2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Intake
[x] Cancel search: IntakePage 1381 of 2199

(7) Connect throttle cable and speed control cable
to throttle body.
(8) Install fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install ignition coil towers (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install coolant temperature sensor (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - INSTALLATION).
(11) Connect electrical connectors for the following
components:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Ignition coil towers
²Fuel injectors
(12) Install top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt and
ground strap.
(13) Install right side engine lifting stud.
(14) Install generator including electrical connec-
tions (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GEN-
ERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(15) Connect Vapor purge hose, Brake booster
hose, Speed control servo hose, Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) hose.
(16) Install air conditioning compressor including
electrical connections.
(17) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(18) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(19) Install cowl to hood seal (Refer to 23 - BODY/
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/COWL WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION).
(20) Install air cleaner housing and throttle body
resonator. Tighten resonator bolts 4.5 N´m (40 in.
lbs.).
(21) Connect negative cable to battery.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - LEFT
DESCRIPTION
The exhaust manifolds are log style with a pat-
ented flow enhancing design to maximize perfor-
mance. The exhaust manifolds are made of high
silicon molybdenum cast iron. A perforated core
graphite exhaust manifold gasket is used to improve
sealing to the cylinder head. The exhaust manifolds
are covered by a three layer laminated heat shield
for thermal protection and noise reduction. The heat
shields are fastened with a torque prevailing nutthat is backed off slightly to allow for the thermal
expansion of the exhaust manifold.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable for battery.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove air cleaner housing and tube.
(6) Remove the front two exhaust heat shield
retaining fasteners. Raise vehicle and remove the
fasteners at rear of heat shield.
(7) Remove heat shield (Fig. 107).
(8) Lower vehicle and remove the upper exhaust
manifold retaining bolts (Fig. 107).
(9) Raise vehicle and remove the lower exhaust
manifold retaining bolts (Fig. 107).
(10) Remove exhaust manifold and gasket (Fig.
107). Manifold is removed from below the engine
compartment.
CLEANING
(1) Clean the exhaust manifold using a suitable
cleaning solvent, then allow to air dry.
(2) Clean all gasket residue from the manifold
mating surface.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks in the
mating surface and at every mounting bolt hole.
(2) Using a straight edge and a feeler gauge, check
the mating surface for warp and twist.
(3) Inspect the manifold to exhaust pipe mating
surface for cracks, gouges, or other damage that
would prevent sealing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install exhaust manifold and gasket from below
engine compartment.
(2) Install lower exhaust manifold fasteners (Fig.
107). DO NOT tighten until all fasteners are in
place.
(3) Lower vehicle and install upper exhaust mani-
fold fasteners (Fig. 107). Tighten all manifold bolts
starting at center and working outward to 25 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(4) Install exhaust manifold heat shield (Fig. 107).
Tighten fasteners to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.), then loosen
45 degrees.
(5) Install air cleaner housing and tube.
(6) Connect exhaust pipe to manifold.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
9 - 138 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1384 of 2199

INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks in the
mating surface and at every mounting bolt hole.
(2) Using a straight edge and a feeler gauge, check
the mating surface for warp and twist.
(3) Inspect the manifold to exhaust pipe mating
surface for cracks, gouges, or other damage that
would prevent sealing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install exhaust manifold and gasket from below
engine compartment.
(2) Install lower exhaust manifold fasteners. DO
NOT tighten until all fasteners are in place.
(3) Lower vehicle and install upper exhaust mani-
fold fasteners. Tighten all manifold bolts starting at
center and working outward to 25 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(4) Install exhaust manifold heat shield. Tighten
fasteners to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.), then loosen 45
degrees.
(5) Install starter and fasteners.
(6) Connect exhaust pipe to manifold.
(7) Connect heater hoses at engine.
(8) Install fastener attaching A/C accumulator.
(9) Install A/C compressor and fasteners.
(10) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(11) Install washer bottle and battery tray assem-
bly.
(12) Install PDC.
(13) Install battery and connect cables.
(14) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The timing drive system has been designed to pro-
vide quiet performance and reliability to support a
non-free wheelingengine. Specifically the intake
valves are non-free wheeling and can be easily dam-
aged with forceful engine rotation if camshaft-to-
crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing drive
system consists of a primary chain and two second-
ary timing chain drives (Fig. 109).
OPERATION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
type. The primary chain drives the large fifty tooth
idler sprocket directly from a 25 tooth crankshaftsprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by a
pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed guide.
The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic wear
faces for low friction and long wear. The primary
chain receives oil splash lubrication from the second-
ary chain drive and oil pump leakage. The idler
sprocket assembly connects the primary and second-
ary chain drives. The idler sprocket assembly con-
sists of two integral thirty tooth sprockets and a fifty
tooth sprocket that is splined to the assembly. The
spline joint is a non ± serviceable press fit anti rattle
type. A spiral ring is installed on the outboard side of
the fifty tooth sprocket to prevent spline disengage-
ment. The idler sprocket assembly spins on a station-
ary idler shaft. The idler shaft is press-fit into the
cylinder block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt
and the rear flange of the idler shaft are used to con-
trol sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is
routed through the center of the idler shaft to pro-
vide lubrication for the two bushings used in the
idler sprocket assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
inverted tooth type, one to drive the camshaft in each
SOHC cylinder head. There are no shaft speed
changes in the secondary chain drive system. Each
secondary chain drives a thirty tooth cam sprocket
directly from the thirty tooth sprocket on the idler
sprocket assembly. A fixed chain guide and a hydrau-
lic oil damped tensioner are used to maintain tension
in each secondary chain system. The hydraulic ten-
sioners for the secondary chain systems are fed pres-
surized oil from oil reservoir pockets in the block.
Each tensioner also has a mechanical ratchet system
that limits chain slack if the tensioner piston bleeds
down after engine shut down. The tensioner arms
and guides also utilize nylon wear faces for low fric-
tion and long wear. The secondary timing chains
receive lubrication from a small orifice in the ten-
sioners. This orifice is protected from clogging by a
fine mesh screen which is located on the back of the
hydraulic tensioners.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE TIMING -
VERIFICATION
CAUTION: The 4.7L is a non free-wheeling design
engine. Therefore, correct engine timing is critical.
NOTE: Components referred to as left hand or right
hand are as viewed from the drivers position inside
the vehicle.
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 141
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - RIGHT (Continued)
Page 1390 of 2199

TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove right and left cylinder head covers
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove radiator fan (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(5) Rotate engine until timing mark on crankshaft
damper aligns with TDC mark on timing chain cover
(Fig. 120) (#1 cylinder exhaust stroke) and the cam-
shaft sprocket ªV8º marks are at the 12 o'clock posi-
tion (Fig. 121).(6) Remove power steering pump.
(7) Remove access plugs (2) from left and right cyl-
inder heads for access to chain guide fasteners (Fig.
122).
(8) Remove the oil fill housing to gain access to the
right side tensioner arm fastener.
(9) Remove crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL) and timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(10) Collapse and pin primary chain tensioner
(Fig. 123).
CAUTION: Plate behind left secondary chain ten-
sioner could fall into oil pan. Therefore, cover pan
opening.
(11) Remove secondary chain tensioners.
(12) Remove camshaft position sensor from right
cylinder head (Fig. 124).
CAUTION: Care should be taken not to damage
camshaft target wheel. Do not hold target wheel
while loosening or tightening camshaft sprocket.
Do not place the target wheel near a magnetic
source of any kind. A damaged or magnetized tar-
get wheel could cause a vehicle no start condition.
CAUTION: Do not forcefully rotate the camshafts or
crankshaft independently of each other. Damaging
intake valve to piston contact will occur. Ensure
negative battery cable is disconnected to guard
against accidental starter engagement.
(13) Remove left and right camshaft sprocket bolts.
(14) While holding the left camshaft steel tube
with adjustable pliers, (Fig. 125) remove the left
camshaft sprocket. Slowly rotate the camshaft
approximately 15 degrees clockwise to a neutral posi-
tion.
(15) While holding the right camshaft steel tube
with adjustable pliers, (Fig. 126) remove the right
camshaft sprocket. Slowly rotate the camshaft
approximately 45 degrees counterclockwise to a neu-
tral position.
Fig. 120 Engine Top Dead Center (TDC) Indicator
Mark
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - CRANKSHAFT TIMING MARKS
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 147
Page 1434 of 2199

(8) Connect fuel return and pressure lines to fuel
pump module fittings (Fig. 16). Refer to Quick-Con-
nect Fittings.
(9) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Installa-
tion.
FUEL RAIL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L
The fuel injector rail is used to mount the fuel
injectors to the engine. It is mounted to the intake
manifold (Fig. 20).
DESCRIPTION - 4.0L
The fuel injector rail is used to mount the fuel
injectors to the engine (Fig. 21). On the 4.0L 6±cylin-
der engine, afuel damperis located near the center
of the fuel rail (Fig. 21).
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.7L
High pressure fuel from the fuel pump is routed to
the fuel rail. The fuel rail then supplies the neces-
sary fuel to each individual fuel injector.
A fuel pressure test port is located on the fuel rail
(Fig. 20). A quick-connect fitting with a safety latch
is used to attach the fuel line to the fuel rail.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
OPERATION - 4.0L
The fuel injector rail supplies the necessary fuel to
each individual fuel injector.
High pressure fuel from the fuel pump is routed to
the fuel rail. The fuel rail then supplies the neces-
sary fuel to each individual fuel injector.
The fuel damper is used only to help control fuel
pressure pulsations. These pulsations are the result
of the firing of the fuel injectors. It isnot usedas a
fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator is
not mountedto the fuel rail on any engine. It is
located near the front of the fuel tank above the rear
axle. Refer to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator in
this group for information.
A fuel pressure test port is located on the fuel rail
(Fig. 21). A quick-connect fitting with a safety latch
is used to attach the fuel line to the fuel rail.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.7L
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT PRESSURE EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL RAIL, FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
Fig. 20 Fuel Injector RailÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - INJ.#7
3 - INJ.#5
4 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
5 - INJ.#3
6 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
7 - INJ.#1
8 - CONNECTOR TUBE
9 - INJ.#2
10 - INJ.#4
11 - INJ.#6
12 - INJ.#8
13 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 15
FUEL PUMP MODULE (Continued)
Page 1437 of 2199
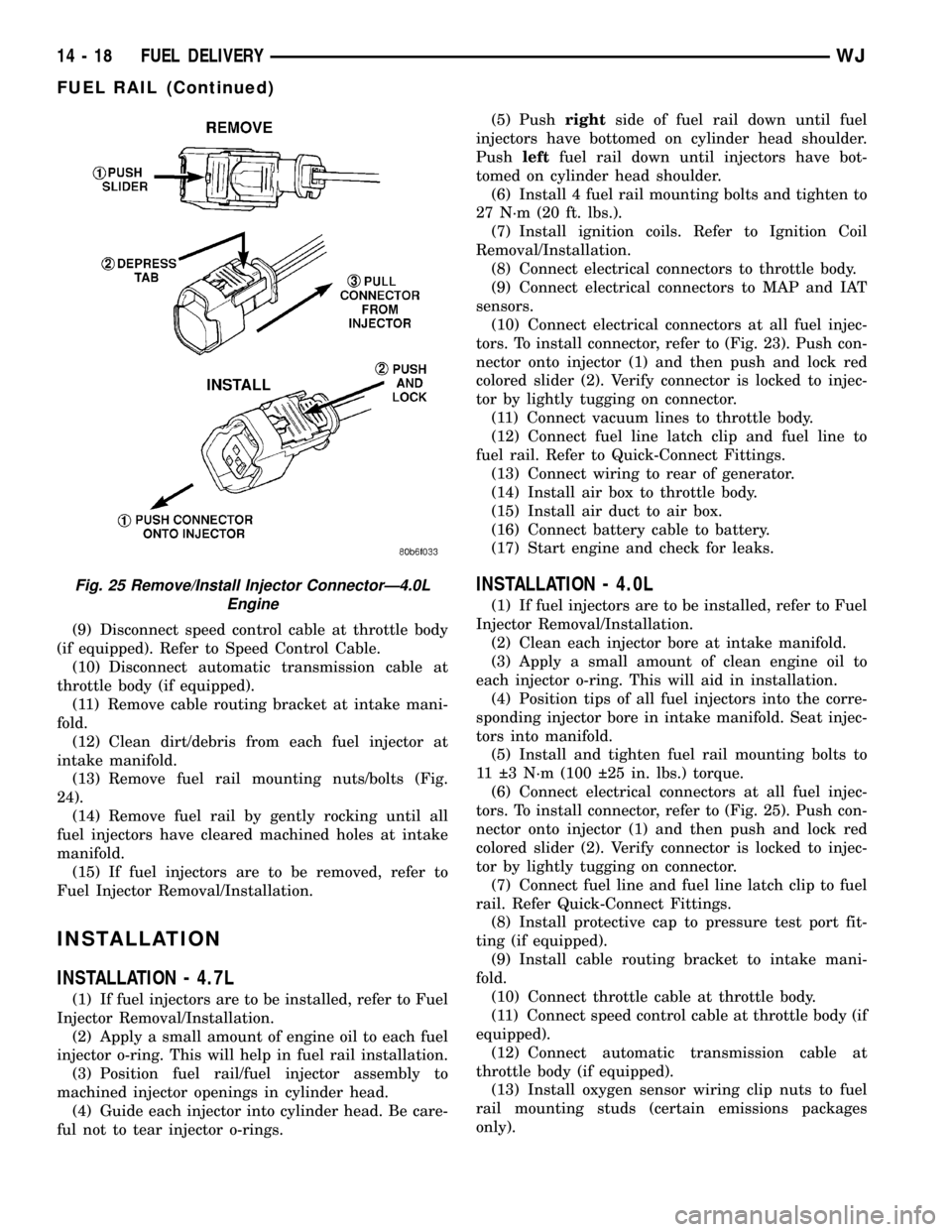
(9) Disconnect speed control cable at throttle body
(if equipped). Refer to Speed Control Cable.
(10) Disconnect automatic transmission cable at
throttle body (if equipped).
(11) Remove cable routing bracket at intake mani-
fold.
(12) Clean dirt/debris from each fuel injector at
intake manifold.
(13) Remove fuel rail mounting nuts/bolts (Fig.
24).
(14) Remove fuel rail by gently rocking until all
fuel injectors have cleared machined holes at intake
manifold.
(15) If fuel injectors are to be removed, refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(3) Position fuel rail/fuel injector assembly to
machined injector openings in cylinder head.
(4) Guide each injector into cylinder head. Be care-
ful not to tear injector o-rings.(5) Pushrightside of fuel rail down until fuel
injectors have bottomed on cylinder head shoulder.
Pushleftfuel rail down until injectors have bot-
tomed on cylinder head shoulder.
(6) Install 4 fuel rail mounting bolts and tighten to
27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install ignition coils. Refer to Ignition Coil
Removal/Installation.
(8) Connect electrical connectors to throttle body.
(9) Connect electrical connectors to MAP and IAT
sensors.
(10) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 23). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
(11) Connect vacuum lines to throttle body.
(12) Connect fuel line latch clip and fuel line to
fuel rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Connect wiring to rear of generator.
(14) Install air box to throttle body.
(15) Install air duct to air box.
(16) Connect battery cable to battery.
(17) Start engine and check for leaks.
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Clean each injector bore at intake manifold.
(3) Apply a small amount of clean engine oil to
each injector o-ring. This will aid in installation.
(4) Position tips of all fuel injectors into the corre-
sponding injector bore in intake manifold. Seat injec-
tors into manifold.
(5) Install and tighten fuel rail mounting bolts to
11 3 N´m (100 25 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 25). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
(7) Connect fuel line and fuel line latch clip to fuel
rail. Refer Quick-Connect Fittings.
(8) Install protective cap to pressure test port fit-
ting (if equipped).
(9) Install cable routing bracket to intake mani-
fold.
(10) Connect throttle cable at throttle body.
(11) Connect speed control cable at throttle body (if
equipped).
(12) Connect automatic transmission cable at
throttle body (if equipped).
(13) Install oxygen sensor wiring clip nuts to fuel
rail mounting studs (certain emissions packages
only).
Fig. 25 Remove/Install Injector ConnectorÐ4.0L
Engine
14 - 18 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1438 of 2199

(14) Install air tube (or duct) at top of throttle
body.
(15) Install fuel tank cap.
(16) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(17) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module and certain ORVR
components.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
A fuel tank check valve(s) is mounted into the top
of the fuel tank (or pump module). Refer to Fuel
Tank Check Valve for additional information.
An evaporation control system is connected to the
check valve(s) to reduce emissions of fuel vapors into
the atmosphere. When fuel evaporates from the fuel
tank, vapors pass through vent hoses or tubes to a
charcoal canister where they are temporarily held.
When the engine is running, the vapors are drawn
into the intake manifold. Certain models are also
equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a Leak
Detection Pump (LDP). Refer to Emission Control
System for additional information.
Refer to ORVR for On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery system information.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BEFORE SERVIC-
ING FUEL TANK.
Two different procedures may be used to drain fuel
tank (through ORVR control valve opening at top of
fuel tank, or using DRB scan tool). The quickest is
draining through ORVR control valve opening at top
of fuel tank (Fig. 26).
As an alternative procedure, the electric fuel pump
may be activated allowing tank to be drained at fuel
rail connection. Refer to DRB scan tool for fuel pump
activation procedures. Before disconnecting fuel line
at fuel rail, release fuel pressure. Refer to the Fuel
System Pressure Release Procedure for procedures.
Attach end of Special Adapter Hose Tool number
6539 at fuel rail disconnection. Position opposite end
of 6539 to an approved gasoline draining station.Activate fuel pump with DRB and drain tank until
empty.
If electric fuel pump is not operating, tankMUST
be drained through ORVR control valve opening at
top of fuel tank (Fig. 26).
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
System Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(3) Raise and support vehicle.
(4) Remove left rear wheel/tire.
CAUTION: HANDLE EVAP, LDP AND ORVR VAPOR /
VACUUM LINES VERY CAREFULLY. THESE LINES
AND HOSES MUST BE FIRMLY CONNECTED.
CHECK THE VAPOR/VACUUM LINES AT THE LDP,
LDP FILTER, EVAP CANISTER, EVAP CANISTER
PURGE SOLENOID AND ORVR COMPONENTS FOR
DAMAGE OR LEAKS. IF A LEAK IS PRESENT, A
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) MAY BE SET.
(5) Clean top of fuel tank at ORVR control valve
(Fig. 26) or (Fig. 27).
(6) Press release tab in direction of arrow in (Fig.
27) and remove ORVR control valve lock ring
(counter-clockwise). Lift up ORVR control slightly.
Using an approved gasoline draining station, drain
tank until empty through this opening.
(7) Remove stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 28). Drill out plastic rivets for removal.
(8) Remove 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 29).
(9) Remove support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 30).
(10) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts at frame rail (Fig. 29).
(11) To separate and lower front section of two-
piece support bracket, remove 3 attaching bolts on
bottom of support bracket (Fig. 30). While lowering
support bracket, disconnect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 31).
(12) Remove hose clamp (Fig. 32) and remove fuel
fill hose from fuel fill tube.
(13) Cut and discard tie wrap from axle vent hose
(Fig. 32).
(14) Disconnect fuel vent hose from fuel vent tube
(Fig. 32).
(15) Disconnect ORVR hose elbow (Fig. 33) at top
of EVAP canister.
(16) Place hydraulic jack to bottom of fuel tank.
(17) Remove fuel tank-to-rear bumper fascia clips
(Fig. 34).
(18) Remove fuel tank heat shield mounting bolts
(Fig. 35).
CAUTION: To protect fuel tank from exhaust heat,
shield must re-installed after tank installation.
WARNING: PLACE SHOP TOWEL AROUND FUEL
LINES TO CATCH ANY EXCESS FUEL.
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 19
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1450 of 2199

FUEL INJECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL INJECTION
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
VISUAL INSPECTION..................32
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - FUEL INJECTION.............39
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................39
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 4.0L...................40
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L...................40
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L....................40
OPERATION - 4.7L....................41
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................41
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................41
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................42
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................43
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION
OPERATION.........................43
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT............43
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL INJECTOR . 44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................45
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................45
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................46
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................46
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................46
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................46
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................47INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................47
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION........................48
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L...................48
OPERATION...........................48
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................48
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................49
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................49
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................49
O2S HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................49
OPERATION...........................49
REMOVAL.............................50
INSTALLATION.........................50
O2S SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................50
OPERATION...........................50
REMOVAL.............................51
INSTALLATION.........................51
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION.........................52
OPERATION...........................52
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................52
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................53
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................53
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................54
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................54
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................55
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION ± 4.0L..................55
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................56
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................56
OPERATION...........................56
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................57
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................57
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................58
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................58
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 31
Page 1453 of 2199

(8) Inspect system body grounds for loose or dirty
connections. Refer to Group 8, Wiring for ground
locations.
(9) Verify crankcase ventilation (CCV) operation.
Refer to Emission Control System for additional
information.
(10) Inspect all fuel line quick-connect fittings for
damage or leaks.
(11) Verify hose connections to all ports of vacuum
fittings on intake manifold, and for emission system
are tight and not leaking.
(12) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt-
tle cable (if equipped) and speed control cable connec-
tions (if equipped). Check their connections to
throttle body linkage for any binding or restrictions.
(13) Verify vacuum booster hose is firmly con-
nected to fitting on intake manifold. Also check con-
nection to brake vacuum booster.(14) Inspect air cleaner inlet and air cleaner ele-
ment for dirt or restrictions.
(15) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
(16) 4.0L Engine: Verify MAP, Intake Manifold Air
Temperature (IAT) sensor, TPS and Idle Air Control
(IAC) motor connectors are firmly connected (Fig. 9).
Be sure throttle body mounting bolts (Fig. 9)are
tight.
(17) 4.7L Engine: Verify Intake Manifold Air Tem-
perature (IAT) sensor, TPS and Idle Air Control (IAC)
motor connectors are firmly connected (Fig. 10). Be
sure throttle body mounting bolts (Fig. 10)are tight.
Fig. 8 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2-STARTER
3 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
Fig. 9 IAT, MAP, IAC, TPS Sensor LocationsÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
5 - TPS
6 - MAP SENSOR
7 - ELEC. CONN.
8 - IAT SENSOR
9 - ELEC. CONN.
14 - 34 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)