2002 JEEP LIBERTY oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 1344 of 1803

(6) Install oil pressure switch and connector. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR/SWITCH - INSTALLATION)
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
ENGINE OIL LEVEL CHECK
The best time to check engine oil level is after it
has sat overnight, or if the engine has been running,
allow the engine to be shut off for at least 5 minutes
before checking oil level.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level
reading. Remove dipstick and observe oil level. Add
oil only when the level is at or below the ADD mark
(Fig. 78).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
Refer to Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations.
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOIST-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Remove oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL)
(7) Install and tighten drain plug in crankcase.
(8) Install new oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION)
(9) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil. (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION)
(10) Install oil fill cap.
(11) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(12) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
NOTE: Care should be exercised when disposing
used engine oil after it has been drained from a
vehicle engine. Refer to the WARNING listed above.
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil filter is a high quality full-flow, dis-
posable type. Replace the oil filter with a Mopartor
the equivalent.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Position an oil collecting container under oil fil-
ter location.
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter avoid
deforming the filter can by installing the remove/in-
stall tool band strap against the can to base lock
seam. The lock seam joining the can to the base is
reinforced by the base plate.
(3) Using a suitable filter wrench, turn oil filter
counterclockwise to remove (Fig. 79).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and check filter mounting surface. The
surface must be smooth, flat and free of debris or
pieces of gasket.
(2) Lubricate new oil filter gasket with clean
engine oil.
Fig. 78 Oil Level
1 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
KJENGINE9s-47
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1395 of 1803

(b) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(c) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage.
Replace as necessary.
(8)Latch Clips:Depending on vehicle model and
engine, 2 different types of safety latch clips are used
(Fig. 16) or (Fig. 17). Type-1 is tethered to fuel line
and type-2 is not. A special tool will be necessary todisconnect fuel line after latch clip is removed. The
latch clip may be used on certain fuel line/fuel rail
connection, or to join fuel lines together.
(a) Type 1: Pry up on latch clip with a screw-
driver (Fig. 16).
(b) Type 2: Separate and unlatch 2 small arms
on end of clip (Fig. 17) and swing away from fuel
line.
(c) Slide latch clip toward fuel rail while lifting
with screwdriver.
(d) Insert special fuel line removal tool (Snap-On
number FIH 9055-1 or equivalent) into fuel line
(Fig. 18). Use tool to release locking fingers in end
of line.
(e) With special tool still inserted, pull fuel line
from fuel rail.
(f) After disconnection, locking fingers will
remain within quick-connect fitting at end of fuel
line.
(9) Disconnect quick-connect fitting from fuel sys-
tem component being serviced.
CONNECTING
(1) Inspect quick-connect fitting body and fuel sys-
tem component for damage. Replace as necessary.
(2) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(3) Insert quick-connect fitting into fuel tube or
fuel system component until built-on stop on fuel
tube or component rests against back of fitting.
(4) Continue pushing until a click is felt.
(5) Single-tab type fitting: Push new tab down
until it locks into place in quick-connect fitting.
(6) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(7) Latch Clip Equipped: Install latch clip (snaps
into position).If latch clip will not fit, this indi-
cates fuel line is not properly installed to fuel
rail (or other fuel line). Recheck fuel line con-
nection.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pressure regulator is located on the bot-
tom of the upper section of the fuel pump module.
The fuel filteris not combinedinto the pressure
regulator on this model.
Fig. 17 LATCH CLIP-TYPE 2
1 - LATCH CLIP
Fig. 18 FUEL LINE DISCONNECTION USING
SPECIAL TOOL
1 - SPECIAL FUEL LINE TOOL
2 - FUEL LINE
3 - FUEL RAIL
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 13
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)
Page 1399 of 1803

WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING TO NEXT STEP,
NOTE THE FUEL PUMP WILL BE ACTIVATED AND
SYSTEM PRESSURE WILL BE PRESENT. THIS WILL
OCCUR AFTER CONNECTING TEST LEADS FROM
LCS ADAPTER INTO FUEL PUMP RELAY CAVITIES.
THE FUEL PUMP WILL OPERATE EVEN WITH IGNI-
TION KEY IN OFF POSITION. BEFORE ATTACHING
TEST LEADS, BE SURE ALL FUEL LINES AND
FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS ARE CONNECTED.
CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the vehi-
cle electrical system and LCS adapter, the test
leads must be connected into relay cavities exactly
as shown in following steps.
Depending upon vehicle model, year or engine con-
figuration, three different types of relays may be
used: Type-1, type-2 and type±3.
(14) If equipped withtype±1 relay(Fig. 22),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 30 and 87. For location of these cav-
ities, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 22).
(15) If equipped withtype±2 relay(Fig. 23),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 30 and 87. For location of these cav-
ities, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 23).
(16) If equipped withtype±3 relay(Fig. 24),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 3 and 5. For location of these cavi-
ties, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 24).
Fig. 22 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 1
Fig. 23 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 2
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 24 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 3
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
1 COIL BATTERY
2 COIL GROUND
3 COMMON FEED
4 NORMALLY CLOSED
5 NORMALLY OPEN
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 17
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1654 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT
The two refrigerant system service ports are used
to charge, recover/recycle, evacuate, and test the air
conditioning refrigerant system. Unique service port
coupler sizes are used on the R-134a system, to
ensure that the refrigerant system is not accidentally
contaminated by the use of the wrong refrigerant
(R-12), or refrigerant system service equipment.
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
The heater and optional air conditioner are blend-
air type systems. In a blend-air system, a blend door
controls the amount of unconditioned air (or cooled
air from the evaporator on models with air condition-
ing) that is allowed to flow through, or around, the
heater core. A temperature control knob on the A/C
Heater control panel determines the discharge air
temperature by controlling an electric actuator,
which moves the blend door. This allows an almost
immediate control of the output air temperature of
the system.
The mode control knob on the heater-only or A/C
Heater control panel is used to direct the conditioned
air to the selected system outlets. Both mode control
switches use engine vacuum to control the mode
doors, which are operated by vacuum actuators.
On all vehicles, the outside air intake can be shut
off by selecting the Recirculation Mode with the
mode control knob. This will operate a vacuum actu-
ated recirculation door that closes off the outside
fresh air intake and recirculates the air that is
already inside the vehicle.
The optional air conditioner for all models is
designed for the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant.
The air conditioning system has an evaporator to cool
and dehumidify the incoming air prior to blending it
with the heated air. This air conditioning system
uses a fixed orifice tube in the liquid line near the
condenser outlet tube to meter refrigerant flow to the
evaporator coil. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, the
A/C low pressure switch on the accumulator cycles
the compressor clutch.
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the
refrigerant line, near the discharge port of the com-
pressor. The low pressure service port is located on
the liquid line at the side of the engine compartment,
near the condensor.Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low humidity air. The evaporator, located in the
HVAC housing on the dash panel below the instru-
ment panel, is cooled to temperatures near the freez-
ing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator and the moisture in the
air condenses on the evaporator fins. During periods
of high heat and humidity, an air conditioning sys-
tem will be more effective in the Recirculation Mode.
With the system in the Recirculation Mode, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, the air conditioning system performance
levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the temper-
ature of the air delivered to the interior of the vehi-
cle. It is important to understand the effect that
humidity has on the performance of the air condition-
ing system. When humidity is high, the evaporator
has to perform a double duty. It must lower the air
temperature, and it must lower the temperature of
the moisture in the air that condenses on the evapo-
rator fins. Condensing the moisture in the air trans-
fers heat energy into the evaporator fins and tubing.
This reduces the amount of heat the evaporator can
absorb from the air. High humidity greatly reduces
the ability of the evaporator to lower the temperature
of the air.
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Remov-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from the
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
Before proceeding, (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION). The air temperature in
the test room and in the vehicle must be a minimum
of 21É C (70É F) for this test.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1661 of 1803
(5) Connect the test set hose or probe to the open
end of the leaking circuit. The test set gauge should
return to the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting shortly after
each connection is made. If OK, replace the faulty
disconnected component. If not OK, go to Step 6.
(6)
To locate a leak in a vacuum line, leave one end
of the line plugged and connect the test set hose or
probe to the other end of the line. Run your fingers
slowly along the line while watching the test set gauge.
The vacuum reading will fluctuate when your fingers
contact the source of the leak. To repair the vacuum
line, cut out the leaking section of the line. Then, insert
the loose ends of the line into a suitable length of 3 mil-
limeter (0.125 inch) inside diameter rubber hose.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable and iso-
late it.
(2) Locate the diode in the harness, and remove
the protective covering.
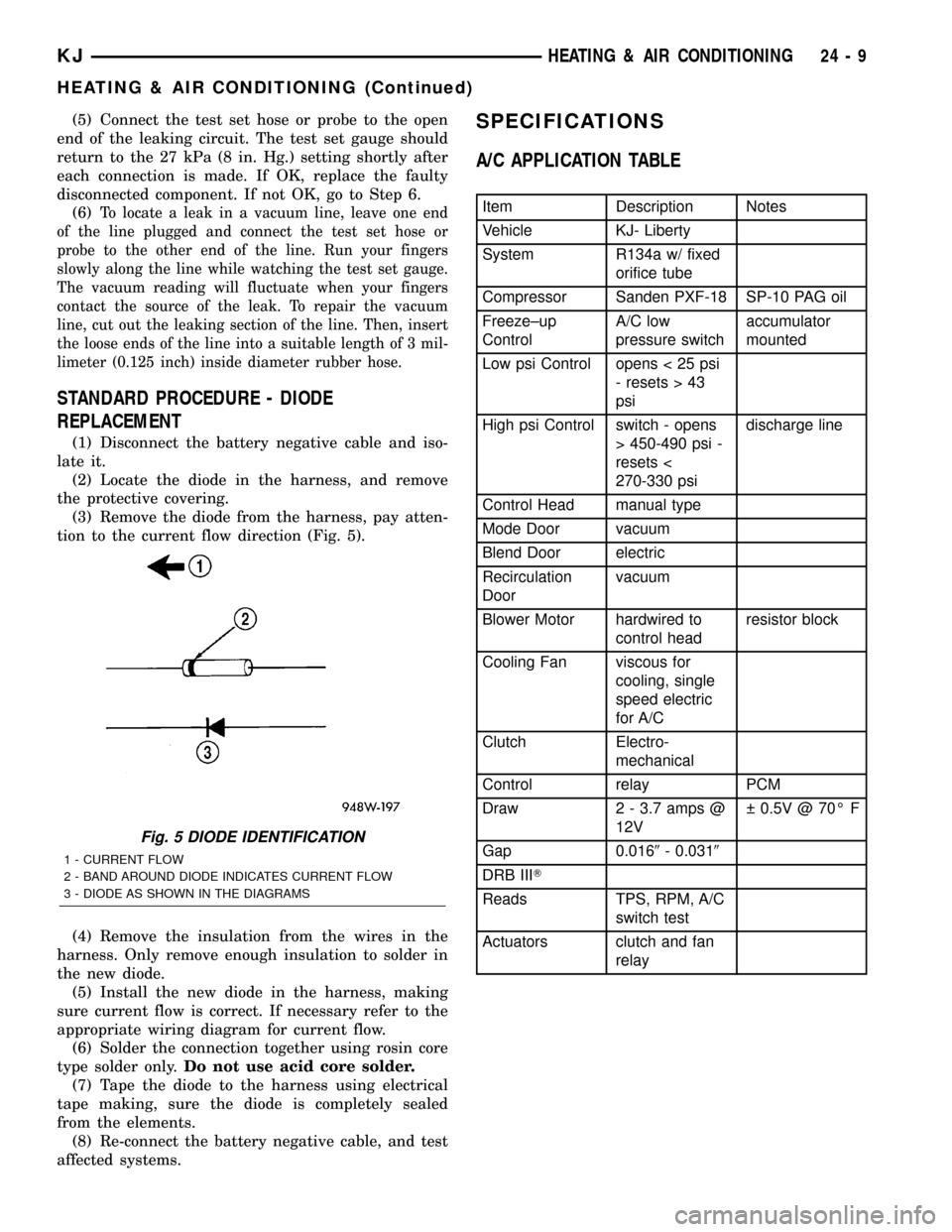
(3) Remove the diode from the harness, pay atten-
tion to the current flow direction (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove the insulation from the wires in the
harness. Only remove enough insulation to solder in
the new diode.
(5) Install the new diode in the harness, making
sure current flow is correct. If necessary refer to the
appropriate wiring diagram for current flow.
(6) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(7) Tape the diode to the harness using electrical
tape making, sure the diode is completely sealed
from the elements.
(8) Re-connect the battery negative cable, and test
affected systems.
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE
Item Description Notes
Vehicle KJ- Liberty
System R134a w/ fixed
orifice tube
Compressor Sanden PXF-18 SP-10 PAG oil
Freeze±up
ControlA/C low
pressure switchaccumulator
mounted
Low psi Control opens < 25 psi
- resets > 43
psi
High psi Control switch - opens
> 450-490 psi -
resets <
270-330 psidischarge line
Control Head manual type
Mode Door vacuum
Blend Door electric
Recirculation
Doorvacuum
Blower Motor hardwired to
control headresistor block
Cooling Fan viscous for
cooling, single
speed electric
for A/C
Clutch Electro-
mechanical
Control relay PCM
Draw 2 - 3.7 amps @
12V 0.5V @ 70É F
Gap 0.0169- 0.0319
DRB IIIT
Reads TPS, RPM, A/C
switch test
Actuators clutch and fan
relay
Fig. 5 DIODE IDENTIFICATION
1 - CURRENT FLOW
2 - BAND AROUND DIODE INDICATES CURRENT FLOW
3 - DIODE AS SHOWN IN THE DIAGRAMS
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 9
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1664 of 1803

A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION - 3.7L and 2.4L
The compressor clutch assembly consists of a sta-
tionary electromagnetic coil, a rotor bearing and
rotor assembly, and a clutch plate (Fig. 1). The elec-
tromagnetic coil unit and the rotor bearing and rotor
assembly are each retained on the nose of the com-
pressor front housing with snap rings. The clutch
plate is keyed to the compressor shaft and secured
with a nut. These components provide the means to
engage and disengage the compressor from the
engine serpentine accessory drive belt.
OPERATION - 3.7L and 2.4L
When the clutch coil is energized, it magnetically
draws the clutch into contact with the rotor and
drives the compressor shaft. When the coil is not
energized, the rotor freewheels on the clutch rotor
bearing, which is part of the rotor. The compressor
clutch and coil are the only serviced parts on the
compressor.
The compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the A/C Heater mode control
switch, the A/C low pressure switch, the A/C high
pressure switch, the compressor clutch relay, and the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM may
delay compressor clutch engagement for up to thirty
seconds. Refer to Electronic Control Modules for
more information on the PCM controls.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information). The battery must
be fully-charged before performing the following
tests. Refer to Battery for more information.
(1) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0 to 20 volt scale) with clip-type leads for measuring
the voltage across the battery and the compressor
clutch coil.
(2) With the A/C Heater mode control switch in
any A/C mode, and the blower motor switch in the
lowest speed position, start the engine and run it at
normal idle.
(3) The compressor clutch coil voltage should read
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage. If there is
voltage at the clutch coil, but the reading is not
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage, test the clutch
coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair
as required. If there is no voltage reading at the
clutch coil, use a DRB IIItscan tool and (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing of the
compressor clutch circuit and PCM control. The fol-
lowing components must be checked and repaired as
required before you can complete testing of the clutch
coil:
²Fuses in the junction block and the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC)
²A/C heater mode control switch
²Compressor clutch relay
²A/C high pressure switch
²A/C low pressure switch
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
(4) The compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the
current draw measured at the clutch coil is 2.0 to 3.9
amperes with the electrical system voltage at 11.5 to
12.5 volts. This should only be checked with the work
area temperature at 21É C (70É F). If system voltage
is more than 12.5 volts, add electrical loads by turn-
ing on electrical accessories until the system voltage
drops below 12.5 volts.
(a) If the clutch coil current reading is four
amperes or more, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced.
(b) If the clutch coil current reading is zero, the
coil is open and should be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C Heater control to the
Recirculation Mode, the blower motor switch in the
highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500
Fig. 1 COMPRESSOR CLUTCH - TYPICAL
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - NOT USED ON KJ
3 - ROTOR
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
24 - 12 CONTROLSKJ
Page 1668 of 1803

(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 67.5 to 82.5 ohms. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, see Relay Circuit Test. If not OK,
replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to fused battery feed. There should be bat-
tery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 30 at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the fuse in the PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is not
used in this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal cavity (87) is
connected to the compressor clutch coil. There should
be continuity between this cavity and the A/C com-
pressor clutch relay output circuit cavity of the com-
pressor clutch coil wire harness connector. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit as
required.
(4) The relay coil battery terminal (86) is con-
nected to the fused ignition switch output (run/start)circuit. There should be battery voltage at the cavity
for relay terminal 86 with the ignition switch in the
On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the
open circuit to the fuse in the junction block as
required.
(5) The coil ground terminal cavity (85) is switched
to ground through the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). There should be continuity between this cav-
ity and the A/C compressor clutch relay control cir-
cuit cavity of the PCM wire harness connector C
(gray) at all times. If not OK, repair the open circuit
as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC).
(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch relay from the
PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the compressor clutch relay by aligning
the relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.
(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
Both the heater-only and A/C heater systems use a
combination of mechanical, electrical, and vacuum
controls. These controls provide the vehicle operator
with a number of setting options to help control the
climate and comfort within the vehicle. Refer to the
owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features, use, and suggested oper-
ation of these controls.
The heater-only or A/C heater control panel is
located to the right of the instrument cluster on the
instrument panel. The control panel contains a rota-
ry-type temperature control knob, a rotary-type mode
control switch knob, and a rotary-type blower motor
speed switch knob. The control also has a push but-
ton to activate the rear window defogger.
The heater-only or A/C heater control panel cannot
be repaired. If faulty or damaged, the entire unit
must be replaced. The illumination lamps are avail-
able for service replacement.
Fig. 10 COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
24 - 16 CONTROLSKJ
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 1670 of 1803

electric cooling fan operations. The switch is located
on the discharge line near the compressor. The
switch is screwed onto a fitting that contains a
Schrader-type valve, which allows the switch to be
serviced without discharging the refrigerant system.
The discharge line fitting is equipped with an O-ring
to seal the switch connection.
OPERATION
The A/C high pressure switch is connected in series
electrically with the A/C low pressure switch between
ground and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The switch contacts open and close causing the PCM
to turn the compressor clutch on and off. This pre-
vents compressor operation when the discharge line
pressure approaches high levels, and also reduces
electrical surging from compressor clutch engage-
ment.
The A/C high pressure switch controls the electric
cooling fan operation by monitoring refrigerant line
pressures. When the discharge line pressure rises
above 1900 to 2200 kPa (280 to 320 psi) the fan will
turn on. The cooling fan will turn off when the dis-
charge line pressure drops to 1600 kPa (235 psi).
The A/C high pressure switch controls the A/C
clutch operation by disengaging the clutch when the
discharge line pressure rises above 3100 to 3375 kPa
(450 to 490 psi). The switch contacts will close and
allow A/C clutch engagement when the discharge line
pressure drops to 1860 to 2275 kPa (270 to 330 psi).
The A/C high pressure switch is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The switch cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C HIGH
PRESSURE SWITCH
Before performing diagnosis of the A/C high pres-
sure switch, verify that the refrigerant system has
the correct refrigerant charge. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE)
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the A/C high pressure switch wire har-
ness connector from the switch on the refrigerant
system fitting.
(3) On the four terminal A/C high pressure switch,
check for continuity between terminals C and D. On
the two terminal A/C high pressure switch, check for
continuity between both terminals of the switch.
There should be continuity. If OK, test and repair theA/C switch sense circuit as required. If not OK,
replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
A/C high pressure switch, which is mounted to a fit-
ting on the non-flexible section of the discharge line
nearest the compressor.
(3) Unscrew the A/C high pressure switch from the
discharge line fitting.
(4) Remove the A/C high pressure switch from the
vehicle.
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the discharge line
fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the discharge line fitting.
Use only the specified O-rings as they are made of a
special material for the R-134a system. Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the com-
pressor in the vehicle(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - SPECIFICATIONS). (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/RE-
FRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
(2) Install and tighten the a/c high pressure switch
on the discharge line fitting. The switch should be
hand-tightened onto the discharge line fitting.
(3) Plug the wire harness connector into the a/c
high pressure switch.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The a/c low pressure switch is located on the top of
the accumulator. The switch is screwed onto an accu-
mulator fitting that contains a Schrader-type valve,
which allows the switch to be serviced without dis-
charging the refrigerant system. The accumulator fit-
ting is equipped with an O-ring to seal the switch
connection.
OPERATION
The a/c low pressure switch is connected in series
electrically with the a/c high pressure switch,
between ground and the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The switch contacts open and close causing
the PCM to turn the a/c compressor clutch on and
off. This regulates the refrigerant system pressure
and controls evaporator temperature. Controlling the
evaporator temperature prevents condensate water
24 - 18 CONTROLSKJ
A/C HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH (Continued)