2002 JEEP LIBERTY gas
[x] Cancel search: gasPage 1385 of 1803

OPERATION
Fuel is picked up in the fuel tank by the fuel pump
module. This module is located on the bottom of the
fuel tank.
A fuel return system is provided within the fuel
pump module using check valves. A separate fuel
return line from the engine to the tank is not used.
The fuel pressure regulator and the main fuel filter
are not combined. They are separate items.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock
ring/gasket, ORVR components. Refer to 25, Emis-
sion Control System for ORVR information.
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap. A one-way check valve is installed into the
tanks fuel fill fitting.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system and ORVR system. This
is designed to reduce the emission of fuel vapors into
the atmosphere. The description and function of the
Evaporative Control System is found in 25, Emission
Control Systems.
Both fuel filters (mounted to front of fuel tank, and
inside the bottom fuel pump module) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. The bottom section of the fuel
pump module (with included filter) should only be
replaced if a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
Also, the fuel filter mounted to the front of the fuel
tank should only be replaced if a diagnostic proce-
dure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Quick Connect Fittings for procedures. On some
engines, air cleaner housing removal may be neces-
sary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 2).
(4) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.The DRBtIII Scan
Tool along with the PEP module, the 500 psi
pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-test
port adapter may also be used in place of the
fuel pressure gauge.
The fittings on both tools must be in good
condition and free from any small leaks before
performing the proceeding test.
(5) Start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(6) Observe test gauge. Normal operating pressure
should be 339 kPa +/±34 kPa (49.2 psi +/±5 psi).
(7) Shut engine off.
Fig. 2 CONNECTING ADAPTER TOOLÐTYPICAL
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 3
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1397 of 1803

FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The bottom section of
the fuel pump module contains a one-way check
valve to prevent fuel flow back into the tank and to
maintain fuel supply line pressure (engine warm)
when pump is not operational. It is also used to keep
the fuel supply line full of gasoline when pump is not
operational. After the vehicle has cooled down, fuel
pressure may drop to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but
liquid gasoline will remain in fuel supply line
between the check valve and fuel injectors.Fuel
pressure that has dropped to 0 psi on a cooled
down vehicle (engine off) is a normal condition.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test for more
information.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a gradu-
ated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.
(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/10 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter.
Refer to Fuel Filter Removal/Installation for addi-
tional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace bottom section of fuel pump module. Refer
to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Capacity Test, Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and
Fuel Pump Amperage Test found elsewhere in this
group.
Check Valve Operation:The bottom section of
the fuel pump module contains a one-way check
valve to prevent fuel flow back into the tank and to
maintain fuel supply line pressure (engine warm)
when pump is not operational. It is also used to keep
the fuel supply line full of gasoline when pump is not
operational. After the vehicle has cooled down, fuel
pressure may drop to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but
liquid gasoline will remain in fuel supply line
between the check valve and fuel injectors.Fuel
pressure that has dropped to 0 psi on a cooled
down vehicle (engine off) is a normal condition.
When the electric fuel pump is activated, fuel pres-
sure shouldimmediately(1±2 seconds) rise to spec-
ification.
The fuel system is equipped with a separate fuel
pump module mounted, fuel pressure regulator. The
fuel filter is remotely mounted. The fuel pressure
regulator is not controlled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 15
Page 1400 of 1803

(17) When LCS adapter test leads are attached
into relay cavities, fuel pumpwill be activated.
Determine fuel pump amperage on DRB screen.
Amperage should be below 10.0 amps. If amperage is
below 10.0 amps, and specifications for the Fuel
Pump Pressure, Fuel Pump Capacity and Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down tests were met, the fuel pump mod-
ule is OK.
(18) If amperage is more than 10.0 amps, replace
fuel pump module assembly. The electric fuel pump
is not serviced separately.
(19) Disconnect test leads from relay cavities
immediately after testing.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump module assembly is located in the
fuel tank (Fig. 1). The assembly is divided into 2±sec-
tions, upper and lower. The lower section is locked to
the bottom of the fuel tank. The complete assembly
contains the following components:
²A fuel pressure regulator
²A separate fuel pick-up, or inlet filter
²An electric fuel pump
²A lockring to retain upper section of pump mod-
ule to tank
²A rollover valve
²A vent fitting for ORVR system
²A soft gasket between tank flange and module
²A fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
²Two fuel line connections (supply and return)
The fuel gauge sending unit may be serviced sepa-
rately. If the electrical fuel pump, primary inlet filter
or fuel pressure regulator require service, the lower
section of the fuel pump module must be replaced.
OPERATION
Refer to Fuel Pump, Inlet Filter, Fuel Pressure
Regulator and Fuel Gauge Sending Unit.
REMOVAL
The fuel pump module is divided into 2 sections,
upper and lower. To service the check (control) valve,
replace only the upper section. To service the fuel
gauge sending unit, remove the upper section. To ser-
vice the electric fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator or
primary inlet filter, remove both sections and replace
lower section.
Fuel tank removal will not be necessary for
fuel pump module removal. Access is from rear
cargo area.
(1) Four cargo holdown clamps are located inside
the vehicle on the floor of the rear cargo area.Remove the 2 rearward mounted clamps by drilling
out the clamp rivets.
(2) Fold carpeting forward to gain access to fuel
pump module access plate (Fig. 25).
(3) Remove 4 fuel pump module access plate nuts
(Fig. 25).
(4) While applying heat from a heat gun, carefully
pry up fuel pump module access plate. Take care not
to bend plate.
(5) Thoroughly clean area around top of pump
module to prevent contaminants from entering fuel
tank or fuel lines.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
(6) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
System Pressure Release procedure.
(7) Disconnect 2 fuel lines at fuel pump module
(Fig. 26) by pressing on 2 buttons at sides of fitting.
(8) Disconnect electrical connector (Fig. 26) at top
of fuel pump module by sliding red colored tab first
to unlock, and push grey colored tab down for
removal.
(9) Disconnect ORVR hose clamp and hose (Fig.
26) at pump module fitting.
(10) Remove module lockring (Fig. 26) using a
brass drift and hammer (counter-clockwise).
(11) Carefully lift upper section of pump module
(Fig. 26) from fuel tank exposing connections(lift
upper section from tank very slowly until rub-
ber gasket can be retained. If not, gasket will
fall into fuel tank.)
(a) Disconnect electrical connector (Fig. 27) at
bottom of upper pump module section.
(b) Disconnect fuel pressure regulator (Fig. 27)
at bottom of upper pump module section. Press on
2 locking tabs.
(c) Disconnect fuel return line (Fig. 27) at bot-
tom of upper pump module section. Press on 2
locking tabs.
(d) Remove upper section of pump module (Fig.
28) from fuel tank.
(12) Using an approved gas holding tank, drain
fuel tank through pump module opening.If check
(control) valve, or, only upper section of pump
module is being serviced, tank draining is not
necessary. If any other fuel pump module com-
ponent is being serviced, the tank must be com-
pletely drained to the bottom.
(13) To remove lower section of pump module from
fuel tank:
(a) Using finger pressure, push on plastic
release tab (Fig. 29) while sliding lock tab upward.
14 - 18 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1401 of 1803

(b) The sides of pump module are equipped with
tension springs (Fig. 29). These springs hold mod-
ule to bottom of fuel tank into 2 formed guides
(Fig. 30). Release module assembly from these 2
guides by sliding toward right side of fuel tank.
(c) Lift assembly from fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Whenever fuel pump module is serviced,
pump module gasket must be replaced.
(1) Position lower section of fuel pump module
assembly into fuel tank.
(2) The bottom of fuel tank has 2 formed guides.
Lock module assembly into these 2 guides by sliding
toward left side of fuel tank.
(3) Push down on plastic tab to lock module to fuel
tank guides.
(4) Connect fuel supply line to bottom of upper
pump module section.
(5) Connect fuel pressure regulator to bottom of
upper pump module section.
(6) Connect electrical connector to bottom of upper
pump module section.
(7) Position pump module into fuel tank. Notch on
module must be facing rear of tank.(8) Position lock ring to module. Tap lockring
using a brass drift and hammer (clockwise) until
rotated up to built-on stops.
(9) Attach (snap on) 2 fuel filter fuel lines to top of
fuel pump module.
(10) Connect hoses/lines to ORVR components.
(11) Fill fuel tank with fuel.
(12) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
(13) Apply silicone sealant to bottom of fuel pump
module metal access plate.
(14) Install fuel pump module metal access plate
and 4 nuts. Tighten nuts to 3 N´m (26 in. lbs.)
torque.
(15) Position carpet and install 2 new cargo clamp
rivets into each cargo holdown clamp.
Fig. 25 ACCESS PLATE
1 - FLOORPAN AT REAR
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE ACCESS PLATE
3 - NUTS (4)
4 - OPENING TO PUMP MODULE
Fig. 26 TOP OF FUEL PUMP MODULE
1 - LOCK RING
2 - ALIGNMENT NOTCH
3 - FUEL FILTER FITTINGS (2)
4 - ORVR SYSTEM HOSE AND CLAMP
5 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
7 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
8 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
9 - FUEL PUMP MODULE (UPPER SECTION)
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 19
FUEL PUMP MODULE (Continued)
Page 1407 of 1803
REMOVAL
Fuel Tank Draining
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY BE UNDER
CONSTANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE
ENGINE OFF. THIS PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED BEFORE SERVICING FUEL TANK.
Two different procedures may be used to drain fuel
tank: removing fuel pump module access plate, or
using DRBtscan tool. Due to a one-way check valve
installed into the fuel fill opening fitting at the tank
(Fig. 38), the tank cannot be drained conventionally
at the fill cap.
The quickest draining procedure involves removing
fuel pump module access plate.
As an alternative procedure, the electric fuel pump
may be activated allowing tank to be drained at fuel
rail connection. Refer to DRB scan tool for fuel pump
activation procedures. Before disconnecting fuel line
at fuel rail, release fuel pressure. Refer to the Fuel
System Pressure Release Procedure for procedures.
Attach end of special test hose tool number 6541,
6539, 6631 or 6923 at fuel rail disconnection (tool
number will depend on model and/or engine applica-
tion). Position opposite end of this hose tool to an
approved gasoline draining station. Activate fuel
pump and drain tank until empty.
If electric fuel pump is not operating, fuel pump
module access plate must be removed for fuel drain-
ing. Refer to following procedures.Fuel tank removal will not be necessary for
fuel tank draining. Access for draining is from
rear cargo area.
(1) Open all windows in vehicle to allow for air
ventilation.
(2) Four cargo holdown clamps are located inside
the vehicle on the floor of the rear cargo area.
Remove the 2 rearward mounted clamps by drilling
out the clamp rivets.
(3) Fold carpeting forward to gain access to fuel
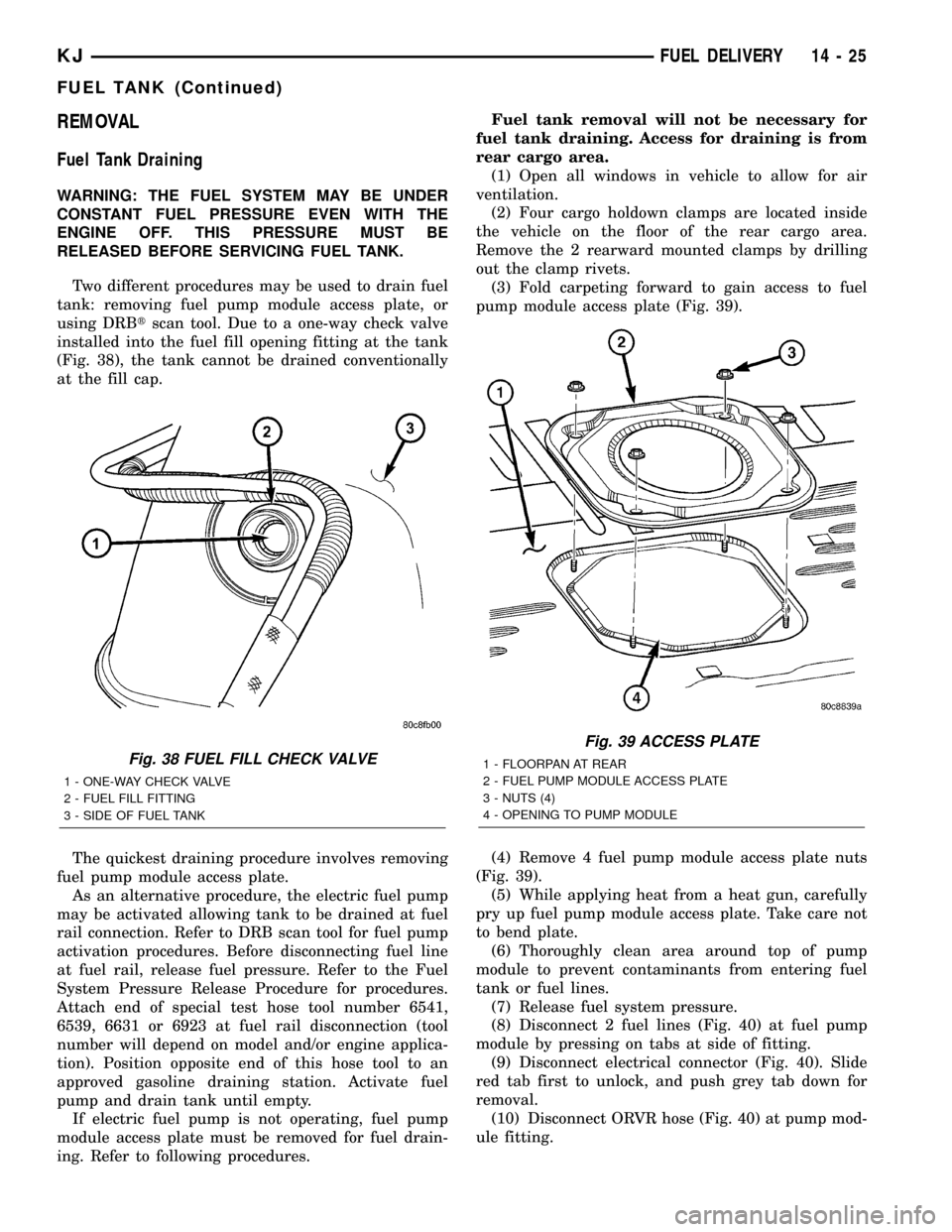
pump module access plate (Fig. 39).
(4) Remove 4 fuel pump module access plate nuts
(Fig. 39).
(5) While applying heat from a heat gun, carefully
pry up fuel pump module access plate. Take care not
to bend plate.
(6) Thoroughly clean area around top of pump
module to prevent contaminants from entering fuel
tank or fuel lines.
(7) Release fuel system pressure.
(8) Disconnect 2 fuel lines (Fig. 40) at fuel pump
module by pressing on tabs at side of fitting.
(9) Disconnect electrical connector (Fig. 40). Slide
red tab first to unlock, and push grey tab down for
removal.
(10) Disconnect ORVR hose (Fig. 40) at pump mod-
ule fitting.
Fig. 38 FUEL FILL CHECK VALVE
1 - ONE-WAY CHECK VALVE
2 - FUEL FILL FITTING
3 - SIDE OF FUEL TANK
Fig. 39 ACCESS PLATE
1 - FLOORPAN AT REAR
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE ACCESS PLATE
3 - NUTS (4)
4 - OPENING TO PUMP MODULE
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 25
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1408 of 1803

(11) Remove module lockring (Fig. 40) using a
brass drift and hammer (counter-clockwise).
(12) Carefully lift upper section of pump module
from fuel tank a few inches(lift upper section
from tank very slowly until rubber gasket can
be retained. If not, gasket will fall into fuel
tank).
(13) Using an approved gas holding tank, drain
fuel tank through fuel pump module opening.
Tank Removal
(1) After draining tank, temporarily place upper
section of fuel pump module back into fuel tank.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) If equipped, remove fuel tank skid plate and
tow hooks. Certain equipment packages will also
require removal of the trailer hitch. Refer to Tow
Hooks, Trailer Hitch or Skid Plate in 23, Body for
removal/installation procedures.
(4) Disconnect fuel filter ground strap.
(5) Disconnect fuel filter outlet line from body
retention clip located on frame near front/center of
tank (Fig. 41). Place a small screwdriver into side of
clip and twist for removal. Also disconnect Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) line (Fig. 41) from this clip.(6) Remove both 3/4º hoses at sides of Leak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP) (Fig. 41).
(7) Disconnect 3/4º flow management valve hose
(Fig. 41) at EVAP canister.
(8) Remove fuel fill hose clamp (Fig. 42) at fuel
tank, and disconnect hose from fuel tank.
(9) A third fuel line is attached to bottom of fuel
filter. The disconnection point (quick-connect fitting)
for this 3rd line is approximately 1 foot from front of
tank towards front of vehicle (Fig. 41). Clean connec-
tion point before disconnection. Disconnect by press-
ing on tabs at side of quick-connect fitting. Also
disconnect LDP vent line near this same point.
(10) Disconnect 2 vacuum/vent hoses from plastic
retention clip at left/front of fuel tank line (Fig. 41).
(11) Support tank with a hydraulic jack.
(12) Remove 4 fuel tank strap bolts (Fig. 41) (2 at
front of tank; 2 at rear of tank), and remove both
tank support straps (Fig. 41).
(13) Carefully lower tank a few inches and discon-
nect electrical connector at top of LDP (Fig. 43). To
disconnect electrical connector: Push upward on red
colored tab to unlock. Push on black colored tab
while removing connector.
Fig. 40 TOP OF FUEL PUMP MODULE
1 - LOCK RING
2 - ALIGNMENT NOTCH
3 - FUEL FILTER FITTINGS (2)
4 - ORVR SYSTEM HOSE AND CLAMP
5 - FLOW MANAGEMENT VALVE
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
7 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
8 - FUEL TANK CHECK (CONTROL) VALVE
9 - FUEL PUMP MODULE (UPPER SECTION)Fig. 41 FRONT OF FUEL TANK
1 - TANK MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - TANK MOUNTING STRAPS (2)
3 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP (LDP)
4 - BODY RETENTION CLIP (CENTER)
5 - LDP HOSES
6 - HOSE TO FUEL MANAGEMENT VALVE
7 - BODY RETENTION CLIP (LEFT/FRONT)
8 - QUICK-CONECT FITTING
9 - LDP LINE
14 - 26 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1423 of 1803

ronment that they operate in, that keep them from
being interchangeable.
Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all
times allows the system to enter into closed loop
operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain
in closed loop operation during periods of extended
idle.
In Closed Loop operation, the PCM monitors cer-
tain O2 sensor input(s) along with other inputs, and
adjusts the injector pulse width accordingly. During
Open Loop operation, the PCM ignores the O2 sensor
input. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based
on preprogrammed (fixed) values and inputs from
other sensors.
Upstream Sensor - 2.4L Engine:The upstream
sensor (1/1) provides an input voltage to the PCM.
The input tells the PCM the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas. The PCM uses this information to fine
tune fuel delivery to maintain the correct oxygen con-
tent at the downstream oxygen sensor. The PCM will
change the air/fuel ratio until the upstream sensor
inputs a voltage that the PCM has determined will
make the downstream sensor output (oxygen content)
correct.
The upstream oxygen sensor also provides an input
to determine catalytic convertor efficiency.
Downstream Sensor - 2.4L Engine:The down-
stream oxygen sensor (1/2) is also used to determine
the correct air-fuel ratio. As the oxygen content
changes at the downstream sensor, the PCM calcu-
lates how much air-fuel ratio change is required. The
PCM then looks at the upstream oxygen sensor volt-
age and changes fuel delivery until the upstream
sensor voltage changes enough to correct the down-
stream sensor voltage (oxygen content).
The downstream oxygen sensor also provides an
input to determine catalytic convertor efficiency.
Upstream Sensors - 3.7L Engine:Two upstream
sensors are used (1/1 and 2/1). The 1/1 sensor is the
first sensor to receive exhaust gases from the #1 cyl-
inder. They provide an input voltage to the PCM. The
input tells the PCM the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas. The PCM uses this information to fine
tune fuel delivery to maintain the correct oxygen con-
tent at the downstream oxygen sensors. The PCM
will change the air/fuel ratio until the upstream sen-
sors input a voltage that the PCM has determined
will make the downstream sensors output (oxygen
content) correct.
The upstream oxygen sensors also provide an input
to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main catalytic
convertor efficiency is not calculated with this pack-
age.
Downstream Sensors - 3.7L Engine:Two down-
stream sensors are used (1/2 and 2/2). The down-
stream sensors are used to determine the correct air-fuel ratio. As the oxygen content changes at the
downstream sensor, the PCM calculates how much
air-fuel ratio change is required. The PCM then looks
at the upstream oxygen sensor voltage, and changes
fuel delivery until the upstream sensor voltage
changes enough to correct the downstream sensor
voltage (oxygen content).
The downstream oxygen sensors also provide an
input to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main cat-
alytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with this
package.
Engines equipped with either a downstream sen-
sor(s), or a post-catalytic sensor, will monitor cata-
lytic convertor efficiency. If efficiency is below
emission standards, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated and a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will be set. Refer to Monitored Systems
in Emission Control Systems for additional informa-
tion.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Never apply any type of grease to the
oxygen sensor electrical connector, or attempt any
soldering of the sensor wiring harness.
Refer to (Fig. 20), (Fig. 21) or (Fig. 22) for O2S
(oxygen sensor) location.
Fig. 20 OXYGEN SENSORS - 2.4L
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
2 - UPSTREAM SENSOR (1/1)
3 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
4 - DOWNSTREAM SENSOR (1/2)
KJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 41
OXYGEN SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1462 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 14).
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 15).
Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 15).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE OR
VIBRATION
Radial-ply tires are sensitive to force impulses
caused by improper mounting, vibration, wheel
defects, or possibly tire imbalance.
To find out if tires are causing the noise or vibra-
tion, drive the vehicle over a smooth road at varyingspeeds. Note the noise level during acceleration,
deceleration and slight left and right steering inputs.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIRING LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 16). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.
Deflate tire completely before removing the tire
from the wheel. Use lubrication such as a mild soap
solution when dismounting or mounting tire. Use
tools free of burrs or sharp edges which could dam-
age the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and tighten to proper
torque specification.
CLEANING
Remove the protective coating on the tires before
delivery of a vehicle. This coating may cause deteri-
oration of the tires.
To remove the protective coating, apply warm
water and let it soak for a few minutes. Afterwards,
scrub the coating away with a soft bristle brush.
Steam cleaning may also be used to remove the coat-
ing.
NOTE: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-based
solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Tire P215/75R16
Tire P235/70R16
Spare Tire P215/75D16
POLYSPARE ONLY ON
169
SPARE TIRE
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the license plate.
(2) Remove the two bolts securing the wheel cover
to the wheel.
(3) Remove the two lug nuts and the one wheel
lock (if equipped) securing the tire/wheel to the spare
tire carrier.
(4) Remove the spare tire.
Fig. 14 Tread Wear Indicators
1 - TREAD ACCEPTABLE
2 - TREAD UNACCEPTABLE
3 - WEAR INDICATOR
22 - 8 TIRES/WHEELSKJ
TIRES (Continued)