2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Engine harness
[x] Cancel search: Engine harnessPage 2091 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C Heater control in the
Recirculation Mode, the A/C button in the on posi-
tion, the blower motor switch in the highest speed
position, and the engine speed at 1500 to 2000 rpm.
This procedure (burnishing) will seat the opposing
friction surfaces and provide a higher compressor
clutch torque capability.
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remain fully-charged
during compressor clutch, pulley, or coil replacement.
The compressor clutch can be serviced in the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(3) Remove the bolt that secures the compressor
clutch to the compressor shaft (Fig. 5). A band-type
oil filter wrench may be used to secure the clutch
during bolt removal.
(4) Tap the clutch plate with a plastic mallet to
release it from the splines on the compressor shaft.
Remove the clutch plate and shim(s) from the com-
pressor shaft (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: Do not pry between the clutch plate
assembly and the pulley to remove it from the com-
pressor shaft. Prying may damage the clutch plate
assembly.(5) Remove the external snap ring that secures the
compressor clutch pulley to the nose of the compres-
sor front housing with snap ring pliers (Special Tool
C-4574) and slide the pulley assembly off of the com-
pressor (Fig. 7).
(6) Remove the screw and retainer from the clutch
coil lead wire harness on the compressor front hous-
ing.
Fig. 5 COMPRESSOR SHAFT BOLT
1 - COMPRESSOR CLUTCH PLATE
2 - COMPRESSOR SHAFT BOLT
Fig. 6 CLUTCH PLATE AND SHIM(S)
1 - COMPRESSOR SHAFT
2 - CLUTCH PLATE
3 - CLUTCH PLATE SHIM
Fig. 7 PULLEY SNAP RING
1 - SNAP RING
24 - 14 CONTROLSWJ
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2093 of 2199

gap should be between 0.35 to 0.65 millimeter (0.014
to 0.026 inch). If the proper air gap is not obtained,
add or subtract shims as needed until the desired air
gap is obtained.
(9) Install the compressor shaft bolt. Tighten the
bolt to 13 N´m (115 in. lbs.).
NOTE: The shims may compress after tightening
the shaft bolt. Check the air gap in four or more
places to verify the air gap is still correct. Spin the
pulley before performing a final check of the air
gap.
(10) To complete the installation, (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - INSTALLATION)
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch relay is a International
Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay. The termi-
nal designations and functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the micro-relay
terminal orientation (footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the relay case dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
OPERATION
The compressor clutch relay is a electromechanical
device that switches battery current to the compres-
sor clutch coil when the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) grounds the coil side of the relay. The PCM
responds to inputs from the a/c compressor switch on
the a/c heater control panel, the Automatic Zone Con-
trol (AZC) control module (if the vehicle is so
equipped), the a/c fin probe, and the a/c high pres-
sure transducer. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
The compressor clutch relay is located in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine compart-
ment. Refer to the PDC label for relay identification
and location.
The compressor clutch relay cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH RELAY
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information.
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 10) is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
PDC label for relay identification and location.Remove the relay from the PDC to perform the fol-
lowing tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, see the Relay Circuit Test procedure
in this group. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information..
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to fused battery feed. There should be bat-
tery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 30 at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the fuse in the PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is not
used in this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal cavity (87) is
connected to the compressor clutch coil. There should
be continuity between this cavity and the A/C com-
pressor clutch relay output circuit cavity of the com-
pressor clutch coil wire harness connector. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit as
required.
(4) The relay coil battery terminal (86) is con-
nected to the fused ignition switch output (run/start)
circuit. There should be battery voltage at the cavity
for relay terminal 86 with the ignition switch in the
On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the
Fig. 10 A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
24 - 16 CONTROLSWJ
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2095 of 2199

Both the manual A/C Heater control panel and the
AZC control panel are serviced only as complete
units and cannot be repaired. If faulty or damaged,
the entire control panel unit must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC ZONE
CONTROL SYSTEM
The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) control module
has a system self-diagnostic mode which continuously
monitors various parameters during normal system
operation. If a system fault is detected, a current and
historical fault is recorded. When the current fault is
cleared, the historical fault remains until reset (man-
ually or automatically). Both the current and histor-
ical fault codes can be accessed through either the
front panel, or over the Programmable Communica-
tions Interface (PCI) bus using a DRBIIItscan tool,
and the appropriate diagnostic information.
The AZC control module is capable of three differ-
ent types of self-diagnostic tests, as follows:
²Fault Code Tests
²Input Circuit Tests
²Output Circuit/Actuator Tests
The information that follows describes:
²How to read the self-diagnostic display
²How to enter the AZC control module self-diag-
nostic test mode
²How to select the self-diagnostic test types
²How to perform the different tests
ENTERING THE AZC SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
To enter the AZC self-diagnostic mode, perform the
following:
(1) Depress the a/c and recirc buttons at the same
time and hold. Rotate the left temperature control
knob clockwise (CW) one detent.
(2) If you continue to keep the a/c and recirc but-
tons depressed, the AZC control module will perform
a Segment Test of the Vacuum Fluorescent (VF) dis-
play. In the Segment Test you should see all of the
display segments illuminate as long as both buttons
are held. If a display segment fails to illuminate, the
vacuum fluorescent display is faulty and the a/c
heater control must be replaced.
(3) After viewing the Segment Test, release the
A/C and Recirc buttons and the display will clear
momentarily.Ifa0isdisplayed, then no faults
are set in the system.Should there be any faults,
either9current9or9historical9, all fault codes will be
displayed in ascending numerical sequence (note no
effort is made to display fault codes in chronological
order). Each fault code is displayed for one second
before the next code is displayed. Once all fault codes
have been displayed, the system will then repeat the
fault code numbers. This will continue until the left
side set temperature control is moved at least onedetent position in the CW direction or the ignition is
turned9OFF9.
FAULT CODE TESTS
Fault codes are two-digit numbers that identify a
circuit that is malfunctioning. There are two differ-
ent kinds of fault codes.
1.Current Fault Codes- Current means the
fault is present right now. There are two types of cur-
rent faults: input faults, and system faults.
2.Historical Fault Codes- Historical or stored
means that the fault occurred previously, but is not
present right now. A majority of historical fault codes
are caused by intermittent wire harness or wire har-
ness connector problems.
CURRENT FAULT CODES
Input faults 01 = IR thermister circuit
open
02 = IR thermister circuit
shorted
03 = Fan pot shorted
04 = Fan pot open
05 = Mode pot shorted
06 = Mode pot open
07 = IR sensor delta too
large
08 = Reserved
09 = Reserved
10 = One of four motor
drivers has drive9A9
shorted to ground
11 = Engine air intake
temperature Buss
message missing
12 = Country code Buss
message missing
24 - 18 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2101 of 2199
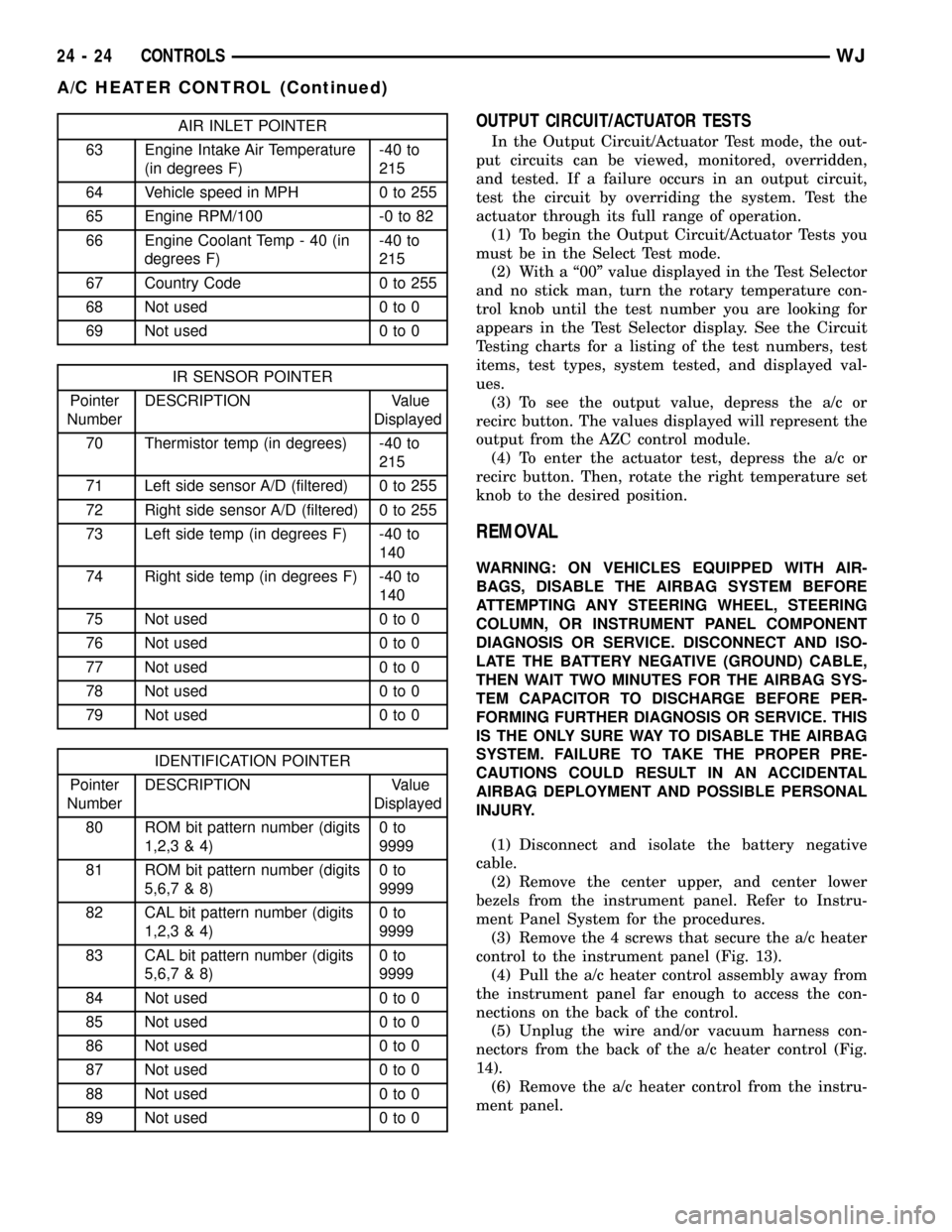
AIR INLET POINTER
63 Engine Intake Air Temperature
(in degrees F)-40 to
215
64 Vehicle speed in MPH 0 to 255
65 Engine RPM/100 -0 to 82
66 Engine Coolant Temp - 40 (in
degrees F)-40 to
215
67 Country Code 0 to 255
68 Not used 0 to 0
69 Not used 0 to 0
IR SENSOR POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
70 Thermistor temp (in degrees) -40 to
215
71 Left side sensor A/D (filtered) 0 to 255
72 Right side sensor A/D (filtered) 0 to 255
73 Left side temp (in degrees F) -40 to
140
74 Right side temp (in degrees F) -40 to
140
75 Not used 0 to 0
76 Not used 0 to 0
77 Not used 0 to 0
78 Not used 0 to 0
79 Not used 0 to 0
IDENTIFICATION POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
80 ROM bit pattern number (digits
1,2,3 & 4)0to
9999
81 ROM bit pattern number (digits
5,6,7 & 8)0to
9999
82 CAL bit pattern number (digits
1,2,3 & 4)0to
9999
83 CAL bit pattern number (digits
5,6,7 & 8)0to
9999
84 Not used 0 to 0
85 Not used 0 to 0
86 Not used 0 to 0
87 Not used 0 to 0
88 Not used 0 to 0
89 Not used 0 to 0
OUTPUT CIRCUIT/ACTUATOR TESTS
In the Output Circuit/Actuator Test mode, the out-
put circuits can be viewed, monitored, overridden,
and tested. If a failure occurs in an output circuit,
test the circuit by overriding the system. Test the
actuator through its full range of operation.
(1) To begin the Output Circuit/Actuator Tests you
must be in the Select Test mode.
(2) With a ª00º value displayed in the Test Selector
and no stick man, turn the rotary temperature con-
trol knob until the test number you are looking for
appears in the Test Selector display. See the Circuit
Testing charts for a listing of the test numbers, test
items, test types, system tested, and displayed val-
ues.
(3) To see the output value, depress the a/c or
recirc button. The values displayed will represent the
output from the AZC control module.
(4) To enter the actuator test, depress the a/c or
recirc button. Then, rotate the right temperature set
knob to the desired position.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the center upper, and center lower
bezels from the instrument panel. Refer to Instru-
ment Panel System for the procedures.
(3) Remove the 4 screws that secure the a/c heater
control to the instrument panel (Fig. 13).
(4) Pull the a/c heater control assembly away from
the instrument panel far enough to access the con-
nections on the back of the control.
(5) Unplug the wire and/or vacuum harness con-
nectors from the back of the a/c heater control (Fig.
14).
(6) Remove the a/c heater control from the instru-
ment panel.
24 - 24 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2111 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RECIRCULATION DOOR
VACUUM ACTUATOR
(1) Install the recirculation door vacuum actuator
on the HVAC housing and tighten the mounting
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(2) Engage the recirculation door actuating rod
with the recirculation door lever.
(3) Engage the recirculation door pivot connection
with the door pivot pin.
(4) Plug in the vacuum harness connector to the
recirculation door vacuum actuator.
(5) Install the instrument panel in the vehicle.
Refer to Instrument Panel System for the procedures.
INSTALLATION - RECIRCULATION DOOR
ELECTRIC ACTUATOR
(1) Install the recirculation door actuator on the
recirculation door housing and tighten the mounting
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(2) Install the recirculation door housing on the
HVAC unit and tighten the mounting screws to 2.2
N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Plug in the wire harness connector to the recir-
culation door actuator.
(4) Install the instrument panel in the vehicle.
Refer to Instrument Panel System for the procedures.
VACUUM CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
Two vacuum check valves (non AZC only) are
installed on the vacuum supply system. One is on the
accessory vacuum supply line in the engine compart-
ment, near the vacuum tap on the engine intake
manifold. A second vacuum check valve is located on
the bottom of the HVAC unit behind the passenger
front floor duct on the black vacuum line. The vac-
uum check valves are designed to allow vacuum to
flow in only one direction through the accessory vac-
uum supply circuits.
OPERATION
The use of a vacuum check valve helps to maintain
the system vacuum needed to retain the selected A/C
Heater mode settings. The check valve will prevent
the engine from bleeding down system vacuum
through the intake manifold during extended heavy
engine load (low engine vacuum) operation.
The vacuum check valve cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
(1) Unplug the HVAC vacuum supply line connec-
tor at the vacuum check valve near the engine intake
manifold vacuum adapter fitting.
(2) Note the orientation of the check valve in the
vacuum supply line for correct installation.
(3) Unplug the vacuum check valve from the vac-
uum supply line fittings.
INSTALLATION
(1) Plug in the vacuum check valve at the vacuum
supply line fittings, noting the orientation of the
check valve in the vacuum supply line for correct
installation.
(2) Plug in the HVAC vacuum supply line connec-
tor at the vacuum check valve near the engine intake
manifold vacuum adapter fitting.
VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION
The vacuum reservoir is mounted in the right front
of the vehicle behind the headlamp mounting module
(Fig. 22). The headlamp mounting module and head-
lamp assembly must be removed from the vehicle to
access the vacuum reservoir for service. Refer to
Lamps/Lighting for the procedures.
OPERATION
Engine vacuum is stored in the vacuum reservoir.
The stored vacuum is used to operate the vacuum-
Fig. 21 RECIRCULATION DOOR HOUSING
1 - RECIRCULATION DOOR HOUSING
2 - ATTACHING SCREWS
24 - 34 CONTROLSWJ
RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2118 of 2199

HVAC HOUSING
REMOVAL
The HVAC housing assembly must be removed
from the vehicle and the two halves of the housing
separated for service access of the heater core, evap-
orator coil, blend door(s), and each of the various
mode doors.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN PLUMBING BEFORE PERFORMING THE
FOLLOWING OPERATION. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION)
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel from the vehi-
cle(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL -
REMOVAL).
(3) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)
(4) Disconnect the liquid line refrigerant line from
the evaporator inlet tube(Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/LIQUID LINE -
REMOVAL) or (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING/LIQUID LINE - REMOV-
AL). Install plugs in, or tape over all of the opened
refrigerant line fittings.
(5) Disconnect the suction line refrigerant line
from the evaporator outlet tube(Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/SUCTION
LINE - REMOVAL), (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/SUCTION LINE -
REMOVAL) or (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING/SUCTION LINE - REMOV-
AL). Install plugs in, or tape over all of the opened
refrigerant line fittings.(6) Disconnect the heater hoses from the heater
core tubes. Clamp off the heater hoses to prevent loss
of coolant. Refer to Cooling for the procedures. Install
plugs in, or tape over the opened heater core tubes.
(7) If the vehicle is equipped with the manual tem-
perature control system, unplug the HVAC system
vacuum supply line connector from the tee fitting
near the heater core tubes.
(8) Remove the coolant reserve/overflow bottle
from the passenger side inner fender shield. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(9) Remove the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
from the passenger side dash panel in the engine
compartment and set it aside. Do not unplug the
PCM wire harness connectors. Refer to Electronic
Control Modules for the procedures.
(10) Remove the nuts from the HVAC housing
mounting studs on the engine compartment side of
the dash panel (Fig. 9).
(11) Remove the rear floor heat ducts from the
floor heat duct outlets (Fig. 10).
(12) Unplug the HVAC housing wire harness con-
nectors.
(13) Remove the HVAC housing mounting nuts
from the studs on the passenger compartment side of
the dash panel (Fig. 11).
Fig. 9 HVAC Housing - (rear view)
1 - Instrument Panel
2 - Air Intake
3 - Expansion Valve
4 - HVAC Housing
5 - Heater Core Input/Output Ports
6 - Instrument Panel Wiring Harness
7 - Blower Motor
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 41
Page 2122 of 2199

NOTE: The blend door sub-assembly is attached to
the housing with 2 screws, and may be removed for
service (Fig. 19).
ASSEMBLY
(1) Place the top half of the HVAC housing on the
bottom half. Be certain that each of the door pivot
pins align with the pivot holes in the HVAC housing.
(2) Install the 10 screws that secure the two hous-
ing halves to each other. Tighten the HVAC housing
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Attach the wire harness electrical connector(s)
to the mounts on the lower case at the blower motor
end of the unit.
(4) Install the 5 clips that secure the two housing
halves to each other. Check doors for binding after
replacement, and after assembly of housing.
(5) Install the screw with plastic washer holding
the lever assembly to the upper case section.
(6) Install the mode door actuator on the left side
of the housing.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN PLUMBING BEFORE PERFORMING THE
FOLLOWING OPERATION. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION)Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Position the HVAC housing to the dash panel.
Be certain that the evaporator condensate drain tube
and the housing mounting studs are inserted into
their correct mounting holes.
(2) Install the HVAC housing mounting nuts to the
studs on the passenger compartment side of the dash
panel. Tighten the nuts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC housing wire harness con-
nectors.
(4) Reinstall the rear floor heat ducts to the center
floor heat duct outlets.
(5) Install and tighten the nuts onto the HVAC
housing mounting studs on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. Tighten the nuts to 7 N´m (60
in. lbs.).
(6) Reinstall the PCM to the passenger side dash
panel in the engine compartment. Refer to Electronic
Control Modules for the procedures.
(7) Reinstall the coolant reserve/overflow bottle to
the passenger side inner fender shield. Refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures.
(8) If the vehicle is equipped with the manual tem-
perature control system, connect the HVAC system
vacuum supply line connector to the tee fitting near
the heater core tubes.
(9) Unclamp/unplug the heater core hoses and
tubes. Connect the heater hoses to the heater core
tubes and fill the engine cooling system. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(10) Unplug or remove the tape from the suction
line and the evaporator outlet tube fittings. Connect
the suction line to the evaporator outlet tube.
Tighten retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Unplug or remove the tape from the liquid
line and the evaporator inlet tube fittings. Connect
the liquid line to the evaporator inlet tube. Tighten
retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(12) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
Fig. 19 BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY (AZC)
1 - PASSENGER SIDE BLEND DOOR
2 - BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY
3 - DOOR PIVOT SHAFT BUSHING
4 - DOOR SHAFT LEVER
5 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 45
HVAC HOUSING (Continued)
Page 2134 of 2199
(10) Allow three to five minutes for the refrigerant
system to stabilize, then take a second set of thermo-
couple measurements. Record the temperature differ-
ence to determine if an additional charge is required.(11) Record the compressor discharge pressure. If
the reading is higher than the pressure shown in the
Compressor Discharge Pressure Chart, the system
could be overcharged. If the reading is equal to, or
lower, than the pressure shown in the chart, continue
with this procedure.
Compressor Discharge Pressure Chart
Ambient
Temperature16ÉC
(60ÉF)21ÉC
(70ÉF)27ÉC
(80ÉF)32ÉC
(90ÉF)38ÉC
(100ÉF)43ÉC
(110ÉF)
Compressor
Discharge
Pressure1378 kPa
(200 psi)1516 kPa
(220 psi)1723 kPa
(250psi)1930 kPa
(280 psi)2206 kPa
(320 psi)2413 kPa
(350 psi)
(12)EXAMPLE:The ambient temperature is 21É
C (70É F). The evaporator inlet tube temperature is
12É C (54É F) and the evaporator outlet tube temper-
ature is 10É C (50É F). Subtract the inlet tube tem-
perature from the outlet tube temperature. The
difference is -2É C (-4É F). With a -2É C (-4É F) tem-
perature differential at 21É C (70É F) ambient tem-
perature, the system is fully charged.
(13) Add enough refrigerant to bring the refriger-
ant system up to a full charge.
(14) Remove the jumper wire from the low pres-
sure cycling clutch switch wire harness connector
and plug the connector back into the switch.
SPECIFICATIONS
CHARGE CAPACITY
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle is 0.765 kilograms (1.687 pounds/27
ounces).
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The air conditioning system uses a Nippondenso
10PA17 ten cylinder, double-acting swash plate-type
compressor on all models. This compressor has a
fixed displacement of 170 cubic centimeters (10.374
cubic inches), and has both the suction and discharge
ports located on the cylinder head. A label identifying
the use of R-134a refrigerant is located on the com-
pressor.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the com-
pressor manifold, which is on the side of the com-
pressor. This mechanical valve is designed to vent
refrigerant from the system to protect against dam-
age to the compressor and other system components,
caused by condenser air flow restriction or an over-
charge of refrigerant.
OPERATION
OPERATION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The compressor is driven by the engine through an
electric clutch, drive pulley and belt arrangement.
The compressor is lubricated by refrigerant oil that is
circulated throughout the refrigerant system with the
refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor, which is then
pumped to the condenser through the compressor dis-
charge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley, and coil, are
available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes
when a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa
(400 psi) is reached.
WJPLUMBING 24 - 57
PLUMBING (Continued)