2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE valve spring
[x] Cancel search: valve springPage 23 of 2199
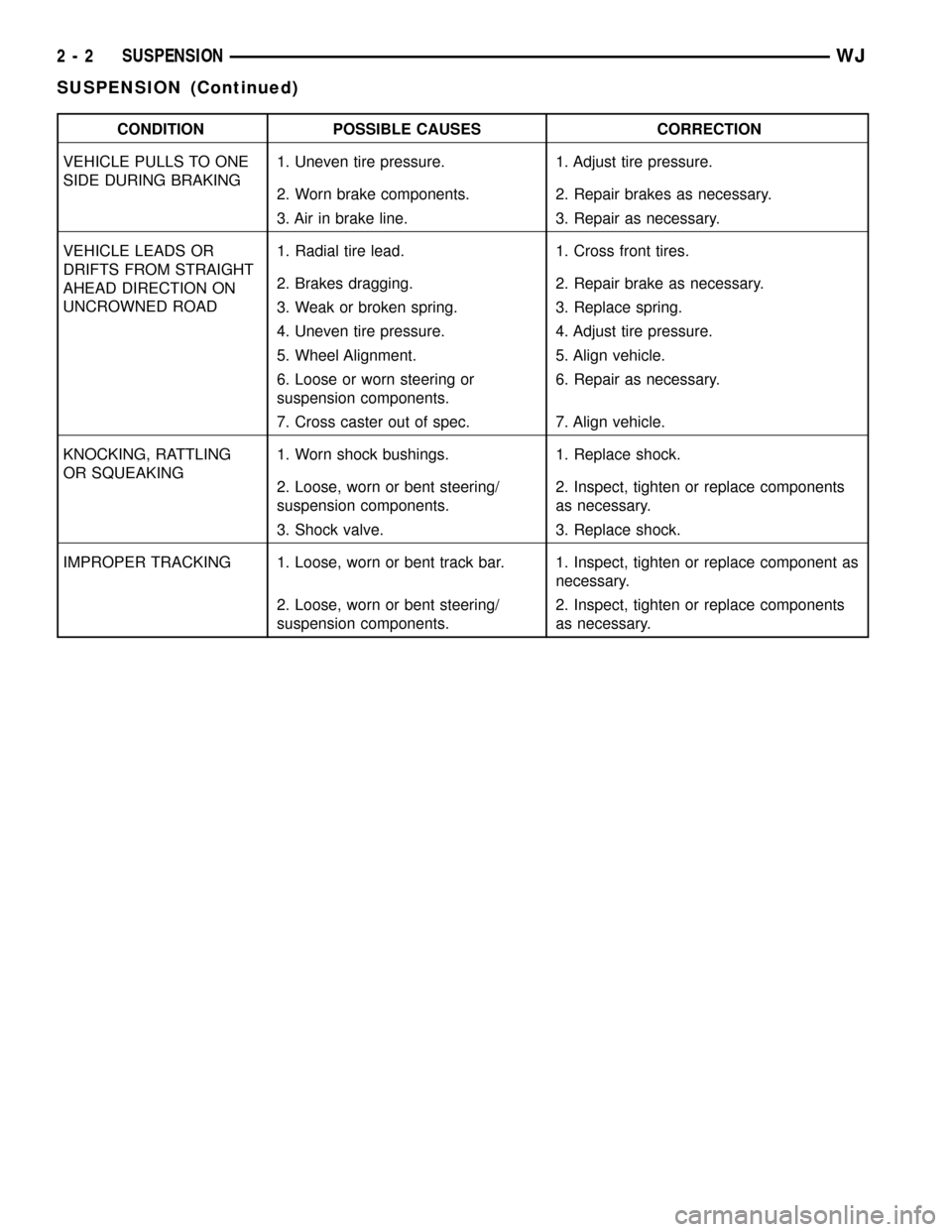
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
VEHICLE PULLS TO ONE
SIDE DURING BRAKING1. Uneven tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Worn brake components. 2. Repair brakes as necessary.
3. Air in brake line. 3. Repair as necessary.
VEHICLE LEADS OR
DRIFTS FROM STRAIGHT
AHEAD DIRECTION ON
UNCROWNED ROAD1. Radial tire lead. 1. Cross front tires.
2. Brakes dragging. 2. Repair brake as necessary.
3. Weak or broken spring. 3. Replace spring.
4. Uneven tire pressure. 4. Adjust tire pressure.
5. Wheel Alignment. 5. Align vehicle.
6. Loose or worn steering or
suspension components.6. Repair as necessary.
7. Cross caster out of spec. 7. Align vehicle.
KNOCKING, RATTLING
OR SQUEAKING1. Worn shock bushings. 1. Replace shock.
2. Loose, worn or bent steering/
suspension components.2. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
3. Shock valve. 3. Replace shock.
IMPROPER TRACKING 1. Loose, worn or bent track bar. 1. Inspect, tighten or replace component as
necessary.
2. Loose, worn or bent steering/
suspension components.2. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
2 - 2 SUSPENSIONWJ
SUSPENSION (Continued)
Page 39 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR
SUSPENSION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
VEHICLE INSTABILITY 1. Loose or worn wheel bearings. 1. Replace wheel bearings.
2. Loose, worn or bent suspension
components.2. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
3. Tire pressure. 3. Adjust tire pressure.
VEHICLE PULLS TO ONE
SIDE1. Weak or broken spring. 1. Replace spring.
2. Alignment. 2. Align vehicle to specifications.
3.Tires. 3. Replace tires.
4. Brakes. 4. Repair as necassary.
KNOCKING, RATTLING
OR SQUEAKING1. Worn shock bushings. 1. Replace shock.
2. Loose shock mounting. 2. Tighten to specifications.
3. Shock valve. 3. Replace shock.
4. Loose upper ball joint. 4. Replace ball joint.
5. Loose, worn or bent suspension
components.5. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
IMPROPER TRACKING 1. Loose, worn or bent suspension
components.1. Inspect, tighten or replace components
as necessary.
2. Bent axle. 2.Replace axle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Shock Absorber Upper Nut 108 80 Ð
Shock Absorber Lower Nut 115 85 Ð
Suspension Arm Upper Ball Joint Nut 142 105 Ð
Suspension Arm Upper Frame Bolts 100 74 Ð
Ball Joint Plate Bolts 136 100 Ð
Suspension Arms Lower Axle Bracket Nut 163 120 Ð
Suspension Arms Lower Frame Bracket Nut 156 115 Ð
Stabilizer Bar Retainer Bolts 54 40 Ð
Stabilizer Bar Bar Link Nut 54 40 Ð
Stabilizer Bar Bracket Link Nut 92 68 Ð
2 - 18 REARWJ
REAR (Continued)
Page 137 of 2199

and therefore creates pressure in the pump. The tun-
ing of the front and rear axle orifices and valves
inside the gerotor pump is unique and each system
includes a torque-limiting pressure relief valve to
protect the clutch pack, which also facilitates vehicle
control under extreme side-to-side traction varia-
tions. The resulting pressure is applied to the clutch
pack and the transfer of torque is completed.
Under conditions in which opposite wheels are on
surfaces with widely different friction characteristics,
Vari-loktdelivers far more torque to the wheel on
the higher traction surface than do conventional
Trac-loktsystems. Because conventional Trac-lokt
differentials are initially pre-loaded to assure torque
transfer, normal driving (where inner and outer
wheel speeds differ during cornering, etc.) produces
torque transfer during even slight side-to-side speed
variations. Since these devices rely on friction from
this preload to transfer torque, normal use tends to
cause wear that reduces the ability of the differential
to transfer torque over time. By design, the Vari-lokt
system is less subject to wear, remaining more con-
sistent over time in its ability to transfer torque. The
coupling assembly is serviced as a unit. From a ser-
vice standpoint the coupling also benefits from using
the same lubricant supply as the ring and pinion
gears.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears, or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side±gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rearend vibra-
tion. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets
and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
3 - 92 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 205 of 2199

Fig. 59 Power Brake Booster±Typical
1 - VACUUM CHECK VALVE
2 - FRONT DIAPHRAGM
3 - REAR DIAPHRAGM
4 - HOUSING
5 - SEAL
6 - AIR FILTER
7 - PRIMARY PUSH ROD (TO BRAKE PEDAL)8 - ATMOSPHERIC INLET VALVE ASSEMBLY
9 - BOOSTER MOUNTING STUDS (4)
10 - SECONDARY PUSH ROD (TO MASTER CYLINDER)
11 - MASTER CYLINDER MOUNTING STUD (2)
12 - SPRING
5 - 30 BRAKES - BASEWJ
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER (Continued)
Page 260 of 2199

The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other prob-
lems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreli-
able warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This conden-
sation can result in sludge formation.
DESCRIPTIONÐ4.0L ENGINE
CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
A pellet-type thermostat controls the operating
temperature of the engine by controlling the amount
of coolant flow to the radiator. On all engines the
thermostat is closed below 195ÉF (90ÉC). Above this
temperature, coolant is allowed to flow to the radia-
tor. This provides quick engine warm up and overall
temperature control. (Fig. 23).
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other prob-
lems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreli-
able warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This conden-
sation can result in sludge formation.
OPERATION
The wax pellet is located in a sealed container at
the spring end of the thermostat. When heated, the
pellet expands, overcoming closing spring tension
and water pump pressure to force the valve to open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
All models are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics for certain cooling system components.If the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) detects low engine
coolant temperature, it will record a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). For other DTC numbers, (Refer to 25
- EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIPTION).
The DTC can also be accessed through the DRB
scan tool.
Fig. 22 Thermostat
1 - FROM HEATER
2 - FROM RADIATOR
3 - TO WATER PUMP
4 - ENGINE BYPASS
5 - THERMOSTAT
Fig. 23 Thermostat and Housing
1 - LONG BOLT
2 - GASKET
3 - THERMOSTAT
4 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
5 - SHORT BOLT
WJENGINE 7 - 37
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT (Continued)
Page 276 of 2199

CAUTION: When installing the serpentine engine
accessory drive belt, the belt MUST be routed cor-
rectly. If not, the engine may overheat due to the
water pump rotating in the wrong direction. Refer to
the Belt Removal and Installtion in this group for
appropriate belt routing. You may also refer to the
Belt Routing Label in the vehicle engine compart-
ment.
Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
(6) Install fan blade and viscous fan drive onto
water pump.
(7) Fill cooling system with coolant and check for
leaks. (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(8) Connect battery cable to battery.
(9) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION
All radiators are equipped with a pressure cap
(Fig. 50). This cap releases pressure at some point
within a range of 124-to-145 kPa (18-to-21 psi). The
pressure relief point (in pounds) is engraved on top of
the cap
The cooling system will operate at pressures
slightly above atmospheric pressure. This results in a
higher coolant boiling point allowing increased radi-
ator cooling capacity. The cap contains a spring-
loaded pressure relief valve. This valve opens when
system pressure reaches the release range of 124-to-
145 kPa (18-to-21 psi).
A rubber gasket seals the radiator filler neck. This is
done to maintain vacuum during coolant cool-down and
to prevent leakage when system is under pressure.
OPERATION
A vent valve in the center of the cap will remain
shut as long as the cooling system is pressurized. As
the coolant cools, it contracts and creates a vacuum
in cooling system. This causes the vacuum valve to
open and coolant in reserve/overflow tank to be
drawn through connecting hose into radiator. If the
vacuum valve is stuck shut, or overflow hose is
kinked, radiator hoses will collapse on cool-down.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP
Remove cap from radiator. Be sure that sealing
surfaces are clean. Moisten rubber gasket with water
and install the cap on pressure tester (tool 7700 or
an equivalent) (Fig. 51).Operate the tester pump and observe the gauge
pointer at its highest point. The cap release pressure
should be 124 to 145 kPa (18 to 21 psi). The cap is
satisfactory when the pressure holds steady. It is also
good if it holds pressure within the 124 to 145 kPa
(18 to 21 psi) range for 30 seconds or more. If the
pointer drops quickly, replace the cap.
CAUTION: Radiator pressure testing tools are very
sensitive to small air leaks, which will not cause
cooling system problems. A pressure cap that does
not have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to tool. Turn tool upside
down and recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap
needs replacement.CLEANING
Clean the radiator pressure cap using a mild soap
and water only.
Fig. 50 Radiator Pressure Cap - Typical
1 - FILLER NECK SEAL
2 - VACUUM VENT VALVE
3 - PRESSURE RATING
4 - PRESSURE VALVE
WJENGINE 7 - 53
WATER PUMP - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 616 of 2199

WASHER SYSTEM
The washer system components should be
inspected periodically, not just when washer perfor-
mance problems are experienced. This inspection
should include the following points:
(1) Check for ice or other foreign material in the
washer reservoir. If contaminated, clean and flush
the washer system. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
FRONT WIPERS/WASHERS - CLEANING).
(2) Inspect the washer plumbing for pinched, leak-
ing, deteriorated, or incorrectly routed hoses and
damaged or disconnected hose fittings. Replace dam-
aged or deteriorated hoses and hose fittings. Leaking
washer hoses can sometimes be repaired by cutting
the hose at the leak and splicing it back together
using an in-line connector fitting. Similarly, sections
of deteriorated hose can be cut out and replaced by
splicing in new sections of hose using in-line connec-
tor fittings. Whenever routing a washer hose or a
wire harness containing a washer hose, it must be
routed away from hot, sharp, or moving parts. Also,
sharp bends that might pinch the washer hose must
be avoided.
FRONT CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
A front washer system check valve is standard
equipment on this model. The front check valve is
integral to the front washer nozzle plumbing wye fit-
ting located in the cowl plenum beneath the cowl ple-
num cover/grille panel near the base of the
windshield. The check valve consists of a molded
plastic body with a round center section. Three
barbed hose nipples are formed in a wye configura-
tion on the outside circumference of the center sec-
tion of the valve body. Within the check valve body, a
small check valve operated by a small coiled spring
restricts flow through the unit until the valve is
unseated by a predetermined inlet fluid pressure.
The front check valve cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The front check valve provides more than one func-
tion in this application. It serves as a wye connector
fitting between the cowl grille panel and washer noz-
zle sections of the front washer supply hose. It also
prevents washer fluid from draining out of the front
washer supply hoses back to the washer reservoir.
This drain-back would result in a lengthy delay from
when the front washer switch is actuated until
washer fluid was dispensed through the front washer
nozzles, because the front washer pump would have
to refill the front washer plumbing from the reservoir
to the nozzles. Finally, the front check valve prevents
washer fluid from siphoning through the front
washer nozzles after the front washer system is
turned Off. When the front washer pump pressurizes
and pumps washer fluid from the reservoir through
the front washer plumbing, the fluid pressure over-
rides the spring pressure applied to the check valve
and unseats the valve, allowing washer fluid to flow
toward the front washer nozzles. When the front
washer pump stops operating, spring pressure seats
the check valve and fluid flow in either direction
within the front washer plumbing is prevented.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the wiper arms from the wiper pivots.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/FRONT WIPERS/WASH-
ERS/FRONT WIPER ARMS - REMOVAL).
(3) Open the hood and pull the hood to plenum
seal off of the forward flanges of the cowl grille cover
and the plenum panel.
Fig. 2 Wiper Blade Inspection
1 - WORN OR UNEVEN EDGES
2 - ROAD FILM OR FOREIGN MATERIAL DEPOSITS
3 - HARD, BRITTLE, OR CRACKED
4 - DEFORMED OR FATIGUED
5 - SPLIT
6 - DAMAGED SUPPORT COMPONENTS
WJFRONT WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 9
FRONT WIPERS/WASHERS (Continued)
Page 646 of 2199

along the left roof side rail to the rear of the vehicle.
At the rear of the vehicle, the headliner hose is
routed above the headliner and along the upper lift-
gate opening panel toward the right side of the vehi-
cle. The headliner hose then passes through a hole
with a rubber grommet in the upper liftgate opening
panel and through another hole with a rubber grom-
met into the upper inner liftgate panel to the rear
washer nozzle.
Washer hose is available for service only as roll
stock, which must then be cut to length. The head-
liner washer hose is integral to the headliner unit
and, if faulty or damaged, the headliner unit must be
replaced. The molded plastic washer hose fittings
cannot be repaired. If these fittings are faulty or
damaged, they must be replaced.
OPERATION
Washer fluid in the washer reservoir is pressurized
and fed by the rear washer pump/motor through the
rear washer system plumbing and fittings to the rear
washer nozzle on the liftgate outer panel above the
liftgate glass. Whenever routing the washer hose or a
wire harness containing a washer hose, it must be
routed away from hot, sharp, or moving parts; and,
sharp bends that might pinch the hose must be
avoided.
REAR WASHER NOZZLE
DESCRIPTION
The rear washer nozzle is a fluidic type unit that
includes an integral check valve (Fig. 3). The nozzle
is constructed of molded plastic and has a rubber
seal and integral snap features on the back of it. The
nozzle is secured by a snap fit in a dedicated mount-
ing hole in the liftgate outer panel above the liftgate
flip-up glass. Within the rear nozzle body, a small
check ball is held against an integral valve seat at
the inlet end of the nozzle by a small coiled spring.
The rear washer nozzle and check valve unit cannot
be adjusted or repaired. If faulty or damaged, the
entire nozzle and check valve unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The rear washer nozzle is designed to dispense
washer fluid into the wiper pattern area on the out-
side of the liftgate glass. Pressurized washer fluid is
fed to the nozzle from the washer reservoir by the
rear washer pump/motor through a single hose,
which is attached to a barbed nipple on the back of
the rear washer nozzle. The rear washer nozzle
incorporates a fluidic design, which causes the nozzle
to emit the pressurized washer fluid as an oscillating
stream to more effectively cover a larger area of the
glass area to be cleaned. The integral rear nozzle
check valve prevents washer fluid from draining out
of the rear washer supply hoses back to the washer
reservoir. This drain-back would result in a lengthy
delay from when the rear washer switch is actuated
until washer fluid was dispensed through the rear
washer nozzle, because the rear washer pump would
have to refill the rear washer plumbing from the res-
ervoir to the nozzle. The check valve also prevents
washer fluid from siphoning through the rear washer
nozzle after the rear washer system is turned Off.
When the rear washer pump pressurizes and pumps
washer fluid from the reservoir through the rear
washer plumbing, the fluid pressure overrides the
spring pressure applied to the check ball within the
valve and unseats the check ball, allowing washer
fluid to flow to the rear washer nozzle. When the
rear washer pump stops operating, spring pressure
seats the check ball in the valve and fluid flow in
either direction within the rear washer plumbing is
prevented.
REMOVAL
The check valve for the rear washer nozzle is inte-
gral to the nozzle.
(1) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry at the sides of the rear
washer nozzle to release the snap features that
secure it in the mounting hole of the liftgate outer
panel.
Fig. 3 Rear Washer Nozzle
1 - HEADLINER WASHER HOSE
2 - ROOF PANEL
3 - REAR WASHER NOZZLE
4 - LIFTGATE
WJREAR WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 39
REAR WASHER HOSES/TUBES (Continued)