2002 JEEP LIBERTY ECO mode
[x] Cancel search: ECO modePage 1671 of 1803

on the evaporator fins from freezing and obstructing
air conditioning system air flow.
The a/c low pressure switch contacts are open
when the suction pressure is approximately 141 kPa
(20.5 psi) or lower. The switch contacts will close
when the suction pressure rises to approximately 234
to 262 kPa (34 to 38 psi) or above. Lower ambient
temperatures, below approximately -1É C (30É F), will
also cause the switch contacts to open. This is due to
the pressure/temperature relationship of the refriger-
ant in the system.
The a/c low pressure switch is a factory-calibrated
unit. It cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if faulty
or damaged, it must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C LOW
PRESSURE SWITCH
Before performing diagnosis of the a/c low pressure
switch, be certain that the switch is properly
installed on the accumulator fitting. If the switch is
too loose it may not open the Schrader-type valve in
the accumulator fitting, which will prevent the
switch from correctly monitoring the refrigerant sys-
tem pressure. Remember that lower ambient temper-
atures, below about -1É C (30É F), during cold
weather will open the switch contacts and prevent
compressor operation due to the pressure/tempera-
ture relationship of the refrigerant.
Also verify that the refrigerant system has the cor-
rect refrigerant charge. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- A/C PERFORMANCE) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the a/c low pressure switch wire har-
ness connector from the switch on the accumulator
fitting.
(3) Install a jumper wire between the two cavities
of the a/c low pressure switch wire harness connector.
(4) Connect a manifold gauge set to the refrigerant
system service ports. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
EQUIPMENT) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE PORT)
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
(6) Place the A/C Heater mode control switch knob
in any A/C position and start the engine.
(7) Check for continuity between the two terminals
of the a/c low pressure switch. There should be con-
tinuity with a suction pressure reading of 262 kPa(38 psi) or above, and no continuity with a suction
pressure reading of 141 kPa (20.5 psi) or below. If
OK, test and repair the A/C switch sense circuit as
required. If not OK, replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the wire harness connector from the a/c
low pressure switch on the top of the accumulator
(Fig. 13).
(3) Unscrew the a/c low pressure switch from the
fitting on the top of the accumulator.
(4) Remove the O-ring seal from the accumulator
fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the accumulator fitting.
Use only the specified O-rings as they are made of a
special material for the R-134a system. Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the com-
pressor in the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT
OIL - DESCRIPTION)
Fig. 13 A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
1 - WIRING HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
3 - A/C LINE TO EVAPORATOR
4 - ACCUMULATOR MOUNTING BRACKET
5 - ACCUMULATOR
6 - A/C LOW PRESSURE LINE
KJCONTROLS 24 - 19
A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1708 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1733 of 1803

EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
is located in the engine compartment. It is attached
to a bracket located between the battery and the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). The EVAP system
test port is located near the solenoid.
OPERATION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP can-
ister to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operat-
ing condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
is located in the engine compartment (Fig. 2). It is
attached to a bracket located between the battery
and the Power Distribution Center (PDC). The EVAP
system test port is located near the solenoid (Fig. 2).
(1) Disconnect electrical wiring connector at sole-
noid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum harness at solenoid.
(3) Remove solenoid and its support bracket (pull
straight up).
INSTALLATION
(1) Slip EVAP canister purge solenoid onto its
mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum harness to solenoid.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION
The plastic fuel tank filler tube cap is threaded
onto the end of the fuel fill tube. All models are
equipped with a 1/4 turn cap.
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of fuel filler tube
is prevented by the use of a pressure-vacuum fuel fill
cap. Relief valves inside the cap will release fuel tank
pressure at predetermined pressures. Fuel tank vac-
uum will also be released at predetermined values.
This cap must be replaced by a similar unit if
replacement is necessary. This is in order for the sys-
tem to remain effective.
CAUTION: Remove fill cap before servicing any fuel
system component to relieve tank pressure. If
equipped with an ORVR system and a Leak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP), the cap must be tightened
securely. If cap is left loose, a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) may be set.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is bolted to the
front of the fuel tank (Fig. 1).
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is used only with
certain emission packages.
The LDP is a device used to detect a leak in the
evaporative system.
Fig. 2 EVAP / PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
1 - BATTERY
2 - EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
3 - MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
5 - SOLENOID ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
6 - EVAP SYSTEM TEST PORT
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 27
Page 1734 of 1803

The pump contains a 3 port solenoid, a pump that
contains a switch, a spring loaded canister vent valve
seal, 2 check valves and a spring/diaphragm.
OPERATION
Immediately after a cold start, engine temperature
between 40ÉF and 86ÉF, the 3 port solenoid is briefly
energized. This initializes the pump by drawing air
into the pump cavity and also closes the vent seal.
During non-test test conditions, the vent seal is held
open by the pump diaphragm assembly which pushes
it open at the full travel position. The vent seal will
remain closed while the pump is cycling. This is due
to the operation of the 3 port solenoid which prevents
the diaphragm assembly from reaching full travel.
After the brief initialization period, the solenoid is
de-energized, allowing atmospheric pressure to enter
the pump cavity. This permits the spring to drive the
diaphragm which forces air out of the pump cavity
and into the vent system. When the solenoid is ener-
gized and de-energized, the cycle is repeated creating
flow in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump
is controlled in 2 modes:
PUMP MODE:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate
to achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten
the overall test time.
TEST MODE:The solenoid is energized with a
fixed duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur
when the diaphragm reaches the switch closure
point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5 inches
of water.
When the pump starts, the cycle rate is quite high.
As the system becomes pressurized pump rate drops.
If there is no leak the pump will quit. If there is a
leak, the test is terminated at the end of the test
mode.
If there is no leak, the purge monitor is run. If the
cycle rate increases due to the flow through the
purge system, the test is passed and the diagnostic is
complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank (Fig. 3). The LDP
fresh air filter is located on the end of a hose. This
hose is attached to the fuel fill tube assembly below
and near the fuel fill opening (Fig. 1). The LDP and
LDP filter are typically replaced (serviced) as one
unit.
(1) Raise vehicle.(2) Carefully remove two 3/4º vent hoses at sides
of LDP.
(3) Carefully remove other vapor/vacuum hoses
from LDP.
(4) Place a hydraulic jack under fuel tank.
(5) Loosen 2 fuel tank strap mounting bolts at
front of tank about 10 turns.
(6) Lower front of fuel tank about 1/2º.
(7) Remove 2 LDP mounting nuts (Fig. 3) and
lower LDP slightly to gain access to electrical connec-
tor (Fig. 4).
(8) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP. To dis-
connect: Slide red colored tab upward. Push on black
colored tab while removing connector.
(9) Remove LDP from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank. The LDP filter is
located on the end of a hose. This hose is attached to
the fuel fill tube assembly below and near the fuel
fill opening. The LDP and LDP filter are replaced
(serviced) as one unit.
(1) Install electrical connector to LDP. Push red
colored tab downward to lock connector to LDP.
(2) Position LDP and LDP bracket to fuel tank
mounting studs and install 2 nuts. Tighten nuts to 1
N´m (11 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Raise fuel tank to body and tighten 2 strap
bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 3 LDP LOCATION / MOUNTING
1 - LDP
2 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
3 - MOUNTING NUTS
4 - FRONT OF FUEL TANK
25 - 28 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1737 of 1803
OPERATION
The PCV system operates by engine intake mani-
fold vacuum. Filtered air is routed into the crankcase
through the air cleaner hose and crankcase breath-
er(s) (if used). The metered air, along with crankcase
vapors, are drawn through the PCV valve and into a
passage in the intake manifold. The PCV system
manages crankcase pressure and meters blow-by
gases to the intake system, reducing engine sludge
formation.
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
This plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
TYPICALPCV valves are shown in (Fig. 9), (Fig.
10) and (Fig. 11).
When the engine is not operating, or during an
engine pop-back, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat (Fig. 9). This will prevent vapors
from flowing through the valve.
During periods of high manifold vacuum, such as
idle or cruising speeds, vacuum is sufficient to com-
pletely compress spring. It will then pull the plunger
to the top of the valve (Fig. 10). In this position there
is minimal vapor flow through the valve.
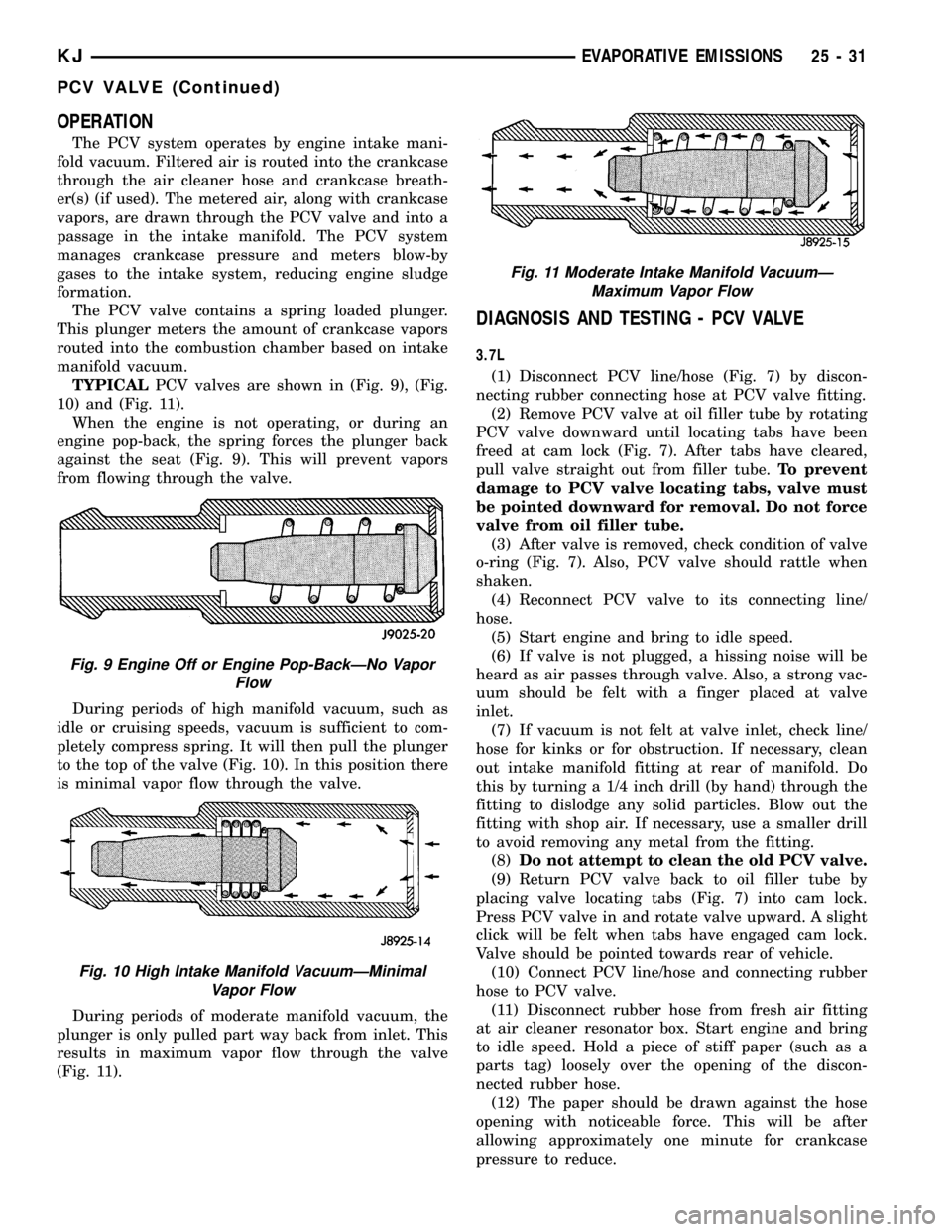
During periods of moderate manifold vacuum, the
plunger is only pulled part way back from inlet. This
results in maximum vapor flow through the valve
(Fig. 11).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE
3.7L
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 7) by discon-
necting rubber connecting hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward until locating tabs have been
freed at cam lock (Fig. 7). After tabs have cleared,
pull valve straight out from filler tube.To prevent
damage to PCV valve locating tabs, valve must
be pointed downward for removal. Do not force
valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 7). Also, PCV valve should rattle when
shaken.
(4) Reconnect PCV valve to its connecting line/
hose.
(5) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(6) If valve is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through valve. Also, a strong vac-
uum should be felt with a finger placed at valve
inlet.
(7) If vacuum is not felt at valve inlet, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at rear of manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out the
fitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
(8)Do not attempt to clean the old PCV valve.
(9) Return PCV valve back to oil filler tube by
placing valve locating tabs (Fig. 7) into cam lock.
Press PCV valve in and rotate valve upward. A slight
click will be felt when tabs have engaged cam lock.
Valve should be pointed towards rear of vehicle.
(10) Connect PCV line/hose and connecting rubber
hose to PCV valve.
(11) Disconnect rubber hose from fresh air fitting
at air cleaner resonator box. Start engine and bring
to idle speed. Hold a piece of stiff paper (such as a
parts tag) loosely over the opening of the discon-
nected rubber hose.
(12) The paper should be drawn against the hose
opening with noticeable force. This will be after
allowing approximately one minute for crankcase
pressure to reduce.
Fig. 9 Engine Off or Engine Pop-BackÐNo Vapor
Flow
Fig. 10 High Intake Manifold VacuumÐMinimal
Vapor Flow
Fig. 11 Moderate Intake Manifold VacuumÐ
Maximum Vapor Flow
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 31
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 1802 of 1803

VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL
INFORMATION (VECI) LABEL
DESCRIPTION
All models have a Vehicle Emission Control Infor-
mation (VECI) Label. DaimlerChrysler permanently
attaches the label in the engine compartment (Fig.
4). The label cannot be removed without defacing
label information and destroying label.
The label contains the vehicle's emission specifica-
tions and vacuum hose routings. All hoses must be
connected and routed according to the label.
The label also contains an engine vacuum sche-
matic. There are unique labels for vehicles built for
sale in the state of California and the country of
Canada. Canadian labels are written in both the
English and French languages.
The VECI label contains the following:
²Engine family and displacement
²Evaporative family
²Emission control system schematic
²Certification application
²Engine timing specifications (if adjustable)
²Idle speeds (if adjustable)
²Spark plug and gap
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION
NUMBER
DESCRIPTION
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) plate is
located on the lower left A-pillar and is visible
through the windshield (Fig. 5). The VIN contains 17
characters that provide data concerning the vehicle.
Refer to the VIN decoding chart to determine the
identification of a vehicle.
The Vehicle Identification Number is also
imprinted on the:
²Vehicle Safety Certification Label.
²Frame rail.
To protect the consumer from theft and possible
fraud the manufacturer is required to include a
Check Digit at the ninth position of the Vehicle Iden-
tification Number. The check digit is used by the
manufacturer and government agencies to verify the
authenticity of the vehicle and official documenta-
tion. The formula to use the check digit is not
released to the general public.
Fig. 4 VECI LABEL LOCATION
1 - RADIATOR SUPPORT
2 - VECI LABEL
Fig. 5 VIN NUMBER LOCATION
1 - A-PILLAR
2 - VIN CODE PLATE
8 INTRODUCTIONKJ
Page 1803 of 1803

VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER DECODING CHART
POSITION INTERPRETATION CODE = DESCRIPTION
1 Country of Origin 1 = United States
2 Make J = Jeep
3 Vehicle Type 4 = MPV W/O Side Airbags.
8 = MPV With Side Airbags.
4 Gross Vehicle Weight Rating F = 4001 - 5000 lbs.
G = 5001 - 6000 lbs.
5 Vehicle Line K = Liberty 4X2 (LHD)
L = Liberty 4X4 (LHD)
M = Cherokee 4X4 (RHD)
6 Series 3 = Liberty Renegade
4 = Liberty Sport/Cherokee Sport
5 = Liberty Limited/Cherokee Limited
7 Body Style 8 = Sport Utility - 4 Door
8 Engine K = 3.7L 6 cyl MPI Gasoline
1 = 2.4L 4 cyl MPI Gasoline
7 = 2.5L 4 cyl Diesel
9 Check Digit 0 through 9 or X
10 Model Year 2=2002
11 Assembly Plant W = Toledo North Assembly Plant
12 thru 17 Vehicle Build Sequence
VEHICLE SAFETY
CERTIFICATION LABEL
DESCRIPTION
A vehicle safety certification label (Fig. 6) is
attached to every DaimlerChrysler Corporation vehi-
cle. The label certifies that the vehicle conforms to all
applicable Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
The label also lists:
²Month and year of vehicle manufacture.
²Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). The gross
front and rear axle weight ratings (GAWR's) arebased on a minimum rim size and maximum cold tire
inflation pressure.
²Vehicle Identification Number (VIN).
²Type of vehicle.
²Bar code.
²Month, Day and Hour (MDH) of final assembly.
²Paint and Trim codes.
²Country of origin.
The label is located above the door hinge on the
driver-side A-pillar.
Fig. 6 Vehicle Safety Certification LabelÐTypical
KJINTRODUCTION 9
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (Continued)