2002 JEEP LIBERTY electric
[x] Cancel search: electricPage 605 of 1803

are closed and the accelerator pedal is depressed.
The rolling door lock feature can be disabled if
desired.
This vehicle also offers several customer program-
mable features, which allows the selection of several
optional electronic features to suit individual prefer-
ences.
The power lock system for this vehicle can also be
operated remotely using the available Remote Key-
less Entry (RKE) system radio frequency transmit-
ters, if equipped.
Certain functions and features of the power lock
system rely upon resources shared with other elec-
tronic modules in the vehicle over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus network.
For proper diagnosis of these electronic modules or of
the PCI data bus network, the use of a DRBIIItscan
tool and the appropriate diagnostic information are
required.
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
A Radio Frequency (RF) type Remote Keyless
Entry (RKE) system is an available factory-installed
option on this model. The RKE system allows the use
of a remote battery-powered radio transmitter to sig-
nal the Body Control Module (BCM) to actuate the
power lock system. The RKE receiver operates on
non-switched battery current through a fuse in the
Junction Block (JB), so that the system remains
operational, regardless of the ignition switch position.
The RKE transmitters are also equipped with a
Panic button. If the Panic button on the RKE trans-
mitter is depressed, the horn will sound and the
exterior lights will flash on the vehicle for about
three minutes, or until the Panic button is depressed
a second time. A vehicle speed of about 25.7 kilome-
ters-per-hour (15 miles-per-hour) will also cancel the
panic event.
The RKE system can also perform other functions
on this vehicle. If the vehicle is equipped with the
optional Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS), the
RKE transmitter will arm the VTSS when the Lock
button is depressed, and disarm the VTSS when the
Unlock button is depressed.
The RKE system includes two transmitters when
the vehicle is shipped from the factory, but the sys-
tem can retain the vehicle access codes of up to four
transmitters. The transmitter codes are retained in
the RKE receiver memory, even if the battery is dis-
connected. If an RKE transmitter is faulty or lost,
new transmitter vehicle access codes can be pro-
grammed into the system using a DRBIIItscan tool.
This vehicle also offers several customer program-
mable features, which allows the selection of several
optional electronic features to suit individual prefer-ences. Customer programmable feature options
affecting the RKE system include:
²Remote Unlock Sequence- Allows the option
of having only the driver side front door unlock when
the RKE transmitter Unlock button is depressed the
first time. The remaining doors and the tailgate
unlock when the button is depressed a second time
within 5 seconds of the first unlock press. Another
option is having all doors and the tailgate unlock
upon the first depression of the RKE transmitter
Unlock button.
²Sound Horn on Lock- Allows the option of
having the horn sound a short chirp as an audible
verification that the RKE system received a valid
Lock request from the RKE transmitter, or having no
audible verification.
²Flash Lights with Lock and Unlock- Allows
the option of having the lights flash as an optical ver-
ification that the RKE system received a valid Lock
request or Unlock request from the RKE transmitter,
or having no optical verification.
²Programming Additional Transmitters-
Allows up to four transmitter vehicle access codes to
be stored in the receiver memory.
Certain functions and features of the RKE system
rely upon resources shared with other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sensor
information. This helps to reduce wire harness com-
plexity, internal controller hardware, and component
sensor current loads. For diagnosis of these electronic
modules or of the PCI data bus network, the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate diagnostic
information are required.
TAILGATE / FLIP-UP GLASS POWER RELEASE
SYSTEM
A power operated tailgate / flip-up glass release
system is standard factory installed equipment on
this model. The entire system is controlled by the
Body Control Module (BCM). The tailgate / flip-up
glass power release system allows the flip-up glass
latch to be released electrically by actuating a switch
located integral to the outside tailgate handle. By
pulling the handle to the first detent or turning the
key cylinder to unlock, the flip-up glass will open.
Pulling the handle to the second detent will allow the
tailgate to open.
The tailgate / flip-up glass release system operates
on non-switched battery current supplied through a
fuse in the junction block so that the system remains
functional, regardless of the ignition switch position.
However, the BCM prevents the flip-up glass latch
from being actuated when the tailgate latch is
locked.
8N - 2 POWER LOCKSKJ
POWER LOCKS (Continued)
Page 607 of 1803

proper Diagnostic Procedures manual. The
DRBIIItscan tool can provide confirmation
that the PCI data bus is functional, that all of
the electronic modules are sending and receiv-
ing the proper messages on the PCI data bus,
and that the power lock motors are being sent
the proper hard wired outputs by the relays for
them to perform their power lock system func-
tions.
Following are tests that will help to diagnose the
hard wired components and circuits of the power lock
system. However, these tests may not prove conclu-
sive in the diagnosis of this system. In order to
obtain conclusive testing of the power lock system,
the Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
data bus network and all of the electronic modules
that provide inputs to, or receive outputs from the
power lock system components must be checked.
The Body Control Module (BCM) will set Diagnos-
tic Trouble Codes (DTC) for the power lock system.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
As a preliminary diagnosis for the power lock sys-
tem, note the system operation while you actuate
both the Lock and Unlock functions with the power
lock switches and with the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) transmitter. Then, proceed as follows:
²If the entire power lock system fails to function
with either the power lock switches or the RKE
transmitter, check the fused B(+) fuse in the junction
Block (JB).
²If the power lock system functions with both
power lock switches, but not with the RKE transmit-
ter, proceed to diagnosis of the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) system. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
LOCKS/KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING) or (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/POWER LOCKS/REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²If the power lock system functions with the RKE
transmitter, but not with one or both power lock
switches, proceed to diagnosis of the door lock
switches. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
LOCKS/POWER LOCK SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
²If the driver side power lock switch operates
only the driver side front door power lock motor, but
all other power lock motors operate with the passen-
ger side power lock switch or the RKE transmitter,
use a DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate diagnos-tic information to diagnose the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus.
²If only one power lock motor fails to operate
with both power lock switches and the RKE trans-
mitter, proceed to diagnosis of the power lock motor.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/POWER
LOCK MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DOOR LOCK / UNLOCK
SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DOOR LOCK/
UNLOCK SWITCH
(1) Remove the switch to be tested (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/POWER LOCK
SWITCH - REMOVAL).
(2) Using an ohmmeter, Test switch for resistance
values (Fig. 1).
DOOR LOCK SWITCH TEST
SWITCH
POSITIONPINS RESISTANCE
VALUE
UNACTUATED 1 AND 4 5.0K OHM 10
%
LOCK 1 AND 4 1.4K OHM 10
%
UNLOCK 1 AND 4 426 OHM 10
%
(3) If test results are not obtained as shown in the
test table, replace the switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
Fig. 1 DOOR LOCK/UNLOCK SWITCH
8N - 4 POWER LOCKSKJ
POWER LOCKS (Continued)
Page 608 of 1803

(2) Remove the door trim panel (Fig. 2) (Refer to
23 - BODY/DOOR - FRONT/TRIM PANEL - REMOV-
AL).
(3) Disconnect electrical harness connector from
switch.
(4) From behind the door trim panel, gently pry
the switch from the door trim panel (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Press the switch into place.
(2) Connect the electrical harness connector to the
switch.(3) Install the door trim panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOOR - FRONT/TRIM PANEL - INSTALLA-
TION).
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
DOOR LOCK MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The lock mechanisms are actuated by a reversible
electric motor mounted within each door and tailgate.
The power lock motors are integral to the door latch
units.
The power lock motors cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the door latch
unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The door lock motors are controlled by relays. A
positive and negative battery connection to the two
motor terminals will cause the motor to move in one
direction. Reversing the current will cause the motor
to move in the opposite direction.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DOOR LOCK
MOTOR
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the power lock system requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool and the proper Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual. The DRBIIItscan tool can provide
confirmation that the PCI data bus is functional, that
all of the electronic modules are sending and receiv-
ing the proper messages on the PCI data bus, and
that the power lock motors are being sent the proper
hard wired outputs by the door modules for them to
perform their power lock system functions.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
FLIP-UP GLASS RELEASE
SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLIP-UP GLASS
RELEASE SWITCH
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the tailgate trim panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE/
TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connector.
Fig. 2 DOOR LOCK SWITCH
1 - DOOR TRIM PANEL
2 - DOOR LOCK SWITCH
3 - POWER MIRROR SWITCH
Fig. 3 DOOR LOCK/MIRROR SWITCH
1 - DOOR TRIM PANEL
2 - DOOR LOCK SWITCH
3 - POWER MIRROR SWITCH
KJPOWER LOCKS 8N - 5
DOOR LOCK / UNLOCK SWITCH (Continued)
Page 610 of 1803

INSTALLATION
(1) Position the horn relay in the proper receptacle
in the Junction Block (JB).
(2) Push down firmly on the relay until the termi-
nals are fully seated.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
When an RKE lock message is sent to the Body
Control Module (BCM), the BCM actuates the doors
and the tailgate lock, the interior lighting is turned
off, the horn chirps (if this feature is enabled), the
exterior lamps flash (if this feature is enabled) and, if
the vehicle is so equipped, the Vehicle Theft Security
System (VTSS) is armed. When an RKE unlock mes-
sage is sent to the BCM, the BCM actuates the
driver side front door (or all doors and the tailgate if
this feature is enabled) unlock, the interior lighting
is turned on and, if the vehicle is so equipped, the
VTSS is disarmed.When an RKE panic message is sent to the BCM,
the BCM actuates the driver side front door (or all
doors and the tailgate if this feature is enabled)
unlock, the interior lighting is turned on and, if the
vehicle is so equipped, the VTSS is disarmed. The
panic message will also cause the exterior lamps
(including the headlights) to flash, and the horn to
pulse for about three minutes, or until a second panic
message is sent to the BCM. A vehicle speed of about
25.7 kilometers-per-hour (15 miles-per-hour) will also
cancel the panic event.
Refer to the owner's manual for more information
on the features, use and operation of the RKE sys-
tem.
OPERATION
Whenever the vehicle battery power is interrupted,
the Remote Keyless Module (RKE) Module will retain
all vehicle access codes in its memory. When replac-
ing or adding a key fob transmitter (maximum of 4) a
DRB IIItscan tool is required to program the RKE
Module to accept the new Vehicle Access Code if a
customer owned transmitter is not available.
If a functioning transmitter is available, (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/KEYLESS ENTRY
TRANSMITTER - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REMOTE KEYLESS
ENTRY MODULE
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds. Refer to the
proper Body Diagnostic Procedures Manual for test-
ing the Remote Keyless Entry system using a DRB
IIItscan tool.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the Junction Block (JB) (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/JUNCTION
BLOCK - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove Remote Keyless Entry module from
Body Control Module (Fig. 5).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install Remote Keyless Entry module to Body
Control Module.
(2) Install Junction Block (JB) (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/JUNCTION
BLOCK - INSTALLATION).
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
Fig. 4 Power Lock Relay
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
KJPOWER LOCKS 8N - 7
DOOR LOCK RELAY (Continued)
Page 614 of 1803

POWER MIRRORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
MIRRORS...........................11
POWER MIRROR SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER MIRROR
SWITCH............................12REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
SIDEVIEW MIRROR
REMOVAL.............................13
POWER MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION
The available power operated sideview mirrors
allow the driver to adjust both outside mirrors elec-
trically from the drivers seat by operating a switch
on the driver side front door trim panel (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The power mirrors receive ignition current through
a fuse in the junction block, and will only operate
when the ignition switch is in the Run position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER MIRRORS
WIRING VOLTAGE TEST
The following wiring test determines whether or
not voltage is continuous through the body harness
to switch.
(1) Remove the power mirror switch (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER MIRRORS/POWER MIRROR
SWITCH - REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect wire connector from back of power
mirror switch.
(3) Switch ignition to the RUN position.
(4) Connect the clip end of a 12 volt test light to
Pin 5 in the harness connector at the mirror switch.
Touch the test light probe to Pin 3.
If the test light illuminates, the wiring circuit
between the battery and switch is OK.
If the lamp does not illuminate, first check fuse 25
in the Junction Block (JB). If fuse 25 is OK, then
check for a broken wire.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
POWER MIRROR MOTOR TEST
If the power mirror switch is receiving proper cur-
rent and ground and mirrors do not operate, proceed
with power mirror motor test. Refer to the appropri-
ate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing
and retention, connector pin-out information and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 1 POWER MIRROR SWITCH
1 - DOOR TRIM PANEL
2 - DOOR LOCK SWITCH
3 - POWER MIRROR SWITCH
KJPOWER MIRRORS 8N - 11
Page 615 of 1803

(1) Remove front door trim panel to gain access to
power mirror wire connector (Refer to 23 - BODY/
DOOR - FRONT/TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect wire harness connector to power
mirror switch (Fig. 2).
(3) Using two jumper wires:
²Connect one to a 12 volt source
²Connect the other to a good body ground
²Refer to the Mirror Motor Test Chart for proper
wire connections at the switch connector
MIRROR MOTOR TEST CHART
12 VOLTS GROUND MIRROR REACTION
SWITCH CONNECTOR RIGHT LEFT
PIN 2 PIN 6 - UP
PIN 6 PIN 1 - LEFT
PIN 6 PIN 2 - DOWN
PIN 1 PIN 6 - RIGHT
PIN 9 PIN 6 UP -
PIN 6 PIN 10 LEFT -
PIN 6 PIN 9 DOWN -
PIN 10 PIN 6 RIGHT -
(4) If results shown in table are not obtained,
check for open or shorted circuit. Replace mirror
assembly as necessary.
POWER MIRROR SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER MIRROR
SWITCH
(1) Remove power mirror switch (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER MIRRORS/POWER MIRROR
SWITCH - REMOVAL).(2) Disconnect wiring harness connector from
switch.
(3) Using a ohmmeter, test for continuity between
the terminals of the switch (Fig. 3).
(4) If results shown in the table are not obtained,
replace the switch.
POWER MIRROR SWITCH TEST
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
MIRROR SELECT SWITCH IN9LEFT9POSITION
UP 5 AND 2
3 AND 6
DOWN 5 AND 6
3 AND 2
LEFT 5 AND 6
3 AND 1
RIGHT 5 AND 1
3 AND 6
MIRROR SELECT SWITCH IN9RIGHT9POSITION
UP 5 AND 9
3 AND 6
DOWN 5 AND 6
3 AND 9
LEFT 5 AND 6
3 AND 10
RIGHT 5 AND 10
3 AND 6Fig. 2 POWER MIRROR SWITCH CONNECTOR
Fig. 3 POWER MIRROR SWITCH
8N - 12 POWER MIRRORSKJ
POWER MIRRORS (Continued)
Page 617 of 1803
POWER SEATS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER SEATS
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER SEATS . . 15
SEAT TRACK
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SEAT TRACK....16
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
LEFT POWER SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................16OPERATION...........................17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LEFT POWER
SEAT SWITCH........................17
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
RIGHT POWER SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RIGHT POWER
SEAT SWITCH........................19
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................20
POWER SEATS
DESCRIPTION
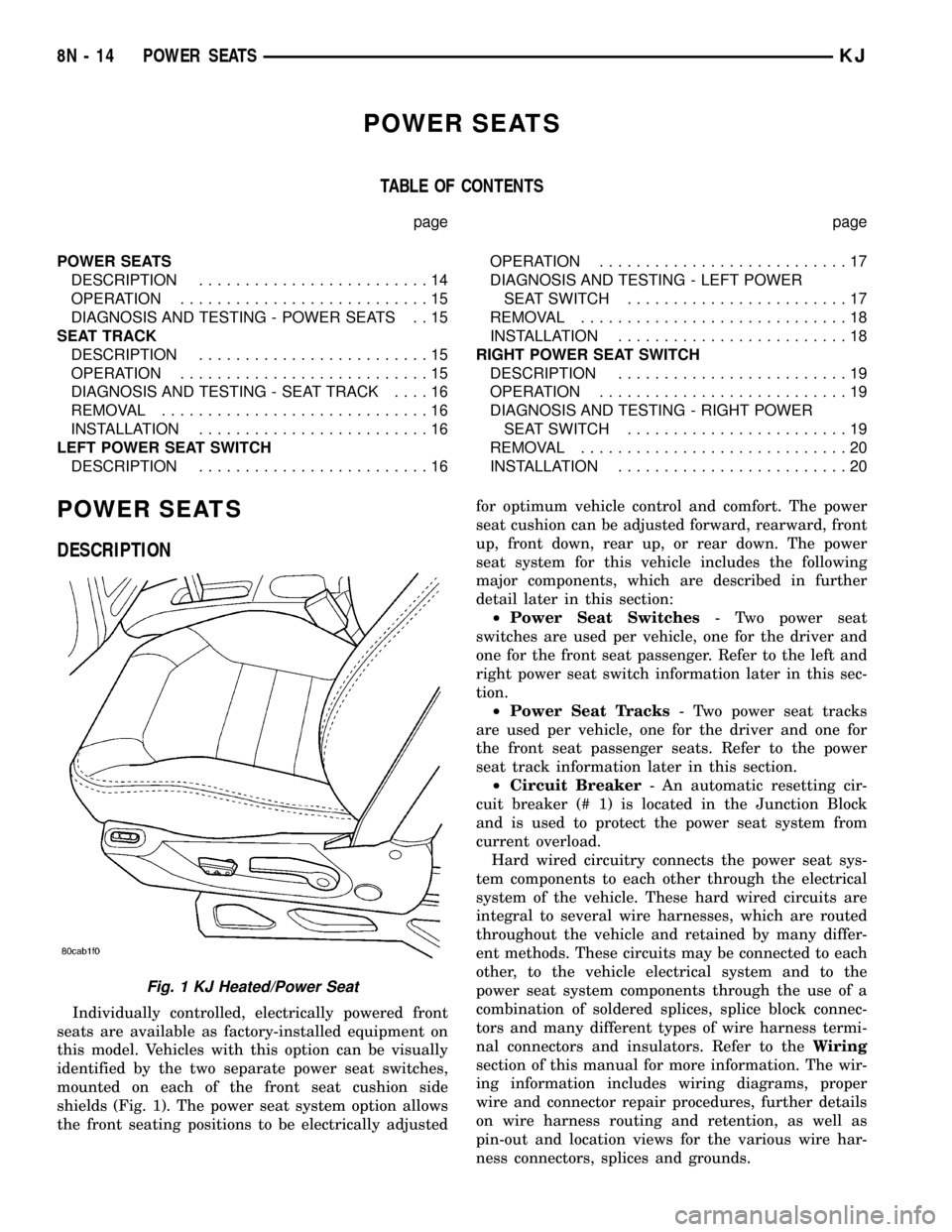
Individually controlled, electrically powered front
seats are available as factory-installed equipment on
this model. Vehicles with this option can be visually
identified by the two separate power seat switches,
mounted on each of the front seat cushion side
shields (Fig. 1). The power seat system option allows
the front seating positions to be electrically adjustedfor optimum vehicle control and comfort. The power
seat cushion can be adjusted forward, rearward, front
up, front down, rear up, or rear down. The power
seat system for this vehicle includes the following
major components, which are described in further
detail later in this section:
²Power Seat Switches- Two power seat
switches are used per vehicle, one for the driver and
one for the front seat passenger. Refer to the left and
right power seat switch information later in this sec-
tion.
²Power Seat Tracks- Two power seat tracks
are used per vehicle, one for the driver and one for
the front seat passenger seats. Refer to the power
seat track information later in this section.
²Circuit Breaker- An automatic resetting cir-
cuit breaker (# 1) is located in the Junction Block
and is used to protect the power seat system from
current overload.
Hard wired circuitry connects the power seat sys-
tem components to each other through the electrical
system of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
power seat system components through the use of a
combination of soldered splices, splice block connec-
tors and many different types of wire harness termi-
nal connectors and insulators. Refer to theWiring
section of this manual for more information. The wir-
ing information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 1 KJ Heated/Power Seat
8N - 14 POWER SEATSKJ
Page 618 of 1803

OPERATION
The power seat system receives battery current
through a fuse in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) and a circuit breaker in the Junction Block,
regardless of the ignition switch position.
When a power seat switch control knob or knobs
are actuated, a battery feed and a ground path are
applied through the switch contacts to the appropri-
ate power seat track adjuster motor. The selected
adjuster motor operates to move the seat track
through its drive unit in the selected direction until
the switch is released, or until the travel limit of the
seat track is reached. When the switch is moved in
the opposite direction, the battery feed and ground
path to the motor are reversed through the switch
contacts. This causes the adjuster motor to run in the
opposite direction.
Refer to the owner's manual in the vehicle glove
box for more information on the features, use and
operation of the power seat system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER SEATS
Before any testing of the power seat system is
attempted, the battery should be fully-charged and
all wire harness connections and pins cleaned and
tightened to ensure proper continuity and grounds.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The wir-
ing information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and joint connector location views for the var-
ious wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) If all power seats are inoperative, check the
automatic resetting circuit breaker in the Junction
Block. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRI-
BUTION/CIRCUIT BREAKER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(2) With the dome lamp on, apply the power seat
switch in the direction of the failure.
(3) If the dome lamp dims, the seat or the power
seat track may be jammed. Check under and behind
the seat for binding or obstructions.
(4) If the dome lamp does not dim, proceed with
testing of the individual power seat system compo-
nents and circuits.
SEAT TRACK
DESCRIPTION
The six-way power seat option includes a power
seat track assembly located under each front seat
(Fig. 2). The power seat track assembly replaces the
standard manually operated seat tracks. The lower
half of the power seat track is secured at the frontwith two bolts to the floor panel seat cross member,
and at the rear with one bolt and one nut to the floor
panel. Four bolts secure the bottom of the seat cush-
ion frame to the upper half of the power seat track
unit.
The power seat track assembly cannot be repaired,
and is serviced only as a complete assembly. If any
component in this assembly is faulty or damaged, the
entire power seat track must be replaced.
OPERATION
The power seat track unit includes three reversible
electric motors that are secured to the upper half of
the track unit. Each motor moves the seat adjuster
through a combination of worm-drive gearboxes and
screw-type drive units. Each of the three driver side
power seat track motors also has a position potenti-
ometer integral to the motor assembly, which elec-
tronically monitors the motor position.
The front and rear of the seat are operated by two
separate vertical adjustment motors. These motors
can be operated independently of each other, tilting
the entire seat assembly forward or rearward; or,
they can be operated in unison by selecting the
proper power seat switch functions, which will raise
or lower the entire seat assembly. The third motor is
the horizontal adjustment motor, which moves the
seat track in the forward and rearward directions.
Fig. 2 Power Seat Track - Typical
1 - POWER SEAT ADJUSTER AND MOTORS
2 - SEAT CUSHION FRAME
3 - POWER SEAT TRACK ASSEMBLY
KJPOWER SEATS 8N - 15
POWER SEATS (Continued)