2002 JEEP LIBERTY evap leak detection
[x] Cancel search: evap leak detectionPage 1732 of 1803
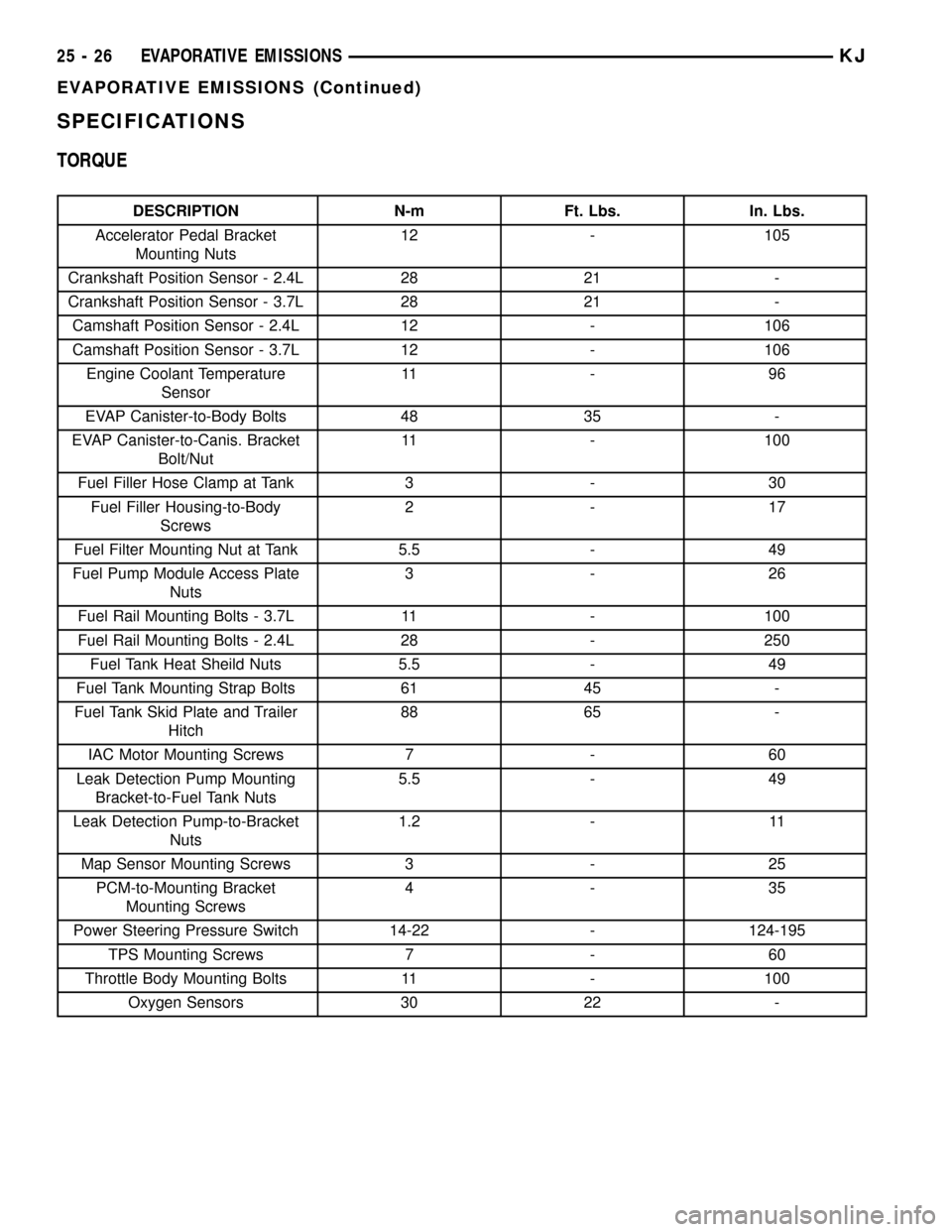
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Accelerator Pedal Bracket
Mounting Nuts12 - 105
Crankshaft Position Sensor - 2.4L 28 21 -
Crankshaft Position Sensor - 3.7L 28 21 -
Camshaft Position Sensor - 2.4L 12 - 106
Camshaft Position Sensor - 3.7L 12 - 106
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor11 - 9 6
EVAP Canister-to-Body Bolts 48 35 -
EVAP Canister-to-Canis. Bracket
Bolt/Nut11 - 100
Fuel Filler Hose Clamp at Tank 3 - 30
Fuel Filler Housing-to-Body
Screws2-17
Fuel Filter Mounting Nut at Tank 5.5 - 49
Fuel Pump Module Access Plate
Nuts3-26
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts - 3.7L 11 - 100
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts - 2.4L 28 - 250
Fuel Tank Heat Sheild Nuts 5.5 - 49
Fuel Tank Mounting Strap Bolts 61 45 -
Fuel Tank Skid Plate and Trailer
Hitch88 65 -
IAC Motor Mounting Screws 7 - 60
Leak Detection Pump Mounting
Bracket-to-Fuel Tank Nuts5.5 - 49
Leak Detection Pump-to-Bracket
Nuts1.2 - 11
Map Sensor Mounting Screws 3 - 25
PCM-to-Mounting Bracket
Mounting Screws4-35
Power Steering Pressure Switch 14-22 - 124-195
TPS Mounting Screws 7 - 60
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts 11 - 100
Oxygen Sensors 30 22 -
25 - 26 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 1733 of 1803

EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
is located in the engine compartment. It is attached
to a bracket located between the battery and the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). The EVAP system
test port is located near the solenoid.
OPERATION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP can-
ister to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operat-
ing condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
is located in the engine compartment (Fig. 2). It is
attached to a bracket located between the battery
and the Power Distribution Center (PDC). The EVAP
system test port is located near the solenoid (Fig. 2).
(1) Disconnect electrical wiring connector at sole-
noid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum harness at solenoid.
(3) Remove solenoid and its support bracket (pull
straight up).
INSTALLATION
(1) Slip EVAP canister purge solenoid onto its
mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum harness to solenoid.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION
The plastic fuel tank filler tube cap is threaded
onto the end of the fuel fill tube. All models are
equipped with a 1/4 turn cap.
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of fuel filler tube
is prevented by the use of a pressure-vacuum fuel fill
cap. Relief valves inside the cap will release fuel tank
pressure at predetermined pressures. Fuel tank vac-
uum will also be released at predetermined values.
This cap must be replaced by a similar unit if
replacement is necessary. This is in order for the sys-
tem to remain effective.
CAUTION: Remove fill cap before servicing any fuel
system component to relieve tank pressure. If
equipped with an ORVR system and a Leak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP), the cap must be tightened
securely. If cap is left loose, a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) may be set.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is bolted to the
front of the fuel tank (Fig. 1).
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is used only with
certain emission packages.
The LDP is a device used to detect a leak in the
evaporative system.
Fig. 2 EVAP / PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
1 - BATTERY
2 - EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
3 - MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
5 - SOLENOID ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
6 - EVAP SYSTEM TEST PORT
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 27
Page 1734 of 1803

The pump contains a 3 port solenoid, a pump that
contains a switch, a spring loaded canister vent valve
seal, 2 check valves and a spring/diaphragm.
OPERATION
Immediately after a cold start, engine temperature
between 40ÉF and 86ÉF, the 3 port solenoid is briefly
energized. This initializes the pump by drawing air
into the pump cavity and also closes the vent seal.
During non-test test conditions, the vent seal is held
open by the pump diaphragm assembly which pushes
it open at the full travel position. The vent seal will
remain closed while the pump is cycling. This is due
to the operation of the 3 port solenoid which prevents
the diaphragm assembly from reaching full travel.
After the brief initialization period, the solenoid is
de-energized, allowing atmospheric pressure to enter
the pump cavity. This permits the spring to drive the
diaphragm which forces air out of the pump cavity
and into the vent system. When the solenoid is ener-
gized and de-energized, the cycle is repeated creating
flow in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump
is controlled in 2 modes:
PUMP MODE:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate
to achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten
the overall test time.
TEST MODE:The solenoid is energized with a
fixed duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur
when the diaphragm reaches the switch closure
point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5 inches
of water.
When the pump starts, the cycle rate is quite high.
As the system becomes pressurized pump rate drops.
If there is no leak the pump will quit. If there is a
leak, the test is terminated at the end of the test
mode.
If there is no leak, the purge monitor is run. If the
cycle rate increases due to the flow through the
purge system, the test is passed and the diagnostic is
complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank (Fig. 3). The LDP
fresh air filter is located on the end of a hose. This
hose is attached to the fuel fill tube assembly below
and near the fuel fill opening (Fig. 1). The LDP and
LDP filter are typically replaced (serviced) as one
unit.
(1) Raise vehicle.(2) Carefully remove two 3/4º vent hoses at sides
of LDP.
(3) Carefully remove other vapor/vacuum hoses
from LDP.
(4) Place a hydraulic jack under fuel tank.
(5) Loosen 2 fuel tank strap mounting bolts at
front of tank about 10 turns.
(6) Lower front of fuel tank about 1/2º.
(7) Remove 2 LDP mounting nuts (Fig. 3) and
lower LDP slightly to gain access to electrical connec-
tor (Fig. 4).
(8) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP. To dis-
connect: Slide red colored tab upward. Push on black
colored tab while removing connector.
(9) Remove LDP from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is attached (bolt-
ed) to the front of the fuel tank. The LDP filter is
located on the end of a hose. This hose is attached to
the fuel fill tube assembly below and near the fuel
fill opening. The LDP and LDP filter are replaced
(serviced) as one unit.
(1) Install electrical connector to LDP. Push red
colored tab downward to lock connector to LDP.
(2) Position LDP and LDP bracket to fuel tank
mounting studs and install 2 nuts. Tighten nuts to 1
N´m (11 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Raise fuel tank to body and tighten 2 strap
bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 3 LDP LOCATION / MOUNTING
1 - LDP
2 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
3 - MOUNTING NUTS
4 - FRONT OF FUEL TANK
25 - 28 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSKJ
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1735 of 1803

(4) Carefully install vapor/vacuum lines to LDP,
and install hose to LDP filter.The vapor/vacuum
lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister duty cycle purge sole-
noid for damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled. Cer-
tain ORVR components can be found in (Fig. 1).
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DESCRIPTION
2.4L
The 2.4L 4-cylinder engine is equipped with a
closed crankcase ventilation system and a Positive
Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
²a PCV valve attached to the left/front side of the
valve cover (Fig. 5). It is secured with 1 bolt. An
o-ring is used to seal valve to valve cover (Fig. 6).
²the air cleaner housing
²tubes and hoses to connect the system compo-
nents.
3.7L
The 3.7L V-6 engine is equipped with a closed
crankcase ventilation system and a Positive Crank-
case Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 7). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 8).
²tubes and hoses to connect the system compo-
nents.
Fig. 4 LDP ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP (LDP)
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - FUEL FILTER
KJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)