2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 590 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 26-1-7
Pipes and hoses
The coolant circuit comprises flexible hoses and metal formed pipes which direct the coolant into and out of the
engine, radiator and heater matrix. Plastic pipes are used for the bleed and overflow pipes to the expansion tank.
A bleed screw is installed in the radiator top hose and is used to bleed air during system filling. A drain plug to drain
the heater and cylinder block circuit of coolant is located on the underside of the coolant pump feed pipe.
Oil cooler
The oil cooler is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil filter. Oil from the oil
pump is passed through a heat exchanger which is surrounded by coolant in a housing on the side of the engine.
Full water pump flow is directed along the cooler housing which also distributes the flow evenly along the block into
three core holes for cylinder cooling. This cools the engine oil before it is passed into the engine. A small percentage
of the coolant from the oil cooler passes into a metal pipe behind the engine. It then flows into the lower radiator via
a hose.
Fuel cooler
The fuel cooler is located on the right hand side of the engine and is attached to the inlet manifold. The cooler is
cylindrical in design and has a coolant feed connection at its forward end. A 'T' connection at the rear of the cooler
provides a connection for the coolant return from the heater matrix and coolant return from the fuel cooler.
The 'T' connection houses a thermostat which opens at approximately 82
°C. This prevents the cooler operating in
cold climates.
Two quick release couplings on the cooler allow for the connection of the fuel feed from the pressure regulator and
return to the fuel tank. A counter flow system is used within the cooler.
Fuel flows around a coolant jacket within the cooler and flows from the back to the front of the cooler. As the hot fuel
cools travelling slowly forwards it meets progressively colder coolant travelling in the opposite direction maintaining a
differential cooling effect.
EGR Cooler
The EGR Cooler is mounted on the front of the cylinder head. Coolant from the oil cooler flows around the EGR cooler,
cooling the exhaust gas, to improve exhaust emissions, before being returned to the expansion tank.
Coolant pump
1Drive lugs (hidden)
2Housing
3'O' rings4Cover
5Feed hose connection
6Impeller
Page 593 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
26-1-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Coolant flow - Engine warm up
Refer to illustration.
+ COOLING SYSTEM - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Cooling system coolant flow.
During warm up the coolant pump moves fluid through the cylinder block and it emerges from the outlet housing. From
the outlet housing, the warm coolant flow is prevented from flowing through the upper and lower radiators because
both thermostats are closed. The coolant is directed into the heater circuit.
Some coolant from the by-pass pipe can pass through small sensing holes in the flow valve. The warm coolant enters
a tube in the thermostat housing and surrounds 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the
radiator bottom hose conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area. In cold ambient temperatures the engine
temperature can be raised by up to 10
°C (50°F) to compensate for the heat loss of the 10% exposure to the cold
coolant return from the radiator bottom hose.
At engine speeds below 1500 rev/min, the by-pass valve is closed only allowing the small flow through the sensing
holes. As the engine speed increases above 1500 rev/min, the greater flow and pressure from pump overcomes the
light spring and opens the by-pass flow valve. The flow valve opens to meet the engine's cooling needs at higher
engine speeds and prevents excess pressure in the cooling system. With both thermostats closed, maximum flow is
directed through the heater circuit.
The heater matrix acts as a heat exchanger reducing the coolant temperature as it passes through the matrix. Coolant
emerges from the heater matrix and flows to the fuel cooler 'T' connection via the heater return hose. From the fuel
cooler the coolant is directed into the coolant pump feed pipe and recirculated around the heater circuit. In this
condition the cooling system is operating at maximum heater performance.
Coolant flow - Engine hot
As the coolant temperature increases the main thermostat opens. This allows some coolant from the outlet housing
to flow through the top hose and into the radiator to be cooled. The hot coolant flows from the left tank in the radiator,
along the tubes to the right tank. The air flowing through the fins between the tubes cools the coolant as it passes
through the radiator.
A controlled flow of the lower temperature coolant is drawn by the pump and blended with hot coolant from the by-
pass and the heater return pipes in the pump feed pipe. The pump then passes this coolant, via the cylinder block, to
the oil cooler housing, cooling the engine oil before entering the block to cool the cylinders.
When the fuel temperature increases, the heat from the fuel conducts through the fuel cooler 'T' connection and
causes the fuel thermostat to open.
Pre EU3 models: Coolant from the cylinder block flows through the oil cooler and via a pipe and hose enters the
lower radiator. The coolant in the lower radiator is subjected to an additional two passes through the lower radiator to
further reduce the coolant temperature. From the lower radiator the coolant flows , via a hose, to the fuel cooler.
As the hot fuel cools, travelling slowly forwards through the cooler, it meets the progressively colder coolant travelling
in the opposite direction from the lower radiator.
EU3 models: Coolant from the cylinder block flows through the oil cooler to the EGR cooler and then back to the
expansion tank. and via a pipe and hose enters the lower radiator. The lower temperature coolant from the oil cooler
housing is subjected to an additional two passes through the lower radiator to further reduce the coolant temperature.
From the lower radiator the coolant flows , via a hose, to the fuel cooler.
As the hot fuel cools, travelling slowly forwards through the cooler, it meets the progressively colder coolant travelling
in the opposite direction from the lower radiator.
Page 624 of 1672

MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 30-1-3
Description
General
The diesel engine has the inlet manifold attached to the right hand side of the engine and the exhaust manifold
attached to the left hand side of the engine. The inlet manifold directs cooled compressed air from the turbocharger
and intercooler into the cylinders, where it is mixed with fuel from the injectors. Exhaust gases from the exhaust
manifold can also be directed into the inlet manifold via a pipe from the exhaust manifold and an Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve on the inlet manifold. The exhaust manifold allows combustion gases from the cylinders to
leave the engine where they are directed into the exhaust system and turbocharger.
The exhaust system is attached to the turbocharger and is directed along the underside of the vehicle to emit exhaust
gases from a tail pipe at the rear of the vehicle. A silencer is installed midway along the system and a second tail
silencer is located at the rear of the vehicle.
Inlet manifold
The inlet manifold is a one piece aluminium casting. The manifold is secured to the cylinder head with two studs and
flanged nuts and eight flanged bolts. A one piece laminated gasket seals the manifold to the cylinder head.
Four threaded bosses on the manifold provide for the attachment of the fuel cooler. The fuel cooler is secured to the
manifold with four bolts. A boss with two threaded holes allows for the attachment of the combined intake air
temperature/pressure sensor. The sensor is secured to the manifold with two screws and sealed with a gasket.
At the forward end of the manifold, a machined face and four threaded holes provide for the attachment of the EGR
valve. The valve is sealed to the manifold with a gasket.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Emission Control Systems.
Exhaust manifold
The exhaust manifold is made from cast iron. The manifold has five ports, one from each cylinder, which merge into
one flanged outlet connection positioned centrally on the manifold.
The manifold is attached to the cylinder head with ten studs and flanged nuts. A laminated metal gasket seals the
manifold to the cylinder head. The flanged outlet on the manifold provides the attachment for the turbocharger, which
is attached with three studs and flanged nuts and sealed with a metal laminated gasket.
A second flanged outlet, located at the forward end of the manifold, provides attachment for the EGR pipe. The EGR
pipe is secured to the manifold with two cap screws and connected to the EGR valve mounted on the inlet manifold.
There is no gasket used between the pipe and the exhaust manifold.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - Td5, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Emission Control Systems.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system comprises a front pipe, an intermediate pipe which incorporates a silencer and a tail pipe
assembly which also has a silencer. The exhaust system is constructed mainly of 63 mm (2.48 in) diameter extruded
pipe with a 1.5 mm (0.06 in) wall thickness. All pipes are aluminized to resist corrosion and the silencers are fabricated
from stainless steel sheet.
Page 628 of 1672

MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - TD5
REPAIRS 30-1-7
11.Remove 2 nuts and 8 bolts securing inlet
manifold to cylinder head.
12.Disconnect multiplugs from turbocharger
pressure sensor, ECT sensor, AAP sensor,
MAF sensor, A/C compressor and fuel injector
harness.
13.Remove 2 bolts securing harness to camshaft
carrier.
Note: Engine with EGR cooler illustrated.
14.Release harness from engine and inlet
manifold.
15.Remove inlet manifold and gasket. Refit
1.Clean inlet manifold and mating faces.
2.Fit new gasket.
3.Fitinlet manifold and, working from the centre
outwards, tighten nuts and bolts to 25 Nm (18
lbf.ft).
4.Position harness to sensors and connect
multiplugs.
5.Tighten bolts securing harness clip to camshaft
carrier to 9 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
6.Clean dip stick tube and fit new 'O' ring.
7.Fit dip stick tube and tighten bolt to 9 Nm (7
lbf.ft).
8.Connect leads to glow plugs.
9.Fit alternator support bracket and tighten bolts
to 45 Nm (33 lbf.ft).
10.Position fuel cooler and tighten bolts to 25 Nm
(18 lbf.ft).
11.Fit new gasket, position EGR valve and tighten
bolts to 9 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
12.Connect multiplug to MAP sensor.
13.Fit upper fan cowl.
14.Fit engine acoustic cover.
15.Connect battery earth lead.
16.Fit battery cover.
Page 644 of 1672

MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - V8
REPAIRS 30-2-15
Refit
1.Clean old RTV sealant from cylinder head and
cylinder block notches.
2.Clean mating faces of cylinder block, cylinder
head and inlet manifold.
3.Apply RTV sealant to cylinder head and
cylinder block notches.
4.Fit new gasket seals, ensuring ends engage
correctly in notches.
5.Fit new inlet manifold gasket.
6.Position gasket clamps and fit bolts, but do not
tighten at this stage.
7.Position inlet manifold to engine. Fit manifold
bolts and, working in the sequence shown,
tighten bolts initially to 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft) then to
51 Nm (38 lbf.ft).
8.Tighten gasket clamp bolts to 18 Nm (13 lbf.ft).
9.Connect fuel pipe.
10.Clean top hose outlet pipe mating faces.
11.Fit new 'O' ring to outlet pipe.
12.Position outlet pipe, fit bolts and tighten to 22
Nm (16 lbf.ft).
13.Position alternator, fit bolts and tighten to 45
Nm (33 lbf.ft).
14.Position PAS pump to auxiliary housing and
locate housing on engine. Fit bolts and tighten
to 40 Nm (30 lbf.ft).
15.Fit and tighten auxiliary housing nut to 10 Nm (7
lbf.ft).
16.Fit bolts securing PAS pump and tighten to 22
Nm (16 lbf.ft). 17.Position oil cooling pipe bracket fit bolt and
tighten to 22 Nm (16 lbf.ft).
18.Fit and tighten PAS pump high pressure pipe.
19.Position jockey pulley and tighten bolt to 50 Nm
(37 lbf.ft).
20.Clean PAS pump pulley mating faces.
21.Position PAS pump pulley, fit bolts and tighten
to 22 Nm (16 lbf.ft).
22.Clean ACE pump dowels and dowel holes.
23.Position ACE pump, fit bolts and tighten to 22
Nm (16 lbf.ft).
24.Fit auxiliary drive belt.
+ CHARGING AND STARTING,
REPAIRS, Belt - auxiliary drive.
25.Secure injector harness and connect injector
multiplugs.
26.Position top hose and secure clips.
27.Fit rocker covers.
l
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket
- rocker cover - LH.
l
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Gasket
- rocker cover - RH.
28.Check and top up PAS fluid
Page 1051 of 1672

BRAKES
70-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
For all control functions, the ABS modulator regulates the hydraulic pressure to the brakes to control the speed of all
four wheels, either individually or in axle pairs. Operation of the ABS modulator is controlled by the Self Levelling and
Anti-lock Braking Systems (SLABS) ECU. The SLABS ECU also operates warning indications in the instrument pack
to provide the driver with status information on each function.
Brake servo assembly
The brake servo assembly provides power assistance to reduce the pedal load when braking. If the brake servo
assembly fails, the hydraulic system still functions but will require greater brake pedal effort due to the lack of vacuum
assistance.
Two integral tie bolts attach the brake servo assembly to the pedal and bracket assembly on the engine bulkhead.
The master cylinder assembly is attached to the forward ends of the tie bolts.
The brake servo assembly consists of a circular housing which contains two diaphragms, a central plate, a control
valve assembly, input and output push rods and a filter. The input push rod is connected to the brake pedal. The output
push rod locates in the primary piston of the master cylinder. A protective gaiter is installed on the control valve
assembly where it extends from the rear of the housing. A non return valve, installed in a port in the front face of the
housing, is connected to a vacuum line from the engine.
The control valve assembly consists of a valve body containing a valve, a piston, a valve spring and an input rod
spring. The valve controls a vacuum port in the valve body. The piston controls an air inlet port between the valve and
the piston. A reaction disc and a ratio disc separate the piston from the output push rod. A guide tube on the front of
the valve body is attached to the front diaphragm and supported in a bush in the central plate. A return spring locates
in the open end of the guide tube.
The two diaphragms and the central plate separate the interior of the housing into four sealed chambers. The
chambers at the front of the diaphragms are connected together through fixed passages in the valve assembly. The
chambers at the rear of the diaphragms are connected together through the interior of minor diaphragms on the tie
bolts.
Brakes off
With the brake pedal released, the piston in the control valve assembly positions the valve so that the vacuum port is
open and the two pairs of chambers are connected together. When the engine is running air is evacuated through the
vacuum line and non return valve, creating a partial vacuum in all four chambers. When the engine stops, the non
return valve closes to maintain the partial vacuum and, on V8 models, prevent fuel vapour entering the brake servo.
Page 1349 of 1672
HEATING AND VENTILATION
80-8DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
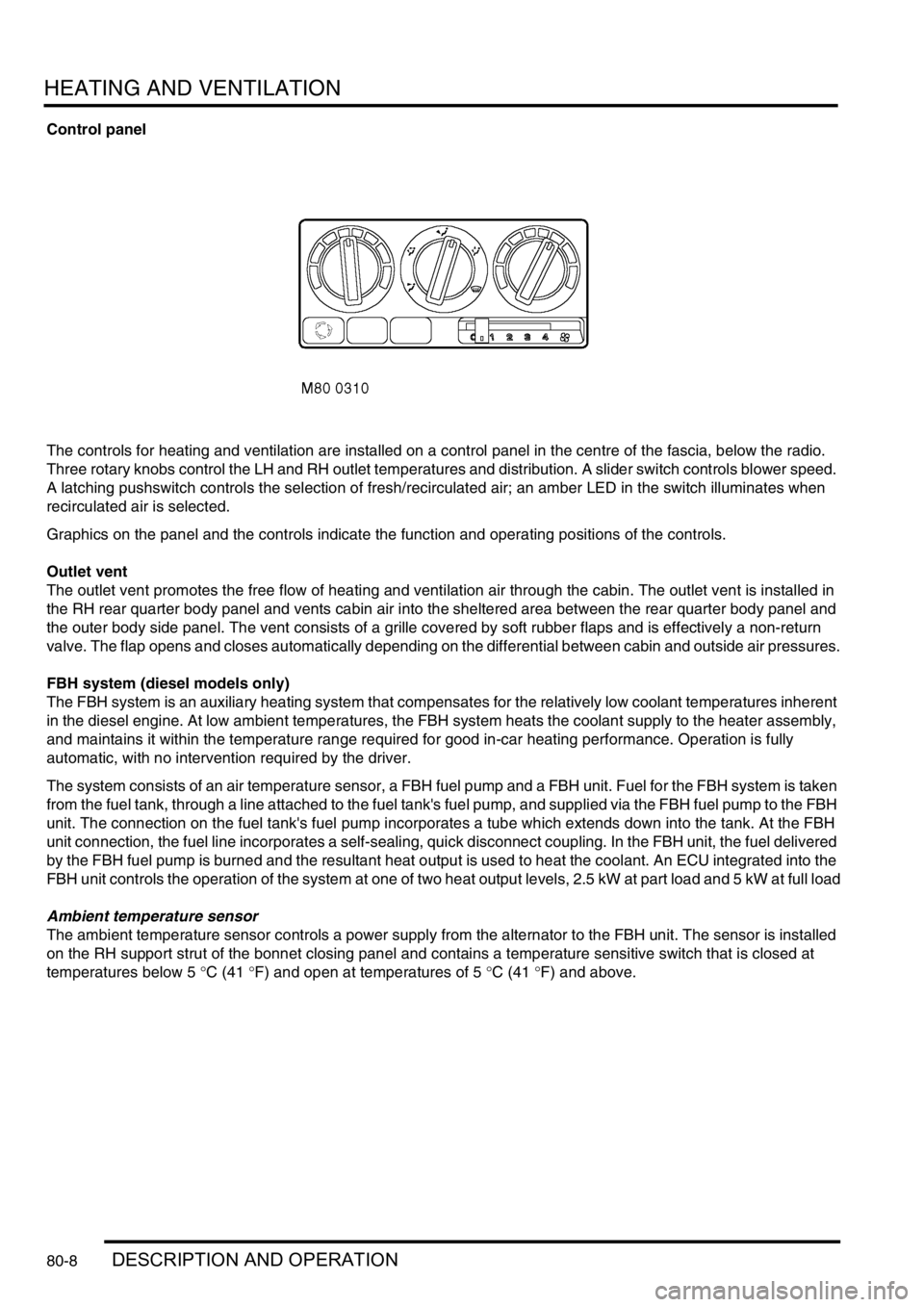
Control panel
The controls for heating and ventilation are installed on a control panel in the centre of the fascia, below the radio.
Three rotary knobs control the LH and RH outlet temperatures and distribution. A slider switch controls blower speed.
A latching pushswitch controls the selection of fresh/recirculated air; an amber LED in the switch illuminates when
recirculated air is selected.
Graphics on the panel and the controls indicate the function and operating positions of the controls.
Outlet vent
The outlet vent promotes the free flow of heating and ventilation air through the cabin. The outlet vent is installed in
the RH rear quarter body panel and vents cabin air into the sheltered area between the rear quarter body panel and
the outer body side panel. The vent consists of a grille covered by soft rubber flaps and is effectively a non-return
valve. The flap opens and closes automatically depending on the differential between cabin and outside air pressures.
FBH system (diesel models only)
The FBH system is an auxiliary heating system that compensates for the relatively low coolant temperatures inherent
in the diesel engine. At low ambient temperatures, the FBH system heats the coolant supply to the heater assembly,
and maintains it within the temperature range required for good in-car heating performance. Operation is fully
automatic, with no intervention required by the driver.
The system consists of an air temperature sensor, a FBH fuel pump and a FBH unit. Fuel for the FBH system is taken
from the fuel tank, through a line attached to the fuel tank's fuel pump, and supplied via the FBH fuel pump to the FBH
unit. The connection on the fuel tank's fuel pump incorporates a tube which extends down into the tank. At the FBH
unit connection, the fuel line incorporates a self-sealing, quick disconnect coupling. In the FBH unit, the fuel delivered
by the FBH fuel pump is burned and the resultant heat output is used to heat the coolant. An ECU integrated into the
FBH unit controls the operation of the system at one of two heat output levels, 2.5 kW at part load and 5 kW at full load
Ambient temperature sensor
The ambient temperature sensor controls a power supply from the alternator to the FBH unit. The sensor is installed
on the RH support strut of the bonnet closing panel and contains a temperature sensitive switch that is closed at
temperatures below 5
°C (41 °F) and open at temperatures of 5 °C (41 °F) and above.
Page 1586 of 1672
HARNESSES
REPAIRS 86-7-15
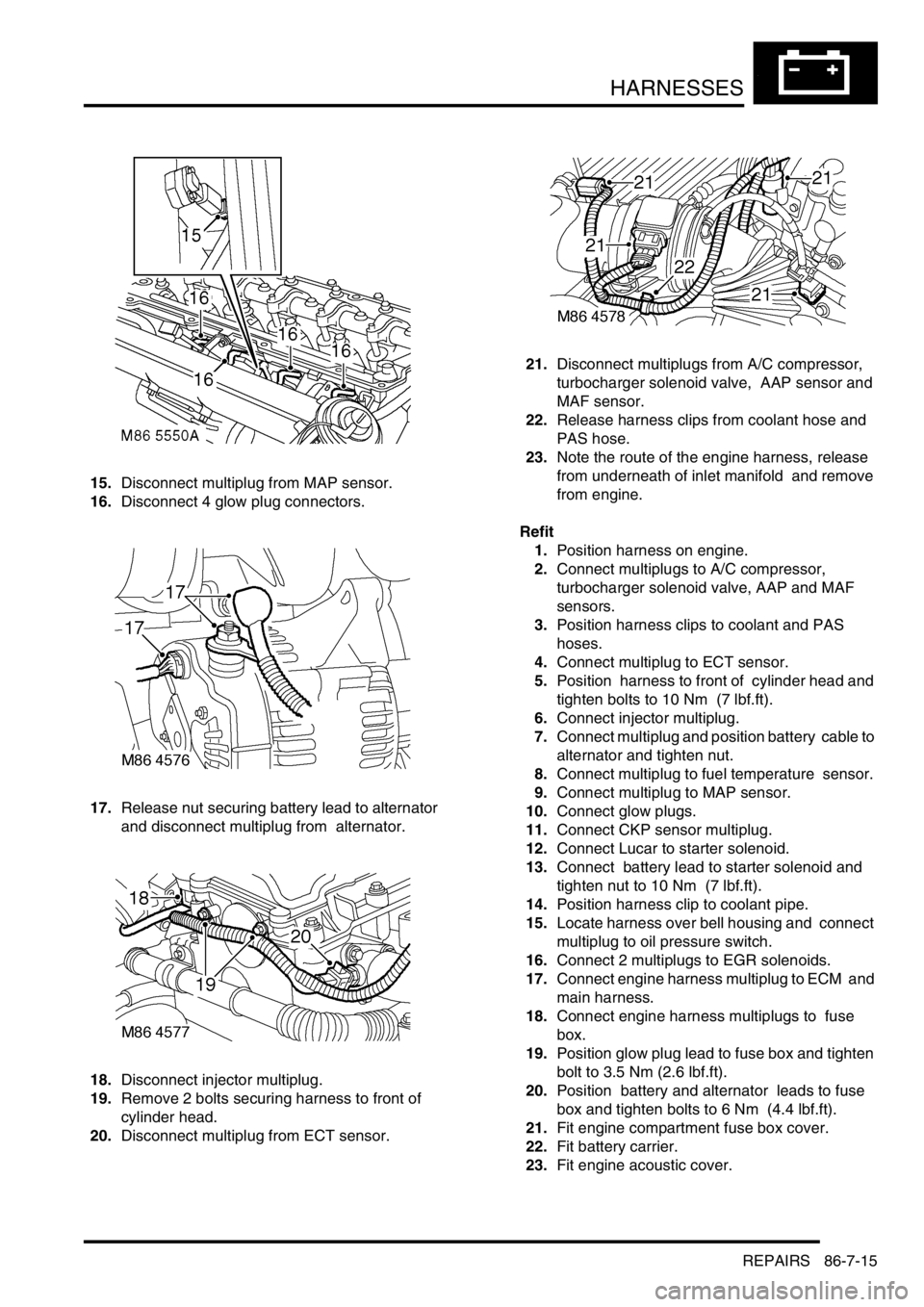
15.Disconnect multiplug from MAP sensor.
16.Disconnect 4 glow plug connectors.
17.Release nut securing battery lead to alternator
and disconnect multiplug from alternator.
18.Disconnect injector multiplug.
19.Remove 2 bolts securing harness to front of
cylinder head.
20.Disconnect multiplug from ECT sensor. 21.Disconnect multiplugs from A/C compressor,
turbocharger solenoid valve, AAP sensor and
MAF sensor.
22.Release harness clips from coolant hose and
PAS hose.
23.Note the route of the engine harness, release
from underneath of inlet manifold and remove
from engine.
Refit
1.Position harness on engine.
2.Connect multiplugs to A/C compressor,
turbocharger solenoid valve, AAP and MAF
sensors.
3.Position harness clips to coolant and PAS
hoses.
4.Connect multiplug to ECT sensor.
5.Position harness to front of cylinder head and
tighten bolts to 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
6.Connect injector multiplug.
7.Connect multiplug and position battery cable to
alternator and tighten nut.
8.Connect multiplug to fuel temperature sensor.
9.Connect multiplug to MAP sensor.
10.Connect glow plugs.
11.Connect CKP sensor multiplug.
12.Connect Lucar to starter solenoid.
13.Connect battery lead to starter solenoid and
tighten nut to 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
14.Position harness clip to coolant pipe.
15.Locate harness over bell housing and connect
multiplug to oil pressure switch.
16.Connect 2 multiplugs to EGR solenoids.
17.Connect engine harness multiplug to ECM and
main harness.
18.Connect engine harness multiplugs to fuse
box.
19.Position glow plug lead to fuse box and tighten
bolt to 3.5 Nm (2.6 lbf.ft).
20.Position battery and alternator leads to fuse
box and tighten bolts to 6 Nm (4.4 lbf.ft).
21.Fit engine compartment fuse box cover.
22.Fit battery carrier.
23.Fit engine acoustic cover.