2002 JEEP LIBERTY Throttle pos
[x] Cancel search: Throttle posPage 1428 of 1803

(8) Using a pick or small screwdriver, press release
tab (Fig. 30) to release plastic cable mount from
bracket.Press on tab only enough to release
cable from bracket. If tab is pressed too much,
it will be broken.Slide plastic mount (Fig. 30)
towards right side of vehicle to remove throttle cable
from throttle body bracket.
(9) Remove throttle cable from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide accelerator cable plastic mount into throt-
tle body mounting bracket. Continue sliding until
release tab (Fig. 30) is aligned to hole in mounting
bracket.
(2) Hold throttle in wide open position. While held
in this position, slide throttle cable pin (Fig. 29) into
throttle body bellcrank.
(3) Push cable housing into rubber grommet and
through opening in dash panel.
(4) From inside vehicle, install metal clip holding
cable to dashpanel (Fig. 28).
(5) From inside vehicle, slide throttle cable core
wire into opening (slot) in top of pedal arm.
(6) Push plastic cable retainer (clip) into pedal arm
opening until it snaps in place.
(7) Install air box to throttle body.
(8) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
Fig. 28 ACCELERATOR PEDAL/BRACKET
ASSEMBLY
1 - METAL THROTTLE CABLE CLIP
2 - THROTTLE CABLE
3 - PLASTIC CABLE RETAINER
4 - PEDAL/BRACKET ASSEMBLY
5 - PEDAL MOUNTING NUTS (2)
6 - PEDAL MOUNTING STUDS (2)
Fig. 29 THROTTLE CABLE PIN-3.7L
1 - THROTTLE CABLE PIN
2 - THROTTLE BODY BELLCRANK
3 - PUSH UP HERE
Fig. 30 THROTTLE CABLE RELEASE TAB-3.7L
1 - THROTTLE CABLE
2 - RELEASE TAB
3 - PICK OR SCREWDRIVER
4 - PLASTIC CABLE MOUNT
14 - 46 FUEL INJECTIONKJ
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE (Continued)
Page 1429 of 1803

THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The 3±wire Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is
mounted on the throttle body and is connected to the
throttle blade shaft.
OPERATION
The 3±wire TPS provides the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) with an input signal (voltage) that
represents the throttle blade position of the throttle
body. The sensor is connected to the throttle blade
shaft. As the position of the throttle blade changes,
the output voltage of the TPS changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The
PCM receives an input signal voltage from the TPS.
This will vary in an approximate range of from .26
volts at minimum throttle opening (idle), to 4.49 volts
at wide open throttle. Along with inputs from other
sensors, the PCM uses the TPS input to determine
current engine operating conditions. In response to
engine operating conditions, the PCM will adjust fuel
injector pulse width and ignition timing.
The PCM needs to identify the actions and position
of the throttle blade at all times. This information is
needed to assist in performing the following calcula-
tions:
²Ignition timing advance
²Fuel injection pulse-width
²Idle (learned value or minimum TPS)
²Off-idle (0.06 volt)
²Wide Open Throttle (WOT) open loop (2.608
volts above learned idle voltage)
²Deceleration fuel lean out
²Fuel cutoff during cranking at WOT (2.608 volts
above learned idle voltage)
²A/C WOT cutoff (certain automatic transmis-
sions only)
REMOVAL
2.4L
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted to
the throttle body (Fig. 31).
(1) Disconnect TPS electrical connector.
(2) Remove 2 TPS mounting screws.
(3) Remove TPS.
Fig. 31 TPS/IAC MOTOR - 2.4L
1 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
3 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (IAC)
4 - MOUNTING SCREWS
KJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 47
Page 1430 of 1803

3.7L
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted to
the throttle body (Fig. 32), or (Fig. 33).
(1) Disconnect TPS electrical connector.
(2) Remove 2 TPS mounting screws.
(3) Remove TPS.
INSTALLATION
2.4L
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted to
the rear of the throttle body.
The throttle shaft end of the throttle body slides
into a socket in the TPS (Fig. 33). The TPS must be
installed so that it can be rotated a few degrees. (If
sensor will not rotate, install sensor with throttle
shaft on other side of socket tangs). The TPS will be
under slight tension when rotated.
(1) Install TPS and retaining screws.
(2) Tighten screws to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect TPS electrical connector to TPS.(4) Manually operate throttle (by hand) to check
for any TPS binding before starting engine.
(5) Install air cleaner tube to throttle body.
3.7L
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted to
the throttle body (Fig. 32).
The throttle shaft end of the throttle body slides
into a socket in the TPS (Fig. 33). The TPS must be
installed so that it can be rotated a few degrees. (If
sensor will not rotate, install sensor with throttle
shaft on other side of socket tangs). The TPS will be
under slight tension when rotated.
(1) Install TPS and retaining screws.
(2) Tighten screws to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect TPS electrical connector to TPS.
(4) Manually operate throttle (by hand) to check
for any TPS binding before starting engine.
(5) Install air cleaner tube to throttle body.
Fig. 32 TPS/IAC MOTOR - 3.7L
1 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
3 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (IAC)
4 - MOUNTING SCREWS
Fig. 33 TPS INSTALLATION - 3.7
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - TPS
3 - THROTTLE BODY SHAFT
4 - SOCKET LOCATING TANGS
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTIONKJ
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1709 of 1803

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0057 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0058 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0071 (M) Amb/Bat Temp Sensor Performance
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
PO111 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Performance
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 Coolant Temp Sensor Performance A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable
voltage range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
P0123 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too HighAPPS voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0125 (M) Closed Loop Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0125 (M) Engine is Cold Too Long Engine does not reach operating temperature.
P0130 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1718 of 1803
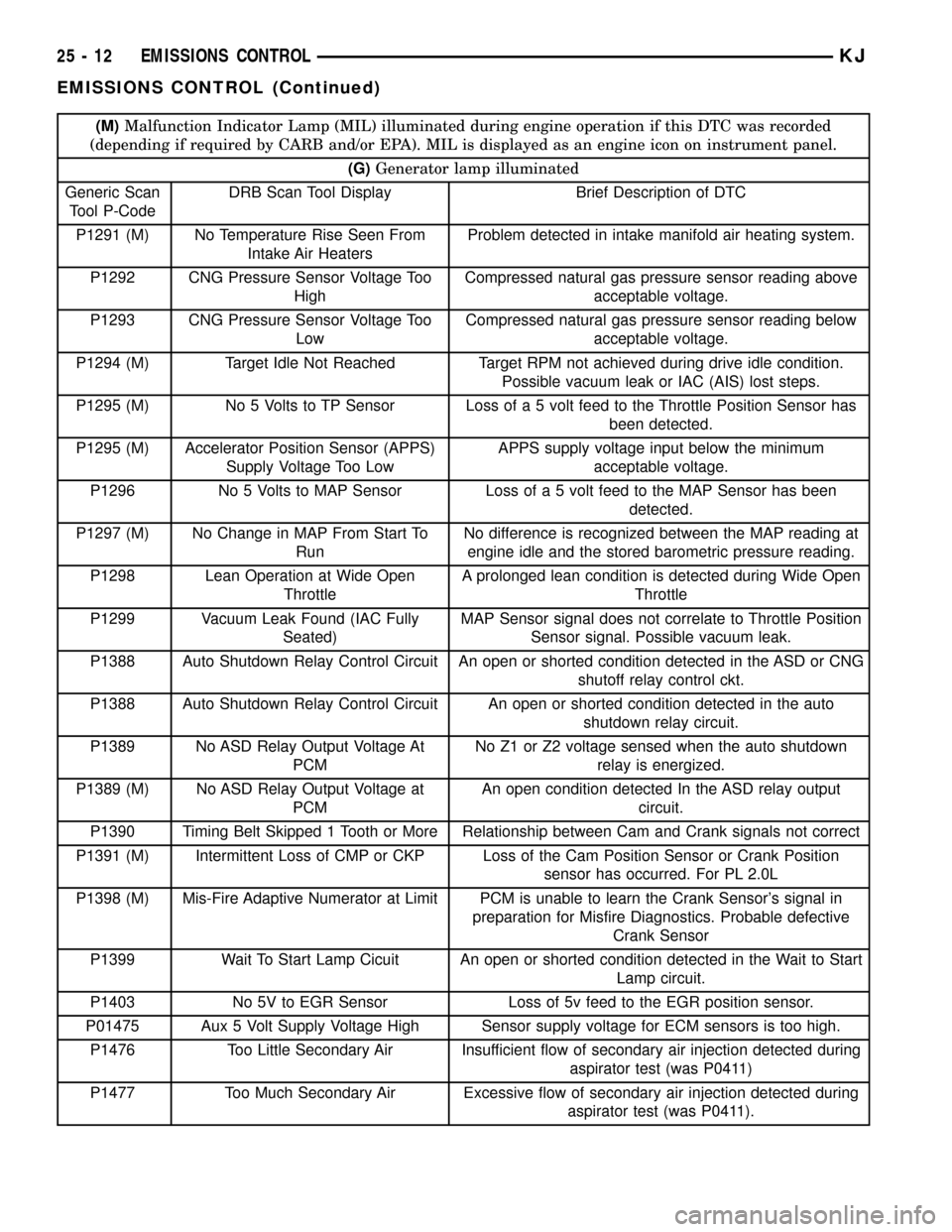
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1291 (M) No Temperature Rise Seen From
Intake Air HeatersProblem detected in intake manifold air heating system.
P1292 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
HighCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading above
acceptable voltage.
P1293 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
LowCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading below
acceptable voltage.
P1294 (M) Target Idle Not Reached Target RPM not achieved during drive idle condition.
Possible vacuum leak or IAC (AIS) lost steps.
P1295 (M) No 5 Volts to TP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the Throttle Position Sensor has
been detected.
P1295 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Supply Voltage Too LowAPPS supply voltage input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
P1296 No 5 Volts to MAP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the MAP Sensor has been
detected.
P1297 (M) No Change in MAP From Start To
RunNo difference is recognized between the MAP reading at
engine idle and the stored barometric pressure reading.
P1298 Lean Operation at Wide Open
ThrottleA prolonged lean condition is detected during Wide Open
Throttle
P1299 Vacuum Leak Found (IAC Fully
Seated)MAP Sensor signal does not correlate to Throttle Position
Sensor signal. Possible vacuum leak.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the ASD or CNG
shutoff relay control ckt.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
P1389 No ASD Relay Output Voltage At
PCMNo Z1 or Z2 voltage sensed when the auto shutdown
relay is energized.
P1389 (M) No ASD Relay Output Voltage at
PCMAn open condition detected In the ASD relay output
circuit.
P1390 Timing Belt Skipped 1 Tooth or More Relationship between Cam and Crank signals not correct
P1391 (M) Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Loss of the Cam Position Sensor or Crank Position
sensor has occurred. For PL 2.0L
P1398 (M) Mis-Fire Adaptive Numerator at Limit PCM is unable to learn the Crank Sensor's signal in
preparation for Misfire Diagnostics. Probable defective
Crank Sensor
P1399 Wait To Start Lamp Cicuit An open or shorted condition detected in the Wait to Start
Lamp circuit.
P1403 No 5V to EGR Sensor Loss of 5v feed to the EGR position sensor.
P01475 Aux 5 Volt Supply Voltage High Sensor supply voltage for ECM sensors is too high.
P1476 Too Little Secondary Air Insufficient flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411)
P1477 Too Much Secondary Air Excessive flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411).
25 - 12 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1725 of 1803

Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. This can increase vehicle emissions
and deteriorate engine performance, driveability and
fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, it
depends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.
If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks or any component that
has an associated limp in will set a fault after 1 trip
with the malfunction present. Components without
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 19
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1732 of 1803
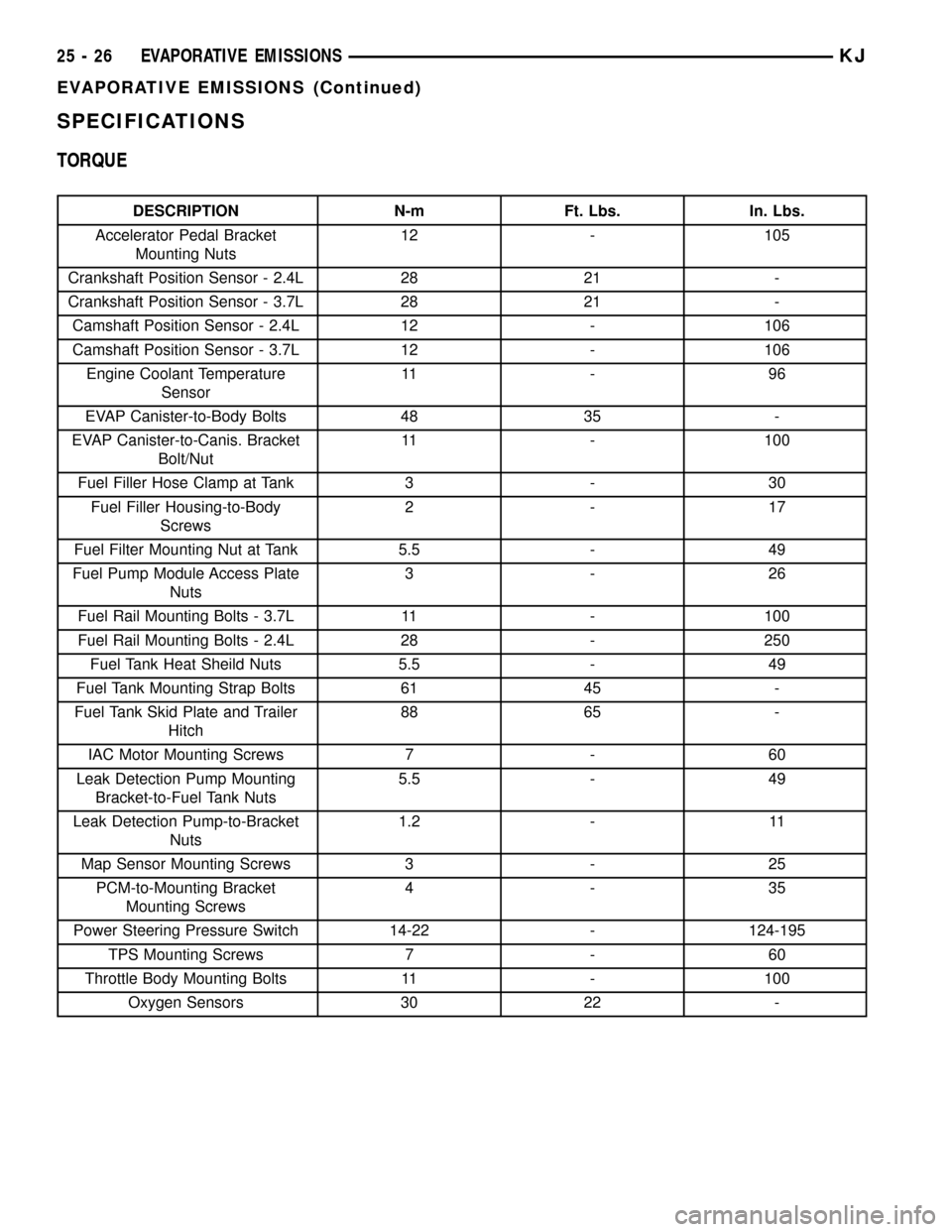
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Accelerator Pedal Bracket
Mounting Nuts12 - 105
Crankshaft Position Sensor - 2.4L 28 21 -
Crankshaft Position Sensor - 3.7L 28 21 -
Camshaft Position Sensor - 2.4L 12 - 106
Camshaft Position Sensor - 3.7L 12 - 106
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor11 - 9 6
EVAP Canister-to-Body Bolts 48 35 -
EVAP Canister-to-Canis. Bracket
Bolt/Nut11 - 100
Fuel Filler Hose Clamp at Tank 3 - 30
Fuel Filler Housing-to-Body
Screws2-17
Fuel Filter Mounting Nut at Tank 5.5 - 49
Fuel Pump Module Access Plate
Nuts3-26
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts - 3.7L 11 - 100
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts - 2.4L 28 - 250
Fuel Tank Heat Sheild Nuts 5.5 - 49
Fuel Tank Mounting Strap Bolts 61 45 -
Fuel Tank Skid Plate and Trailer
Hitch88 65 -
IAC Motor Mounting Screws 7 - 60
Leak Detection Pump Mounting
Bracket-to-Fuel Tank Nuts5.5 - 49
Leak Detection Pump-to-Bracket
Nuts1.2 - 11
Map Sensor Mounting Screws 3 - 25
PCM-to-Mounting Bracket
Mounting Screws4-35
Power Steering Pressure Switch 14-22 - 124-195
TPS Mounting Screws 7 - 60
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts 11 - 100
Oxygen Sensors 30 22 -
25 - 26 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 1743 of 1803

BRAKE CALIPERS - OPERATION, DISC.....5-14
BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL, DISC......5-14
BRAKE COMPONENTS, SPECIFICATIONS....5-6
BRAKE DRUM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................5-27
BRAKE DRUM MACHINING - STANDARD
PROCEDURES........................5-27
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............5-26
BRAKE FLUID, SPECIFICATIONS..........5-27
BRAKE HOSE - INSTALLATION, FRONT.....5-10
BRAKE HOSE - INSTALLATION, REAR......5-10
BRAKE HOSE - REMOVAL, REAR..........5-9
BRAKE INDICATOR - DESCRIPTION,
BRAKE/PARK........................8J-13
BRAKE INDICATOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8J-14
BRAKE INDICATOR - OPERATION,
BRAKE/PARK........................8J-13
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION . . . 8L-16
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING.......................8L-17
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - INSTALLATION . . . 8L-18
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - OPERATION.....8L-16
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL......8L-17
BRAKE LINE AND HOSES - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING.........................5-8
BRAKE LINES - DESCRIPTION............5-8
BRAKE PADS - INSTALLATION, FRONT.....5-11
BRAKE PADS - REMOVAL, FRONT........5-11
BRAKE ROTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, DISC.......................5-18
BRAKE ROTOR - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, DISC....................5-19
BRAKE SHOES - INSTALLATION, DRUM....5-11
BRAKE SHOES - REMOVAL, DRUM.......5-11
BRAKE SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, BASE........................5-3
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION....21-124
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING......................21-125
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK SYSTEM - OPERATION.....21-125
BRAKE/PARK BRAKE INDICATOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................8J-13
BRAKE/PARK BRAKE INDICATOR -
OPERATION.........................8J-13
BRAKES - ABS - DESCRIPTION...........5-32
BRAKES - ABS - OPERATION............5-32
BRAKES - ABS - SPECIFICATIONS........5-33
BRAKES - BASE - DESCRIPTION...........5-2
BRAKES - BASE - WARNING..............5-2
BRAKES, SPECIAL TOOLS - BASE.........5-7
BRAKING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, ANTILOCK...................5-33
BREAK-IN - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH............24-12
BUCKLE - INSTALLATION, FRONT SEAT
BELT ..............................8O-26
BUCKLE - INSTALLATION, REAR SEAT
BELT ..............................8O-35
BUCKLE - REMOVAL, FRONT SEAT BELT . . 8O-25
BUCKLE - REMOVAL, REAR SEAT BELT . . . 8O-34
BUILT-IN INDICATOR TEST - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................8F-10
BULB - INSTALLATION, ASH RECEIVER
LAMP..............................8L-71
BULB - INSTALLATION, CARGO LAMP....8L-73
BULB - INSTALLATION, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP LAMP................8L-19
BULB - INSTALLATION, COMPASS
MINI-TRIP ILLUMINATION..............8L-75
BULB - INSTALLATION, COURTESY
LAMP..............................8L-76
BULB - INSTALLATION, FRONT FOG
LAMP..............................8L-22
BULB - INSTALLATION, FRONT LAMP....8L-27
BULB - INSTALLATION, FRONT POSITION
LAMP..............................8L-28
BULB - INSTALLATION, HEADLAMP
......8L-32
BULB - INSTALLATION, HEATER-A/C
CONTROL ILLUMINATION
..............8L-78
BULB - INSTALLATION, LICENSE PLATE
LAMP
..............................8L-45
BULB - INSTALLATION, READING LAMP
. . . 8L-79
BULB - INSTALLATION, REAR LAMP
.....8L-59BULB - INSTALLATION, REPEATER LAMP . . 8L-60
BULB - INSTALLATION, TRANSMISSION
RANGE INDICATOR ILLUMINATION.......8L-83
BULB - INSTALLATION, VANITY LAMP....8L-84
BULB - REMOVAL, ASH RECEIVER LAMP . . 8L-71
BULB - REMOVAL, CARGO LAMP........8L-72
BULB - REMOVAL, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP LAMP................8L-18
BULB - REMOVAL, COMPASS MINI-TRIP
ILLUMINATION......................8L-74
BULB - REMOVAL, COURTESY LAMP.....8L-75
BULB - REMOVAL, FRONT FOG LAMP....8L-21
BULB - REMOVAL, FRONT LAMP........8L-26
BULB - REMOVAL, FRONT POSITION
LAMP..............................8L-28
BULB - REMOVAL, HEADLAMP..........8L-31
BULB - REMOVAL, HEATER-A/C
CONTROL ILLUMINATION..............8L-78
BULB - REMOVAL, LICENSE PLATE
LAMP..............................8L-44
BULB - REMOVAL, READING LAMP......8L-79
BULB - REMOVAL, REAR LAMP.........8L-58
BULB - REMOVAL, REPEATER LAMP.....8L-60
BULB - REMOVAL, TRANSMISSION
RANGE INDICATOR ILLUMINATION.......8L-82
BULB - REMOVAL, VANITY LAMP........8L-83
BUMPER - INSTALLATION, JOUNCE.......2-19
BUMPER - REMOVAL, JOUNCE...........2-19
BURNT FLUID - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, CAUSES OF................21-125
BUSHING - NV3550 - INSTALLATION,
EXTENSION HOUSING.................21-74
BUSHING - NV3550 - REMOVAL,
EXTENSION HOUSING.................21-73
BUSHINGS - INSTALLATION, STABILIZER
BAR.................................2-9
BUSHINGS - REMOVAL, STABILIZER BAR . . . 2-9
BUSHINGS, AND BALL JOINT -
DESCRIPTION, UPPER SUSPENSION
ARM ...............................2-20
BUSHINGS, AND BALL JOINT -
OPERATION, UPPER SUSPENSION
ARM ...............................2-20
CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS, GEARSHIFT....21-130
CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS, PARK-
INTERLOCK........................21-154
CABLE - DESCRIPTION.................8P-3
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, ANTENNA BODY . . . 8A-4
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ANTENNA BODY......................8A-5
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
GEARSHIFT........................21-128
CABLE - INSTALLATION, ANTENNA BODY . . 8A-6
CABLE - INSTALLATION, GEARSHIFT....21-129
CABLE - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL ANTENNA......................8A-8
CABLE - INSTALLATION, LATCH RELEASE . 23-120
CABLE - INSTALLATION, PARK -
INTERLOCK........................21-153
CABLE - INSTALLATION, THROTTLE
CONTROL..........................14-46
CABLE - OPERATION...................8P-3
CABLE - OPERATION, ANTENNA BODY.....8A-5
CABLE - REMOVAL, ANTENNA BODY......8A-6
CABLE - REMOVAL, GEARSHIFT........21-128
CABLE - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
ANTENNA...........................8A-7
CABLE - REMOVAL, LATCH RELEASE....23-120
CABLE - REMOVAL, PARK - INTERLOCK . 21-153
CABLE - REMOVAL, THROTTLE
CONTROL..........................14-45
CABLE RESISTANCE, 2.4L - SPARK PLUG . . . 8I-3
CABLES - DESCRIPTION, BATTERY.......8F-18
CABLES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BATTERY...........................8F-19
CABLES - INSTALLATION...............5-30
CABLES - OPERATION, BATTERY........8F-18
CABLES - REMOVAL...................5-30
CALIBRATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
COMPASS...........................8M-2
CALIPER ADAPTER - INSTALLATION,
DISC BRAKE.........................5-18
CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL, DISC
BRAKE
..............................5-18
CALIPERS - ASSEMBLY, DISC BRAKE
......5-16
CALIPERS - CLEANING, DISC BRAKE
......5-16
CALIPERS - DESCRIPTION, DISC BRAKE
. . . 5-13
CALIPERS - DISASSEMBLY, DISC BRAKE
. . . 5-14CALIPERS - INSPECTION, DISC BRAKE....5-16
CALIPERS - INSTALLATION, DISC BRAKE . . . 5-17
CALIPERS - OPERATION, DISC BRAKE.....5-14
CALIPERS - REMOVAL, DISC BRAKE......5-14
CAMBER AND CASTER ADJUSTMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................2-5
CAMBER, CASTER AND TOE
ADJUSTMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE..........................2-5
CAMSHAFT(S) - DESCRIPTION.......9-23,9-33
CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION......9-25,9-33
CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL..........9-24,9-33
CANISTER - DESCRIPTION, VAPOR......25-33
CANISTER - INSTALLATION, VAPOR......25-33
CANISTER - OPERATION, VAPOR........25-33
CANISTER - REMOVAL, VAPOR..........25-33
CAP - CLEANING, RADIATOR PRESSURE . . . 7-25
CAP - DESCRIPTION, FUEL FILLER.......25-27
CAP - DESCRIPTION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE..........................7-25
CAP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
RADIATOR PRESSURE.................7-25
CAP - INSPECTION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE..........................7-25
CAP - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL END........................23-153
CAP - OPERATION, FUEL FILLER........25-27
CAP - OPERATION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE..........................7-25
CAP - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
END ..............................23-153
CAPACITIES - SPECIFICATIONS, FLUID......0-4
CAPACITOR - DESCRIPTION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-16
CAPACITOR - INSTALLATION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-16
CAPACITOR - OPERATION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-16
CAPACITOR - REMOVAL, IGNITION COIL . . . 8I-16
CAPACITY - SPECIFICATIONS, CHARGE . . . 24-42
CAPACITY TEST - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, FUEL PUMP.................14-15
CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS -
ASSEMBLY, SINGLE.....................3-9
CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS -
DISASSEMBLY, SINGLE..................3-8
CARGO LAMP BULB - INSTALLATION.....8L-73
CARGO LAMP BULB - REMOVAL........8L-72
CARGO LAMP SWITCH - INSTALLATION . . 8L-74
CARGO LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL......8L-73
CARGO LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION.....8L-74
CARGO LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL.........8L-74
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS -
INSTALLATION......................23-158
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS - REMOVAL . 23-158
CASE - NV231 - ASSEMBLY, TRANSFER . . 21-194
CASE - NV231 - CLEANING, TRANSFER . . 21-190
CASE - NV231 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER............................0-3
CASE - NV231 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-178
CASE - NV231 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-180
CASE - NV231 - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-182
CASE - NV231 - INSPECTION, TRANSFER . 21-190
CASE - NV231 - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-205
CASE - NV231 - OPERATION, TRANSFER
. 21-179
CASE - NV231 - REMOVAL, TRANSFER
. . 21-181
CASE - NV242 - ASSEMBLY, TRANSFER
. . 21-230
CASE - NV242 - CLEANING, TRANSFER
. . 21-227
CASE - NV242 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER
............................0-3
CASE - NV242 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER
.........................21-215
CASE - NV242 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER
.................21-216
CASE - NV242 - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER
.........................21-218
CASE - NV242 - INSPECTION, TRANSFER
. 21-228
CASE - NV242 - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER
.........................21-243
CASE - NV242 - OPERATION, TRANSFER
. 21-215
CASE - NV242 - REMOVAL, TRANSFER
. . 21-217
CASE BEARINGS - INSTALLATION,
DIFFERENTIAL
...............3-110,3-44,3-79
4 INDEXKJ
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page