2003 CHEVROLET SILVERADO stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 271 of 556
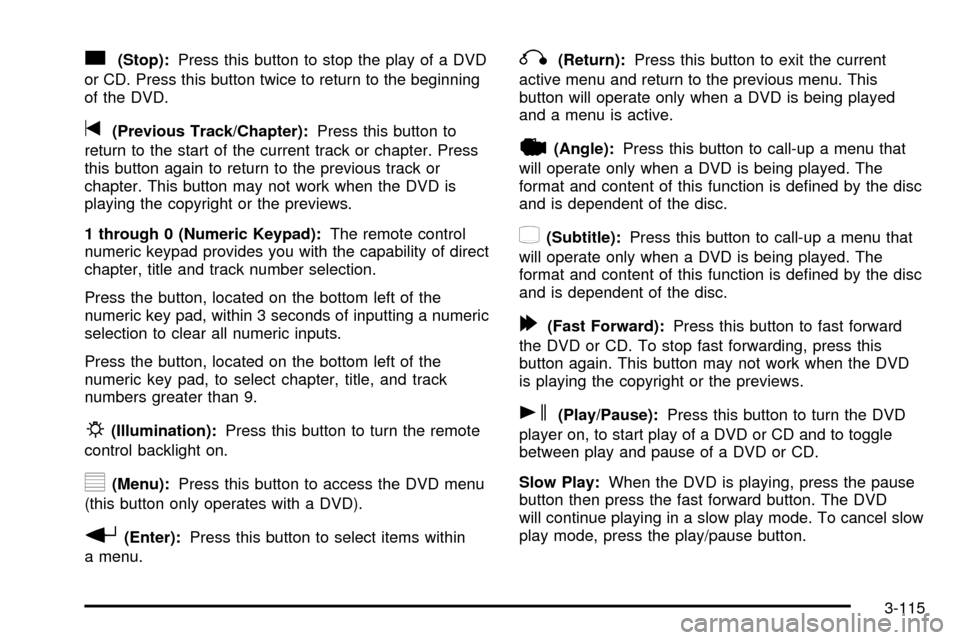

c(Stop):Press this button to stop the play of a DVD
or CD. Press this button twice to return to the beginning
of the DVD.
t(Previous Track/Chapter):Press this button to
return to the start of the current track or chapter. Press
this button again to return to the previous track or
chapter. This button may not work when the DVD is
playing the copyright or the previews.
1 through 0 (Numeric Keypad):The remote control
numeric keypad provides you with the capability of direct
chapter, title and track number selection.
Press the button, located on the bottom left of the
numeric key pad, within 3 seconds of inputting a numeric
selection to clear all numeric inputs.
Press the button, located on the bottom left of the
numeric key pad, to select chapter, title, and track
numbers greater than 9.
P(Illumination):Press this button to turn the remote
control backlight on.
y(Menu):Press this button to access the DVD menu
(this button only operates with a DVD).
r(Enter):Press this button to select items within
a menu.
q(Return):Press this button to exit the current
active menu and return to the previous menu. This
button will operate only when a DVD is being played
and a menu is active.
|(Angle):Press this button to call-up a menu that
will operate only when a DVD is being played. The
format and content of this function is de®ned by the disc
and is dependent of the disc.
{(Subtitle):Press this button to call-up a menu that
will operate only when a DVD is being played. The
format and content of this function is de®ned by the disc
and is dependent of the disc.
[(Fast Forward):Press this button to fast forward
the DVD or CD. To stop fast forwarding, press this
button again. This button may not work when the DVD
is playing the copyright or the previews.
s(Play/Pause):Press this button to turn the DVD
player on, to start play of a DVD or CD and to toggle
between play and pause of a DVD or CD.
Slow Play:When the DVD is playing, press the pause
button then press the fast forward button. The DVD
will continue playing in a slow play mode. To cancel slow
play mode, press the play/pause button.
3-115
Page 275 of 556
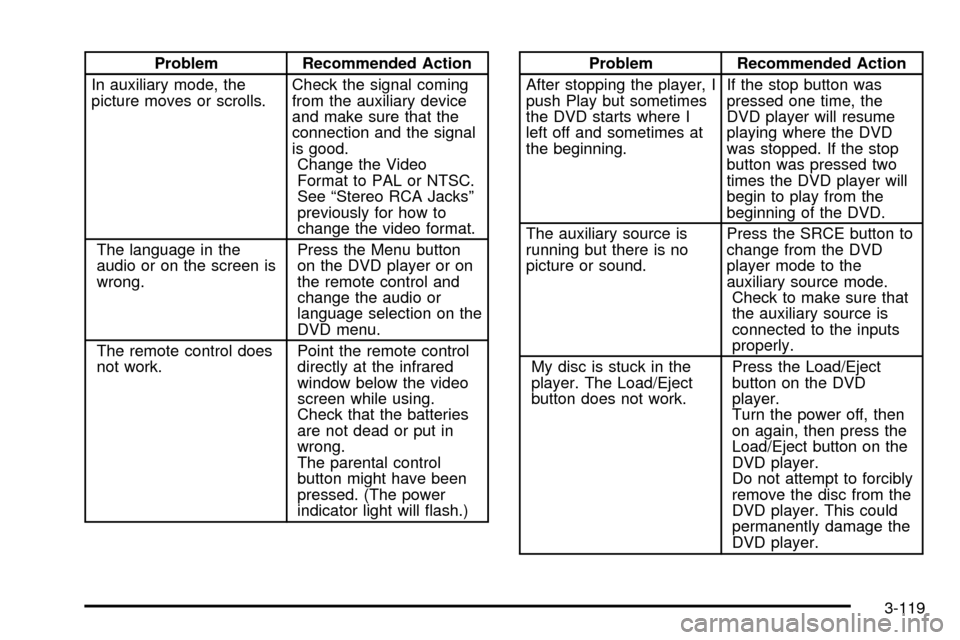
Problem Recommended Action
In auxiliary mode, the
picture moves or scrolls.Check the signal coming
from the auxiliary device
and make sure that the
connection and the signal
is good.
Change the Video
Format to PAL or NTSC.
See ªStereo RCA Jacksº
previously for how to
change the video format.
The language in the
audio or on the screen is
wrong.Press the Menu button
on the DVD player or on
the remote control and
change the audio or
language selection on the
DVD menu.
The remote control does
not work.Point the remote control
directly at the infrared
window below the video
screen while using.
Check that the batteries
are not dead or put in
wrong.
The parental control
button might have been
pressed. (The power
indicator light will ¯ash.)Problem Recommended Action
After stopping the player, I
push Play but sometimes
the DVD starts where I
left off and sometimes at
the beginning.If the stop button was
pressed one time, the
DVD player will resume
playing where the DVD
was stopped. If the stop
button was pressed two
times the DVD player will
begin to play from the
beginning of the DVD.
The auxiliary source is
running but there is no
picture or sound.Press the SRCE button to
change from the DVD
player mode to the
auxiliary source mode.
Check to make sure that
the auxiliary source is
connected to the inputs
properly.
My disc is stuck in the
player. The Load/Eject
button does not work.Press the Load/Eject
button on the DVD
player.
Turn the power off, then
on again, then press the
Load/Eject button on the
DVD player.
Do not attempt to forcibly
remove the disc from the
DVD player. This could
permanently damage the
DVD player.
3-119
Page 288 of 556

Braking
Braking action involvesperception timeandreaction time.
First, you have to decide to push on the brake pedal.
That isperception time.Then you have to bring up your
foot and do it. That isreaction time.
Averagereaction timeis about 3/4 of a second. But that
is only an average. It might be less with one driver
and as long as two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition, alertness, coordination
and eyesight all play a part. So do alcohol, drugs and
frustration. But even in 3/4 of a second, a vehicle moving
at 60 mph (100 km/h) travels 66 feet (20 m). That
could be a lot of distance in an emergency, so keeping
enough space between your vehicle and others is
important.
And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of the road (whether it is pavement
or gravel); the condition of the road (wet, dry, icy); tire
tread; the condition of your brakes; the weight of
the vehicle and the amount of brake force applied.
Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive in
spurts Ð heavy acceleration followed by heavy
braking Ð rather than keeping pace with traffic. This is a
mistake. Your brakes may not have time to cool between
hard stops. Your brakes will wear out much faster if you
do a lot of heavy braking. If you keep pace with the trafficand allow realistic following distances, you will eliminate a
lot of unnecessary braking. That means better braking
and longer brake life.
If your engine ever stops while you are driving, brake
normally but do not pump your brakes. If you do,
the pedal may get harder to push down. If your engine
stops, you will still have some power brake assist.
But you will use it when you brake. Once the power
assist is used up, it may take longer to stop and
the brake pedal will be harder to push.
Anti-lock Brake System
Your vehicle has anti-lock brakes. ABS is an advanced
electronic braking system that will help prevent a
braking skid.
When you start your engine and begin to drive away,
your anti-lock brake system will check itself. You
may hear a momentary motor or clicking noise while
this test is going on. This is normal.
4-6
Page 291 of 556

Supplemental Brake Assist System
If your vehicle has vacuum assist power brakes, it is also
equipped with a supplemental brake assist system
that supplies additional vacuum to the vacuum brake
booster if engine vacuum is reduced. Under certain
conditions, the supplemental brake assist system may
run brie¯y after starting your vehicle or when you
apply and release the brake pedal and it may continue
to run even after you have removed your foot from
the brake pedal. When the supplemental brake assist
system is operating, you may hear a motor running
or feel a slight vibration in the steering wheel or brake
pedal. This indicates that the supplemental brake
assist system is working to supply additional vacuum for
your vacuum assist power brakes. This is a normal
operation of your brake system and does not require that
the brake system be serviced.Each time you start your vehicle and accelerate to
10 mph, the supplemental brake assist system
will perform a self-diagnostic check of the system and
you may hear or feel the supplemental brake assist
motor run brie¯y. While you are driving your vehicle, the
supplemental brake assist system monitors itself to
ensure that it is operating properly. If there is a problem
with the supplemental brake assist system, the
SERVICE BRAKE BOOSTER message will be displayed
on the Driver Information Center. See
DIC Warnings
and Messages on page 3-65.
If your supplemental brake assist system runs every
time you apply and release the brake pedal or you notice
that the brake pedal has suddenly become much
harder to push and the vehicle takes longer to stop, you
should have your vehicle serviced as soon as possible.
4-9
Page 293 of 556

The traction off light will come on under the following
conditions:
·The Traction Assist System is turned off, either by
pressing the TAS on/off button or turning off the
automatic engagement feature of the TAS.
·The transmission is in FIRST (1); TAS will not
operate in this gear. This is normal.
·The vehicle is driven on an extremely rough road.
When the vehicle leaves the rough surface, slows
down or stops, the light will go off and TAS will
be on again. This is normal.
·A Traction Assist System, Anti-Lock Brake System
or engine-related problem has been detected and
the vehicle needs service.
·If the vehicle has been driven with the TAS system
on for long periods of time, or if the vehicle has
gone through many several high speed braking
maneuvers the system may be automatically
disabled. The system will automatically re-enable
after approximately two minutes of not using
the brakes.
See
Traction Off Light on page 3-46.The Traction Assist System, as delivered from the
factory, will automatically come on whenever you start
your vehicle. To limit wheel spin, especially in
slippery road conditions, you should always leave the
system on. But you can turn the TAS off if you ever need
to. You should turn the TAS off if your vehicle ever
gets stuck in sand, mud or snow and rocking the vehicle
is required. See
Rocking Your VehicleunderIf You
Are Stuck: In Sand, Mud, Ice or Snow on page 4-52.
To turn the system on or
off press the TAS on/off
button located on the
instrument panel.
If you used the button to turn the system off, the traction
off light will come on and stay on. You can turn the
system back on at any time by pressing the button
again. The traction off light should go off.
4-11
Page 302 of 556

·Do not get too close to the vehicle you want to
pass while you're awaiting an opportunity. For
one thing, following too closely reduces your area
of vision, especially if you're following a larger
vehicle. Also, you won't have adequate space if the
vehicle ahead suddenly slows or stops. Keep
back a reasonable distance.
·When it looks like a chance to pass is coming up,
start to accelerate but stay in the right lane and
don't get too close. Time your move so you will be
increasing speed as the time comes to move
into the other lane. If the way is clear to pass, you
will have a ªrunning startº that more than makes
up for the distance you would lose by dropping
back. And if something happens to cause you to
cancel your pass, you need only slow down
and drop back again and wait for another
opportunity.
·If other vehicles are lined up to pass a slow vehicle,
wait your turn. But take care that someone isn't
trying to pass you as you pull out to pass the slow
vehicle. Remember to glance over your shoulder
and check the blind spot.
·Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder and
start your left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane to pass. When you are far
enough ahead of the passed vehicle to see its front
in your inside mirror, activate your right lane
change signal and move back into the right lane.
(Remember that if your right outside mirror is
convex, the vehicle you just passed may seem to
be farther away from you than it really is.)
·Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time on
two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
·Don't overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not ¯ashing, it
may be slowing down or starting to turn.
·If you're being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little to the right.
4-20
Page 303 of 556

Loss of Control
Let's review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes,
steering and acceleration) don't have enough friction
where the tires meet the road to do what the driver has
asked.
In any emergency, don't give up. Keep trying to steer
and constantly seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not
ªoverdrivingº those conditions. But skids are always
possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle's
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren't rolling. In the steering or cornering skid, too much
speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip and lose
cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too much
throttle causes the driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.If you have the Traction Assist System, remember: It
helps avoid only the acceleration skid. If you do not have
this system, or if the system is off, then an acceleration
skid is also best handled by easing your foot off the
accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough,
your vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel or other material is on the road. For safety, you'll
want to slow down and adjust your driving to these
conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration
or braking (including engine braking by shifting to a
lower gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires
to slide. You may not realize the surface is slippery
until your vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning
clues Ð such as enough water, ice or packed snow
on the road to make a ªmirrored surfaceº Ð and slow
down when you have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock brake system (ABS) helps
avoid only the braking skid.
4-21
Page 309 of 556

Scanning the Terrain
Off-road driving can take you over many different kinds
of terrain. You need to be familiar with the terrain
and its many different features. Here are some things to
consider.
Surface Conditions:Off-roading can take you over
hard-packed dirt, gravel, rocks, grass, sand, mud, snow
or ice. Each of these surfaces affects the steering,
acceleration and braking of your vehicle in different
ways. Depending upon the kind of surface you are on,
you may experience slipping, sliding, wheel spinning,
delayed acceleration, poor traction and longer braking
distances.
Surface Obstacles:Unseen or hidden obstacles can
be hazardous. A rock, log, hole, rut or bump can startle
you if you're not prepared for them. Often these
obstacles are hidden by grass, bushes, snow or even
the rise and fall of the terrain itself. Here are some
things to consider:
·Is the path ahead clear?
·Will the surface texture change abruptly up ahead?
·Does the travel take you uphill or downhill?
(There's more discussion of these subjects later.)
·Will you have to stop suddenly or change direction
quickly?When you drive over obstacles or rough terrain, keep a
®rm grip on the steering wheel. Ruts, troughs or
other surface features can jerk the wheel out of your
hands if you're not prepared.
When you drive over bumps, rocks, or other obstacles,
your wheels can leave the ground. If this happens,
even with one or two wheels, you can't control
the vehicle as well or at all.
Because you will be on an unpaved surface, it's
especially important to avoid sudden acceleration,
sudden turns or sudden braking.
In a way, off-road driving requires a different kind of
alertness from driving on paved roads and highways.
There are no road signs, posted speed limits or
signal lights. You have to use your own good judgment
about what is safe and what isn't.
Drinking and driving can be very dangerous on any
road. And this is certainly true for off-road driving. At the
very time you need special alertness and driving
skills, your re¯exes, perceptions and judgment can be
affected by even a small amount of alcohol. You
could have a serious Ð or even fatal Ð accident if you
drink and drive or ride with a driver who has been
drinking. See
Drunken Driving on page 4-2.
4-27