the rear of the front
propeller shaft for installation reference.
(6) Mark a line across the C/V joints and the pin-
ion companion flanges for installation reference.
(7) Remove bolts from the front C/V joint to the
pinion companion flange.
(8) Remove bolts from the rear C/V joint to the
transfer case companion flange.
(9) Push the propeller shaft forward to clear trans-
fer case companion flange and remove the shaft.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Different length propeller shafts are used for
different drivetrain applications. Ensure that the
correct propeller shaft is used.
(1) Install the shaft between companion flanges.
(2) The shaft should rotate freely in the pinion
flange.
(3) Align marks on the companion flanges with the
marks on the C/V joints.
(4) Install bolts to the front C/V joint and tighten
bolts to 32 N´m (24 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install the bolts to the rear C/V joint and
tighten bolts to 32 N´m (24 ft. lbs.).
(6) Verify propeller shaft length.
(7) Lower vehicle.
PROPELLER SHAFT - FRONT
4.7L
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove crossmember/skid plate as necessary to
gain access to the propeller shaft.
(3) Shift transmission and transfer case, if neces-
sary into Neutral.
(4) Mark a line across the yoke at the transfer
case, link yoke and propeller shaft yoke at the rear of
the front propeller shaft for installation reference
(Fig. 9).
(5) Mark a line across the propeller shaft yoke and
pinion shaft yoke for installation reference.
Fig. 8 MEASUREMENT
1 - C/V JOINT CUP
2 - C/V BOOT END
3 - MEASUREMENT
Fig. 9 REFERENCE MARKS ON YOKES
1 - REFERENCE MARKS
3 - 6 PROPELLER SHAFTWJ
Page 661 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS
All circuits in the diagrams use an alpha/numeric
code to identify the wire and it's function. To identify
which circuit code applies to a system, refer to the
Circuit Identification Code Chart. This chart shows
the main circuits only and does not show the second-
ary codes that may apply to some models.
CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION CODE CHART
CIRCUIT FUNCTION
A BATTERY FEED
B BRAKE CONTROLS
C CLIMATE CONTROLS
D DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUITS
E DIMMING ILLUMINATION
CIRCUITS
F FUSED CIRCUITS
G MONITORING CIRCUITS
(GAUGES)
H OPEN
I NOT USED
J OPEN
K POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE
L EXTERIOR LIGHTING
M INTERIOR LIGHTING
N NOT USED
O NOT USED
P POWER OPTION (BATTERY
FEED)
Q POWER OPTIONS (IGNITION
FEED)
R PASSIVE RESTRAINT
S SUSPENSION/STEERING
T TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
TRANSFER CASE
U OPEN
V SPEED CONTROL, WIPER/
WASHER
W OPEN
X AUDIO SYSTEMS
Y OPEN
Z GROUNDS
DESCRIPTION - SECTION IDENTIFICATION AND
INFORMATION
The wiring diagrams are grouped into individual
sections. If a component is most likely found in a par-
ticular group, it will be shown complete (all wires,
connectors, and pins) within that group. For exam-
ple, the Auto Shutdown Relay is most likely to be
found in Group 30, so it is shown there complete. It
can, however, be shown partially in another group if
it contains some associated wiring.
Splice diagrams in Section 8W-70 show the entire
splice and provide references to other sections the
splices serves. Section 8W-70 only contains splice dia-
grams that are not shown in their entirety some-
where else in the wiring diagrams.
Section 8W-80 shows each connector and the cir-
cuits involved with that connector. The connectors
are identified using the name/number on the dia-
gram pages.
WIRING SECTION CHART
GROUP TOPIC
8W-01 thru
8W-09General information and Diagram
Overview
8W-10 thru
8W-19Main Sources of Power and
Vehicle Grounding
8W-20 thru
8W-29Starting and Charging
8W-30 thru
8W-39Powertrain/Drivetrain Systems
8W-40 thru
8W-49Body Electrical items and A/C
8W-50 thru
8W-59Exterior Lighting, Wipers and
Trailer Tow
8W-60 thru
8W-69Power Accessories
8W-70 Splice Information
8W-80 Connector Pin Outs
8W-91 Connector, Ground and Splice
Locations
8W - 01 - 6 8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATIONWJ
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1800 of 2199
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. It drives the mainshaft through the plan-
etary gear and range hub. The front output shaft is
operated by a drive chain that connects the shaft to a
drive sprocket on the mainshaft. The drive sprocket
is engaged/disengaged by the mode fork, which oper-
ates the mode sleeve and hub. The sleeve and hub
are not equipped with a synchro mechanism for shift-
ing.
OPERATING RANGES
NV242 operating ranges are 2WD (2-wheel drive),
4x4 part-time, 4x4 full time, and 4 Lo.
The 2WD and 4x4 full time ranges can be used at
any time and on any road surface.
The 4x4 part-time and 4 Lo ranges are for off road
use only. The only time these ranges can be used on
hard surface roads, is when the surface is covered
with snow and ice.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case shift linkage
binding.1) Repair or replace linkage as
necessary.
2) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 2) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
3) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Transfer case will not shift through
4X4 part time range (light remains
on)1) Incomplete shift due to drivetrain
torque load.1) Momentarily release the
accelerator pedal to complete the
shift.
2) Incorrect tire pressure. 2) Correct tire pressure as
necessary.
3) Excessive Tire wear. 3) Correct tire condition as
necessary.
4) Excessive vehicle loading. 4) Correct as necessary.
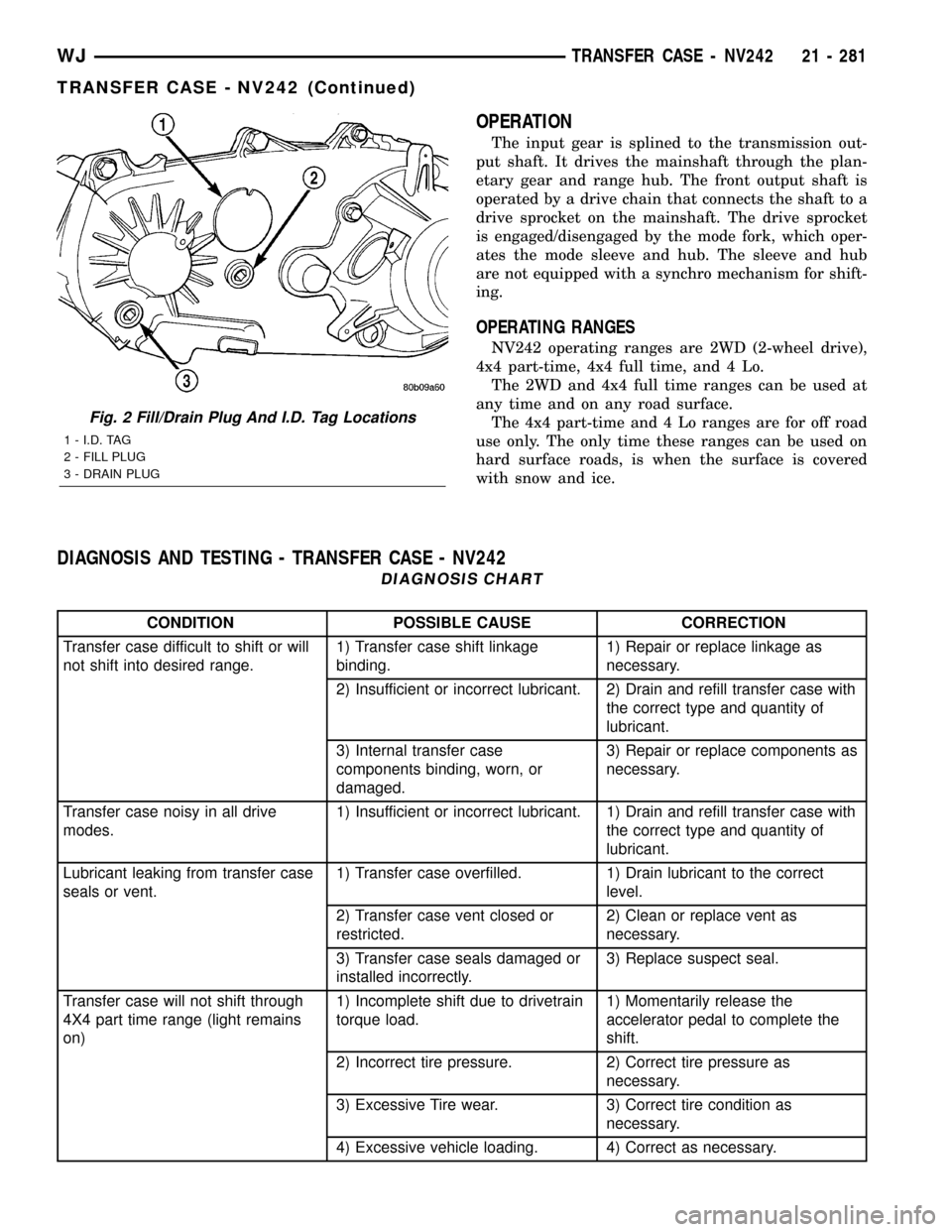
Fig. 2 Fill/Drain Plug And I.D. Tag Locations
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 281
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1843 of 2199

(2) Remove retainer (Fig. 28).
(3) Remove front tabbed thrust washer (Fig. 29).
(4) Remove input gear (Fig. 30).
(5) Remove rear tabbed thrust washer from low
range gear (Fig. 31).
CLEANING
Clean the transfer case components with parts
cleaning solvent. Flush the oil passages in the cases
and drivetrain components with solvent. This will
help remove dirt and particles from these passages.
Dry the transfer case components with compressed
air or allow them to air dry on clean shop towels.
Apply compressed air through all oil passages in
the cases and gear components to clear them of any
residue.
INSPECTION
MAINSHAFT
Examine the mainshaft components carefully for
evidence of wear or damage.
Replace the thrust washers if worn or damaged.
Replace the mainshaft and sprocket gears if the
teeth or gear bores are worn or damaged.
Replace the mainshaft bearings if worn, flat spot-
ted, brinelled, or damaged in any way.
Replace the mainshaft if it is bent, exhibits wear or
damage to the bearing surfaces, splines or gear teeth.
Fig. 28 Input Gear Retainer
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - LOW RANGE GEAR
3 - RETAINER
Fig. 29 Front Tabbed Thrust Washer
1 - FRONT TABBED THRUST WASHER
Fig. 30 Input Gear Removal
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - LOW RANGE GEAR
Fig. 31 Rear Tabbed Thrust Washer Removal
1 - LOW RANGE GEAR
2 - REAR TABBED THRUST WASHER
21 - 324 TRANSFER CASE - NV247WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV247 (Continued)
Page 1869 of 2199

SPARE TIRE
DESCRIPTION - SPARE / TEMPORARY TIRE
The temporary spare tire is designed for emer-
gency use only. The original tire should be repaired
or replaced at the first opportunity, then reinstalled.
Do not exceed speeds of 50 M.P.H. when using the
temporary spare tire. Refer to Owner's Manual for
complete details.
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION
The rim size is on the vehicle safety certification
label located on the drivers door shut face. The size
of the rim is determined by the drivetrain package.
Original equipment wheels/rims are designed for
operation up to the specified maximum vehicle capac-
ity.
All models use stamped steel, cast aluminum or
forged aluminum wheels. Every wheel has raised sec-
tions between the rim flanges and rim drop well
called safety humps (Fig. 18) .
Initial inflation of the tire forces the bead over
these raised sections. In case of rapid loss of air pres-
sure, the raised sections help hold the tire on the
wheel.
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. All aluminum and some steel wheels
have wheel stud nuts with an enlarged nose. This
enlarged nose is necessary to ensure proper retentionof the wheels. Do not use replacement studs or nuts
with a different design or lesser quality.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive run out
²Dents or cracks
²Damaged wheel lug nut holes
²Air Leaks from any area or surface of the rim
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they should be equivalent in
load carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset,
pilot hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the
same as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE. USED WHEELS ARE NOT RECOM-
MENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF THE WHEEL
MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREATMENT OR
VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD FAIL WITH-
OUT WARNING.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
REPLACEMENT
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. They must be replaced with equivalent
parts. Do not use replacement parts of lesser quality
or a substitute design. All aluminum and some steel
wheels have wheel stud nuts which feature an
enlarged nose. This enlarged nose is necessary to
ensure proper retention of the aluminum wheels.
NOTE: Do not use chrome plated lug nuts with
chrome plated wheels.
Before installing the wheel, be sure to remove any
build up of corrosion on the wheel mounting surfaces.
Ensure wheels are installed with good metal-to-metal
contact. Improper installation could cause loosening
of wheel nuts. This could affect the safety and han-
dling of your vehicle.
To install the wheel, first position it properly on
the mounting surface. All wheel nuts should then be
tightened just snug. Gradually tighten them in
sequence to the proper torque specification.Never
use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
Wheels must be replaced if they have:
²Excessive runout
Fig. 18 Safety Rim
1 - FLANGE
2 - RIDGE
3 - WELL
22 - 10 TIRES/WHEELSWJ