2002 JEEP LIBERTY Fuel regulator
[x] Cancel search: Fuel regulatorPage 405 of 1803

TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
WAIT-TO-START INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
WASHER FLUID INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WASHER FLUID
INDICATOR..........................36
WATER-IN-FUEL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................37
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION
The instrument cluster for this model is an Elec-
troMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) module
that is located in the instrument panel above the
steering column opening, directly in front of the
driver (Fig. 1). The remainder of the EMIC, including
the mounts and the electrical connections, are con-
cealed behind the cluster bezel. The EMIC gauges
and indicators are protected by an integral clear
plastic cluster lens, and are visible through a dedi-
cated opening in the cluster bezel on the instrument
panel. Just behind the cluster lens is the cluster hood
and an integral cluster mask, which are constructed
of molded black plastic. Two cluster masks are used;
a base black version is used on base models, while a
premium black version features a chrome trim ring
around the perimeter of each gauge opening is used
on premium models. The cluster hood serves as a
visor and shields the face of the cluster from ambient
light and reflections to reduce glare, while the cluster
mask serves to separate and define the individual
gauges and indicators of the EMIC. On the lower
edge of the cluster lens just right of the speedometer,
the black plastic odometer/trip odometer switch but-
ton protrudes through dedicated holes in the clustermask and the cluster lens. The molded plastic EMIC
lens, hood and mask unit has three integral mount-
ing tabs, one each on the lower outboard corners of
the unit and one on the upper surface of the hood
near the center. These mounting tabs are used to
secure the EMIC to the molded plastic instrument
panel cluster carrier with two screws at the top, and
one screw at each outboard tab. A single molded con-
nector receptacle located on the EMIC electronic cir-
cuit board is accessed from the back of the cluster
housing and is connected to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through a single dedicated take out and connec-
tor of the instrument panel wire harness.
Behind the cluster lens, hood, and mask unit is the
cluster overlay and gauges. The overlay is a lami-
nated plastic unit. The dark, visible, outer surface of
the overlay is marked with all of the gauge dial faces
and graduations, but this layer is also translucent.
The darkness of this outer layer prevents the cluster
from appearing cluttered or busy by concealing the
cluster indicators that are not illuminated, while the
translucence of this layer allows those indicators and
icons that are illuminated to be readily visible. The
underlying layer of the overlay is opaque and allows
light from the various indicators and illumination
lamps behind it to be visible through the outer layer
of the overlay only through predetermined cutouts.
The orange gauge pointers are each illuminated
internally. The EMIC electronic circuitry is protected
by a molded plastic rear cover that features several
round access holes for service of the cluster illumina-
tion lighting and a single rectangular access hole for
the EMIC connector receptacle. The EMIC housing,
circuit board, gauges, and overlay unit are sand-
wiched between the lens, hood, and mask unit and
the rear cover with screws.
Twelve versions of the EMIC module are offered on
this model, six base and six premium. These versions
accommodate all of the variations of optional equip-
ment and regulatory requirements for the various
markets in which the vehicle will be offered. This
module utilizes integrated circuitry and information
carried on the Programmable Communications Inter-
face (PCI) data bus network for control of all gauges
and many of the indicators. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/COM-
MUNICATION - DESCRIPTION - PCI BUS). The
EMIC also uses several hard wired inputs in order to
Fig. 1 Instrument Cluster
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL
2 - INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
8J - 2 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERKJ
Page 1383 of 1803
FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY..........................1FUEL INJECTION........................29
FUEL DELIVERY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL
PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST...........3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE...................4
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE..............5
TORQUE.............................5
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL SYSTEM........................6
FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................7
FUEL FILTER
DESCRIPTION..........................7
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................8
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL LEVEL
SENDING UNIT........................9
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION.........................10
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................10
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION.........................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS...........................10
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13OPERATION...........................14
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST......................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST.....................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
AMPERAGE TEST.....................16
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................19
FUEL RAIL
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................24
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................27
FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
KJFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1384 of 1803
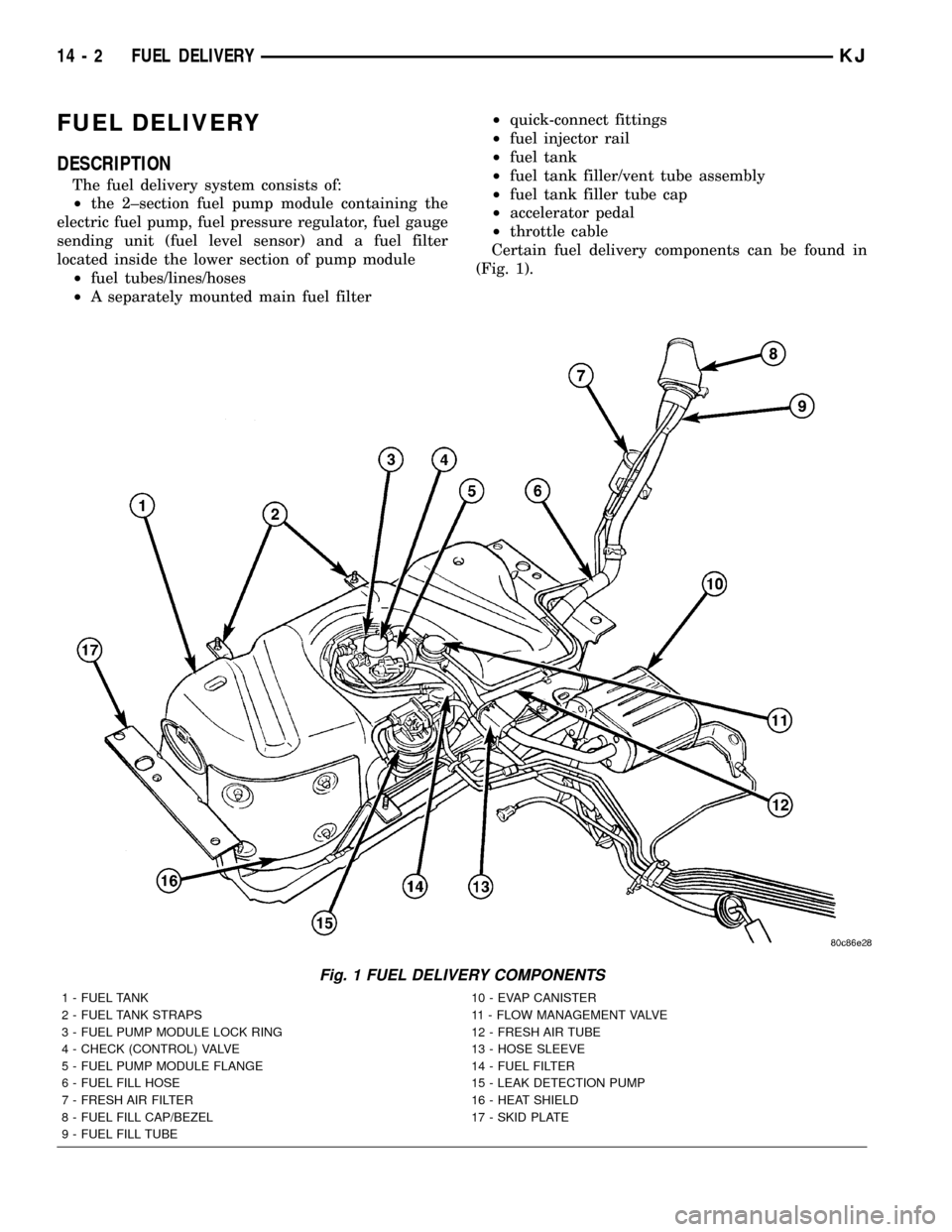
FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the 2±section fuel pump module containing the
electric fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, fuel gauge
sending unit (fuel level sensor) and a fuel filter
located inside the lower section of pump module
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²A separately mounted main fuel filter²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
Certain fuel delivery components can be found in
(Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 FUEL DELIVERY COMPONENTS
1 - FUEL TANK 10 - EVAP CANISTER
2 - FUEL TANK STRAPS 11 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
3 - FUEL PUMP MODULE LOCK RING 12 - FRESH AIR TUBE
4 - CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE 13 - HOSE SLEEVE
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE FLANGE 14 - FUEL FILTER
6 - FUEL FILL HOSE 15 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
7 - FRESH AIR FILTER 16 - HEAT SHIELD
8 - FUEL FILL CAP/BEZEL 17 - SKID PLATE
9 - FUEL FILL TUBE
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
Page 1385 of 1803

OPERATION
Fuel is picked up in the fuel tank by the fuel pump
module. This module is located on the bottom of the
fuel tank.
A fuel return system is provided within the fuel
pump module using check valves. A separate fuel
return line from the engine to the tank is not used.
The fuel pressure regulator and the main fuel filter
are not combined. They are separate items.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock
ring/gasket, ORVR components. Refer to 25, Emis-
sion Control System for ORVR information.
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap. A one-way check valve is installed into the
tanks fuel fill fitting.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system and ORVR system. This
is designed to reduce the emission of fuel vapors into
the atmosphere. The description and function of the
Evaporative Control System is found in 25, Emission
Control Systems.
Both fuel filters (mounted to front of fuel tank, and
inside the bottom fuel pump module) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. The bottom section of the fuel
pump module (with included filter) should only be
replaced if a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
Also, the fuel filter mounted to the front of the fuel
tank should only be replaced if a diagnostic proce-
dure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Quick Connect Fittings for procedures. On some
engines, air cleaner housing removal may be neces-
sary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 2).
(4) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.The DRBtIII Scan
Tool along with the PEP module, the 500 psi
pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-test
port adapter may also be used in place of the
fuel pressure gauge.
The fittings on both tools must be in good
condition and free from any small leaks before
performing the proceeding test.
(5) Start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(6) Observe test gauge. Normal operating pressure
should be 339 kPa +/±34 kPa (49.2 psi +/±5 psi).
(7) Shut engine off.
Fig. 2 CONNECTING ADAPTER TOOLÐTYPICAL
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 3
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1386 of 1803

(8) Pressure should not fall below30 psi for five
minutes.
(9) If pressure falls below 30 psi, it must be deter-
mined if a fuel injector, the check valve within the
fuel pump module, or a fuel tube/line is leaking.
(10) Again, start engine and bring to normal oper-
ating temperature.
(11) Shut engine off.
(12)Testing for fuel injector or fuel rail leak-
age:Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor
Tool between the fuel rail and the test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a fuel injector or the fuel rail is leaking.
(13)Testing for fuel pump check valve, filter,
regulator check valve or fuel tube/line leakage:
Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor Tool
between the vehicle fuel line and test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a leak may be found at a fuel tube/line. If no
leaks are found at fuel tubes or lines, one of the
check valves in either the electric fuel pump, fuel fil-
ter or fuel pressure regulator may be leaking.
Note: A quick loss of pressure usually indicates a
defective check valve in the pressure regulator. A
slow loss of pressure usually indicates a defective
check valve in the bottom of the fuel pump module.
The check valves are not serviced separately. Also,
the electric fuel pump is not serviced separately.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.
(2) Remove fuel pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.(3) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(4) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(5) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(6) Unplug connector from any fuel injector.
(7) Attach one end of a jumper wire with alligator
clips (18 gauge or smaller) to either injector terminal.
(8) Connect other end of jumper wire to positive
side of battery.
(9) Connect one end of a second jumper wire to
remaining injector terminal.
CAUTION: Powering an injector for more than a few
seconds will permanently damage the injector.
(10) Momentarily touch other end of jumper wire
to negative terminal of battery for no more than a
few seconds.
(11) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(12) Disconnect quick-connect fitting at fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(14) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRBtscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1389 of 1803

(3) Remove 4 fuel pump module access plate nuts
(Fig. 3).
(4) While applying heat from a heat gun, carefully
pry up fuel pump module access plate. Take care not
to bend plate.
(5) Disconnect flow management valve hose clamp
and hose (Fig. 4) at pump module fitting. Also discon-
nect small recirculation line at top half of manage-
ment valve.
(6) Raise vehicle.
(7) Disconnect opposite end of flow management
valve hose at EVAP canister (Fig. 1).
(8) Remove valve and 2 hoses as an assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Attach 2 large hoses and 1 small line to flow
management valve. Position this assembly to top of
fuel tank.
(3) Connect valve hose at EVAP canister.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Attach valve hose and clamp to top of fuel
pump module.
(6) Apply silicone sealant to bottom of fuel pump
module metal access plate.(7) Install fuel pump module metal access plate
and 4 nuts. Tighten nuts to 3 N´m (26 in. lbs.)
torque.
(8) Position carpet and install 2 new cargo clamp
rivets.
FUEL FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pressure regulator and fuel filter are not
combined on this vehicle. The main fuel filter is
attached to the front of the fuel tank (Fig. 1) and is a
serviceable/replaceable item. Also refer to Inlet Filter
and Fuel Pressure Regulator.
REMOVAL
The main fuel filter is attached to the front of fuel
tank (Fig. 1). Three fuel lines are used at filter.
Fuel tank removal will not be necessary for
fuel filter removal. Access is from rear cargo
area.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY BE UNDER A
CONSTANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING MOST FUEL SYSTEM
COMPONENTS, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL SYS-
TEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Release fuel system pressure.
(2) Four cargo holdown clamps are located inside
vehicle on floor of rear cargo area. Two of these four
clamps must be removed. Remove 2 rearward
mounted clamps by drilling out clamp rivets.
(3) Fold carpeting forward to gain access to fuel
pump module access plate (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove 4 fuel pump module access plate nuts
(Fig. 5).
(5) While applying heat from a heat gun, carefully
pry up metal fuel pump module access plate. Take
care not to bend plate.
(6) Clean top of fuel pump module area around
fuel line connection points.
(7) Disconnect 2 fuel lines at fuel pump module
(Fig. 6) by pressing on tabs at side of fitting.
(8) Raise vehicle.
(9) Place drain pan under fuel filter.
(10) A third fuel line is attached to bottom of filter
(Fig. 7). The disconnection point for this 3rd line is
approximately 1 foot towards front of vehicle. Clean
fuel line connection point before disconnection. Dis-
connect by pressing on tabs at side of fitting.
(11) Disconnect 3rd fuel line from body retention
clip. Place a small screwdriver into side of clip and
twist for removal.
Fig. 4 TOP OF FUEL PUMP MODULE
1 - LOCK RING
2 - ALIGNMENT NOTCH
3 - FUEL FILTER FITTINGS (2)
4 - ORVR SYSTEM HOSE AND CLAMP
5 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
7 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
8 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
9 - FUEL PUMP MODULE (UPPER SECTION)
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 7
FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE (Continued)
Page 1392 of 1803

INSTALLATION
(1) Connect necessary wiring into electrical con-
nectors. Connect 4±wire connector to upper section of
pump module.
(2) Position sending unit to pump module. Slide
and snap into place.
(3) Install lower section of fuel pump module.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY BE UNDER A
CONSTANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM
HOSES, FITTINGS, LINES, OR MOST COMPO-
NENTS, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used to
prevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Some are equipped with
safety latch clips. Some may require the use of a spe-
cial tool for disconnection and removal. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings Removal/Installation for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, clips)
of quick-connect fittings are not serviced sepa-
rately, but new plastic spacers are available for
some types. If service parts are not available, do
not attempt to repair the damaged fitting or fuel line
(tube). If repair is necessary, replace the complete
fuel line (tube) assembly.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
Also refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps.
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Safety latch clips are
used on certain components/lines. Certain fittings
may require use of a special tool for disconnection.
DISCONNECTING
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSE,
FITTING OR LINE, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST
BE RELEASED. REFER TO FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
Fig. 9 FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR/SENDING
UNIT ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
1 - UPPER SECTION OF PUMP MODULE
2 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
3 - FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - 4-WIRE ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1395 of 1803

(b) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(c) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage.
Replace as necessary.
(8)Latch Clips:Depending on vehicle model and
engine, 2 different types of safety latch clips are used
(Fig. 16) or (Fig. 17). Type-1 is tethered to fuel line
and type-2 is not. A special tool will be necessary todisconnect fuel line after latch clip is removed. The
latch clip may be used on certain fuel line/fuel rail
connection, or to join fuel lines together.
(a) Type 1: Pry up on latch clip with a screw-
driver (Fig. 16).
(b) Type 2: Separate and unlatch 2 small arms
on end of clip (Fig. 17) and swing away from fuel
line.
(c) Slide latch clip toward fuel rail while lifting
with screwdriver.
(d) Insert special fuel line removal tool (Snap-On
number FIH 9055-1 or equivalent) into fuel line
(Fig. 18). Use tool to release locking fingers in end
of line.
(e) With special tool still inserted, pull fuel line
from fuel rail.
(f) After disconnection, locking fingers will
remain within quick-connect fitting at end of fuel
line.
(9) Disconnect quick-connect fitting from fuel sys-
tem component being serviced.
CONNECTING
(1) Inspect quick-connect fitting body and fuel sys-
tem component for damage. Replace as necessary.
(2) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(3) Insert quick-connect fitting into fuel tube or
fuel system component until built-on stop on fuel
tube or component rests against back of fitting.
(4) Continue pushing until a click is felt.
(5) Single-tab type fitting: Push new tab down
until it locks into place in quick-connect fitting.
(6) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(7) Latch Clip Equipped: Install latch clip (snaps
into position).If latch clip will not fit, this indi-
cates fuel line is not properly installed to fuel
rail (or other fuel line). Recheck fuel line con-
nection.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pressure regulator is located on the bot-
tom of the upper section of the fuel pump module.
The fuel filteris not combinedinto the pressure
regulator on this model.
Fig. 17 LATCH CLIP-TYPE 2
1 - LATCH CLIP
Fig. 18 FUEL LINE DISCONNECTION USING
SPECIAL TOOL
1 - SPECIAL FUEL LINE TOOL
2 - FUEL LINE
3 - FUEL RAIL
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 13
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)