2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Electrical
[x] Cancel search: ElectricalPage 2169 of 2199
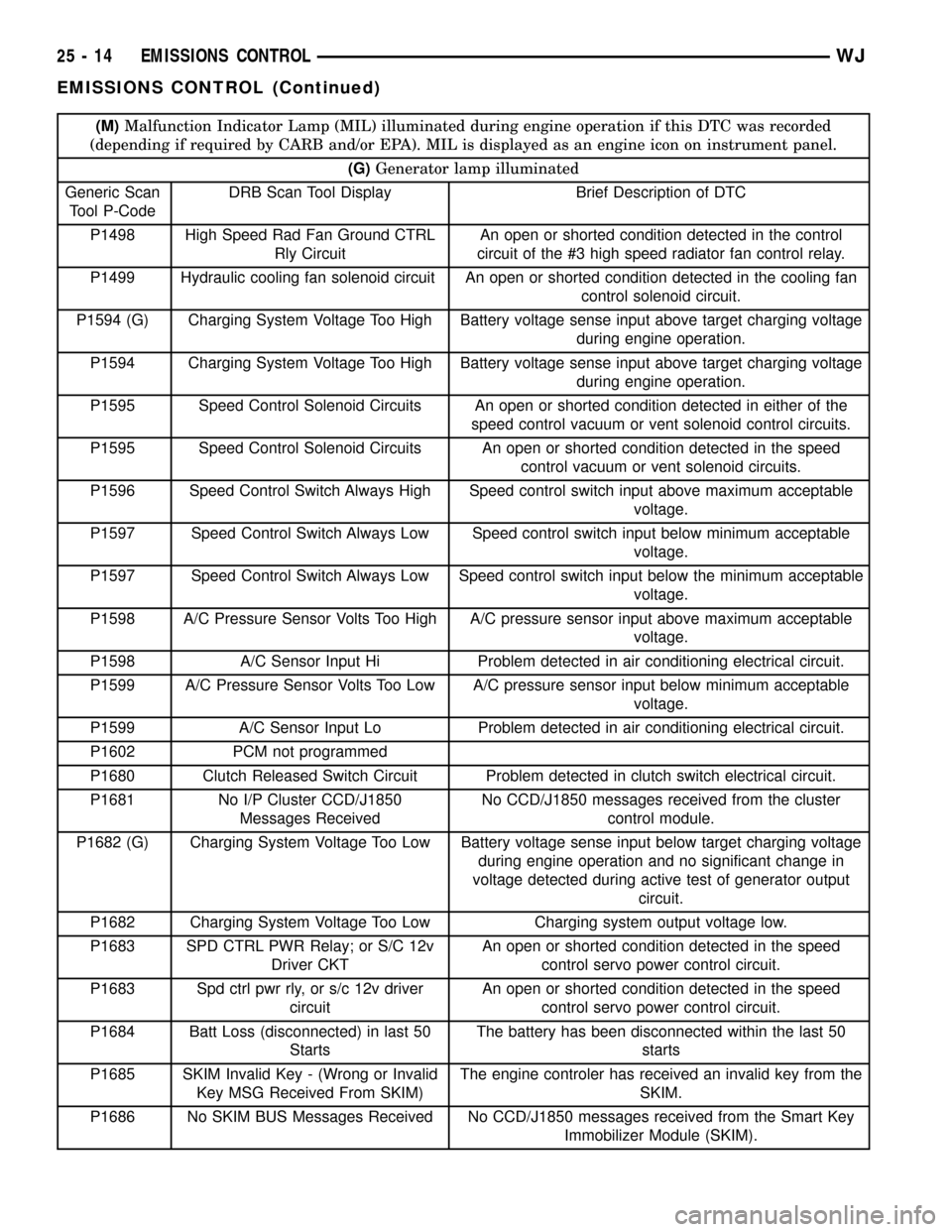
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1498 High Speed Rad Fan Ground CTRL
Rly CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the #3 high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1499 Hydraulic cooling fan solenoid circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the cooling fan
control solenoid circuit.
P1594 (G) Charging System Voltage Too High Battery voltage sense input above target charging voltage
during engine operation.
P1594 Charging System Voltage Too High Battery voltage sense input above target charging voltage
during engine operation.
P1595 Speed Control Solenoid Circuits An open or shorted condition detected in either of the
speed control vacuum or vent solenoid control circuits.
P1595 Speed Control Solenoid Circuits An open or shorted condition detected in the speed
control vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
P1596 Speed Control Switch Always High Speed control switch input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P1597 Speed Control Switch Always Low Speed control switch input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
P1597 Speed Control Switch Always Low Speed control switch input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P1598 A/C Pressure Sensor Volts Too High A/C pressure sensor input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P1598 A/C Sensor Input Hi Problem detected in air conditioning electrical circuit.
P1599 A/C Pressure Sensor Volts Too Low A/C pressure sensor input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
P1599 A/C Sensor Input Lo Problem detected in air conditioning electrical circuit.
P1602 PCM not programmed
P1680 Clutch Released Switch Circuit Problem detected in clutch switch electrical circuit.
P1681 No I/P Cluster CCD/J1850
Messages ReceivedNo CCD/J1850 messages received from the cluster
control module.
P1682 (G) Charging System Voltage Too Low Battery voltage sense input below target charging voltage
during engine operation and no significant change in
voltage detected during active test of generator output
circuit.
P1682 Charging System Voltage Too Low Charging system output voltage low.
P1683 SPD CTRL PWR Relay; or S/C 12v
Driver CKTAn open or shorted condition detected in the speed
control servo power control circuit.
P1683 Spd ctrl pwr rly, or s/c 12v driver
circuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the speed
control servo power control circuit.
P1684 Batt Loss (disconnected) in last 50
StartsThe battery has been disconnected within the last 50
starts
P1685 SKIM Invalid Key - (Wrong or Invalid
Key MSG Received From SKIM)The engine controler has received an invalid key from the
SKIM.
P1686 No SKIM BUS Messages Received No CCD/J1850 messages received from the Smart Key
Immobilizer Module (SKIM).
25 - 14 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2174 of 2199

and deteriorate engine performance, driveability and
fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3
good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, itdepends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.
If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks or any component that
has an associated limp in will set a fault after 1 trip
with the malfunction present. Components without
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 19
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2184 of 2199

INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
When installing fixed orifice fitting, be sure loca-
tions of fixed orifice fitting and air inlet fitting (Fig.
9) have not been inadvertently exchanged. The fixed
orifice fitting is light grey in color and is located at
rearof valve cover. The air inlet fitting is black in
color and is located atfrontof valve cover.
(1) Connect fitting to CCV breather tube.
(2) Return fixed orifice fitting to valve cover grom-
met.
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP can-
ister to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid.
OPERATION
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operat-
ing condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle evaporative (EVAP) canister purge
solenoid is located in the engine compartment near
the brake master cylinder (Fig. 10).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at solenoid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum lines at solenoid.
(3) Lift solenoid slot (Fig. 10) from mounting
bracket for removal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position solenoid slot to mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum lines to solenoid. Be sure vac-
uum lines are firmly connected and not leaking or
damaged. If leaking, a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) may be set with certain emission packages.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION
The plastic fuel tank filler tube cap is threaded
onto the end of the fuel fill tube. Certain models are
equipped with a 1/4 turn cap.
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of fuel filler tube
is prevented by the use of a pressure-vacuum fuel fill
cap. Relief valves inside the cap will release fuel tank
pressure at predetermined pressures. Fuel tank vac-
uum will also be released at predetermined values.
This cap must be replaced by a similar unit if
replacement is necessary. This is in order for the sys-
tem to remain effective.
CAUTION: Remove fill cap before servicing any fuel
system component to relieve tank pressure. If
equipped with a California emissions package and a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP), the cap must be tight-
ened securely. If cap is left loose, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
REMOVAL
If replacement of the 1/4 turn fuel tank filler tube
cap is necessary, it must be replaced with an identi-
cal cap to be sure of correct system operation.
Fig. 10 EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
1 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
2 - EVAP SOLENOID
3 - SLOT
4 - ELEC. CONNEC.
5 - VACUUM LINE CONNEC.
6 - TEST PORT
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 29
CCV HOSE (Continued)
Page 2185 of 2199

CAUTION: Remove the fuel tank filler tube cap to
relieve fuel tank pressure. The cap must be
removed prior to disconnecting any fuel system
component or before draining the fuel tank.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The evaporative emission system is designed to
prevent the escape of fuel vapors from the fuel sys-
tem (Fig. 11). Leaks in the system, even small ones,
can allow fuel vapors to escape into the atmosphere.
Government regulations require onboard testing to
make sure that the evaporative (EVAP) system is
functioning properly. The leak detection system tests
for EVAP system leaks and blockage. It also performs
self-diagnostics. During self-diagnostics, the Power-
train Control Module (PCM) first checks the Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) for electrical and mechanical
faults. If the first checks pass, the PCM then uses
the LDP to seal the vent valve and pump air into the
system to pressurize it. If a leak is present, the PCM
will continue pumping the LDP to replace the air
that leaks out. The PCM determines the size of the
leak based on how fast/long it must pump the LDP
as it tries to maintain pressure in the system.
EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM COMPONENTS
Service Port: Used with special tools like the Miller
Evaporative Emissions Leak Detector (EELD) to test
for leaks in the system.
EVAP Purge Solenoid: The PCM uses the EVAP
purge solenoid to control purging of excess fuel
vapors stored in the EVAP canister. It remains closed
during leak testing to prevent loss of pressure.
EVAP Canister: The EVAP canister stores fuel
vapors from the fuel tank for purging.
EVAP Purge Orifice: Limits purge volume.
EVAP System Air Filter: Provides air to the LDP
for pressurizing the system. It filters out dirt while
allowing a vent to atmosphere for the EVAP system.
Fig. 11 TYPICAL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1 - Throttle Body
2 - Service Vacuum Supply Tee (SVST)
3 - LDP Solenoid
4 - EVAP System Air Filter
5 - LDP Vent Valve
6 - EVAP Purge Orifice
7 - EVAP Purge Solenoid
8 - Service Port
9 - To Fuel Tank
10 - EVAP Canister
11 - LDP
12 - Intake Air Plenum
25 - 30 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
FUEL FILLER CAP (Continued)
Page 2186 of 2199

OPERATION
The main purpose of the LDP is to pressurize the
fuel system for leak checking. It closes the EVAP sys-
tem vent to atmospheric pressure so the system can
be pressurized for leak testing. The diaphragm is
powered by engine vacuum. It pumps air into the
EVAP system to develop a pressure of about 7.59
H2O (1/4) psi. A reed switch in the LDP allows the
PCM to monitor the position of the LDP diaphragm.
The PCM uses the reed switch input to monitor how
fast the LDP is pumping air into the EVAP system.
This allows detection of leaks and blockage. The LDP
assembly consists of several parts (Fig. 12). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM, and it connects the
upper pump cavity to either engine vacuum or atmo-
spheric pressure. A vent valve closes the EVAP sys-
tem to atmosphere, sealing the system during leak
testing. The pump section of the LDP consists of a
diaphragm that moves up and down to bring air in
through the air filter and inlet check valve, and
pump it out through an outlet check valve into the
EVAP system. The diaphragm is pulled up by engine
vacuum, and pushed down by spring pressure, as the
LDP solenoid turns on and off. The LDP also has a
magnetic reed switch to signal diaphragm position to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is down, the switch is
closed, which sends a 12 V (system voltage) signal to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is up, the switch is
open, and there is no voltage sent to the PCM. This
allows the PCM to monitor LDP pumping action as it
turns the LDP solenoid on and off.
LDP AT REST (NOT POWERED)
When the LDP is at rest (no electrical/vacuum) the
diaphragm is allowed to drop down if the internal
(EVAP system) pressure is not greater than the
return spring. The LDP solenoid blocks the engine
vacuum port and opens the atmospheric pressure
port connected through the EVAP system air filter.
The vent valve is held open by the diaphragm. This
allows the canister to see atmospheric pressure (Fig.
13).
DIAPHRAGM UPWARD MOVEMENT
When the PCM energizes the LDP solenoid, the
solenoid blocks the atmospheric port leading through
the EVAP air filter and at the same time opens the
engine vacuum port to the pump cavity above the
diaphragm. The diaphragm moves upward when vac-
uum above the diaphragm exceeds spring force. This
upward movement closes the vent valve. It also
causes low pressure below the diaphragm, unseating
the inlet check valve and allowing air in from the
EVAP air filter. When the diaphragm completes its
upward movement, the LDP reed switch turns from
closed to open (Fig. 14).
DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
Based on reed switch input, the PCM de-energizes
the LDP solenoid, causing it to block the vacuum
port, and open the atmospheric port. This connects
the upper pump cavity to atmosphere through the
EVAP air filter. The spring is now able to push the
diaphragm down. The downward movement of the
diaphragm closes the inlet check valve and opens the
outlet check valve pumping air into the evaporative
system. The LDP reed switch turns from open to
closed, allowing the PCM to monitor LDP pumping
(diaphragm up/down) activity (Fig. 15). During the
pumping mode, the diaphragm will not move down
far enough to open the vent valve. The pumping cycle
is repeated as the solenoid is turned on and off.
When the evaporative system begins to pressurize,
the pressure on the bottom of the diaphragm will
begin to oppose the spring pressure, slowing the
pumping action. The PCM watches the time from
when the solenoid is de-energized, until the dia-
phragm drops down far enough for the reed switch to
Fig. 12 EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
1 - Reed Switch
2 - Solenoid
3 - Spring
4 - Pump Cavity
5 - Diaphragm
6 - Inlet Check Valve
7 - Vent Valve
8 - From Air Filter
9 - To Canister
10 - Outlet Check Valve
11 - Engine Vacuum
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 31
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2188 of 2199

²No engine stall during test.
NOTE: IF BATTERY VOLTAGE DROPS BELOW 10
VOLTS FOR MORE THAN 5 SECONDS DURING
ENGINE CRANKING, THE EVAP LEAK DETECTION
TEST WILL NOT RUN.
NOTE: THE FOLLOWING VALUES ARE APPROXI-
MATE AND VEHICLE SPECIFIC. USE THE VALUES
SEEN IN PRE TEST/MONITOR TEST SCREEN ON
THE DRB IIIT. SEE TSB 25-02-98 FOR MORE
DETAIL.
A DTC will not be set if a one-trip fault is set or if
the MIL is illuminated for any of the following:
²Purge Solenoid Electrical Fault
²All TPS Faults
²All Engine Controller Self Test Faults
²LDP Pressure Switch Fault
²All Cam and/or Crank Sensor Fault
²EGR Solenoid Electrical Fault
²All MAP Sensor Faults
²All Injector Faults
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensor Electrical
Faults²Baro Out of Range
²Vehicle Speed Faults
²All Coolant Sensor Faults
²LDP Solenoid Circuit
NOTE: IF BATTERY TEMPERATURE IS NOT WITHIN
RANGE, OR IF THE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERA-
TURE IS NOT WITHIN A SPECIFIED RANGE OF THE
BATTERY TEMPERATURE, THE PCM WILL NOT
RUN TESTS FOR DTC P1494, P1486, P0442, P0455
AND P0441. THESE TEMPERATURE CALIBRATIONS
MAY BE DIFFERENT BETWEEN MODELS.
SECTION 1 - P1495 Leak Detection Pump
Solenoid Circuit-When the ignition key is turned
to9ON9, the LDP diaphragm should be in the down
position and the LDP reed switch should be closed. If
the EVAP system has residual pressure, the LDP dia-
phragm may be up. This could result in the LDP reed
switch being open when the key is turned to9ON9
and a P1494 fault could be set because the PCM is
expecting the reed switch to be closed.
After the key is turned9ON9, the PCM immedi-
ately tests the LDP solenoid circuit for electrical
faults. If a fault is detected, DTC P1495 will set, the
Fig. 15 DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Closed)
3 - Vent Valve (Closed)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Open)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Closed)EVAP LDP TEST SEQUENCE
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - LDP DIAPHRAM
3 - LDP SWITCH
4 - LDP SOLENOID
5 - SECTION 1
6 - SECTION 2
7 - SECTION 3
8 - SECTION 4
9 - SECTION 5
10 - 3 TEST CYCLES TO TEST FOR BLOCKAGE
11- RAPID PUMP CYCLING FOR 70 CYCLES
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 33
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2190 of 2199

set a temporary fault without turning on the MIL
and continue the leak portion of the test. However,
the PCM will assume that the system is already
pressurized and skip the rapid pump cycles.
Always diagnose leaks, if possible, before discon-
necting connections. Disconnecting connections may
mask a leak condition.
Keep in mind that if the purge solenoid seat is
leaking, it could go undetected since the leak would
end up in the intake manifold. Disconnect the purge
solenoid at the manifold when leak checking. In addi-
tion, a pinched hose fault (P1486) could set if the
purge solenoid does not purge the fuel system prop-
erly (blocked seat). The purge solenoid must vent the
fuel system prior to the LDP system test. If the
purge solenoid cannot properly vent the system the
LDP cannot properly complete the test for P1486 and
this fault can set due to pressure being in the EVAP
system during the test sequence.
Multiple actuation's of the DRB IIItLeak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP) Monitor Test can hide a 0.020 leak
because of excess vapor generation. Additionally, any
source for additional vapor generation can hide a
small leak in the EVAP system. Excess vapor gener-
ation can delay the fall of the LDP diaphragm thus
hiding the small leak. An example of this condition
could be bringing a cold vehicle into a warm shop for
testing or high ambient temperatures.
Fully plugged and partially plugged underhood
vacuum lines have been known to set MIL condi-
tions. P1494 and P0456 can be set for this reason.
Always, thoroughly, check plumbing for pinches or
blockage before condemning components.
TEST EQUIPMENT The Evaporative Emission
Leak Detector (EELD) Miller Special Tool 8404 is
capable of visually detecting leaks in the evaporative
system and will take the place of the ultrasonic leak
detector 6917A. The EELD utilizes shop air and a
smoke generator to visually detect leaks down to
0.020 or smaller. The food grade oil used to make the
smoke includes an UV trace dye that will leave tell-
tale signs of the leak under a black light. This is
helpful when components have to be removed to
determine the exact leak location. For detailed test
instructions, follow the operators manual packaged
with the EELD.
NOTE: Be sure that the PCM has the latest software
update. Reprogram as indicated by any applicable
Technical Service Bulletin. After LDP repairs are
completed, verify the repair by running the DRB IIIT
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) Monitor Test as
described in Technical Service Bulletin 18-12-99.REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is located under
the left quarter panel behind the left/rear wheel (Fig.
16). It is attached to a two-piece support bracket
(Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are replaced (ser-
viced) as one unit.
(1) Remove stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Drill out plastic rivets for removal.
(2) Remove 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17).
(4) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts at frame rail (Fig. 19).
(5) To separate and lower front section of two-piece
support bracket, remove 3 attaching bolts on bottom
of support bracket (Fig. 17). While lowering support
bracket, disconnect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(6) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP (Fig.
20).
(7) Carefully remove vapor/vacuum lines at LDP
(Fig. 20).
(8) Remove LDP.
INSTALLATION
The LDP is located in the left quarter panel behind
the left/rear wheel. It is attached to a two-piece sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are
replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Position LDP and carefully install vapor/vac-
uum lines to LDP and LDP filter.The vapor/vac-
uum lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Fig. 16 LOCATION, LDP / EVAP CANISTER
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
2 - EVAP CANISTER
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 35
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2192 of 2199

Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister purge solenoid for
damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
(2) Connect electrical connector to LDP.
(3) While raising front section of support bracket,
connect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(4) Install 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19). Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(5) Join front and rear sections of two-piece sup-
port bracket by installing 3 bolts on bottom of sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). Do not tighten bolts at this
time.
(6) Install support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17). Do
not tighten bolt at this time.
(7) Tighten 2 support bracket nuts at frame rail
(Fig. 19). Refer to Torque Specifications.
(8) Tighten 3 support bracket bolts and brace bolt.
Refer to Torque Specifications.
(9) Position stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Install new plastic rivets.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister. Certain ORVR components can be
found in (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled. Cer-
tain ORVR components can be found in (Fig. 1).
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,
the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 21) by discon-
necting rubber connecting hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward until locating tabs have been
freed at cam lock (Fig. 21). After tabs have cleared,
pull valve straight out from filler tube.To prevent
damage to PCV valve locating tabs, valve must
be pointed downward for removal. Do not force
valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 21). Also, PCV valve should rattle when
shaken.
(4) Reconnect PCV valve to its connecting line/
hose.
(5) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(6) If valve is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through valve. Also, a strong vac-
uum should be felt with a finger placed at valve
inlet.
(7) If vacuum is not felt at valve inlet, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at rear of manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out the
fitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 37
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)