2002 JEEP LIBERTY 3.7 v6
[x] Cancel search: 3.7 v6Page 1239 of 1803

REMOVAL
CAUTION: When the timing chain is removed and
the cylinder heads are still installed, DO NOT force-
fully rotate the camshafts or crankshaft indepen-
dently of each other. Severe valve and/or piston
damage can occur.
CAUTION: When removing the cam sprocket, timing
chains or camshaft, Failure to use Special Tool
8379 will result in hydraulic tensioner ratchet over
extension, requiring timing chain cover removal to
reset the tensioner ratchet.
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. Refer to CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER in this section.
(2) Set engine to TDC cylinder #1, camshaft
sprocket V6 marks at the 12 o'clock position.
(3) Mark one link on the secondary timing chain
on both sides of the V6 mark on the camshaft
sprocket to aid in installation.
CAUTION: Do not hold or pry on the camshaft tar-
get wheel (Located on the right side camshaft
sprocket) for any reason, Severe damage will occur
to the target wheel resulting in a vehicle no start
condition.
(4) Loosen butDO NOTremove the camshaft
sprocket retaining bolt. Leave the bolt snug against
the sprocket.
NOTE: The timing chain tensioners must be
secured prior to removing the camshaft sprockets.
Failure to secure tensioners will allow the tension-
ers to extend, requiring timing chain cover removal
in order to reset tensioners.
CAUTION: Do not force wedge past the narrowest
point between the chain strands. Damage to the
tensioners may occur.
(5) Position Special Tool 8379 timing chain wedge
between the timing chain strands, tap the tool to
securely wedge the timing chain against the ten-
sioner arm and guide (Fig. 12).
(6) Hold the camshaft with Special Tool 8428 Cam-
shaft Wrench, while removing the camshaft sprocket
bolt and sprocket (Fig. 13).
(7) Using Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench,
gently allow the camshaft to rotate 5É clockwise until
the camshaft is in the neutral position (no valve
load).
(8) Starting at the outside working inward, loosen
the camshaft bearing cap retaining bolts 1/2 turn at
a time. Repeat until all load is off the bearing caps.CAUTION: DO NOT STAMP OR STRIKE THE CAM-
SHAFT BEARING CAPS. SEVERE DAMAGE WILL
OCCUR TO THE BEARING CAPS.
Fig. 12 SECURING TIMING CHAIN TENSIONERS
USING TIMING CHAIN WEDGE Ð Typical
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8379
2 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
3 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT
Fig. 13 Special Tool 8428
1 - Camshaft hole
2 - Special Tool 8428
9 - 24 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
Page 1240 of 1803
NOTE: When the camshaft is removed the rocker
arms may slide downward, mark the rocker arms
before removing camshaft.
(9) Remove the camshaft bearing caps and the
camshaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate camshaft journals with clean engine
oil.
NOTE: Position the left side camshaft so that the
camshaft sprocket dowel is near the 1 o'clock posi-
tion, This will place the camshaft at the neutral
position easing the installation of the camshaft
bearing caps.
(2) Position the camshaft into the cylinder head.
(3) Install the camshaft bearing caps, hand tighten
the retaining bolts.
NOTE: Caps should be installed so that the
stamped numbers on the caps are in numerical
order, ( 1 thru 4 ) from the front to the rear of the
engine. All caps should be installed so that the
stamped arrows on the caps point toward the front
of the engine.
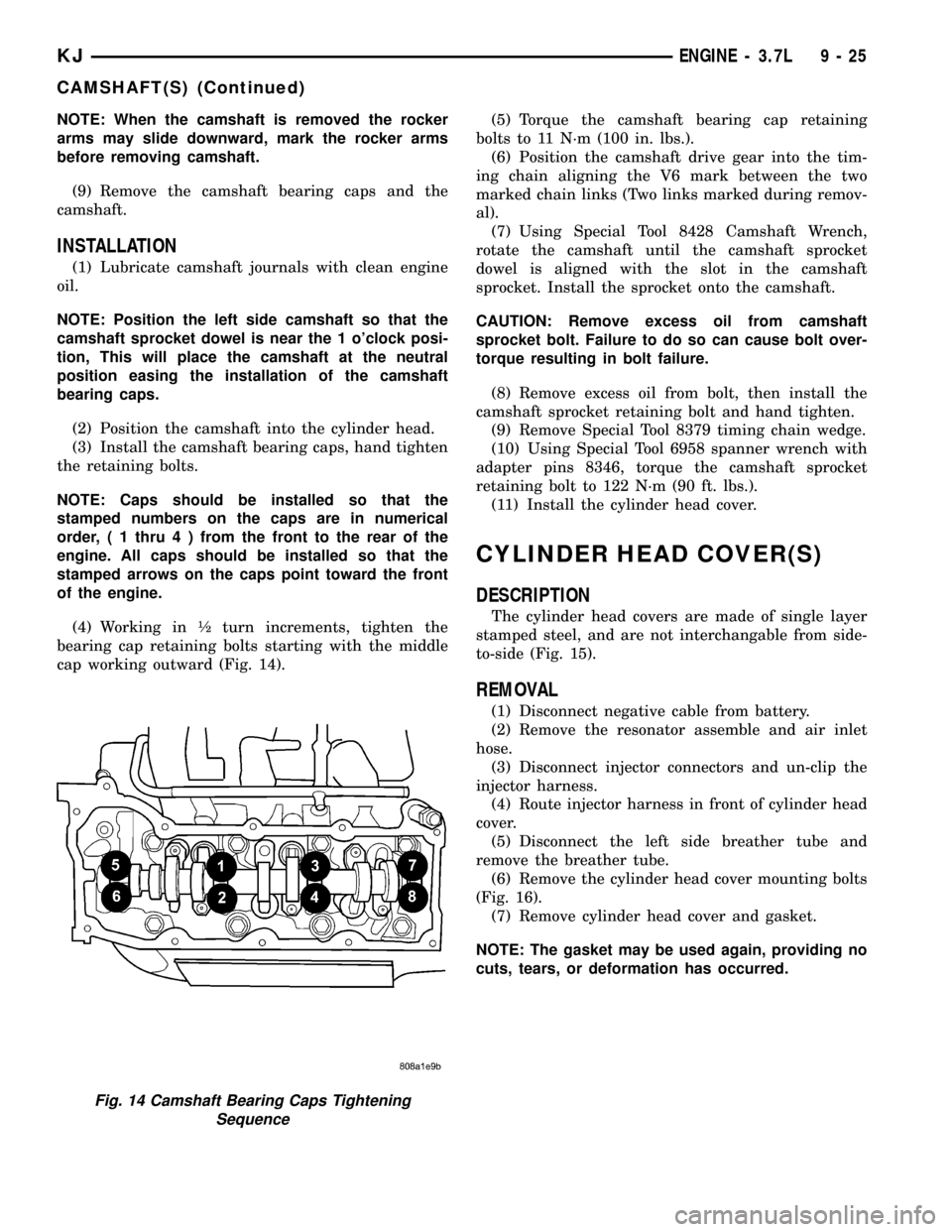
(4) Working in ó turn increments, tighten the
bearing cap retaining bolts starting with the middle
cap working outward (Fig. 14).(5) Torque the camshaft bearing cap retaining
bolts to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(6) Position the camshaft drive gear into the tim-
ing chain aligning the V6 mark between the two
marked chain links (Two links marked during remov-
al).
(7) Using Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench,
rotate the camshaft until the camshaft sprocket
dowel is aligned with the slot in the camshaft
sprocket. Install the sprocket onto the camshaft.
CAUTION: Remove excess oil from camshaft
sprocket bolt. Failure to do so can cause bolt over-
torque resulting in bolt failure.
(8) Remove excess oil from bolt, then install the
camshaft sprocket retaining bolt and hand tighten.
(9) Remove Special Tool 8379 timing chain wedge.
(10) Using Special Tool 6958 spanner wrench with
adapter pins 8346, torque the camshaft sprocket
retaining bolt to 122 N´m (90 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install the cylinder head cover.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of single layer
stamped steel, and are not interchangable from side-
to-side (Fig. 15).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the resonator assemble and air inlet
hose.
(3) Disconnect injector connectors and un-clip the
injector harness.
(4) Route injector harness in front of cylinder head
cover.
(5) Disconnect the left side breather tube and
remove the breather tube.
(6) Remove the cylinder head cover mounting bolts
(Fig. 16).
(7) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, providing no
cuts, tears, or deformation has occurred.
Fig. 14 Camshaft Bearing Caps Tightening
Sequence
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 25
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
Page 1241 of 1803

INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not use harsh cleaners to clean the
cylinder head covers. Severe damage to covers
may occur.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no
cuts, tears, or deformation has occurred.
(1) Clean cylinder head cover and both sealing sur-
faces. Inspect and replace gasket as necessary.
(2) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts and double
ended studs to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Install left side breather and connect breather
tube.
(4) Connect injector electrical connectors and injec-
tor harness retaining clips.
(5) Install the resonator and air inlet hose.
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Each
valve is actuated by a roller rocker arm which pivots
on a stationary lash adjuster. All valves use three
bead lock keepers to retain the springs and promote
valve rotation.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING
NOTE: Valve seats that are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise the cylinder head
must be replaced.
NOTE: When refacing valves and valve seats, it is
important that the correct size valve guide pilot be
used for reseating stones. A true and complete sur-
face must be obtained.
(1) Using a suitable dial indicator measure the
center of the valve seat Total run out must not
exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in).
(2) Apply a small amount of Prussian blue to the
valve seat, insert the valve into the cylinder head,
while applying light pressure on the valve rotate the
Fig. 15 CYLINDER HEAD COVERS
1 - LEFT SIDE CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - RIGHT SIDE CYLINDER HEAD COVER
Fig. 16 CYLINDER HEAD COVER -TYPICAL
1 - SCREWS
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
9 - 26 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) (Continued)
Page 1242 of 1803

valve. Remove the valve and examine the valve face.
If the blue is transferred below the top edge of the
valve face, lower the valve seat using a 15 degree
stone. If the blue is transferred to the bottom edge of
the valve face, raise the valve seat using a 65 degree
stone.
(3) When the seat is properly positioned the width
of the intake seat must be 1.75 ± 2.36 mm (0.0689 ±
0.0928 in.) and the exhaust seat must be 1.71 ± 2.32
mm (0.0673 ± 0.0911 in.).
(4) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat. The installed height for
both intake and exhaust valve springs must not
exceed 41.44 mm (1.6315 in.).
(5) The valve seat and valve face must maintain a
face angle of 44.5 ± 45 degrees angle (Fig. 17).
REMOVAL
NOTE: The cylinder heads must be removed in
order to perform this procedure.
(1) Remove rocker arms and lash adjusters. Refer
to procedures in this section (Fig. 18).
(2) Remove the camshaft bearing caps and the
camshaft.NOTE: All six valve springs and valves are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve and valve spring.
(3) Using Special Tool C-3422±B or C-3422±C
Valve Spring Compressor and Special tool 8519
Adapter, compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
(4) Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(5) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(6) Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
NOTE: Check for sharp edges on the keeper
grooves. Remove any burrs from the valve stem
before removing the valve from the cylinder head.
(7) Remove the valve from the cylinder head.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
(8) Remove the valve stem seal. Mark the valve for
proper installation.
Fig. 17 Valve Assembly Configuration
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
Fig. 18 Rocker Arm Removal
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8516
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 27
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1243 of 1803

TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
NOTE: Whenever the valves are removed from the
cylinder head it is recommended that the valve
springs be inspected and tested for reuse.
Inspect the valve springs for physical signs of wear
or damage. Turn table of tool C-647 until surface is
in line with the 40.69 mm (1.602 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over the stud on the table and lift compress-
ing lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench
until Ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench
at this instant. Multiply this reading by two. This
will give the spring load at test length. Fractional
measurements are indicated on the table for finer
adjustments. Refer to Specifications Section to obtain
specified height and allowable tensions. Replace any
springs that do not meet specifications (Fig. 19).
INSTALLATION
(1) coat the valve stem with clean engine oil and
insert it into the cylinder head.
(2) Install the valve stem seal. make sure the seal
is fully seated and that the garter spring at the top
of the seal is intact.
(3) Install the spring and the spring retainer (Fig.
20).
(4) Using the valve spring compressor, compress
the spring and install the two valve spring retainer
halves.(5) Release the valve spring compressor and make
sure the two spring retainer halves and the spring
retainer are fully seated.
(6) lubricate the camshaft journal with clean
engine oil then Position the camshaft (with the
sprocket dowel on the left camshaft at 11 o'clock and
the right camshaft at 12 o'clock), then position the
camshaft bearing caps.
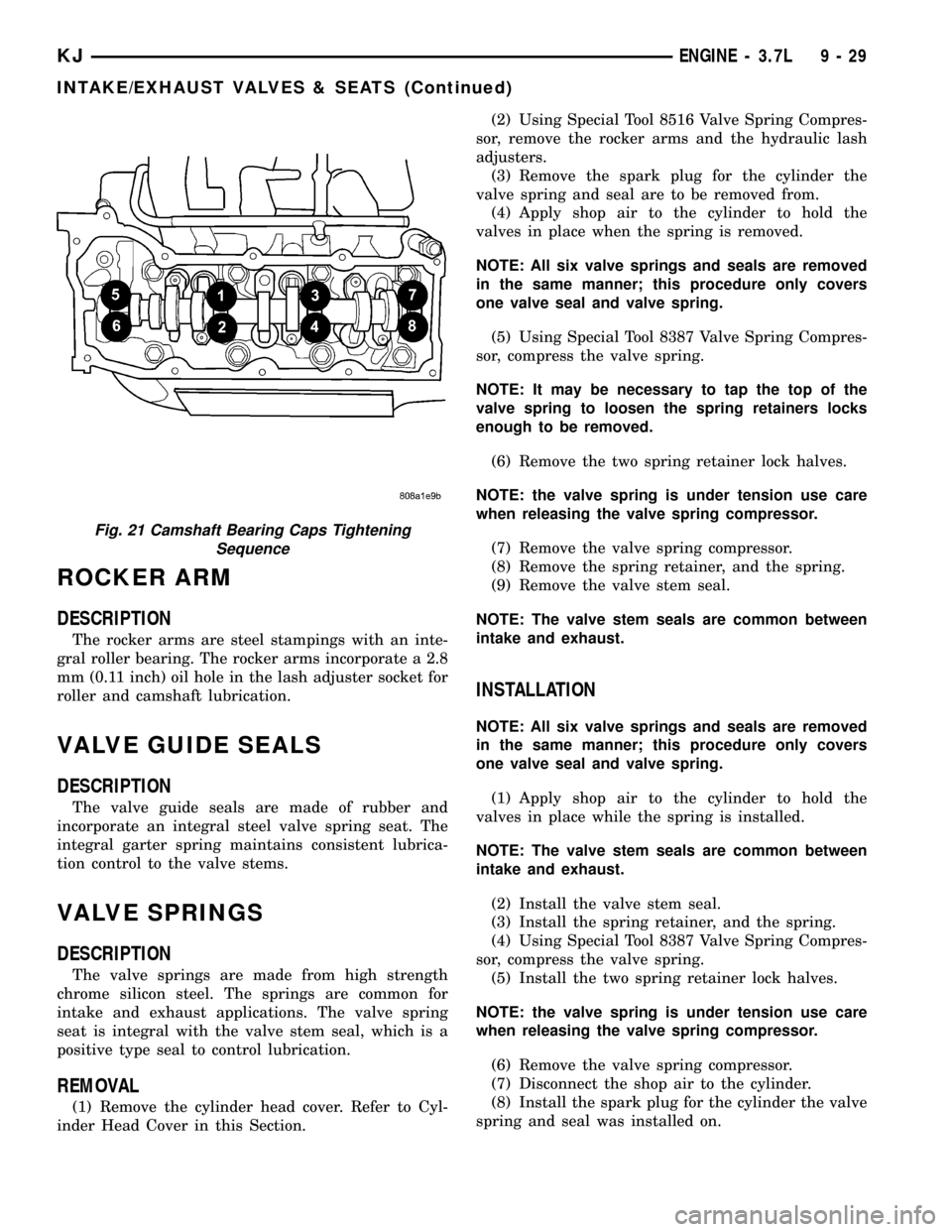
(7) Install the camshaft bearing cap retaining
bolts. Tighten the bolts 9±13 N´m (100 in. lbs.) in ó
turn increments in the sequence shown (Fig. 21).
(8) Position the hydraulic lash adjusters and
rocker arms.
Fig. 19 Testing Valve Springs
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-647
Fig. 20 Valve Assembly Configuration
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
9 - 28 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1244 of 1803
ROCKER ARM
DESCRIPTION
The rocker arms are steel stampings with an inte-
gral roller bearing. The rocker arms incorporate a 2.8
mm (0.11 inch) oil hole in the lash adjuster socket for
roller and camshaft lubrication.
VALVE GUIDE SEALS
DESCRIPTION
The valve guide seals are made of rubber and
incorporate an integral steel valve spring seat. The
integral garter spring maintains consistent lubrica-
tion control to the valve stems.
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs are made from high strength
chrome silicon steel. The springs are common for
intake and exhaust applications. The valve spring
seat is integral with the valve stem seal, which is a
positive type seal to control lubrication.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover. Refer to Cyl-
inder Head Cover in this Section.(2) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, remove the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(3) Remove the spark plug for the cylinder the
valve spring and seal are to be removed from.
(4) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place when the spring is removed.
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(5) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
(6) Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(7) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(8) Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
(9) Remove the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(1) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place while the spring is installed.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
(2) Install the valve stem seal.
(3) Install the spring retainer, and the spring.
(4) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
(5) Install the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(6) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(7) Disconnect the shop air to the cylinder.
(8) Install the spark plug for the cylinder the valve
spring and seal was installed on.
Fig. 21 Camshaft Bearing Caps Tightening
Sequence
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 29
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1245 of 1803

(9) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, install the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(10) Install the cylinder head cover. Refer to Cylin-
der Head Cover in this Section.
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder heads are made of an aluminum alloy.
The cylinder head features two valves per cylinder
with pressed in powdered metal valve guides. The
cylinder heads also provide enclosures for the timing
chain drain, necessitating unique left and right cylin-
der heads.
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and
are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are
not replaceable or serviceable, and valve guide ream-
ing is not recommended. If the guides are worn
beyond acceptable limits, replace the cylinder heads.
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Each
valve is actuated by a roller rocker arm which pivots
on a stationary lash adjuster. All valves use three
bead lock keepers to retain the springs and promote
valve rotation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
²Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
²Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
²Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
9 - 30 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1246 of 1803

VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the right side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant. Refer to COOLING
SYSTEM.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold. Refer to proce-
dure.
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover. Refer to proce-
dure.
(8) Remove the fan shroud. Refer to COOLING
SYSTEM.
(9) Remove oil fill housing from cylinder head.
(10) Remove accessory drive belt. Refer to COOL-
ING SYSTEM.
(11) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper timing
mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark.
(12) Verify the V6 mark on the camshaft sprocket
is at the 12 o'clock position. Rotate the crankshaft
one turn if necessary.
(13) Remove the crankshaft damper. Refer to pro-
cedure.
(14) Remove the timing chain cover. Refer to pro-
cedure.
(15) Lock the secondary timing chains to the idler
sprocket using Special Tool 8429 Timing Chain Hold-
ing Fixture.NOTE: Mark the secondary timing chain prior to
removal to aid in installation.
(16) Mark the secondary timing chain, one link on
each side of the V6 mark on the camshaft drive gear.
(17) Remove the right side secondary chain ten-
sioner. Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets in this
section.
(18) Remove the cylinder head access plug.
(19) Remove the right side secondary chain guide.
Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets in this section.
CAUTION: The nut on the right side camshaft
sprocket should not be removed for any reason, as
the sprocket and camshaft sensor target wheel is
serviced as an assembly. If the nut was removed
retorque nut to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.).
(20) Remove the retaining bolt and the camshaft
drive gear.
CAUTION: Do not allow the engine to rotate. severe
damage to the valve train can occur.
CAUTION: Do not overlook the four smaller bolts at
the front of the cylinder head. Do not attempt to
remove the cylinder head without removing these
four bolts.
CAUTION: Do not hold or pry on the camshaft tar-
get wheel for any reason. A damaged target wheel
can result in a vehicle no start condition.
NOTE: The cylinder head is attached to the cylinder
block with twelve bolts.
(21) Remove the cylinder head retaining bolts.
(22) Remove the cylinder head and gasket. Discard
the gasket.
CAUTION: Do not lay the cylinder head on its gas-
ket sealing surface, do to the design of the cylinder
head gasket any distortion to the cylinder head
sealing surface may prevent the gasket from prop-
erly sealing resulting in leaks.
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components (Fig. 22). (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 31
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT (Continued)