2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE compress
[x] Cancel search: compressPage 1669 of 2199
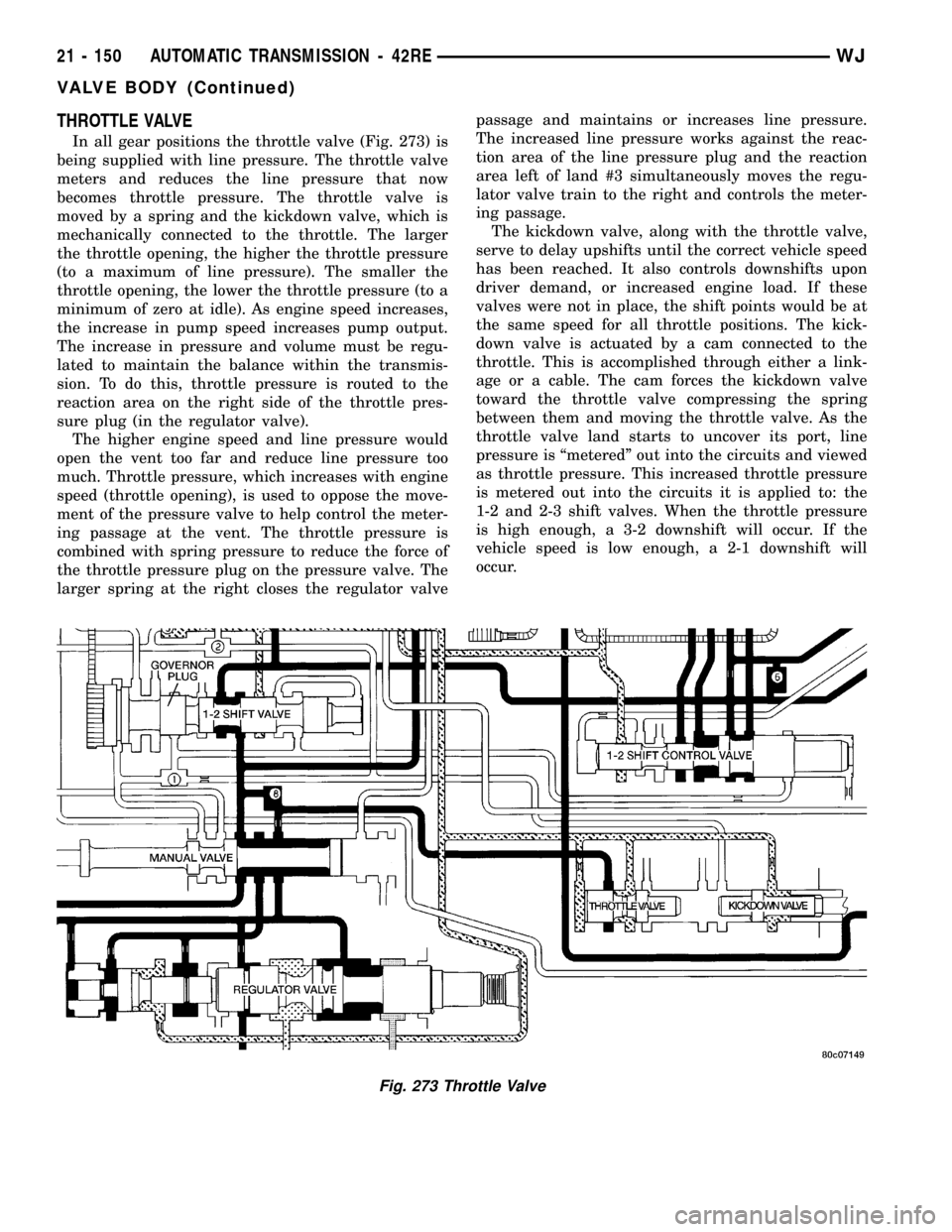
THROTTLE VALVE
In all gear positions the throttle valve (Fig. 273) is
being supplied with line pressure. The throttle valve
meters and reduces the line pressure that now
becomes throttle pressure. The throttle valve is
moved by a spring and the kickdown valve, which is
mechanically connected to the throttle. The larger
the throttle opening, the higher the throttle pressure
(to a maximum of line pressure). The smaller the
throttle opening, the lower the throttle pressure (to a
minimum of zero at idle). As engine speed increases,
the increase in pump speed increases pump output.
The increase in pressure and volume must be regu-
lated to maintain the balance within the transmis-
sion. To do this, throttle pressure is routed to the
reaction area on the right side of the throttle pres-
sure plug (in the regulator valve).
The higher engine speed and line pressure would
open the vent too far and reduce line pressure too
much. Throttle pressure, which increases with engine
speed (throttle opening), is used to oppose the move-
ment of the pressure valve to help control the meter-
ing passage at the vent. The throttle pressure is
combined with spring pressure to reduce the force of
the throttle pressure plug on the pressure valve. The
larger spring at the right closes the regulator valvepassage and maintains or increases line pressure.
The increased line pressure works against the reac-
tion area of the line pressure plug and the reaction
area left of land #3 simultaneously moves the regu-
lator valve train to the right and controls the meter-
ing passage.
The kickdown valve, along with the throttle valve,
serve to delay upshifts until the correct vehicle speed
has been reached. It also controls downshifts upon
driver demand, or increased engine load. If these
valves were not in place, the shift points would be at
the same speed for all throttle positions. The kick-
down valve is actuated by a cam connected to the
throttle. This is accomplished through either a link-
age or a cable. The cam forces the kickdown valve
toward the throttle valve compressing the spring
between them and moving the throttle valve. As the
throttle valve land starts to uncover its port, line
pressure is ªmeteredº out into the circuits and viewed
as throttle pressure. This increased throttle pressure
is metered out into the circuits it is applied to: the
1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. When the throttle pressure
is high enough, a 3-2 downshift will occur. If the
vehicle speed is low enough, a 2-1 downshift will
occur.
Fig. 273 Throttle Valve
21 - 150 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1684 of 2199
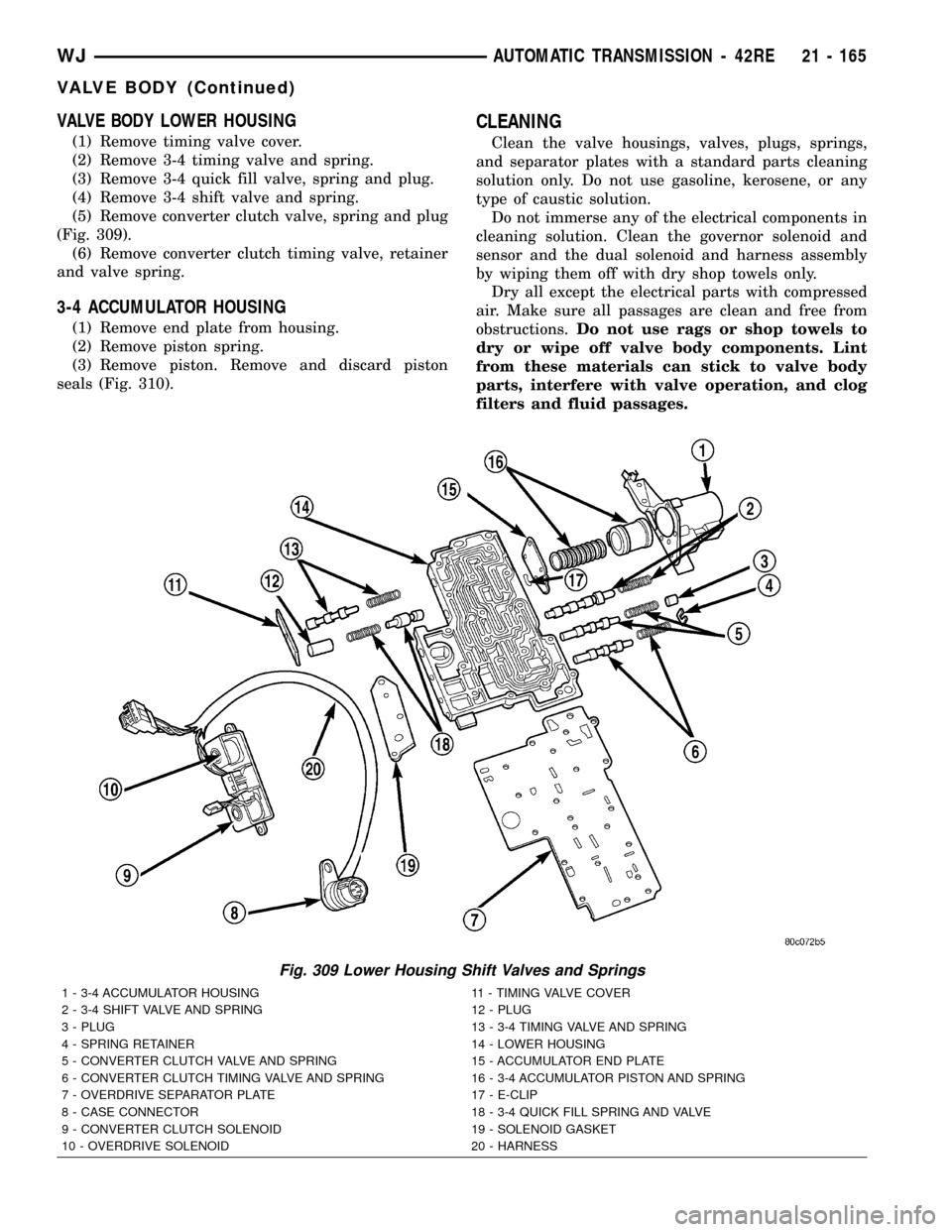
VALVE BODY LOWER HOUSING
(1) Remove timing valve cover.
(2) Remove 3-4 timing valve and spring.
(3) Remove 3-4 quick fill valve, spring and plug.
(4) Remove 3-4 shift valve and spring.
(5) Remove converter clutch valve, spring and plug
(Fig. 309).
(6) Remove converter clutch timing valve, retainer
and valve spring.
3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
(1) Remove end plate from housing.
(2) Remove piston spring.
(3) Remove piston. Remove and discard piston
seals (Fig. 310).
CLEANING
Clean the valve housings, valves, plugs, springs,
and separator plates with a standard parts cleaning
solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or any
type of caustic solution.
Do not immerse any of the electrical components in
cleaning solution. Clean the governor solenoid and
sensor and the dual solenoid and harness assembly
by wiping them off with dry shop towels only.
Dry all except the electrical parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and free from
obstructions.Do not use rags or shop towels to
dry or wipe off valve body components. Lint
from these materials can stick to valve body
parts, interfere with valve operation, and clog
filters and fluid passages.
Fig. 309 Lower Housing Shift Valves and Springs
1 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING 11 - TIMING VALVE COVER
2 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 12 - PLUG
3 - PLUG 13 - 3-4 TIMING VALVE AND SPRING
4 - SPRING RETAINER 14 - LOWER HOUSING
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE AND SPRING 15 - ACCUMULATOR END PLATE
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH TIMING VALVE AND SPRING 16 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR PISTON AND SPRING
7 - OVERDRIVE SEPARATOR PLATE 17 - E-CLIP
8 - CASE CONNECTOR 18 - 3-4 QUICK FILL SPRING AND VALVE
9 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID 19 - SOLENOID GASKET
10 - OVERDRIVE SOLENOID 20 - HARNESS
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 165
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1689 of 2199

(6) Install limit valve housing and cover plate.
Tighten screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.).
(7) Install shuttle valve as follows:
(a) Insert plastic guides in shuttle valve second-
ary spring and install spring on end of valve.
(b) Install shuttle valve into housing.
(c) Hold shuttle valve in place.
(d) Compress secondary spring and install E-clip
in groove at end of shuttle valve.
(e) Verify that spring and E-clip are properly
seated before proceeding.(8) Install shuttle valve cover plate. Tighten cover
plate screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install 1-2 and 2-3 valve governor plugs in
valve body.
(10) Install shuttle valve primary spring and
throttle plug.
(11) Align and install governor plug cover. Tighten
cover screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 319 Upper Housing Control Valve Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - REGULATOR VALVE 9 - 1-2 GOVERNOR PLUG
3 - SWITCH VALVE 10 - GOVERNOR PLUG COVER
4 - REGULATOR VALVE SPRING 11 - THROTTLE PLUG
5 - KICKDOWN VALVE 12 - 2-3 GOVERNOR PLUG
6 - KICKDOWN DETENT 13 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
7 - THROTTLE VALVE AND SPRING
21 - 170 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1692 of 2199

3-4 ACCUMULATOR
(1) Position converter clutch valve and 3-4 shift
valve springs in housing (Fig. 324).
(2) Loosely attach accumulator housing with right-
side screw (Fig. 324). Install only one screw at this
time as accumulator must be free to pivot upward for
ease of installation.
(3) Install 3-4 shift valve and spring.
(4) Install converter clutch timing valve and
spring.
(5) Position plug on end of converter clutch valve
spring. Then compress and hold springs and plug in
place with fingers of one hand.
(6) Swing accumulator housing upward over valve
springs and plug.
(7) Hold accumulator housing firmly in place and
install remaining two attaching screws. Be sure
springs and clutch valve plug are properly seated
(Fig. 325). Tighten screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.).
VALVE BODY FINAL
(1) Install boost valve, valve spring, retainer and
cover plate. Tighten cover plate screws to 4 N´m (35
in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Insert manual lever detent spring in upper
housing.
(3) Position detent ball on end of spring. Then hold
detent ball and spring in detent housing with
Retainer Tool 6583 (Fig. 326).(4) Install throttle lever in upper housing. Then
install manual lever over throttle lever and start
manual lever into housing.
(5) Align manual lever with detent ball and man-
ual valve. Hold throttle lever upward. Then press
down on manual lever until fully seated. Remove
detent ball retainer tool after lever is seated.
(6) Then install manual lever seal, washer and
E-clip.
(7) Verify that throttle lever is aligned with end of
kickdown valve stem and that manual lever arm is
engaged in manual valve (Fig. 327).
(8) Position line pressure adjusting screw in
adjusting screw bracket.
(9) Install spring on end of line pressure regulator
valve.
(10) Install switch valve spring on tang at end of
adjusting screw bracket.
(11) Install manual valve.
(12) Install throttle valve and spring.
(13) Install kickdown valve and detent.
(14) Install pressure regulator valve.
(15) Install switch valve.
(16) Position adjusting screw bracket on valve
body. Align valve springs and press bracket into
place. Install short, upper bracket screws first and
long bottom screw last. Verify that valve springs and
bracket are properly aligned. Then tighten all three
bracket screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(17) Perform Line Pressure and Throttle Pressure
adjustments. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC/VALVE BODY - ADJUST-
MENTS)
(18) Lubricate solenoid case connector O-rings and
shaft of manual lever with light coat of petroleum
jelly.
Fig. 324 Converter Clutch And 3-4 Shift Valve
Springs
1 - RIGHT-SIDE SCREW
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR
3 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE SPRING
4 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE SPRING
Fig. 325 Seating 3-4 Accumulator On Lower
Housing
1 - ACCUMULATOR BOX
2 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE PLUG
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 173
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1695 of 2199

LINE PRESSURE ADJUSTMENT
Measure distance from the valve body to the inner
edge of the adjusting screw with an accurate steel
scale (Fig. 333).
Distance should be 33.4 mm (1-5/16 in.).
If adjustment is required, turn the adjusting screw
in, or out, to obtain required distance setting.
NOTE: The 33.4 mm (1-5/16 in.) setting is an
approximate setting. Manufacturing tolerances may
make it necessary to vary from this dimension to
obtain desired pressure.
One complete turn of the adjusting screw changes
line pressure approximately 1-2/3 psi (9 kPa).
Turning the adjusting screw counterclockwise
increases pressure while turning the screw clockwise
decreases pressure.THROTTLE PRESSURE ADJUSTMENT
Insert Gauge Tool C-3763 between the throttle
lever cam and the kickdown valve stem (Fig. 334).
Push the gauge tool inward to compress the kick-
down valve against the spring and bottom the throt-
tle valve.
Maintain pressure against kickdown valve spring.
Turn throttle lever stop screw until the screw head
touches throttle lever tang and the throttle lever cam
touches gauge tool.
NOTE: The kickdown valve spring must be fully
compressed and the kickdown valve completely
bottomed to obtain correct adjustment.
Fig. 331 Manual Lever Shaft Seal
1 - 15/1688SOCKET
2 - SEAL
Fig. 332 Accumulator Piston Components
1 - INNER SPRING
2 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
3 - OUTER SPRING
4 - SEAL RINGS
Fig. 333 Line Pressure Adjustment
1 - WRENCH
2 - 1±5/16 INCH
Fig. 334 Throttle Pressure Adjustment
1 - HEX WRENCH (IN THROTTLE LEVER ADJUSTING SCREW)
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3763 (POSITIONED BETWEEN THROTTLE
LEVER AND KICKDOWN VALVE)
21 - 176 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1709 of 2199

(48) Remove the manual selector shaft seal.
(49) Remove the dipstick tube seal.
CLEANING
The use of crocus cloth is permissible where neces-
sary, providing it is used carefully. When used on
shafts, or valves, use extreme care to avoid rounding
off sharp edges. Sharp edges are vital as they pre-
vent foreign matter from getting between the valve
and valve bore.
Do not reuse oil seals, gaskets, seal rings, or
O-rings during overhaul. Replace these parts as a
matter of course. Also do not reuse snap rings or
E-clips that are bent or distorted. Replace these parts
as well.
Lubricate transmission parts with MopartATF +4,
Type 9602, transmission fluid during overhaul and
assembly. Use petroleum jelly, MopartDoor Ease, or
Ru-Glyde to prelubricate seals, O-rings, and thrust
washers. Petroleum jelly can also be used to hold
parts in place during reassembly.Clean the case in a solvent tank. Flush the case
bores and fluid passages thoroughly with solvent.
Dry the case and all fluid passages with compressed
air. Be sure all solvent is removed from the case and
that all fluid passages are clear.
NOTE: Do not use shop towels or rags to dry the
case (or any other transmission component) unless
they are made from lint-free materials. Lint will stick
to case surfaces and transmission components and
circulate throughout the transmission after assem-
bly. A sufficient quantity of lint can block fluid pas-
sages and interfere with valve body operation.
INSPECTION
Inspect the case for cracks, porous spots, worn
bores, or damaged threads. Damaged threads can be
repaired with Helicoil thread inserts. However, the
case will have to be replaced if it exhibits any type of
damage or wear.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.
(2) Install the cooler filter bypass valve.
(3) Torque the bypass valve to specification. The
valve uses a tapered pipe thread and excessive
torque can damage the transmission case. Tighten
the cooler filter bypass valve to 4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(4) Install a new selector shaft seal using Seal
Installer 8253 (Fig. 31).
Fig. 30 Manual Shaft/Park Lock Components
1 - GUIDE
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - SHAFT
4 - SPRING
5 - PARK PAWL
6 - MANUAL SHAFT/LEVER
7 - PARK ROD
Fig. 31 Install Selector Shaft
1 - SEAL
2 - TOOL 8253
21 - 190 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1740 of 2199
SPECIAL TOOLS
RFE TRANSMISSION
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3292
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3293SP
Dial Indicator - C-3339
Installer, Seal - C-3860-A
Flusher, Oil Cooler - 6906-C
Compressor, Spring - 8249
Compressor, Spring - 8250
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 221
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1741 of 2199
Compressor, Spring - 8251
Installer, Piston - 8252
Installer, Seal - 8253
Installer, Seal - 8254
Installer, Snap-ring - 8255
Stand, Support - 8257
Adapter, Pressure Tap - 8258-A
Adapter, Line Pressure - 8259
21 - 222 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)