2002 JEEP LIBERTY belt
[x] Cancel search: beltPage 1651 of 1803

(4) When installing a new weatherstrip on the rear
door opening, remove the tear strip starting at the
splice and moving around the back of the door to the
front of the opening.
DOOR LOWER WEATHERSTRIP
REMOVAL
(1) Carefully disengage the push pin fasteners and
remove the seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the seal and seat the push pin fasten-
ers.
FRONT DOOR OUTER BELT
MOLDING
REMOVAL
(1) Lower the window.
(2) Pull the outer belt molding off of the door
flange starting at the rear and moving forward.
INSTALLATION
(1) Press the belt molding onto the outer door win-
dow flange starting at the rear and working forward.
SWING GATE BELTLINE
WEATHERSTRIP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the swing gate trim panel. (Refer to 23
- BODY/SWING GATE/TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL)
(2) Pull seal away from the corner tabs and
remove from the swing gate flange.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the seal over the swing gate flange and
seat the corner tabs.
(2) Install the swing gate trim panel. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/SWING GATE/TRIM PANEL - INSTALLA-
TION)
SWING GATE OPENING
WEATHERSTRIP
REMOVAL
(1) Open the swing gate and peal seal off of the
gate opening flange.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the seal to the bottom of the gate
opening starting the installation at the center of the
flange. Press the seal onto the sill flange and work
around the perimeter of the door opening until fully
seated. Work in one direction, smoothing the seal to
avoid puckers or wrinkles.
REAR DOOR OUTER BELT
MOLDING
REMOVAL
(1) Lower the window.
(2) Pull the outer belt molding off of the door
flange starting at the rear and moving forward.
INSTALLATION
(1) Press the belt molding onto the outer door win-
dow flange starting at the front and working back.
SIDE RAIL WEATHERSTRIP/
RETAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the windshield weatherstrip retainer.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/
WINDSHIELD A-PILLAR WEATHERSTRIP/RE-
TAINER - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the two screws.
(3) Using a trim stick C-4755 or equivalent,
release the push in fasteners and remove the weath-
erstrip.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the weatherstrip and seat the push in
fasteners.
(2) Install the two screws.
(3) Install the windshield weatherstrip. (Refer to
23 - BODY/WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/WINDSHIELD
A-PILLAR WEATHERSTRIP/RETAINER - INSTAL-
LATION)
WINDSHIELD A-PILLAR
WEATHERSTRIP/RETAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Open the doors and peal the a-pillar seal away
from the a-pillar/windshield and the side rail
weather strip flanges.
(2) Remove the seven screws and remove the
weatherstrip.
23 - 186 WEATHERSTRIP/SEALSKJ
DOOR PRIMARY WEATHERSTRIP (Continued)
Page 1657 of 1803
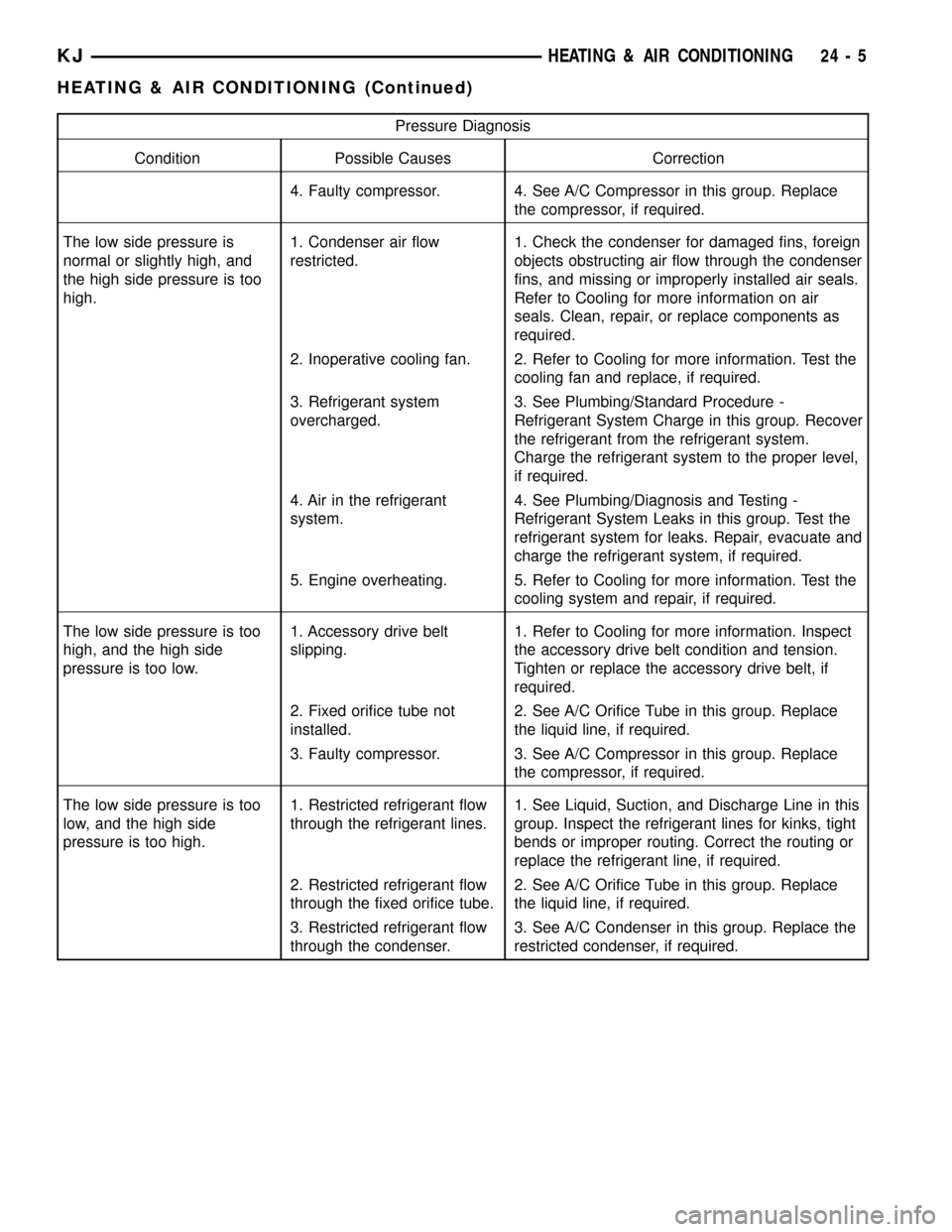
Pressure Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
4. Faulty compressor. 4. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly high, and
the high side pressure is too
high.1. Condenser air flow
restricted.1. Check the condenser for damaged fins, foreign
objects obstructing air flow through the condenser
fins, and missing or improperly installed air seals.
Refer to Cooling for more information on air
seals. Clean, repair, or replace components as
required.
2. Inoperative cooling fan. 2. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling fan and replace, if required.
3. Refrigerant system
overcharged.3. See Plumbing/Standard Procedure -
Refrigerant System Charge in this group. Recover
the refrigerant from the refrigerant system.
Charge the refrigerant system to the proper level,
if required.
4. Air in the refrigerant
system.4. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
5. Engine overheating. 5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling system and repair, if required.
The low side pressure is too
high, and the high side
pressure is too low.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect
the accessory drive belt condition and tension.
Tighten or replace the accessory drive belt, if
required.
2. Fixed orifice tube not
installed.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty compressor. 3. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 5
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1658 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures to check the radiator coolant
level, serpentine drive belt tension, radiator air flow
and the radiator fan operation. Also be certain that
the accessory vacuum supply line is connected at the
engine intake manifold.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT
Engine coolant is delivered to the heater core
through two heater hoses. With the engine idling atnormal operating temperature, set the temperature
control knob in the full hot position, the mode control
switch knob in the floor heat position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged at the HVAC housing floor
outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the
Temperature Reference chart.
Temperature Reference
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet52.2É C
(126É F)56.1É C
(133É F)59.4É C
(139É F)62.2É C
(144É F)
If the floor outlet air temperature is too low, refer
to Cooling to check the engine coolant temperature
specifications. Both of the heater hoses should be hot
to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should
be slightly cooler than the coolant supply heater
hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the sup-
ply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. Refer to Cooling
for the procedures.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow:
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²A plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is still
low, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible locations or
causes of insufficient heat:
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²A blend door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on theA/C Heater control panel, the following could require
service:
²The A/C Heater control.
²The blend door actuator.
²The blend door.
²Improper engine coolant temperature.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM SYSTEM
Vacuum control is used to operate the mode doors
in the heater-only and a/c heater housings. Testing of
the heater-only and A/C Heater mode control switch
operation will determine if the vacuum, electrical,
and mechanical controls are functioning. However, it
is possible that a vacuum control system that oper-
ates perfectly at engine idle (high engine vacuum)
may not function properly at high engine speeds or
loads (low engine vacuum). This can be caused by
leaks in the vacuum system, or a faulty vacuum
check valve.
A vacuum system test will help to identify the
source of poor vacuum system performance or vac-
uum system leaks. Before starting this test, stop the
engine and make certain that the problem is not a
disconnected vacuum supply tube at the engine
intake manifold vacuum tap or at the vacuum reser-
voir.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1664 of 1803

A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION - 3.7L and 2.4L
The compressor clutch assembly consists of a sta-
tionary electromagnetic coil, a rotor bearing and
rotor assembly, and a clutch plate (Fig. 1). The elec-
tromagnetic coil unit and the rotor bearing and rotor
assembly are each retained on the nose of the com-
pressor front housing with snap rings. The clutch
plate is keyed to the compressor shaft and secured
with a nut. These components provide the means to
engage and disengage the compressor from the
engine serpentine accessory drive belt.
OPERATION - 3.7L and 2.4L
When the clutch coil is energized, it magnetically
draws the clutch into contact with the rotor and
drives the compressor shaft. When the coil is not
energized, the rotor freewheels on the clutch rotor
bearing, which is part of the rotor. The compressor
clutch and coil are the only serviced parts on the
compressor.
The compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the A/C Heater mode control
switch, the A/C low pressure switch, the A/C high
pressure switch, the compressor clutch relay, and the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM may
delay compressor clutch engagement for up to thirty
seconds. Refer to Electronic Control Modules for
more information on the PCM controls.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information). The battery must
be fully-charged before performing the following
tests. Refer to Battery for more information.
(1) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0 to 20 volt scale) with clip-type leads for measuring
the voltage across the battery and the compressor
clutch coil.
(2) With the A/C Heater mode control switch in
any A/C mode, and the blower motor switch in the
lowest speed position, start the engine and run it at
normal idle.
(3) The compressor clutch coil voltage should read
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage. If there is
voltage at the clutch coil, but the reading is not
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage, test the clutch
coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair
as required. If there is no voltage reading at the
clutch coil, use a DRB IIItscan tool and (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information) for testing of the
compressor clutch circuit and PCM control. The fol-
lowing components must be checked and repaired as
required before you can complete testing of the clutch
coil:
²Fuses in the junction block and the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC)
²A/C heater mode control switch
²Compressor clutch relay
²A/C high pressure switch
²A/C low pressure switch
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
(4) The compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the
current draw measured at the clutch coil is 2.0 to 3.9
amperes with the electrical system voltage at 11.5 to
12.5 volts. This should only be checked with the work
area temperature at 21É C (70É F). If system voltage
is more than 12.5 volts, add electrical loads by turn-
ing on electrical accessories until the system voltage
drops below 12.5 volts.
(a) If the clutch coil current reading is four
amperes or more, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced.
(b) If the clutch coil current reading is zero, the
coil is open and should be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C Heater control to the
Recirculation Mode, the blower motor switch in the
highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500
Fig. 1 COMPRESSOR CLUTCH - TYPICAL
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - NOT USED ON KJ
3 - ROTOR
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
24 - 12 CONTROLSKJ
Page 1665 of 1803

to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing) will seat
the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher
compressor clutch torque capability.
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remain fully-charged
during compressor clutch, rotor, or coil replacement.
The compressor clutch can be serviced in the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Unplug the compressor clutch coil wire harness
connector.
(4) Remove the four bolts that secure the compres-
sor to the mounting bracket.
(5) Remove the compressor from the mounting
bracket. Support the compressor in the engine com-
partment while servicing the clutch.
(6) Insert the two pins of the spanner wrench
(Special Tool C-4489 or equivalent) into the holes of
the clutch plate. Hold the clutch plate stationary and
remove the hex nut (Fig. 2).(7) Remove the clutch plate.
(8) Remove the compressor clutch shims.
(9) Remove the external front housing snap ring
with snap ring pliers (Fig. 3).
(10) Install the lip of the rotor puller (Special Tool
C-6141-1 or equivalent) into the snap ring groove
exposed in the previous step, and install the shaft
protector (Special Tool C-6141-2 or equivalent) (Fig.
4).
Fig. 2 CLUTCH NUT REMOVE
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SPANNER
Fig. 3 EXTERNAL SNAP RING REMOVE
1 - PULLEY
2 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 4 SHAFT PROTECTOR AND PULLER
1 - PULLER JAW
2 - SHAFT PROTECTOR
KJCONTROLS 24 - 13
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1694 of 1803

used to charge the refrigerant system with R-134a
refrigerant. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for proper care
and use of this equipment.
SPECIFICATIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle is 0.737 kilograms (1.63 pounds).
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The air conditioning system uses a Sanden
PXF-18, reciprocating swash plate-type compressor
on all models. This compressor has a fixed displace-
ment of 180 cubic centimeters (10.984 cubic inches),
and has both the suction and discharge ports located
on the cylinder head. A label identifying the use of
R-134a refrigerant is located on the compressor.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the com-
pressor cylinder head, which is on the rear of the
compressor. This mechanical valve is designed to
vent refrigerant from the system to protect against
damage to the compressor and other system compo-
nents, caused by condenser air flow restriction or an
overcharge of refrigerant.
OPERATION
OPERATION
The compressor is driven by the engine through an
electric clutch, drive rotor and belt arrangement. The
compressor is lubricated by refrigerant oil that is cir-
culated throughout the refrigerant system with the
refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor, which is then
pumped to the condenser through the compressor dis-
charge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley and clutch
coil are available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes
when a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa
(400 psi) is reached.
The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean that the valve is faulty.
The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
NOISE
When investigating an air conditioning related
noise, you must first know the conditions under
which the noise occurs. These conditions include:
weather, vehicle speed, transmission in gear or neu-
tral, engine speed, engine temperature, and any
other special conditions. Noises that develop during
air conditioning operation can often be misleading.
For example: What sounds like a failed front bearing
or connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts,
mounting brackets, or a loose compressor clutch
assembly.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. At different engine
speeds and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop noises that are mistaken for a compressor
noise. Improper belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor clutch is engaged, which
may not occur when the compressor clutch is disen-
gaged. Check the serpentine drive belt condition and
tension as described in Cooling before beginning this
procedure.
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate the
complaint conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly iden-
tify the compressor noise. Listen to the compressor
while the clutch is engaged and disengaged. Probe
the compressor with an engine stethoscope or a long
screwdriver with the handle held to your ear to bet-
ter localize the source of the noise.
(2) Loosen all of the compressor mounting hard-
ware and retighten. Tighten the compressor clutch
mounting nut. Be certain that the clutch coil is
mounted securely to the compressor, and that the
clutch plate and rotor are properly aligned and have
the correct air gap. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION)
24 - 42 PLUMBINGKJ
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 1695 of 1803

(3) To duplicate a high-ambient temperature condi-
tion (high head pressure), restrict the air flow
through the condenser. Install a manifold gauge set
to be certain that the discharge pressure does not
exceed 2760 kPa (400 psi).
(4) Check the refrigerant system plumbing for
incorrect routing, rubbing or interference, which can
cause unusual noises. Also check the refrigerant lines
for kinks or sharp bends that will restrict refrigerant
flow, which can cause noises. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAU-
TION)
(5) If the noise is from opening and closing of the
high pressure relief valve, evacuate and recharge the
refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIG-
ERANT SYSTEM CHARGE) If the high pressure
relief valve still does not seat properly, replace the
compressor.
(6) If the noise is from liquid slugging on the suc-
tion line, replace the accumulator. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/AC-
CUMULATOR - REMOVAL) Check the refrigerant oil
level and the refrigerant system charge. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
REFRIGERANT OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - SPECIFICATIONS - CHARGE
CAPACITY) If the liquid slugging condition continues
following accumulator replacement, replace the com-
pressor. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRESSOR -
REMOVAL)
(7) If the noise continues, replace the compressor
and repeat Step 1.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
The compressor may be removed and repositioned
without disconnecting the refrigerant lines or dis-
charging the refrigerant system. Discharging is not
necessary if servicing the compressor clutch or clutch
coil, the engine, the cylinder head, or the generator.
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the serpentine drive belt(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch coil wire harness
connector.
(5) Remove the suction and discharge refrigerant
line manifold from the compressor. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
SUCTION LINE - REMOVAL) (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
DISCHARGE LINE - REMOVAL) Install plugs in, or
tape over all of the opened refrigerant fittings.
(6) Remove the bolts that secure the compressor to
the mounting bracket (Fig. 2) or (Fig. 3) or (Fig. 4).
(7) Remove the compressor from the mounting
bracket.
Fig. 2 A/C COMPRESSOR - 2.4L ENGINE
1 - COMPRESSOR BOLT
2 - COMPRESSOR BOLT
3 - COMPRESSOR CLUTCH AND PULLY
4 - IDLER PULLEY
5 - ENGINE BLOCK
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR
KJPLUMBING 24 - 43
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 1696 of 1803

INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
The compressor may be removed and repositioned
without disconnecting the refrigerant lines or dis-
charging the refrigerant system. Discharging is not
necessary if servicing the compressor clutch or clutch
coil, the engine, the cylinder head, or the generator.
NOTE: If a replacement compressor is being
installed, be certain to check the refrigerant oil
level. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL) Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the
compressor in the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL -
DESCRIPTION)(1) Install the compressor to the mounting bracket.
Tighten the three mounting bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft.
lbs.), (2.4L gasoline and 2.5L diesel engines only).
(2) On the 3.7L gasoline engine install and tighten
the bolts in the following sequence (Fig. 5):
²The number one bolt (rear) is hand tightened
first then tightened to 55 N´m (41 ft. lbs.)
²The number three bolt is then hand tightened
and torqued to 40 N´m ( 30 ft. lbs.)
²The number two bolt is also hand tightened and
torqued to 55 N´m ( 41 ft. lbs.)
(3) Remove the tape or plugs from all of the
opened refrigerant line fittings. Install the suction
and discharge line manifold to the compressor.
Tighten the fastener to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).(Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
SUCTION LINE - INSTALLATION) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
DISCHARGE LINE - INSTALLATION)
(4) Install the serpentine drive belt(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 3 A/C COMPRESSOR - 3.7L ENGINE
1 - COMPRESSOR BOLT #1
2 - COMPRESSOR BOLT #2
3 - COMPRESSOR BOLT #3
4 - A/C COMPRESSOR
5 - A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH AND PULLEY
6 - COMPRESSOR MOUNT
Fig. 4 A/C COMPRESSOR - 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE
1 - SUCTION LINE MOUNTING NUT
2- SUCTION LINE MOUNTING CLIP
3- SUCTION LINE
4- MOUNTING SCREW FOR SUCTION LINE
5- SUCTION LINE MOUNTING FLANG
6- MOUNTING SCREW FOR DISCHARGE LINE
7- DISCHARGE LINE MOUNTING FLANG
8- A/C PRESSURE SENSOR
9- A/C DISCHARGE LINE
10- A/C COMPRESSOR ASSEMBLY
11- A/C DISCHARGE LINE SERVICE PORT
24 - 44 PLUMBINGKJ
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)