2002 JEEP LIBERTY turn signal light
[x] Cancel search: turn signal lightPage 562 of 1803

the center of the headlamp reflector and thoroughly
clean any fingerprints from the reflector.
(6) Push the mounting flange of the headlamp lev-
eling motor into the mounting hole on the back of
headlamp unit housing unit the motor is firmly
seated (Fig. 32).
(7) Rotate the headlamp leveling motor on the
back of the headlamp unit housing clockwise about
30 degrees.
(8) Reinstall the headlamp bulb into the headlamp
unit housing. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/
LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/HEADLAMP BULB -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
HEADLAMP LEVELING
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The headlamp leveling switch (Fig. 34) is used only
on vehicles manufactured for certain markets where
the headlamp leveling system is required. The head-
lamp leveling switch is mounted in the driver side
inboard trim bezel on the instrument panel, where it
is secured by molded latch features that are integral
to the switch housing. Only the switch bezel and
thumbwheel are visible on the outer surface of the
instrument panel trim bezel. The black plastic switch
thumbwheel is marked with white numbers ª0,º ª1,º
ª2,º and ª3,º each of which indicates one of the four
switch detent positions. Each higher number repre-sents a lower aiming position of the headlamp beam
relative to the road surface. The black, molded plas-
tic switch housing has an integral connector recepta-
cle on the back, a single latch feature on the top, and
two latch features (one on each side) on the bottom.
The switch is connected to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through a dedicated take out and connector of
the instrument panel wire harness. Within the
switch housing is the leveling switch circuitry includ-
ing the switch contacts and a series resistor configu-
ration.
The headlamp leveling switch cannot be adjusted
or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the unit must
be replaced.
OPERATION
The headlamp leveling switch receives battery cur-
rent on a fused park lamp relay output circuit from a
fuse in the Junction Block (JB) whenever the park
lamp relay is energized (park lamps are turned On).
The switch receives a path to ground through a splice
block located in the instrument panel wire harness
with an eyelet terminal connector that is secured by
a nut to a ground stud on the driver side instrument
panel end bracket near the JB. The only output from
the switch is a voltage signal that it provides to the
headlamp leveling motors on a headlamp adjust sig-
nal circuit. Each switch position selects a different
tap on a series resistor within the switch to provide a
different voltage signal to the leveling motors. The
higher the switch position number, the higher the
output voltage level.
The headlamp leveling switch can be tested using
conventional diagnostic tools and methods.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEADLAMP
LEVELING SWITCH
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
Fig. 34 Headlamp Leveling Switch
1 - SWITCH
2 - UPPER LATCH FEATURE (1)
3 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
4 - LOWER LATCH FEATURE (2)
5 - THUMBWHEEL
KJLAMPS8Ls-37
HEADLAMP LEVELING MOTOR (Continued)
Page 572 of 1803

knob on its end with a flattened face to allow it to be
easily rotated. On vehicles equipped with optional
front fog lamps, the knob on the end of left control
stalk can also be pulled outward to select those
lamps. Each control stalk also features a knurled
control ring located just below the control knob. The
left control stalk is dedicated to providing driver con-
trols for the interior and exterior lighting systems,
while the right control stalk is dedicated to providing
driver controls for the front and rear wiper systems.
Two integral connector receptacles on the forward
facing surface of the multi-function switch housing
connect the switch two the vehicle electrical system
through two take outs and connectors of the instru-
ment panel wire harness. The left connector recepta-
cle contains nine terminal pins for the lighting
control circuits of the switch, while the right connec-
tor receptacle contains six terminal pins for the
wiper control circuits of the switch. The multi-func-
tion switch cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
LEFT CONTROL STALK The left (lighting) control
stalk of the multi-function switch supports the fol-
lowing functions and features:
²Front Fog Lamps- For vehicles so equipped,
the internal circuitry and hardware of the multi-
function switch left (lighting) control stalk provide
detent switching for the optional front fog lamps.
²Headlamps- The internal circuitry and hard-
ware of the multi-function switch left (lighting) con-trol stalk provide detent switching for the
headlamps.
²Headlamp Beam Selection- The internal cir-
cuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch left
(lighting) control stalk provide detent switching for
selection of the headlamp high or low beams.
²Headlamp Optical Horn- The internal cir-
cuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch left
(lighting) control stalk includes momentary switching
of the headlamp high beam circuits to provide an
optical horn feature (sometimes referred to as flash-
to-pass), which allows the vehicle operator to momen-
tarily flash the headlamp high beams as an optical
signalling device.
²Interior Lamps Defeat- The internal circuitry
and hardware of the multi-function switch left (light-
ing) control stalk provide detent switching to defeat
the illumination of all interior courtesy lamps when a
door, the rear flip-up glass, or the tailgate are
opened.
²Interior Lamps On- The internal circuitry and
hardware of the multi-function switch left (lighting)
control stalk provide detent switching to simulta-
neously illuminate all interior courtesy lamps.
²Panel Lamps Dimming- The internal cir-
cuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch left
(lighting) control stalk provide simultaneous adjust-
able control of the illumination intensity of all instru-
ment panel lighting at one of six available
illumination intensity levels.
Fig. 50 Multi-Function Switch
1 - MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH
2 - RIGHT (WIPER) CONTROL STALK
3 - LEFT (LIGHTING) CONTROL STALK
4 - TURN SIGNAL CANCEL ACTUATOR5 - RIGHT (WIPER) CONTROL KNOB
6 - RIGHT (WIPER) CONTROL RING
7 - LEFT (LIGHTING) CONTROL RING
8 - LEFT (LIGHTING) CONTROL KNOB
KJLAMPS8Ls-47
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 573 of 1803

²Parade Mode- The internal circuitry and hard-
ware of the multi-function switch left (lighting) con-
trol stalk provide detent switching for a parade mode
that maximizes the illumination intensity of all
instrument panel lighting for visibility when driving
in daylight with the exterior lamps turned on.
²Park Lamps- The internal circuitry and hard-
ware of the multi-function switch left (lighting) con-
trol stalk provide detent switching for the park
lamps.
²Rear Fog Lamps- For vehicles so equipped,
the internal circuitry and hardware of the multi-
function switch left (lighting) control stalk provide
detent switching for the optional rear fog lamps.
Rear fog lamps are optional only for vehicles manu-
factured for certain markets, where they are
required.
²Turn Signal Control- The internal circuitry
and hardware of the multi-function switch left (light-
ing) control stalk provide both momentary non-detent
switching and detent switching with automatic can-
cellation for both the left and right turn signal
lamps.
RIGHT CONTROL STALK The right (wiper) con-
trol stalk of the multi-function switch supports the
following functions and features:
²Continuous Front Wipe Modes- The internal
circuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch
right (wiper) control stalk provide two continuous
front wipe switch positions, low speed or high speed.
²Continuous Rear Wipe Mode- The internal
circuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch
right (wiper) control stalk provide one continuous
rear wipe switch position.
²Front Washer Mode- The internal circuitry
and hardware of the multi-function switch right
(wiper) control stalk switch provide front washer sys-
tem operation.
²Front Wipe-After-Wash Mode- The internal
circuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch
right (wiper) control stalk provide a wipe-after-wash
mode.
²Front Wiper Mist Mode- The internal cir-
cuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch
right (wiper) control stalk provide a front wiper sys-
tem mist mode.
²Intermittent Front Wipe Mode- The internal
circuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch
right (wiper) control stalk provide an intermittent
front wipe mode with five delay interval positions.
²Intermittent Rear Wipe Mode- The internal
circuitry and hardware of the multi-function switch
right (wiper) control stalk provide one fixed interval
intermittent rear wipe mode switch position.²Rear Washer Mode- The internal circuitry and
hardware of the multi-function switch right (wiper)
control stalk provide rear washer system operation.
OPERATION
The multi-function switch uses a combination of
resistor multiplexed and conventionally switched out-
puts to control the many functions and features it
provides. The switch receives battery current on a
fused ignition switch output (run-acc) circuit from a
fuse in the Junction Block (JB) whenever the ignition
switch is in the On or Accessory positions. The switch
receives a path to ground at all times through a
splice block located in the instrument panel wire har-
ness with an eyelet terminal connector that is
secured by a nut to a ground stud on the driver side
instrument panel end bracket near the Junction
Block (JB). Following are descriptions of how each of
the two multi-function switch control stalks operate
to control the functions and features they provide.
LEFT CONTROL STALK The left (lighting) control
stalk of the multi-function switch operates as follows:
²Front Fog Lamps- For vehicles so equipped,
the control knob on the end of the multi-function
switch left (lighting) control stalk is pulled outward
to activate the optional front fog lamps. The control
knob is mechanically keyed so that it cannot be
pulled outward unless it is first rotated to turn on
the exterior lighting. The multi-function switch pro-
vides a resistor multiplexed output to the Body Con-
trol Module (BCM) on a fog lamp switch sense
circuit, and the BCM responds by energizing or de-
energizing the front fog lamp relay in the Junction
Block (JB) as required.
²Headlamps-
The control knob on the end of the
multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk is
rotated forward (counterclockwise) to its second detent
position to activate the headlamps. The multi-function
switch provides a resistor multiplexed output to the
Body Control Module (BCM) on a headlamp switch
sense circuit, and the BCM responds by energizing or
de-energizing the selected low or high beam relay
(Daytime Running Lamp relay in Canadian vehicles)
in the Junction Block (JB) as required.
²Headlamp Beam Selection-The left (lighting)
control stalk of the multi-function switch is pulled
towards the steering wheel past a detent to actuate
the integral beam select switch circuitry. Each time the
control stalk is activated in this manner, the opposite
headlamp beam from what is currently selected will be
energized. The multi-function switch provides a ground
output to the Body Control Module (BCM) on a high
beam switch sense circuit, and the BCM responds by
energizing or de-energizing the selected low or high
beam relay (Daytime Running Lamp relay in Canadian
vehicles) in the Junction Block (JB) as required.
8Ls - 48 LAMPSKJ
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 574 of 1803

²Headlamp Optical Horn- The left (lighting)
control stalk of the multi-function switch is pulled
towards the steering wheel to just before a detent, to
momentarily activate the headlamp optical horn fea-
ture. The high beams will remain illuminated until
the control stalk is released. The multi-function
switch provides a ground output on a high beam
relay control circuit to energize the headlamp high
beam relay (Daytime Running Lamp relay in Cana-
dian vehicles) in the Junction Block (JB) as required.
²Interior Lamps Defeat- The control ring on
the multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk
is rotated to a full rearward (clockwise) detent to
defeat the illumination of all interior courtesy lamps.
The multi-function switch provides a resistor multi-
plexed output to the Body Control Module (BCM) on
a panel lamps dimmer switch mux circuit, and the
BCM responds by de-energizing its internal courtesy
lamp driver circuit.
²Interior Lamps On- The control ring on the
multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk is
rotated to a full forward (counterclockwise) detent to
illuminate all interior courtesy lamps. The multi-
function switch provides a resistor multiplexed out-
put to the Body Control Module (BCM) on a panel
lamps dimmer switch mux circuit, and the BCM
responds by energizing its internal courtesy lamp
driver circuit.
²Panel Lamps Dimming- The control ring on
the multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk
is rotated to one of six minor intermediate detents to
simultaneously select the desired illumination inten-
sity of all adjustable instrument panel and instru-
ment cluster lighting. The control ring is rotated
rearward (clockwise) to dim, or forward (counter-
clockwise) to brighten. The multi-function switch pro-
vides a resistor multiplexed output to the Body
Control Module (BCM) on a panel lamps dimmer
switch mux circuit, and the BCM responds by send-
ing an electronic panel lamps dimming level message
to the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC)
over the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus. The EMIC electronic circuitry then
provides the proper PWM output to the cluster illu-
mination lamps and the VFD on the EMIC circuit
board, then provides a matching PWM output on the
hard wired fused panel lamps dimmer switch signal
circuit.
²Parade Mode- The control ring on the multi-
function switch left (lighting) control stalk is rotated
to an intermediate detent that is one detent rear-
ward (clockwise) from the full forward (counterclock-
wise) detent to select the Parade mode. The multi-
function switch provides a resistor multiplexed
output to the Body Control Module (BCM) on a panel
lamps dimmer switch mux circuit, and the BCMresponds by sending an electronic panel lamps dim-
ming level message to the ElectroMechanical Instru-
ment Cluster (EMIC) over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus. The EMIC
electronic circuitry then provides the proper PWM
output to the cluster illumination lamps and the
VFD on the EMIC circuit board, then provides a
matching PWM output on the hard wired fused panel
lamps dimmer switch signal circuit to illuminate all
lamps at full (daylight) intensity with the exterior
lamps turned On.
²Park Lamps- The control knob on the end of
the multi-function switch left (lighting) control stalk
is rotated forward (counterclockwise) to its first
detent from the Off position to activate the park
lamps. The multi-function switch provides a resistor
multiplexed output to the Body Control Module
(BCM) on a headlamp switch sense circuit, and the
BCM responds by energizing or de-energizing the
park lamp relay in the Junction Block (JB) as
required.
²Rear Fog Lamps- For vehicles so equipped,
the control knob on the end of the multi-function
switch left (lighting) control stalk is rotated forward
(counterclockwise) to its third detent position to acti-
vate the rear fog lamps. The multi-function switch
provides a resistor multiplexed output to the Body
Control Module (BCM) on a headlamp switch sense
circuit, and the BCM responds by energizing or de-
energizing the rear fog lamp relay in the Junction
Block (JB) as required. Rear fog lamps are optional
only for vehicles manufactured for certain markets,
where they are required.
²Turn Signal Control- The left (lighting) con-
trol stalk of the multi-function switch is moved
upward to activate the right turn signal circuitry,
and, downward to activate the left turn signal cir-
cuitry. The turn signal switch has a detent position
in each direction that provides turn signals with
automatic cancellation, and an intermediate, momen-
tary position in each direction that provides turn sig-
nals only until the left multi-function switch control
stalk is released. When the control stalk is moved to
a turn signal switch detent position, the cancel
actuator extends toward the center of the steering
column. A turn signal cancel cam that is integral to
the clockspring rotates with the steering wheel and
the cam lobes contact the cancel actuator when it is
extended from the left multi-function switch. When
the steering wheel is rotated during a turning
maneuver, one of the two turn signal cancel cam
lobes will contact the turn signal cancel actuator. The
cancel actuator latches against the cancel cam rota-
tion in the direction opposite that which is signaled.
In other words, if the left turn signal detent is
selected, the lobes of the cancel cam will ratchet past
KJLAMPS8Ls-49
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 577 of 1803

MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH TESTS
EXTERIOR LIGHTING FUNCTIONS
SWITCH POSITION CONNECTOR C-1 PINS RESISTANCE (OHMS) 10%
Off 4 & 5 3781
Park Lamps On 4 & 5 911
Headlamp Low Beams On 4 & 5 349
Rear Fog Lamps On 4 & 5 75
Headlamp High Beams On 8 & 9 0 - 1
Front Fog Lamps On 2 & 4 0 - 1
Optical Horn (Flash-to-Pass) On 7 & 8 0 - 1
Turn Signal Neutral 6 & 8,8&10Infinite (Open)
Turn Signal Left 6 & 8 0 - 1
Turn Signal Right 8 & 10 0 - 1
INTERIOR LIGHTING FUNCTIONS
SWITCH POSITION CONNECTOR C-1 PINS RESISTANCE (OHMS) 10%
Off (Courtesy Disable) 1 & 4 63
Dimming 1 1 & 4 200
Dimming 2 1 & 4 557
Dimming 3 1 & 4 914
Dimming 4 1 & 4 1271
Dimming 5 1 & 4 1628
Dimming 6 1 & 4 1985
Parade Mode On 1 & 4 3565
Courtesy On 1 & 4 7885
FRONT WIPER FUNCTIONS
SWITCH POSITIONCONNECTOR C-1 & C-2
PINSRESISTANCE (OHMS) 10%
Front Wiper Off C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 4587
Delay 1 C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 1267
Delay 2 C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 792
Delay 3 C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 531
Delay 4 C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 369
Delay 5 C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 262
Front Wiper Low C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 125
Front Wiper High C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 38
Front Wiper Mist C-1 Pin 4 & C-2 Pin 4 125
Front Washer On C-2 Pins5&7 0-1
REAR WIPER FUNCTIONS
SWITCH POSITION CONNECTOR C-2 PINS RESISTANCE (OHMS) 10%
Rear Wiper Off 1 & 5,2&5Infinite (Open)
Rear Wiper Intermittent 2 & 5 0 - 1
Rear Wiper On 1 & 5 0 - 1
Rear Washer On 2 & 5,3&5 0-1
8Ls - 52 LAMPSKJ
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 587 of 1803

TRAILER TOW RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The trailer tow relays are located in a connector
bank above the right rear wheelhouse and behind the
quarter trim panel on vehicles equipped with the
optional factory-installed trailer towing package.
Four individual relays are used, one each for fused
ignition switch output (run), brake lamps, right turn
signal, and left turn signal outputs to a trailer
through the rear body wiring and connectors. The
trailer tow relays are conventional International
Standards Organization (ISO) micro relays (Fig. 64).
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The relay is
contained within a small, rectangular, molded plastic
housing and is connected to all of the required inputs
and outputs by five integral male spade-type termi-
nals that extend from the bottom of the relay base.
The trailer tow relays cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the inoperative
relay must be replaced.
OPERATION
The trailer tow relays are electromechanical
switches. The relays each use an input from the cir-
cuit that they isolate from the trailer wiring to con-
trol a high current output to the trailer. The movable
common feed contact point is held against the fixed
normally closed contact point by spring pressure.When the relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic
field is produced by the coil windings. This electro-
magnetic field draws the movable relay contact point
away from the fixed normally closed contact point,
and holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. A
resistor is connected in parallel with the relay coil in
the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes and
electromagnetic interference that can be generated as
the electromagnetic field of the relay coil collapses.
The terminals of each trailer tow relay are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a con-
nector bank in the rear lighting wire harness above
the right rear wheelhouse. Refer to the appropriate
wiring information. The wiring information includes
wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector repair
procedures, details of wire harness routing and
retention, connector pin-out information and location
views for the various wire harness connectors, splices
and grounds. The trailer tow relays can be diagnosed
using conventional diagnostic tools and methods.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRAILER TOW
RELAY
The trailer tow relays (Fig. 65) are located in a
connector bank above the right rear wheelhouse.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The wir-
ing information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
Fig. 64 Trailer Tow Relays
1 - RELAY CONNECTOR BANK
2 - REAR BODY WIRE HARNESS
3 - LEFT TURN RELAY
4 - RIGHT TURN RELAY
5 - BRAKE LAMP RELAY
6 - FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN) RELAY
8Ls - 62 LAMPSKJ
Page 589 of 1803

WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT
SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, DRIVER AIRBAG,
PASSENGER AIRBAG, SEAT BELT TENSIONER,
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS, SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG,
OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS
OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN
WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FUR-
THER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Position the trailer tow relay to the proper con-
nector in the connector bank (Fig. 67).
(2) Align the trailer tow relay terminals with the
terminal cavities in the connector.
(3) Push firmly and evenly on the top of the trailer
tow relay until the terminals are fully seated in the
terminal cavities in the connector.
(4) Carefully restore the foam wrap around the
trailer tow relay connector bank (Fig. 66).
(5) Reach through the access hole in the quarter
inner panel behind the right rear wheelhouse to
place the trailer tow relay connector bank on the top
of the right rear wheelhouse between the quarter
inner and outer panels.(6) Reinstall the trim onto the right side quarter
inner panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/QUAR-
TER TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION).
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
TRAILER TOW WIRING
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with an optional factory-in-
stalled (not dealer-installed or port-installed) trailer
towing package have a rear body wire harness that
includes an integral trailer tow wiring take out that
connects to a heavy duty, sealed, 7-pin trailer tow
connector located on a bracket on the trailer hitch
receiver (Fig. 68). This harness includes a second
take out with a trailer tow relay connector bank and
four trailer tow relays that isolate the right turn sig-
nal, left turn signal, and brake lamp circuits of the
vehicle from the electrical system of the trailer. The
fourth relay in the connector bank provides a fused
ignition switch output (run) source of battery current
to the trailer tow connector through a trailer tow
relay output circuit. The package also includes an
adapter harness (stored beneath the left rear seat
cushion of the vehicle when it is shipped from the
factory) that adapts the 7-pin trailer tow connector to
a standard, light-duty, 4-pin trailer tow connector.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The wir-
ing information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 67 Trailer Tow Relay Remove/Install
1 - RELAY CONNECTOR BANK
2 - REAR BODY WIRE HARNESS
3 - LEFT TURN RELAY
4 - RIGHT TURN RELAY
5 - BRAKE LAMP RELAY
6 - FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN) RELAY
Fig. 68 Trailer Tow Wiring
1 - RETAINER CLIP (4)
2 - REAR BODY HARNESS (TRAILER TOW TAKE OUT)
3 - RETAINER CLIP (2)
4 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
8Ls - 64 LAMPSKJ
TRAILER TOW RELAY (Continued)
Page 602 of 1803
NOTE: Individual channels cannot be erased. Eras-
ing the transmitter codes will erase ALL pro-
grammed codes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SETTING
TRANSMITTER CODES
(1) Turn off the engine.
(2) Erase the factory test codes by pressing but-
tons 1 and 3. Release the buttons when the two
green lights begin to flash (about 20 seconds).
(3) Choose one of the three buttons to train. Place
the hand-held transmitter within one inch of the uni-
versal transmitter and push the buttons on both
transmitters. The green dot below the house symbol
will begin to flash slowly.
(4) When the red light on the universal transmit-
ter begins to flash rapidly (this may take as long as
60 seconds), release both buttons. Your universal
transmitter is now ªtrainedº. To train the other but-
tons, repeat Step 3 and Step 4. Be sure to keep your
hand-held transmitter in case you need to retrain the
universal transmitter.
AMBIENT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Ambient air temperature is monitored by the Com-
pass Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC) through ambient
temperature sensor messages received from the Body
Control Module (BCM) over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
BCM receives a hard wired input from the ambient
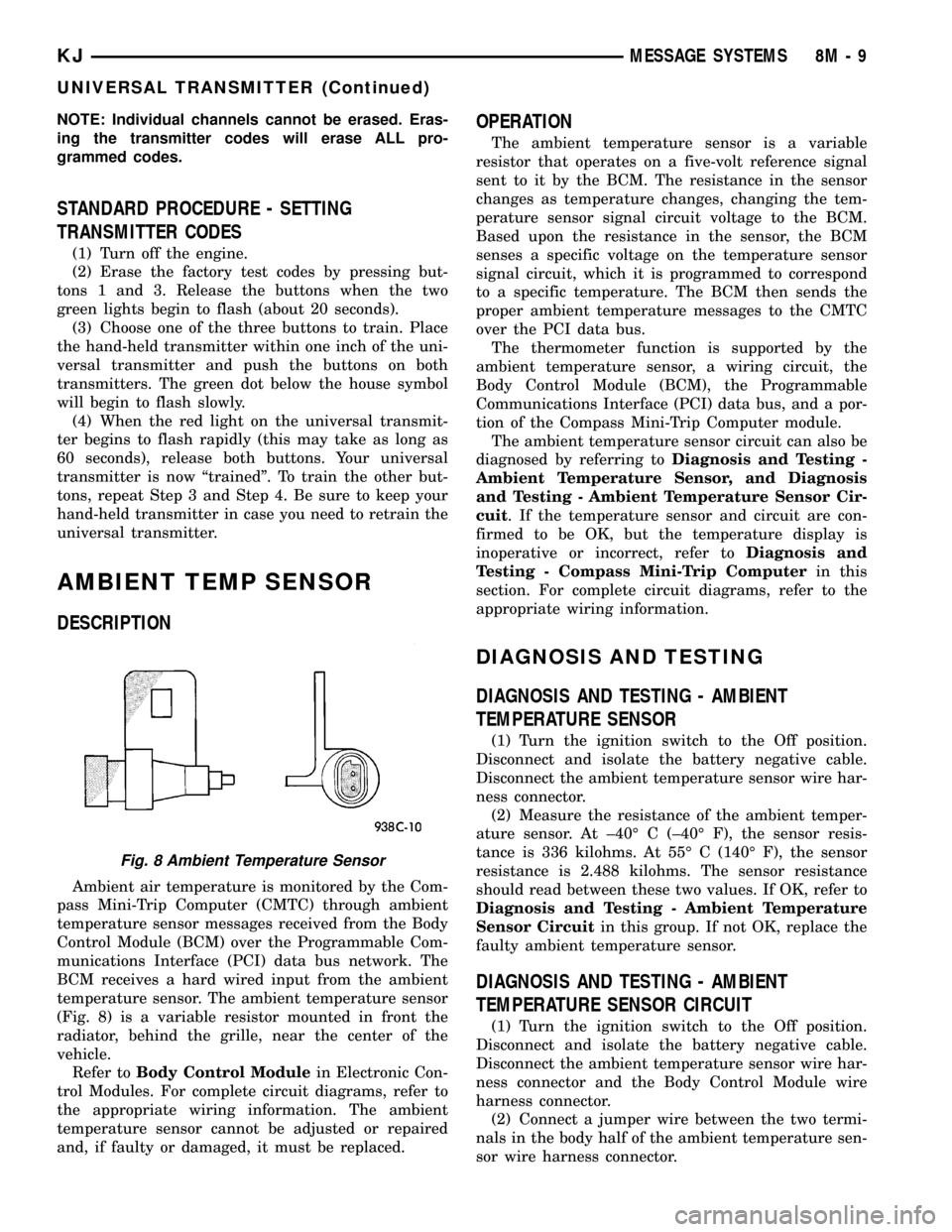
temperature sensor. The ambient temperature sensor
(Fig. 8) is a variable resistor mounted in front the
radiator, behind the grille, near the center of the
vehicle.
Refer toBody Control Modulein Electronic Con-
trol Modules. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The ambient
temperature sensor cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ambient temperature sensor is a variable
resistor that operates on a five-volt reference signal
sent to it by the BCM. The resistance in the sensor
changes as temperature changes, changing the tem-
perature sensor signal circuit voltage to the BCM.
Based upon the resistance in the sensor, the BCM
senses a specific voltage on the temperature sensor
signal circuit, which it is programmed to correspond
to a specific temperature. The BCM then sends the
proper ambient temperature messages to the CMTC
over the PCI data bus.
The thermometer function is supported by the
ambient temperature sensor, a wiring circuit, the
Body Control Module (BCM), the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus, and a por-
tion of the Compass Mini-Trip Computer module.
The ambient temperature sensor circuit can also be
diagnosed by referring toDiagnosis and Testing -
Ambient Temperature Sensor, and Diagnosis
and Testing - Ambient Temperature Sensor Cir-
cuit. If the temperature sensor and circuit are con-
firmed to be OK, but the temperature display is
inoperative or incorrect, refer toDiagnosis and
Testing - Compass Mini-Trip Computerin this
section. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Disconnect the ambient temperature sensor wire har-
ness connector.
(2) Measure the resistance of the ambient temper-
ature sensor. At ±40É C (±40É F), the sensor resis-
tance is 336 kilohms. At 55É C (140É F), the sensor
resistance is 2.488 kilohms. The sensor resistance
should read between these two values. If OK, refer to
Diagnosis and Testing - Ambient Temperature
Sensor Circuitin this group. If not OK, replace the
faulty ambient temperature sensor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Disconnect the ambient temperature sensor wire har-
ness connector and the Body Control Module wire
harness connector.
(2) Connect a jumper wire between the two termi-
nals in the body half of the ambient temperature sen-
sor wire harness connector.
Fig. 8 Ambient Temperature Sensor
KJMESSAGE SYSTEMS 8M - 9
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER (Continued)