2002 JEEP LIBERTY check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 437 of 1803

ible when it is not illuminated. An amber Light
Emitting Diode (LED) behind the cutout in the
opaque layer of the overlay causes the ªTRANS
TEMPº text to appear in amber through the translu-
cent outer layer of the overlay when the indicator is
illuminated from behind by the LED, which is sol-
dered onto the instrument cluster electronic circuit
board. The transmission over-temperature indicator
is serviced as a unit with the instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The transmission over-temperature indicator gives
an indication to the vehicle operator when the trans-
mission fluid temperature is excessive, which may
lead to accelerated transmission component wear or
failure. This indicator is controlled by a transistor on
the instrument cluster electronic circuit board based
upon the cluster programming and electronic mes-
sages received by the cluster from the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus. The transmis-
sion over-temperature indicator Light Emitting Diode
(LED) is completely controlled by the instrument
cluster logic circuit, and that logic will only allow
this indicator to operate when the instrument cluster
receives a battery current input on the fused ignition
switch output (run-start) circuit. Therefore, the LED
will always be off when the ignition switch is in any
position except On or Start. The LED only illumi-
nates when it is provided a path to ground by the
instrument cluster transistor. The instrument cluster
will turn on the transmission over-temperature indi-
cator for the following reasons:
²Bulb Test- Each time the ignition switch is
turned to the On position the transmission over-tem-
perature indicator is illuminated for about three sec-
onds as a bulb test.
²Trans Over-Temp Lamp-On Message- Each
time the cluster receives a trans over-temp lamp-on
message from the PCM indicating that the transmis-
sion fluid temperature is 135É C (275É F) or higher,
the indicator will be illuminated. The indicator
remains illuminated until the cluster receives a trans
over-temp lamp-off message from the PCM, or until
the ignition switch is turned to the Off position,
whichever occurs first.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the trans over-temp indi-
cator will be turned on, then off again during the
bulb check portion of the test to confirm the function-
ality of the LED and the cluster control circuitry.
The PCM continually monitors the transmission
temperature sensor to determine the transmission
operating condition. The PCM then sends the proper
trans over-temp lamp-on and lamp-off messages to
the instrument cluster. If the instrument clusterturns on the transmission over-temperature indicator
due to a high transmission oil temperature condition,
it may indicate that the transmission and/or the
transmission cooling system are being overloaded or
that they require service. For further diagnosis of the
transmission over-temperature indicator or the
instrument cluster circuitry that controls the indica-
tor, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). For
proper diagnosis of the transmission temperature
sensor, the PCM, the PCI data bus, or the electronic
message inputs to the instrument cluster that control
the transmission over-temperature indicator, a
DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the appropri-
ate diagnostic information.
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
Two turn signal indicators, one right and one left,
are standard equipment on all instrument clusters.
The turn signal indicators are located near the upper
edge of the instrument cluster, between the speedom-
eter and the tachometer. Each turn signal indicator
consists of a stencil-like cutout of the International
Control and Display Symbol icon for ªTurn Warningº
in the opaque layer of the instrument cluster overlay.
The dark outer layer of the overlay prevents these
icons from being clearly visible when they are not
illuminated. A green Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
behind each cutout in the opaque layer of the cluster
overlay causes the indicator to appear in green
through the translucent outer layer of the overlay
when it is illuminated from behind by the LED,
which is soldered onto the instrument cluster elec-
tronic circuit board. The turn signal indicators are
serviced as a unit with the instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The turn signal indicators give an indication to the
vehicle operator that the turn signal (left or right
indicator flashing) or hazard warning (both left and
right indicators flashing) have been selected and are
operating. These indicators are controlled by two
individual hard wired inputs from the combination
flasher circuitry within the hazard switch to the
instrument cluster electronic circuit board. Each turn
signal indicator Light Emitting Diode (LED) is
grounded on the instrument cluster electronic circuit
board at all times; therefore, these indicators remain
functional regardless of the ignition switch position.
Each LED will only illuminate when it is provided
battery current by the combination flasher circuitry
of the hazard switch.
8J - 34 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERKJ
TRANS TEMP INDICATOR (Continued)
Page 609 of 1803

(4) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity
between the pins of the wire harness connector while
pulling on the tailgate handle.
(5) If no continuity is found, replace the tailgate
handle assembly (Refer to 23 - BODY/DECKLID/
HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE/EXTERIOR HAN-
DLE - REMOVAL).
DOOR LOCK RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The power door lock system uses the following
relays for the front and rear passenger doors only:
²Driver door unlock relay
²Door lock relay
²Passenger Doors unlock relay
The tailgate uses outputs from the Body Control
Module (BCM).
The relays are electromechanical devices that
switch battery current to the door lock circuit when
the Body Control Module (BCM) grounds the relay
coil. These relays are located in the Junction Block
(JB). For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
The relays are a International Standards Organi-
zation (ISO) micro-relay. Relays conforming to the
ISO specifications have common physical dimensions,
current capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal
functions. The ISO micro-relay terminal functions
are the same as a conventional ISO relay. However,
the ISO micro-relay terminal pattern (or footprint) is
different, the current capacity is lower, and the phys-
ical dimensions are smaller than those of the conven-
tional ISO relay.
The relay cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor and three (two fixed and one movable) elec-
trical contacts. The movable (common feed) relay con-
tact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor is connected in
parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the relay,
and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are pro-
duced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DOOR LOCK
RELAY
The power lock relays (Fig. 4) are located in the
Junction Block (JB) under the instrument panel. For
complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appropriate
wiring information. The wiring information includes
wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector repair
procedures, details of wire harness routing and
retention, connector pin-out information and location
views for the various wire harness connectors, splices
and grounds.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, SEAT BELT TENSIONER, SIDE
AIRBAG, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Remove suspected faulty relay from the (JB).
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 8 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Reach up under instrument panel and remove
the relay from Junction Block (JB).
8N - 6 POWER LOCKSKJ
FLIP-UP GLASS RELEASE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 710 of 1803

OPERATION
The front check valve provides more than one func-
tion in this application. It serves as a wye connector
fitting between the cowl grille panel and washer noz-
zle sections of the front washer supply hose. It also
prevents washer fluid from draining out of the front
washer supply hoses back to the washer reservoir.
This drain-back would result in a lengthy delay when
the front washer switch is actuated until washer
fluid was dispensed through the front washer noz-
zles, because the washer pump would have to refill
the front washer plumbing from the reservoir to the
nozzles. Finally, the front check valve prevents
washer fluid from siphoning through the front
washer nozzles after the front washer system is
turned Off.
Within the check valve body, a small check valve is
held in place against a seat by a small coiled spring
to restrict flow through the unit until the valve is
unseated by a predetermined inlet fluid pressure.
When the washer pump pressurizes and pumps
washer fluid from the reservoir through the front
washer plumbing, the fluid pressure overrides the
spring pressure applied to the check valve and
unseats the valve, allowing washer fluid to flow
toward the front washer nozzles. When the washer
pump stops operating, spring pressure seats the
check valve and fluid flow in either direction within
the front washer plumbing is prevented.
REMOVAL
(1) Unlatch and open the hood.
(2) Remove both front wiper arms from the wiper
pivots. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASH-
ERS - FRONT/FRONT WIPER ARM - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the cowl plenum cover/grille panel
from over the cowl plenum. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EX-
TERIOR/COWL GRILLE - REMOVAL).
(4) From the underside of the cowl plenum cover/
grille panel, disconnect the cowl plenum and washer
nozzle hoses from the three barbed nipples of the
front check valve (Fig. 4).
(5) Remove the front check valve from the under-
side of the cowl plenum cover/grille panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the front check valve to the underside
of the cowl plenum cover/grille panel (Fig. 4). Be cer-
tain that the flow direction arrow molded into the
front check valve body is oriented towards the front
washer nozzles.
(2) From the underside of the cowl plenum cover/
grille panel, reconnect the cowl plenum and washer
nozzle hoses to the three barbed nipples of the front
check valve.
(3) Reinstall the cowl plenum cover/grille panel
over the cowl plenum. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/COWL GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(4) Reinstall both front wiper arms onto the wiper
pivots. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/FRONT WIPERS/
WASHERS/FRONT WIPER ARM - INSTALLATION).
(5) Close and latch the hood.
Fig. 3 Front Check Valve
1 - INLET NIPPLE
2 - FRONT CHECK VALVE
3 - OUTLET NIPPLE (2)
4 - FLOW DIRECTION ARROW
Fig. 4 Front Check Valve Remove/Install
1 - WASHER NOZZLE HOSE (RIGHT)
2 - FRONT CHECK VALVE
3 - COWL PLENUM WASHER HOSE
4 - ROUTING CLIP
5 - COWL GRILLE COVER (UNDERSIDE)
6 - WASHER NOZZLE HOSE (LEFT)
KJFRONT WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 9
FRONT CHECK VALVE (Continued)
Page 714 of 1803

(4) If necessary, use a suitable battery terminal
puller to disengage the wiper arm from the wiper
pivot shaft (Fig. 11).
(5) Remove the front wiper arm pivot end from the
wiper pivot shaft.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Be certain that the wiper motor is in the park
position before attempting to install the front wiper
arms. Turn the ignition switch to the On position
and move the control knob on the right (wiper) con-
trol stalk of the multi-function switch to its Off posi-
tion. If the wiper pivots move, wait until they stop
moving, then turn the ignition switch back to the
Off position. The wiper motor is now in its park
position.
(1) The front wiper arms must be indexed to the
wiper pivot shafts with the wiper motor in the park
position to be properly installed. Position the front
wiper arm pivot ends onto the wiper pivot shafts so
that the tip of the wiper blade is aligned with the
T-shaped wiper alignment lines located in the lower
edge of the windshield glass (Fig. 10).
(2) Once the wiper blade is aligned, lift the wiper
arm away from the windshield slightly to relieve the
spring tension on the pivot end and push the pivot
hole on the end of the wiper arm down firmly and
evenly over the wiper pivot shaft.
(3) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
wiper arm to the wiper pivot shaft. Tighten the nut
to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(4) Wet the windshield glass, then operate the
front wipers. Turn the front wipers Off, then checkfor the correct wiper arm position and readjust as
required.
(5) Reinstall the plastic nut cap onto the wiper
arm pivot nut.
FRONT WIPER BLADE
DESCRIPTION
Each front wiper blade is secured by an integral
latching pivot block to the hook formation on the tip
of the front wiper arms, and rests on the glass near
the base of the windshield when the wipers are not
in operation (Fig. 12). The wiper blade consists of the
following components:
²Superstructure- The superstructure includes
several stamped steel bridges and links with claw
formations that grip the wiper blade element. Also
included in this unit is the latching, molded plastic
pivot block that secures the superstructure to the
wiper arm. The driver side front wiper blade has an
additional molded black plastic airfoil secured to the
superstructure, which is oriented toward the base of
the windshield when the front wipers are in their
parked position. All of the metal components of the
wiper blade have a satin black finish applied.
²Element- The wiper element or squeegee is the
resilient rubber member of the wiper blade that con-
tacts the glass.
²Flexor- The flexor is a rigid metal component
running along the length of each side of the wiper
Fig. 11 Wiper Arm Puller - Typical
1 - WIPER ARM
2 - WIPER PIVOT SHAFT
3 - BATTERY TERMINAL PULLER
Fig. 12 Front Wiper Blade
1 - SUPERSTRUCTURE
2 - ELEMENT
3 - PIVOT BLOCK
4 - RELEASE TAB
5 - PIVOT PIN
6 - CLAWS
7 - FLEXOR
KJFRONT WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 13
FRONT WIPER ARM (Continued)
Page 735 of 1803

REAR WASHER SYSTEM
The washer system components should be
inspected periodically, not just when washer perfor-
mance problems are experienced. This inspection
should include the following points:
(1) Check for ice or other foreign material in the
washer reservoir. If contaminated, clean and flush
the washer system. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
REAR WIPERS/WASHERS - CLEANING).
(2) Inspect the washer plumbing for pinched, leak-
ing, deteriorated, or incorrectly routed hoses and
damaged or disconnected hose fittings. Replace dam-
aged or deteriorated hoses and hose fittings. Leaking
washer hoses can sometimes be repaired by cutting
the hose at the leak and splicing it back together
using an in-line connector fitting. Similarly, sections
of deteriorated hose can be cut out and replaced by
splicing in new sections of hose using in-line connec-
tor fittings. Whenever routing a washer hose or a
wire harness containing a washer hose, it must be
routed away from hot, sharp, or moving parts. Also,
sharp bends that might pinch the washer hose must
be avoided.
REAR CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
A rear washer system check valve is standard
equipment on this model (Fig. 3). The rear check
valve is located in the washer plumbing between the
rear roof header and the roof outer panel near the
rear washer nozzle. The rear check valve consists of
a molded plastic body with a round center sectionand barbed hose nipples at each end. An arrow for-
mation molded into the center section of the valve
body indicates the direction of flow through the
valve. The rear check valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The rear check valve prevents washer fluid from
draining out of the rear washer supply hoses back to
the washer reservoir. This drain-back would result in
a lengthy delay from when the rear washer switch is
actuated until washer fluid was dispensed through
the rear washer nozzle, because the washer pump
would have to refill the rear washer plumbing from
the reservoir to the nozzle. The check valve also pre-
vents washer fluid from siphoning through the rear
washer nozzle after the rear washer system is turned
Off.
Within the check valve body, a small check valve is
held in place against a seat by a small coiled spring
to restrict flow through the unit until the valve is
unseated by a predetermined inlet fluid pressure.
When the washer pump pressurizes and pumps
washer fluid from the reservoir through the rear
washer plumbing, the fluid pressure overrides the
spring pressure applied to the check ball within the
valve and unseats the valve, allowing washer fluid to
flow toward the rear washer nozzle. When the
washer pump stops operating, spring pressure seats
the check valve and fluid flow in either direction
within the rear washer plumbing is prevented.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the Center High Mounted Stop Lamp
(CHMSL) unit from the rear of the roof panel. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERI-
OR/CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP UNIT
- REMOVAL).
WARNING: THE EDGES OF THE SHEET METAL
AROUND THE CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP
LAMP MOUNTING HOLE IN THE ROOF PANEL.
TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS TO AVOID PER-
SONAL INJURY.
(3) Reach through the CHMSL unit mounting hole
in the rear of the roof panel to access and disconnect
the rear washer hose at the barbed nipple of the rear
washer nozzle (Fig. 4).
(4) Pull the rear washer hose through the CHMSL
unit mounting hole far enough to access and discon-
nect the headliner washer hose from the barbed nip-
ple of the rear check valve.
Fig. 3 Rear Check Valve
1 - INLET NIPPLE
2 - REAR CHECK VALVE
3 - OUTLET NIPPLE
4 - FLOW DIRECTION ARROW
8R - 34 REAR WIPERS/WASHERSKJ
REAR WIPERS/WASHERS (Continued)
Page 1221 of 1803
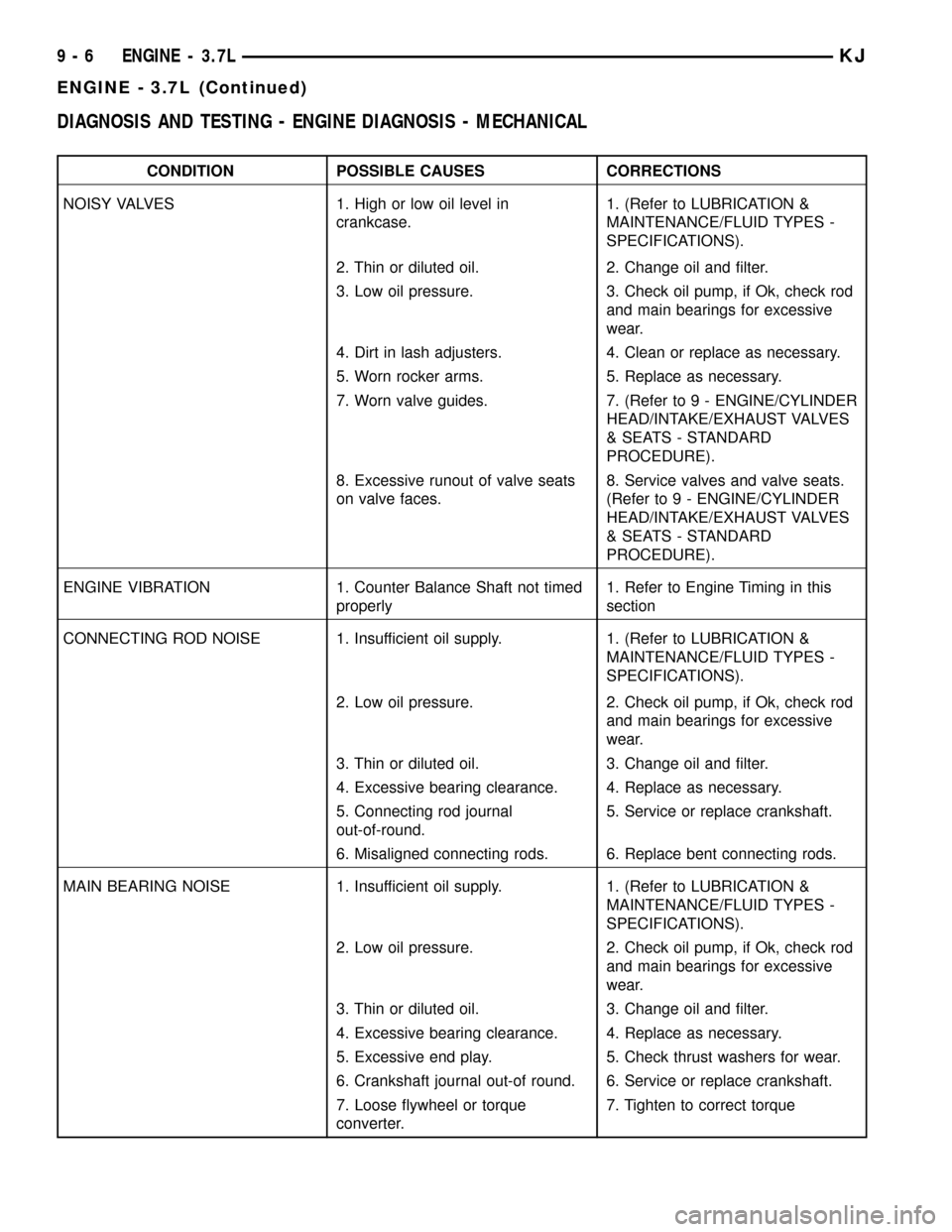
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Clean or replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. Service valves and valve seats.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
ENGINE VIBRATION 1. Counter Balance Shaft not timed
properly1. Refer to Engine Timing in this
section
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
9 - 6 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1222 of 1803
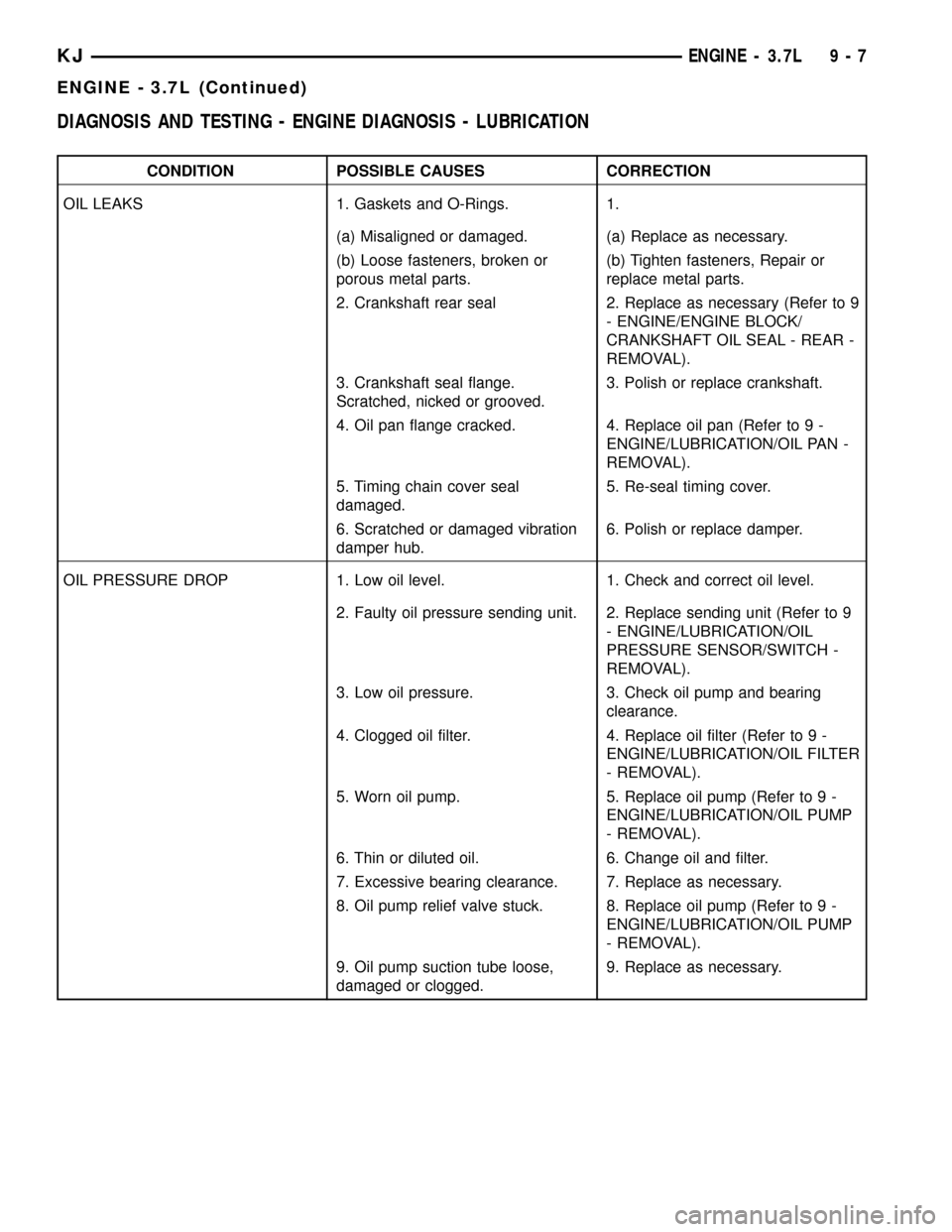
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL LEAKS 1. Gaskets and O-Rings. 1.
(a) Misaligned or damaged. (a) Replace as necessary.
(b) Loose fasteners, broken or
porous metal parts.(b) Tighten fasteners, Repair or
replace metal parts.
2. Crankshaft rear seal 2. Replace as necessary (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR -
REMOVAL).
3. Crankshaft seal flange.
Scratched, nicked or grooved.3. Polish or replace crankshaft.
4. Oil pan flange cracked. 4. Replace oil pan (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN -
REMOVAL).
5. Timing chain cover seal
damaged.5. Re-seal timing cover.
6. Scratched or damaged vibration
damper hub.6. Polish or replace damper.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER
- REMOVAL).
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP
- REMOVAL).
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP
- REMOVAL).
9. Oil pump suction tube loose,
damaged or clogged.9. Replace as necessary.
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 7
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1223 of 1803

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
5. Leaking valve guide seals. 5. Replace valve guide seals.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.
(4) Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
(5) Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUT DOWN
RELAY - REMOVAL).
(6) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(7) Record the compression pressure on the 3rd
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(8) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
(1) Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
(2) Start and operate the engine until it attains
normal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
(3) Remove the spark plugs.
(4) Remove the oil filler cap.
(5) Remove the air cleaner.
(6) Calibrate the tester according to the manufac-
turer's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
(7) Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
Set piston of cylinder to be tested at TDC compres-
sion,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE
LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
9 - 8 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)