2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY wheel bolts
[x] Cancel search: wheel boltsPage 275 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-32 REPAIRS
9.Fit alignment tool LRT-12-001 to spigot
bearing in crankshaft.
10.Fit drive plate onto tool LRT-12-001 ensure
side marked 'flywheel side' is towards flywheel.
11.Fit clutch cover and locate on dowels.
12.Fit clutch cover bolts and tighten in diagonal
sequence to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft).
13.Fit gearbox assembly.
+ MANUAL GEARBOX - R380,
REPAIRS, Gearbox - V8.
Plate - drive - automatic
$% 12.53.13
Remove
1.Remove automatic gearbox.
+ AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22
- 24, REPAIRS, Gearbox - convertor and
transfer gearbox - V8.
2.Remove 2 bolts securing CKP sensor cover.
3.Remove CKP sensor cover.
4.Remove 2 nuts securing CKP sensor.
5.Remove CKP sensor.
Page 276 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
REPAIRS 12-2-33
6.Remove 4 bolts securing drive plate clamp ring
and remove ring.
7.Remove drive plate from hub.
8.Remove 6 Allen screws securing hub, remove
hub and collect spacer.
On early engines, balance weights are on
engine side of drive plate; replacement drive
plates will have balance weights on torque
converter side of drive plate.
Refit
1.Clean hub and mating face, spacer and clamp
ring.
2.Clean drive plate and ensure free from cracks
and distortion.
3.Fit spacer and hub to crankshaft, tighten Allen
screws to 78 Nm (58 lbf.ft).
4.Fit drive plate and clamp ring, tighten bolts to
45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
5.Clean CKP sensor and mating face.
6.Fit crankshaft sensor and tighten nuts to 6 Nm
(5 lbf.ft).
7.Fit CKP sensor cover and tighten bolts to 6 Nm
(5 lbf.ft).
8.Fit CKP sensor multiplug to bracket.
9.Fit automatic gearbox.
+ AUTOMATIC GEARBOX - ZF4HP22
- 24, REPAIRS, Gearbox - convertor and
transfer gearbox - V8.
Ring gear - starter
$% 12.53.19
Remove
1.Remove flywheel.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Flywheel.
2.Drill a 3 mm (0.12 in) diameter hole at root of 2
teeth.
3.Apply a cold chisel in root of one of ring gear
teeth, strike chisel with hammer to break ring
gear.
WARNING: SUITABLE EYE PROTECTION
MUST BE WORN.
4.Remove starter ring gear.
Refit
1.Clean flywheel and starter ring gear.
2.Heat new starter ring gear evenly to 350
°C
(660
°F), indicated when the ring is a light blue
colour.
3.Locate ring gear on flywheel and press ring
gear hard against flange on flywheel.
Page 293 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-50 OVERHAUL
5.Clean hub and mating face, spacer and clamp
ring.
6.Clean drive plate and ensure free from cracks
and distortion.
7.Fit spacer and hub to crankshaft, tighten Allen
screws to 78 Nm (58 lbf.ft).
8.Fit drive plate and clamp ring, tighten bolts to
45 Nm (35 lbf.ft).
9.Fit CKP sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Sensor - crankshaft position
(CKP).
Seal - crankshaft - rear - manual models
$% 12.21.20.01
Disassembly
1.Restrain flywheel.
2.Working in sequence, loosen and remove 6
bolts securing clutch cover to flywheel.
3.Remove clutch cover.
4.Remove clutch plate.
5.Remove CKP sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Sensor - crankshaft position
(CKP).
6.Remove 6 bolts securing flywheel.
7.Remove flywheel.
Page 294 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
OVERHAUL 12-2-51
8.Carefully remove oil seal from cylinder block to
avoid damage to seal location or running
surface on crankshaft.
Reassembly
1.Ensure both seal location and running surface
on crankshaft are clean.
2.Fit tool LRT-12-095 to crankshaft.
3.Fit new seal squarely onto crankshaft and
guide.
CAUTION: Oil seal must be fitted dry.4.Fit seal into location using tools LRT-12-091
and LRT-99-003.
5.Clean mating faces of flywheel and crankshaft,
dowel and dowel hole.
6.Fit flywheel to crankshaft and, working in a
diagonal sequence, tighten bolts to 78 Nm (58
lbf.ft).
7.Fit CKP sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
V8, REPAIRS, Sensor - crankshaft position
(CKP).
8.Clean clutch cover, drive plate and spigot bush
in end of crankshaft.
9.Renew worn components as necessary.
10.If refitting existing drive plate, apply Molycote
FB 108 to splines.
11.Fit LRT-12-001 alignment tool to spigot bearing
in crankshaft.
12.Fit drive plate onto alignment tool, ensure side
marked 'flywheel side' is against flywheel.
13.Fit clutch cover and locate on dowels.
14.Fit clutch cover bolts and tighten in diagonal
sequence to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft).
Page 295 of 1672

ENGINE - V8
12-2-52 OVERHAUL
Bearing - spigot - crankshaft
$% 12.21.45.01
Disassembly
1.Remove 6 bolts securing clutch cover.
2.Remove clutch cover.
3.Tap a thread in spigot bush to accommodate a
suitable impulse extractor.
4.Fit extractor to bush.
5.Remove bush from crankshaft. Reassembly
1.Clean bush register in rear of crankshaft.
2.Using a suitable drift, fit new bush to crankshaft
so that it is flush with or up to a maximum of 1.6
mm (0.06 in) below the end of the crankshaft.
3.Ream spigot bush to 19.117 + 0.025
− 0.00 mm
(0.75 + 0.001
− 0.00 in) .
4.Remove all traces of swarf on completion.
5.Clean mating faces of flywheel and crankshaft,
dowel and dowel hole.
6.Fit clutch cover to flywheel and tighten bolts by
diagonal slection to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft).
Page 657 of 1672

CLUTCH - TD5
33-1-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The clutch system is a diaphragm type clutch operated by a hydraulic cylinder. The drive plate is of the rigid centre
type with no integral damping springs. The flywheel is of the dual mass type with damping springs integral with the
flywheel. The clutch requires no adjustment to compensate for wear.
Hydraulic clutch
The hydraulic clutch comprises a master cylinder, slave cylinder and a hydraulic reservoir. The master and slave
cylinders are connected to each other hydraulically by plastic and metal pipes. The plastic section of the pipe allows
ease of pipe routing and also absorbs engine movements and vibrations.
The master cylinder comprises a body with a central bore. Two ports in the body connect the bore to the hydraulic
feed pipe to the slave cylinder and the fluid reservoir. The bore is also connected to a damper which prevents engine
pulses being transferred hydraulically to the clutch pedal. A piston is fitted in the bore and has an external rod which
is attached to the clutch pedal with a pin. Two coil springs on the clutch pedal reduce the effort required to depress
the pedal.
The master cylinder is mounted on the bulkhead and secured with two bolts. The cylinder is connected to the shared
brake/clutch reservoir on the brake servo by a braided connecting hose.
The slave cylinder is located on the left hand side of the gearbox housing and secured with two bolts. A heat shield
is fitted to protect the underside of the slave cylinder from heat generated from the exhaust system. The slave cylinder
comprises a cylinder with a piston and a rod. A port in the cylinder body provides the attachment for the hydraulic feed
pipe from the master cylinder. A second port is fitted witha bleed nipple used for removing air from the hydraulic
system after servicing. The piston rod locates on a clutch release lever located in the gearbox housing. The rod is
positively retained on the release lever with a clip.
Clutch mechanism
The clutch mechanism comprises a flywheel, drive plate, pressure plate, release lever and a release bearing. The
clutch mechanism is fully enclosed at the rear of the engine by the gearbox housing.
A clutch release bearing sleeve is attached in the gearbox housing with two bolts and located on two dowels. A spigot
with a ball end is formed on the release bearing sleeve and provides amounting and pivot point for the clutch release
lever. A dished pivot washer is located on the ball of the spigot. When the release lever is located on the ball, the pivot
washer seats against the rear face of the release lever. A spring clip is located on the lever and the pivot washer and
secures the lever on the spigot. A small bolt retains the spring clip in position.
The release lever is forked at its inner end and locates on the clutch release bearing carrier. The outer end of the
release lever has a nylon seat which locates the slave cylinder piston rod. A second nylon seat, positioned centrally
on the release lever, locates on the ball spigot of the release bearing sleeve and allows the release lever to pivot freely
around the ball.
The clutch release bearing locates on the clutch release lever and release bearing sleeve. The bearing is retained on
a carrier which has two flats to prevent the carrier rotating on the release lever. A clip retains the release lever on the
carrier. The bearing and carrier are not serviceable individually.
Page 658 of 1672

CLUTCH - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 33-1-7
Dual mass flywheel
1Ring gear
2Primary flywheel
3Inner drive plate
4Spring housing
5Secondary flywheel
6Rivet
7Ball bearing8Dowel location hole
9Mounting hole
10Inner spring
11Outer spring
12Crankshaft position sensing holes
13Pressure plate locating dowel
The dual mass flywheel is bolted on the rear of the crankshaft with eight bolts. A dowel on the crankshaft flange
ensures that the flywheel is correctly located. A ring gear is fitted on the outer diameter of the flywheel. The ring gear
is not serviceable. Thirty blind holes are drilled in the outer diameter of the flywheel adjacent to the ring gear. The
holes are positioned at 10
° intervals with four 20° spaces. The holes are used by the crankshaft position sensor for
engine management.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Page 659 of 1672
CLUTCH - TD5
33-1-8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The dual mass flywheel is used to insulate the gearbox from torsional and transient vibrations produced by the engine.
The flywheel comprises primary and secondary flywheels with the drive between the two transferred by a torsional
damper which comprises four coil springs. The springs are located in the inside diameter of the primary flywheel. Two
of the springs are of smaller diameter and fit inside the larger diameter springs.
The primary flywheel locates the ring gear and is attached to the crankshaft flange with eight bolts. The two pairs of
coil springs are located in a recess in the flywheel between two riveted retainers. A roller bearing is pressed onto the
central boss of the primary flywheel and retained with a riveted plate. The bearing provides the mounting for the
secondary flywheel.
The secondary flywheel comprises two parts; an outer flywheel which provides the friction surface for the clutch drive
plate and an inner drive plate which transfers the drive from the primary flywheel, via the coil springs, to the outer
flywheel. The two components of the secondary flywheel are secured to each other with rivets. The inner drive plate
is located between the two pairs of coil springs and can rotate on the ball bearing in either direction against the
combined compression force of the four coil springs. Under high torque loading conditions the secondary flywheel can
rotate in either direction up to 70
° in relation to the primary flywheel.
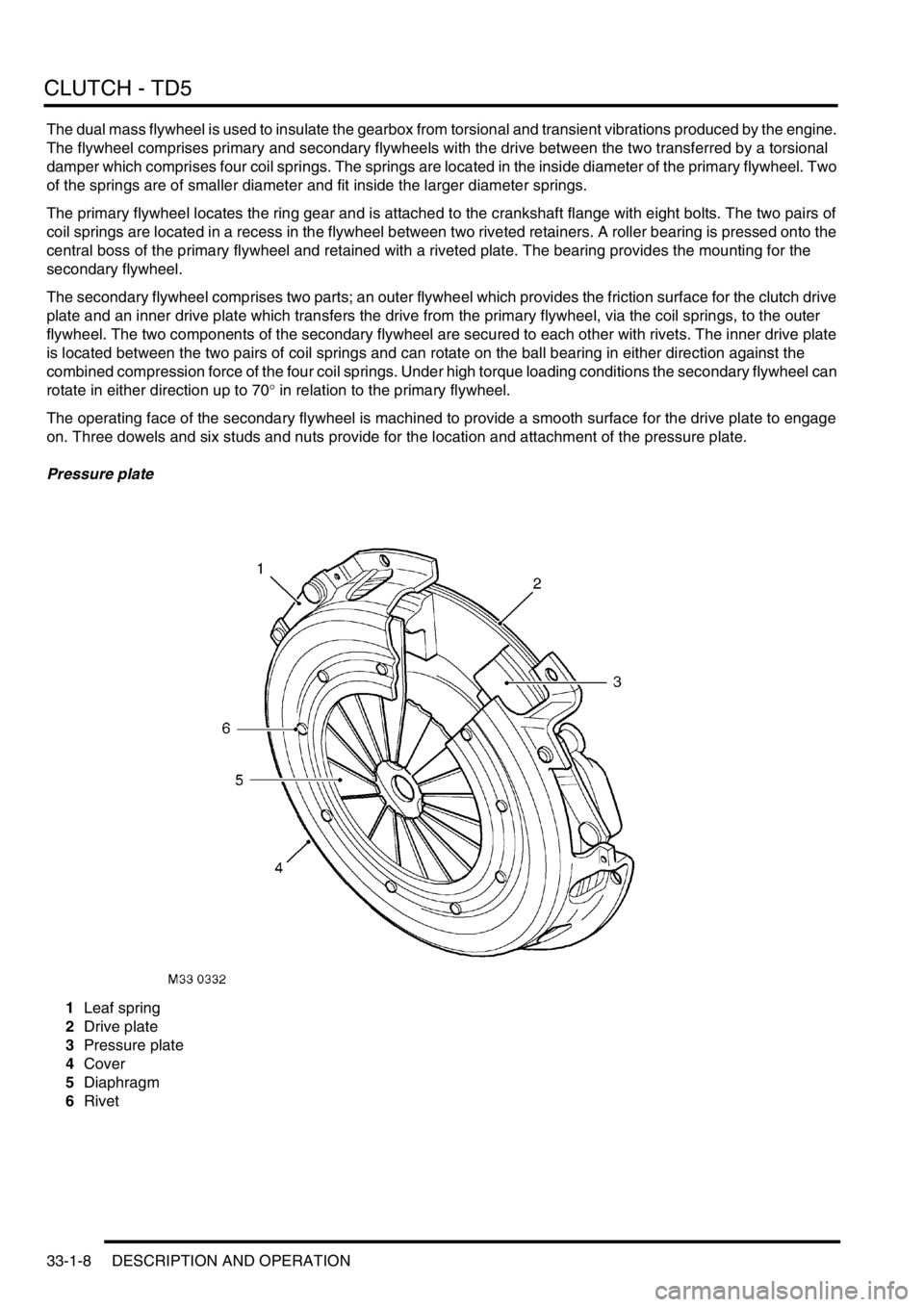
The operating face of the secondary flywheel is machined to provide a smooth surface for the drive plate to engage
on. Three dowels and six studs and nuts provide for the location and attachment of the pressure plate.
Pressure plate
1Leaf spring
2Drive plate
3Pressure plate
4Cover
5Diaphragm
6Rivet