2002 JEEP LIBERTY piston removal
[x] Cancel search: piston removalPage 1265 of 1803
90É turn. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
(6) Remove the bearing cap and determine amount
of bearing-to-journal clearance by measuring the
width of compressed Plastigage. Refer to Engine
Specifications for the proper clearance.Plastigage
should indicate the same clearance across the
entire width of the insert. If the clearance var-
ies, it may be caused by either a tapered jour-
nal, bent connecting rod or foreign material
trapped between the insert and cap or rod.
(7) If the correct clearance is indicated, replace-
ment of the bearing inserts is not necessary. Remove
the Plastigage from crankshaft journal and bearing
insert. Proceed with installation.
(8) If bearing-to-journal clearance exceeds the
specification, determin which services bearing set to
use the bearing sizes are as follows:
Bearing
MarkSIZE USED WITH
JOURNAL SIZE
.025 US.025 mm 57.871-57.879 mm
(.001 in.) (2.2783-2.2786 in.)
Std.STANDARD 57.896-57.904 mm
(2.2793-2.2810 in.)
.250 US.250 mm 57.646-57.654 mm
(.010 in.) (2.2695-2.2698 in.)
(9) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
(10) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a 90É turn.
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the con-
necting rod and crankshaft journal flange. Refer to
Engine Specifications for the proper clearance.
Replace the connecting rod if the side clearance is
not within specification.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING
(1) To correctly select the proper size piston, a cyl-
inder bore gauge, capable of reading in 0.003 mm (
.0001 in.) INCREMENTS is required. If a bore gauge
is not available, do not use an inside micrometer.
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at a point 38.0 mm (1.5 inches) below top of
bore. Start perpendicular (across or at 90 degrees) to
the axis of the crankshaft at point A and then take
an additional bore reading 90 degrees to that at point
B (Fig. 54).
(3) The coated pistons will be serviced with the
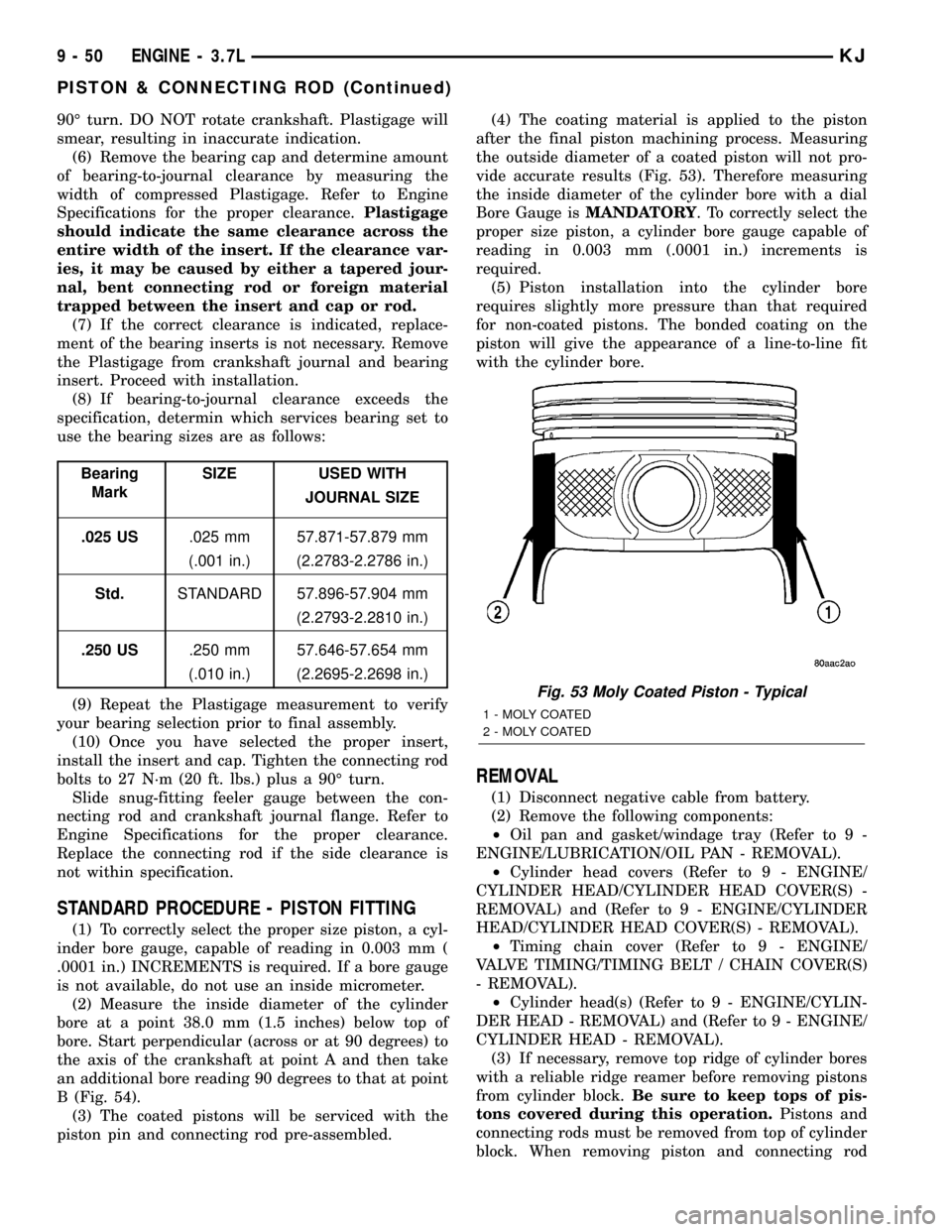
piston pin and connecting rod pre-assembled.(4) The coating material is applied to the piston
after the final piston machining process. Measuring
the outside diameter of a coated piston will not pro-
vide accurate results (Fig. 53). Therefore measuring
the inside diameter of the cylinder bore with a dial
Bore Gauge isMANDATORY. To correctly select the
proper size piston, a cylinder bore gauge capable of
reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.) increments is
required.
(5) Piston installation into the cylinder bore
requires slightly more pressure than that required
for non-coated pistons. The bonded coating on the
piston will give the appearance of a line-to-line fit
with the cylinder bore.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the following components:
²Oil pan and gasket/windage tray (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
²Timing chain cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head(s) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) If necessary, remove top ridge of cylinder bores
with a reliable ridge reamer before removing pistons
from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops of pis-
tons covered during this operation.Pistons and
connecting rods must be removed from top of cylinder
block. When removing piston and connecting rod
Fig. 53 Moly Coated Piston - Typical
1 - MOLY COATED
2 - MOLY COATED
9 - 50 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1266 of 1803

assemblies from the engine, rotate crankshaft so the
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
CAUTION: DO NOT use a number stamp or a punch
to mark connecting rods or caps, as damage to
connecting rods could occur
NOTE: Connecting rods and bearing caps are not
interchangeable and should be marked before
removing to ensure correct reassembly.
(4) Mark connecting rod and bearing cap positions
using a permanent ink marker or scribe tool.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to damage the
fractured rod and cap joint face surfaces, as engine
damage may occur.
(5) Remove connecting rod cap. Install Special Tool
8507 Connecting Rod Guides into the connecting rod
being removed. Remove piston from cylinder bore.
Repeat this procedure for each piston being removed.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to nick crank-
shaft journals, as engine damage may occur
(6) Immediately after piston and connecting rod
removal, install bearing cap on the mating connect-
ing rod to prevent damage to the fractured cap and
rod surfaces.
CLEANING
CAUTION: DO NOT use a wire wheel or other abra-
sive cleaning devise to clean the pistons or con-
necting rods. The pistons have a Moly coating, this
coating must not be damaged.
(1) Using a suitable cleaning solvent clean the pis-
tons in warm water and towel dry.
(2) Use a wood or plastic scraper to clean the ring
land grooves.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove the piston pin from the
piston and connecting rod assembly.
INSPECTION
Check the connecting rod journal for excessive
wear, taper and scoring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the connecting rod for signs of twist or bend-
ing.
Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the piston for scoring, or scraping marks in
the piston skirts. Check the ring lands for cracks
and/or deterioration.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing piston and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, install the piston rings.
(2) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings. Tighten ring compressor.Ensure posi-
tion of rings do not change during this opera-
tion.
(3) Position bearing onto connecting rod. Ensure
that tabs in bearing shell aligns with slots in con-
necting rod. Verify that parting line of bearing is
aligned with parting line of connecting rod.
(4) Lubricate bearing surface with clean engine oil.
(5) Install Special Tool 8507 Connecting Rod
Guides into connecting rod bolt threads (Fig. 55).
(6) The pistons are marked on the piston pin bore
surface with an raised ªFº indicating installation
position. This mark must be pointing toward the
front of engine on both cylinder banks. The connect-
ing rod oil slinger slot faces the front of the engine
(Fig. 56).
(7) Wipe cylinder bore clean and lubricate with
engine oil.
(8) Rotate crankshaft until connecting rod journal
is on the center of cylinder bore. Insert rod and pis-
Fig. 54 Bore Gauge - Typical
1 - FRONT
2 - BORE GAUGE
3 - CYLINDER BORE
4 - 38 MM (1.5 in)
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 51
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1269 of 1803

VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
NOTE: Transmission cooler line snaps into shroud
lower right hand corner.
(3) Remove crankshaft damper bolt.
(4) Remove damper using Special Tools 8513
Insert and 1026 Three Jaw Puller (Fig. 62).
Fig. 59 Side RailÐInstallation
1 - SIDE RAIL END
Fig. 60 Upper and Intermediate RingsÐInstallation
Fig. 61 Piston Ring End Gap Position
1 - SIDE RAIL UPPER
2 - NO. 1 RING GAP
3 - PISTON PIN
4 - SIDE RAIL LOWER
5 - NO. 2 RING GAP AND SPACER EXPANDER GAP
Fig. 62 Crankshaft DamperÐRemoval
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8513 INSERT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 1026
9 - 54 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
PISTON RINGS (Continued)
Page 1298 of 1803

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE - 2.4L
DESCRIPTION..........................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST................................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST.........3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK INSPECTION.....................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE.......5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE............5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
MECHANICAL.........................7
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE
AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS...............9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS..........9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE......................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-
PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS.........10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION........11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING
PLASTIGAGE.........................11
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY...........12
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ASSEMBLY........12
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 2.4L ENGINE.........13
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE............16
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.4L ENGINE.........................17
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 2.4L........................19
INSTALLATION - 2.4L....................19
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET............................19
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD.............20
CLEANING............................20
INSPECTION..........................21
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD..........21CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S)
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
CAMSHAFT(S)
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CAMSHAFT
END-PLAY...........................23
REMOVAL.............................24
CLEANING............................24
INSPECTION..........................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL.............................26
CLEANING............................26
INSPECTION..........................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION.........................27
CLEANING............................27
VALVE SPRINGS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON.........27
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF........27
INSPECTION..........................28
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON.....28
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF....28
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LASH ADJUSTER
(TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS............28
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
ROCKER ARMS
REMOVAL.............................29
INSPECTION..........................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION.........................30
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON TO
CYLINDER BORE FITTING..............30
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER
BORE HONING.......................31
CLEANING............................31
INSPECTION..........................32
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE
CONNECTING ROD - FITTING...........32
KJENGINE 9s - 1
Page 1299 of 1803

CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................32
OPERATION...........................33
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT
ENDPLAY ...........................33
REMOVAL.............................33
INSPECTION..........................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MAIN BEARING -
FITTING.............................35
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................39
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION.........................40
OPERATION...........................40
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................41
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE
PISTON RING - FITTING................42
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
STRUCTURAL COLLAR
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
ENGINE MOUNTING
DESCRIPTION.........................44
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................45
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE CHECKING.................46
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
ENGINE OIL LEVEL CHECK.............47
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
AND FILTER CHANGE..................47
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION.........................47
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
OIL PAN
REMOVAL.............................48INSTALLATION.........................48
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................48
OPERATION...........................48
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL.............................49
DISASSEMBLY.........................49
CLEANING............................49
INSPECTION..........................50
ASSEMBLY............................50
INSTALLATION.........................50
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................51
OPERATION...........................51
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS.....................51
REMOVAL.............................52
INSPECTION..........................52
INSTALLATION.........................52
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................53
OPERATION...........................53
REMOVAL.............................53
CLEANING............................53
INSPECTION..........................53
INSTALLATION.........................53
TIMING BELT COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................53
INSTALLATION.........................53
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S)
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TIMING BELT...............55
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET....55
CLEANING............................55
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET . 56
INSTALLATION - TIMING BELT...........56
TIMING BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY
REMOVAL.............................59
INSTALLATION.........................59
BALANCE SHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................59
OPERATION...........................59
REMOVAL.............................60
INSTALLATION
BALANCE SHAFT TIMING...............61
BALANCE SHAFT CARRIER
REMOVAL.............................64
INSTALLATION.........................64
BALANCE SHAFT CHAIN
REMOVAL.............................64
INSTALLATION.........................64
9s - 2 ENGINEKJ
Page 1306 of 1803

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL CONSUMPTION OR SPARK
PLUGS FOULED1. PCV system malfunction. 1. Check system and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 25 -
EMISSIONS CONTROL/
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/PCV
VALVE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
2. Worn, scuffed or broken rings. 2. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings.
3. Carbon in oil ring slots. 3. Install new rings.
4. Rings fitted too tightly in grooves. 4. Remove rings and check
grooves. If groove is not proper
width, replace piston.
5. Worn valve guide(s). 5. Replace cylinder head assembly.
6. Valve stem seal(s) worn or
damaged.6. Replace seal(s).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
Fig. 2 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
KJENGINE9s-9
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1316 of 1803

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 2.4L
Housing removal is not necessary for element (fil-
ter) replacement.
(1) Disconnect air intake duct at side of element
cover.
(2) Pry up 2 spring clips from front of housing
cover (spring clips retain cover to housing).
(3) Release housing cover from locating tabs
located on rear of housing, and remove cover.
(4) Remove air cleaner element (filter) from hous-
ing.
(5) Clean inside of housing before replacing ele-
ment.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install element into housing.
(2) Position housing cover into housing locating
tabs.
(3) Pry up spring clips and lock cover to housing.
(4) Connect air intake duct.
If any air filter, air resonator, air intake tubes or
air filter housing clamps had been loosened or
removed, tighten them to 5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cross flow designed, aluminum cylinder head
contains dual over-head camshafts with four valves
per cylinder (Fig. 5). The valves are arrange in two
in-line banks. The intake valves face toward the left
side of the vehicle. The exhaust valves face the right
side. The cylinder head incorporates powdered metalvalve guides and seats. The cylinder head is sealed to
the block using a multi-layer steel head gasket and
retaining bolts.
Integral oil galleries providing lubrication passages
to the hydraulic lash adjusters, camshafts, and valve
mechanisms.
OPERATION
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber,
allowing the pistons to compress the fuel/air mixture
for ignition. The valves are actuated by the lobe pro-
files on the camshaft to open and close at specified
duration to either allow clean air in the combustion
chamber or the exhaust gases out; depending on the
stroke of the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Combustion Leak Tester C-3685-A
Cylinder Compression Pressure Adaptor 8116
Fig. 5 Cylinder Head and Camshafts
CAM PLUG - NOT SHOWN
1 - CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS
2 - PLUG
3 - CAMSHAFT
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5 - CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL
KJENGINE9s-19
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1324 of 1803

(4) Install cylinder head cover assembly to cylin-
der head. Install all bolts, ensuring the two (2) bolts
containing the sealing washer are located in the cen-
ter locations of cover. Tighten bolts in sequence
shown in (Fig. 25). Using a 3 step torque method as
follows:
(a) Tighten all bolts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(b) Tighten all bolts to 9.0 N´m (80 in. lbs.).
(c) Tighten all bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(5) Install intake manifold.
(6) Install ignition coil and spark plug wires.
Tighten fasteners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(7) If the PCV valve was removed, apply Mopart
Thread Sealant with Teflon to threads and install
valve to cylinder head cover. Tighten PCV valve to 8
N´m (70 in. lbs.).
(8) Connect PCV and make-up air hoses to cylin-
der head cover.
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The four valves per cylinder are opened by using
roller rocker arms which pivot on hydraulic lash
adjusters. The valves have chrome plated valve
stems. Viton rubber valve stem seals are integral
with the spring seats.They have chrome plated stems
to prevent scuffing. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with the spring seats. The valves, spring
retainers,and locks, are the 3 - bead lock design
CLEANING
(1) Clean all valves thoroughly and discard
burned, warped and cracked valves.
VALVE SPRINGS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Remove camshafts.
(2) Rotate crankshaft until piston is at TDC on
compression.
(3) With air hose attached to adapter tool installed
in spark plug hole, apply 90-120 psi air pressure.
(4) Using Special Tool MD-998772-A with adapter
6779 (Fig. 26), compress valve springs and remove
valve locks.
(5) Remove valve spring(s).
(6) Remove valve stem seal(s) by a using valve
stem seal tool (Fig. 28).
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) With cylinder head removed from cylinder
block, compress valve springs using a universal valve
spring compressor.
(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves, locks and
retainers to insure installation in original location.
(4) Inspect the valves. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - INSPECTION)
Fig. 25 CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
Fig. 26 Valve Spring - Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE SPRING COMPRESSOR MD 998772A
2 - AIR HOSE
KJENGINE9s-27
CYLINDER HEAD COVER (Continued)