2002 JEEP LIBERTY fuel unit
[x] Cancel search: fuel unitPage 598 of 1803

The CMTC may also be integrated with the Uni-
versal Transmitter. If so, your CMTC module will
have three buttons centered together between the
outer four buttons. Below the three buttons are cor-
responding dots to indicate which button you are
using.
The Compass Mini-Trip Computer includes the fol-
lowing display options:
²Compass and thermometer- provides the out-
side temperature and one of eight compass readings
to indicate the direction the vehicle is facing.
²Average fuel economy- shows the average
fuel economy since the last trip computer reset.
²Distance to empty- shows the estimated dis-
tance that can be travelled with the fuel remaining
in the fuel tank. This estimated distance is computed
using the average miles-per-gallon from the last 30
gallons of fuel used.
²Instant fuel economy- shows the present fuel
economy based upon the current vehicle distance and
fuel used information.
²Trip odometer- shows the distance travelled
since the last trip computer reset.
²Elapsed time- shows the accumulated igni-
tion-on time since the last trip computer reset.
²Blank screen- the CMTC compass/thermome-
ter/trip computer VFD is turned off.
If the vehicle is equipped with the optional Univer-
sal Transmitter transceiver, the CMTC will also dis-
play messages and an icon indicating when the
Universal Transmitter is being trained, which of the
three transmitter buttons is transmitting, and when
the transceiver is cleared.
Data input for all CMTC functions, including VFD
dimming level, is received through PCI data bus
messages. The CMTC module uses its internal pro-
gramming and all of its data inputs to calculate and
display the requested data. If the data displayed is
incorrect, perform the self-diagnostic tests as
described in this group. If these tests prove inconclu-
sive, the use of a DRBIIItscan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual are recommended for
further testing of the CMTC module and the PCI
data bus.
The CMTC module cannot be repaired, and is
available for service only as a unit. This unit
includes the push button switches and the plastic
module and display lens. If any of these components
is faulty or damaged, the complete CMTC module
must be replaced. The incandescent bulbs used for
CMTC push button back-lighting are available for
service replacement.
DESCRIPTION - COMPASS
While in the compass/thermometer mode, the com-
pass will display the direction in which the vehicle ispointed using the eight major compass headings
(Examples: north is N, northeast is NE). The self-cal-
ibrating compass unit requires no adjusting in nor-
mal use. The only calibration that may prove
necessary is to drive the vehicle in three complete
circles at 5 to 8 kilometers-per-hour (3 to 5 miles-per-
hour), on level ground, in not less than forty-eight
seconds. This will reorient the compass unit to its
vehicle.
The compass unit also will compensate for magne-
tism the body of the vehicle may acquire during nor-
mal use. However, avoid placing anything magnetic
directly on the roof of the vehicle. Magnetic mounts
for an antenna, a repair order hat, or a funeral pro-
cession flag can exceed the compensating ability of
the compass unit if placed on the roof panel. Mag-
netic bit drivers used on the fasteners that hold the
overhead console assembly to the roof header can
also affect compass operation. If the vehicle roof
should become magnetized, the demagnetizing and
calibration procedures found in this group may be
required to restore proper compass operation.
DESCRIPTION - THERMOMETER
The thermometer displays the outside ambient
temperature in whole degrees. The temperature dis-
play can be toggled from Fahrenheit to Celsius by
using the U.S./Metric button. The displayed temper-
ature is not an instant reading of conditions, but an
average temperature. It may take the thermometer
display several minutes to respond to a major tem-
perature change, such as driving out of a heated
garage into winter temperatures.
When the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion, the last displayed temperature reading stays in
the Body Control Module (BCM) unit memory. When
the ignition switch is turned to the On position
again, the CMTC will display the memory tempera-
ture for one minute; then update the display to the
current average temperature reading within five
minutes.
The thermometer function is supported by an
ambient temperature sensor. The sensor is mounted
outside the passenger compartment near the front
and center of the vehicle, and is hard wired to the
Body Control Module (BCM). The BCM sends tem-
perature status messages to the CMTC module over
the PCI data bus network. The ambient temperature
sensor is available as a separate service item, refer to
additional information later in this section.
OPERATION
The compass mini-trip computer operates when the
ignition is in the ON position. The VFD will display
the last display before ignition was turned OFF. The
four outer buttons operate:
KJMESSAGE SYSTEMS 8M - 5
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (Continued)
Page 599 of 1803

²STEP
²C/T - Compass/Temperature
²US/M - English/Metric
²RESET
1. STEP BUTTON
Pressing the STEP button selects one of the follow-
ing 6 displays:
²Average fuel economy
²Distance to empty
²Instantaneous fuel economy
²Trip odometer
²Elapsed time
²Blank Screen
2. C/T (COMPASS/TEMPERATURE)
BUTTON
Pressing the C/T button selects the Compass/Tem-
perature display.
3. US/M (ENGLISH/METRIC
MEASUREMENT) BUTTON
Pressing the US/M button switches the display
units between English and Metric readings.
4. RESET BUTTON
Pressing the RESET button resets the function on
the display, provided that function can be reset. The
functions which can be reset are Average fuel econ-
omy, Trip odometer and Elapsed time.
Global ResetThis feature allows all three dis-
plays (Average fuel economy, Trip odometer and
Elapsed time) to be reset easily, by pressing the
RESET button twice within three seconds with any
of the screens in display. This eliminates the need to
reset each display individually.
The RESET button is also used to set the variance
and/or calibrate the compass. Refer to the Variance
Procedure and Calibration Procedure in this section.
For more information on the features, control func-
tions and setting procedures for the CMTC module,
see the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPASS
MINI-TRIP COMPUTER
The following diagnostic procedure can be used if
the compass mini-trip computer is not operational in
any way. If the problem is specific to a individual
CMTC display, go to the appropriate display title
noted below and diagnose using the information pro-
vided on how these displays are generated.
(1) Remove the overhead console from the head-
liner (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CON-
SOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Using a ohmmeter, check the ground circuit
cavity of the compass mini-trip computer electricalconnector for proper continuity to ground. Continuity
should be present, If OK go to Step 3, If not OK
repair the open or shorted ground circuit as required.
NOTE: Connect the negative battery cable before
proceeding.
(3) Using a voltmeter, check the fused (B+) circuit
cavity of the compass mini-trip computer electrical
connector for 12v. Voltage should be present, If OK go
to Step 4, If not OK repair the open or shorted fused
(B+) circuit as required.
(4) Using a voltmeter, check the fused ignition
switch output circuit cavity of the compass mini-trip
computer electrical connector for 12v with Key ON.
Voltage should be present, If OK, replace the inoper-
ative CMTC module, If not OK repair the open or
shorted fused ignition switch output circuit as
required.
TEMPERATURE
The compass mini-trip computer receives Program-
mable Communications Interface bus (PCI bus) mes-
sages from the Body Control Module (BCM) for all
displayed information except the compass display. If
a dash (-) is displayed, the compass mini-trip com-
puter is not receiving a PCI bus message from the
BCM. To check out the PCI bus line and the BCM,
use the DRB llltscan tool and proper Body Diagnos-
tic Procedure Manual.
If the compass mini-trip computer displays a tem-
perature more than 54É C (130É F), check for a short
circuit between the temperature sensor and the
BCM.
If the compass mini-trip computer displays a tem-
perature less than -40É C (-67É F), check for an open
circuit between the temperature sensor and the
BCM.
AVERAGE FUEL ECONOMY
The compass mini-trip computer receives average
fuel economy information from the BCM over the PCI
bus line. If the compass mini-trip computer displays
-.- instead of an average fuel economy value, it is not
receiving a PCI bus message for the average fuel
economy from the BCM. To check out the PCI bus
line and the BCM use the DRB llltscan tool and
proper Body Diagnostic Procedure Manual.
DISTANCE TO EMPTY
The compass mini-trip computer receives distance
to empty information from the BCM over the PCI bus
line. If compass mini-trip computer displays a dash
(-) instead of a distance to empty value, it is not
receiving a PCI bus message for the distance to
empty from the BCM. To check out the PCI bus line
8M - 6 MESSAGE SYSTEMSKJ
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (Continued)
Page 1219 of 1803
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING)ÐPERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Incorrect right bank cam timing. 6. Refer to engine timing in this
section.
7. Dirt or water in fuel system. 7. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
8.Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 8.Repair or replace as necessary.
9. Faulty cam or crank sensor 9. Refer to Ignition system.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Vacuum leak. 1. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
2. Faulty crank position sensor 2. Replace crank position sensor.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
9 - 4 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1276 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL AREA
LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, camshaft bore
cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil filter runoff,
and main bearing cap to cylinder block mating sur-
faces. See Engine, for proper repair procedures of
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in the section, Inspection (Engine oil
Leaks in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING), under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL).
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied. MOPARtprovides engine oils that conform to
this service grade.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. Use only engine oils with multi-
Fig. 70 Oil Pressure Sending Unit -Typical
1 - BELT
2 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 61
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1302 of 1803

crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).Refer to the Engine Mechanical and the Engine
Performance diagnostic charts, for possible causes
and corrections of malfunctions (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MECHANICAL)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- PERFORMANCE).
For fuel system diagnosis, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace
as necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. Test starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
4. Faulty coil(s) or control unit. 4. Test and replace as needed.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. Set gap. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL
- SPECIFICATIONS)
6. Contamination in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump. 7. Test fuel pump and replace as
needed. (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information)
8. Incorrect engine timing. 8. Check for a skipped timing
belt/chain.
KJENGINE9s-5
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1383 of 1803
FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY..........................1FUEL INJECTION........................29
FUEL DELIVERY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL
PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST...........3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE...................4
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE..............5
TORQUE.............................5
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL SYSTEM........................6
FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................7
FUEL FILTER
DESCRIPTION..........................7
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................8
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL LEVEL
SENDING UNIT........................9
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION.........................10
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................10
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION.........................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS...........................10
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13OPERATION...........................14
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST......................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST.....................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
AMPERAGE TEST.....................16
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................19
FUEL RAIL
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................24
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................27
FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
KJFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1384 of 1803
FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the 2±section fuel pump module containing the
electric fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, fuel gauge
sending unit (fuel level sensor) and a fuel filter
located inside the lower section of pump module
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²A separately mounted main fuel filter²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
Certain fuel delivery components can be found in
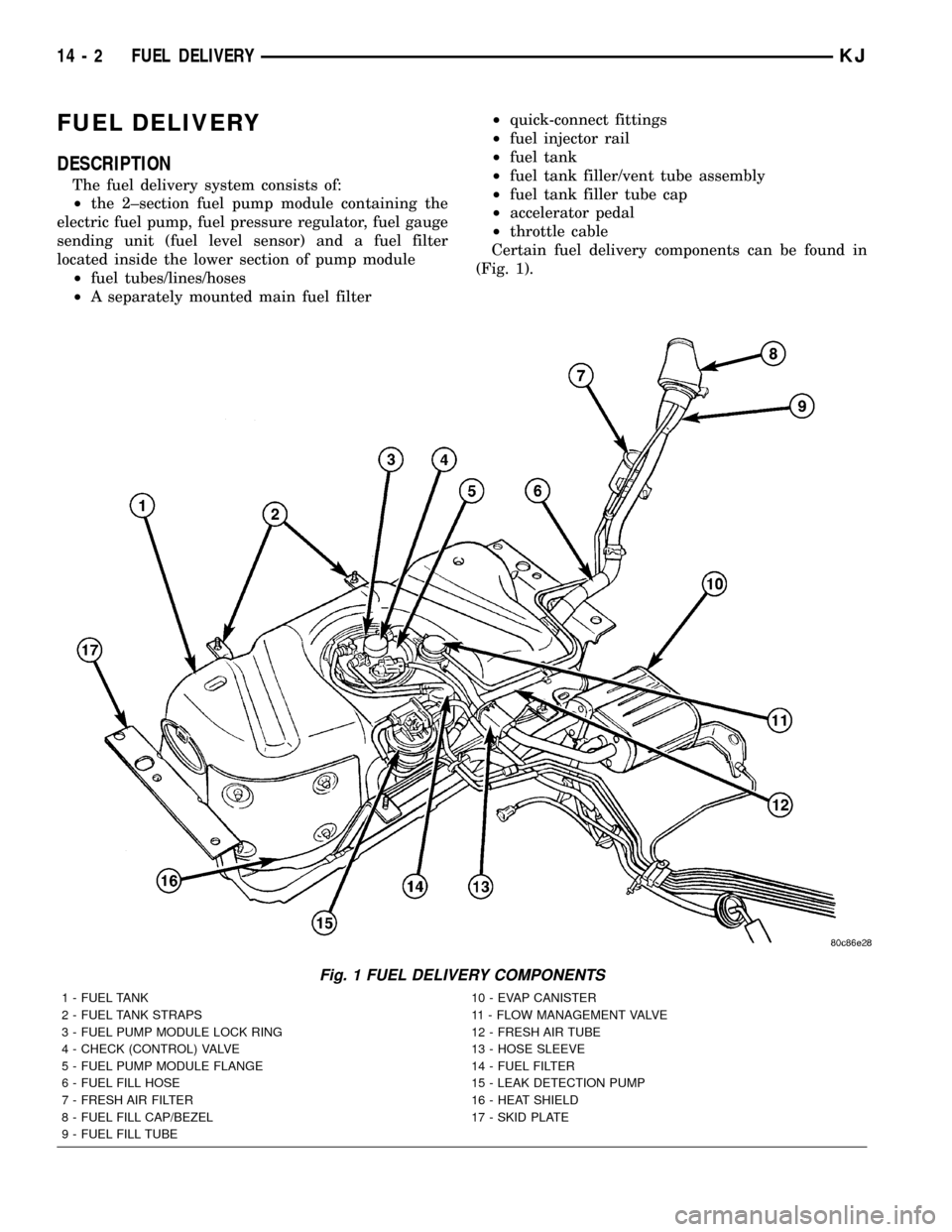
(Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 FUEL DELIVERY COMPONENTS
1 - FUEL TANK 10 - EVAP CANISTER
2 - FUEL TANK STRAPS 11 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
3 - FUEL PUMP MODULE LOCK RING 12 - FRESH AIR TUBE
4 - CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE 13 - HOSE SLEEVE
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE FLANGE 14 - FUEL FILTER
6 - FUEL FILL HOSE 15 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
7 - FRESH AIR FILTER 16 - HEAT SHIELD
8 - FUEL FILL CAP/BEZEL 17 - SKID PLATE
9 - FUEL FILL TUBE
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
Page 1391 of 1803
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant current
source of approximately 32 milliamps is supplied to
the resistor track on the fuel gauge sending unit.
This is fed directly from the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM).NOTE: For diagnostic purposes, this
12V power source can only be verified with the
circuit opened (fuel pump module electrical
connector unplugged). With the connectors
plugged, output voltages will vary from about
0.6 volts at FULL, to about 8.6 volts at EMPTY
(about 8.6 volts at EMPTY for Jeep models, and
about 7.0 volts at EMPTY for Dodge Truck mod-
els).The resistor track is used to vary the voltage
(resistance) depending on fuel tank float level. As
fuel level increases, the float and arm move up,
which decreases voltage. As fuel level decreases, the
float and arm move down, which increases voltage.
The varied voltage signal is returned back to the
PCM through the sensor return circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL LEVEL
SENDING UNIT
The fuel level sending unit contains a variable
resistor (track). As the float moves up or down, elec-
trical resistance will change. Refer to Instrument
Panel and Gauges for Fuel Gauge testing. To test the
gauge sending unit only, it must be removed from
vehicle. The unit is a separate part of the lower fuel
pump module section. Refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation for procedures (remove only the
upper section of the fuel pump module). Measure the
resistance across the sending unit terminals. With
float in up position, resistance should be 20 ohms (+/-
5%). With float in down position, resistance should be
270 ohms (+/- 5%).
REMOVAL
The fuel level sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of the lower sec-
tion of the fuel pump module. The lower section of
the fuel pump module is located within the fuel tank.
(1) Remove lower section of fuel pump module
from fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/
Installation.
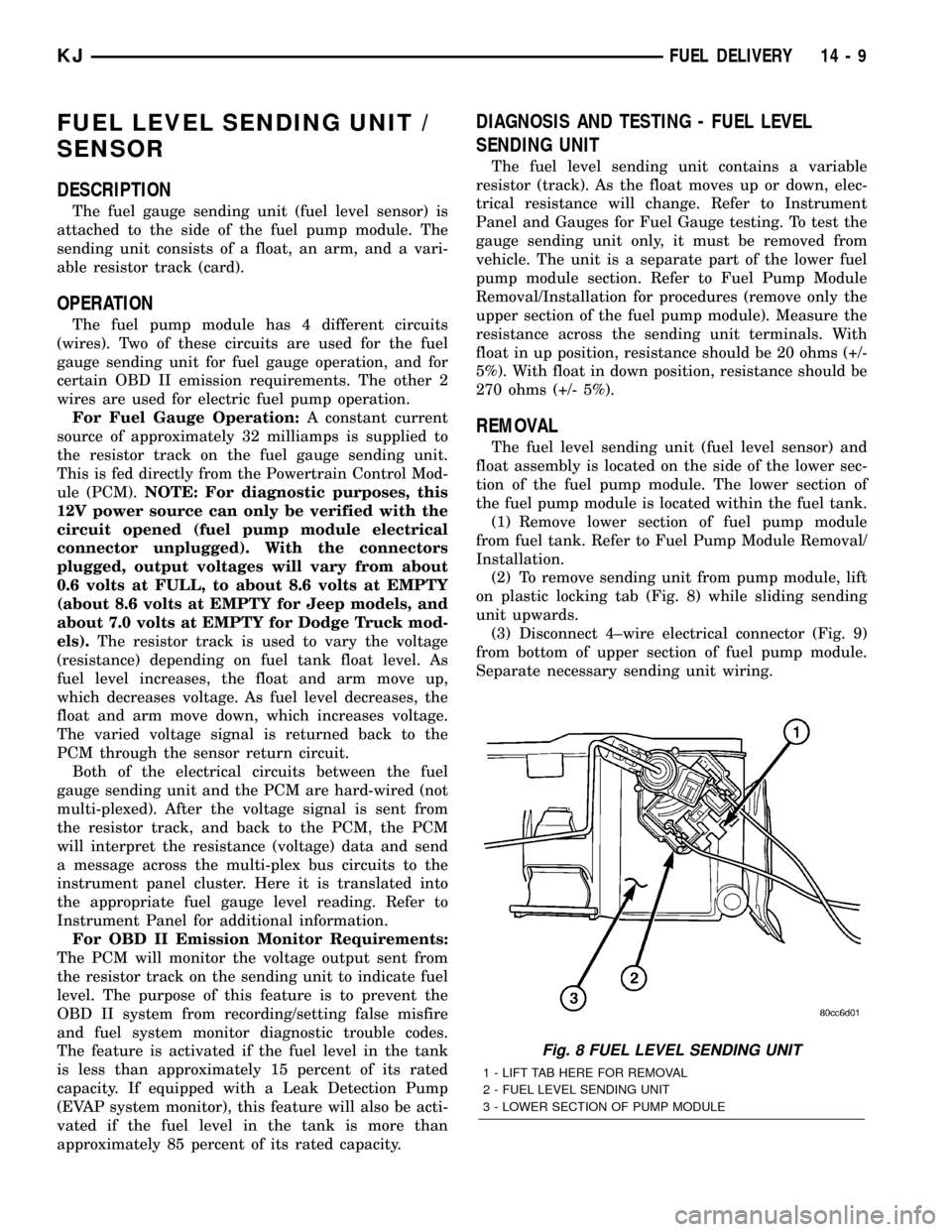
(2) To remove sending unit from pump module, lift
on plastic locking tab (Fig. 8) while sliding sending
unit upwards.
(3) Disconnect 4±wire electrical connector (Fig. 9)
from bottom of upper section of fuel pump module.
Separate necessary sending unit wiring.
Fig. 8 FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT
1 - LIFT TAB HERE FOR REMOVAL
2 - FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT
3 - LOWER SECTION OF PUMP MODULE
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 9