2002 JEEP LIBERTY heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 1690 of 1803

PLUMBING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT LINE.......38
WARNING
SERVICE WARNINGS..................39
CAUTION
SERVICE CAUTIONS..................39
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/
TUBES PRECAUTIONS.................40
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE EQUIPMENT..........40
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY..........................41
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM EVACUATE...................41
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE.....................41
SPECIFICATIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY.....42
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION........................42
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE..............................42
OPERATION
OPERATION.........................42
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE..............................42
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
COMPRESSOR NOISE.................42
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................44
A/C CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION.........................45
OPERATION...........................45
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
A/C DISCHARGE LINE
REMOVAL.............................46INSTALLATION.........................47
A/C LIQUID LINE
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
A/C SUCTION LINE
REMOVAL.............................48
INSTALLATION.........................49
A/C EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................49
OPERATION...........................49
REMOVAL.............................49
INSTALLATION.........................49
A/C ORIFICE TUBE
DESCRIPTION.........................50
OPERATION...........................50
REMOVAL.............................50
INSTALLATION.........................50
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................51
OPERATION...........................51
REMOVAL.............................51
INSTALLATION.........................51
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION.........................52
OPERATION...........................52
REMOVAL.............................52
INSTALLATION.........................53
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION.........................53
OPERATION...........................53
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION.........................53
OPERATION...........................54
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
OIL LEVEL...........................54
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT LINE
The refrigerant lines and hoses are used to carry
the refrigerant between the various air conditioning
system components. A barrier hose design with a
nylon tube, which is sandwiched between rubber lay-
ers, is used for the R-134a air conditioning system on
this vehicle. This nylon tube helps to further containthe R-134a refrigerant, which has a smaller molecu-
lar structure than R-12 refrigerant. The ends of the
refrigerant hoses are made from lightweight alumi-
num or steel, and commonly use braze-less fittings.
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
24 - 38 PLUMBINGKJ
Page 1702 of 1803

(1) Install the evaporator coil unit into of the lower
half of the HVAC housing. Be certain that the evap-
orator foam insulator wrap and rubber tube seal are
reinstalled.
(2) Reassemble and install the HVAC housing.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - ASSEMBLY)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLA-
TION)
NOTE: If the evaporator was replaced, add 60 milli-
liters (2 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the refrig-
erant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
A/C ORIFICE TUBE
DESCRIPTION
The fixed orifice tube is installed in the liquid line
(left-hand drive) or liquid line jumper (right-hand
drive) between the outlet of the condenser and the
inlet of the evaporator. The fixed orifice tube islocated in the end of the liquid line or liquid line
jumper that is closest to the condenser outlet tube.
The inlet end of the fixed orifice tube has a nylon
mesh filter screen, which filters the refrigerant and
helps to reduce the potential for blockage of the
metering orifice by refrigerant system contaminants
(Fig. 11). The outlet end of the tube has a nylon
mesh diffuser screen. The O-rings on the plastic body
of the fixed orifice tube seal the tube to the inside of
the liquid line and prevent the refrigerant from
bypassing the fixed metering orifice.
OPERATION
The fixed orifice tube is used to meter the flow of
liquid refrigerant into the evaporator coil. The high-
pressure liquid refrigerant from the condenser
expands into a low-pressure liquid as it passes
through the metering orifice and diffuser screen of
the fixed orifice tube.
The fixed orifice tube cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or plugged, the liquid line and fixed orifice
tube unit or liquid line jumper and fixed orifice tube
unit must be replaced.
REMOVAL
The fixed orifice tube is located in the liquid line
(Left-Hand Drive) or the liquid line jumper (Right-
Hand Drive) near the condenser. The orifice has filter
screens on the inlet and outlet ends of the tube body.
If the fixed orifice tube is faulty or plugged, the liq-
uid line unit or liquid line jumper unit must be
replaced. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/LIQUID LINE - REMOVAL)
INSTALLATION
The fixed orifice tube is located in the liquid line
(Left-Hand Drive) or the liquid line jumper (Right-
Hand Drive) near the condenser. The orifice has filter
screens on the inlet and outlet ends of the tube body.
If the fixed orifice tube is faulty or plugged, the liq-
uid line unit or liquid line jumper unit must be
Fig. 10 Blend Door
1 - DEFROSTER DOOR
2- HEATER CORE
3- BLEND DOORS
4- BLOWER MOTOR HOUSING
5- EVAPORATOR (A/C ONLY)
6- LOWER HVAC CASE ASSEMBLY
Fig. 11 FIXED ORIFICE TUBE - TYPICAL
1 - DIFFUSER SCREEN
2-9O9RINGS
3 - INLET FILTER SCREENS
4 - ORIFICE
24 - 50 PLUMBINGKJ
A/C EVAPORATOR (Continued)
Page 1704 of 1803

evaporator outlet tube. Connect the accumulator inlet
tube refrigerant line coupler to the evaporator outlet
tube. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C
LINE COUPLERS)
(3) Tighten the accumulator retaining band screw
to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(4) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the suction line and the accumulator
outlet tube. Connect the suction line to the accumu-
lator outlet tube refrigerant line coupler. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COUPLERS)
(5) Plug the wire harness connector into the low
pressure cycling clutch switch.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable.
(7) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(8) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)NOTE: If the accumulator is replaced, add 120 mil-
liliters (4 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the
refrigerant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the
type recommended for the compressor in the vehi-
cle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The heater core is located in the HVAC housing,
under the instrument panel. It is a heat exchanger
made of rows of tubes and fins and uses warm engine
coolant as its heat source.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through heater hoses
to the heater core at all times. As the coolant flows
through the heater core, heat removed from the
engine is transferred to the heater core fins and
tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks up
the heat from the heater core fins. The temperature
control door allows control of the heater output air
temperature by controlling how much of the air flow-
ing through the HVAC housing is directed through
the heater core. The blower motor speed controls the
volume of air flowing through the HVAC housing.
The heater core cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced. Refer to Cooling for
more information on the engine cooling system, the
engine coolant and the heater hoses.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
Fig. 13 A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
1 - WIRING HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
3 - A/C LINE TO EVAPORATOR
4 - ACCUMULATOR MOUNTING BRACKET
5 - ACCUMULATOR
6 - A/C LOW PRESSURE LINE
24 - 52 PLUMBINGKJ
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 1705 of 1803

WARNING: IF THE VEHICLE IS EQUIPPED WITH AIR
CONDITIONING, REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND
CAUTIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION
BEFORE PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERA-
TION. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Remove the HVAC housing. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the two heater core retaining screws (if
equipped). (Fig. 14).
(3) Gently push back on two of the heater core
retaining tabs and pull up on heater core to remove.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: IF THE VEHICLE IS EQUIPPED WITH AIR
CONDITIONING, REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND
CAUTIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION
BEFORE PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERA-
TION. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
(1) Install the heater core into the top of the
HVAC housing.
(2) Push on top of heater core until all for tabs are
locked into place.
(3) Install the two heater core retainer screws.
(4) Install the HVAC housing. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - INSTALLATION)
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant used in this air conditioning sys-
tem is a HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC), type R-134a.
Unlike R-12, which is a ChloroFluoroCarbon (CFC),
R-134a refrigerant does not contain ozone-depleting
chlorine. R-134a refrigerant is a non-toxic, non-flam-
mable, clear, and colorless liquefied gas.
Even though R-134a does not contain chlorine, it
must be reclaimed and recycled just like CFC-type
refrigerants. This is because R-134a is a greenhouse
gas and can contribute to global warming.
OPERATION
R-134a refrigerant is not compatible with R-12
refrigerant in an air conditioning system. Even a
small amount of R-12 added to an R-134a refrigerant
system will cause compressor failure, refrigerant oil
sludge or poor air conditioning system performance.
In addition, the PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG) synthetic
refrigerant oils used in an R-134a refrigerant system
are not compatible with the mineral-based refriger-
ant oils used in an R-12 refrigerant system.
R-134a refrigerant system service ports, service
tool couplers and refrigerant dispensing bottles have
all been designed with unique fittings to ensure that
an R-134a system is not accidentally contaminated
with the wrong refrigerant (R-12). There are also
labels posted in the engine compartment of the vehi-
cle and on the compressor identifying to service tech-
nicians that the air conditioning system is equipped
with R-134a.
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant oil used in R-134a refrigerant sys-
tems is a synthetic-based, PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG),
wax-free lubricant. Mineral-based R-12 refrigerant
Fig. 14 HEATER CORE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
1 - HEATER CORE
2- MOUNTING SCREW HOLE
3- INLET AND OUTLET TUBES
4- VACUUM HARNESS
5- ACTUATOR SCREWS (3)
6- ELECTRIC BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
7- MOUNTING SCREW HOLE
8- HEATER CORE RETAINER TABS (4)
KJPLUMBING 24 - 53
HEATER CORE (Continued)
Page 1708 of 1803

DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0031 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0032 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionProblem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0037 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0038 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0043 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0044 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0051 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0052 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1709 of 1803

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0057 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0058 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0071 (M) Amb/Bat Temp Sensor Performance
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
PO111 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Performance
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 Coolant Temp Sensor Performance A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable
voltage range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
P0123 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too HighAPPS voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0125 (M) Closed Loop Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0125 (M) Engine is Cold Too Long Engine does not reach operating temperature.
P0130 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1710 of 1803

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0135 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0136 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0137 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0138 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0139 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response not as expected.
P0140 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0141 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0143 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0144 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0145 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0146 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0147 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0151 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0152 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage sustained above normal
operating range.
P0153 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0154 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0155 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0157 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0158 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0159 2/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0160 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0161 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
PO165 Starter Relay Circuit Problem detected in starter relay circuit.
P0168 Decreased Engine Performance Due
To High Injection Pump Fuel TempFuel temperature is above the engine protection limit.
Engine power will be derated.
P0171 (M) 1/1 Fuel System Lean A lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an
abnormally rich correction factor.
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLKJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 1713 of 1803
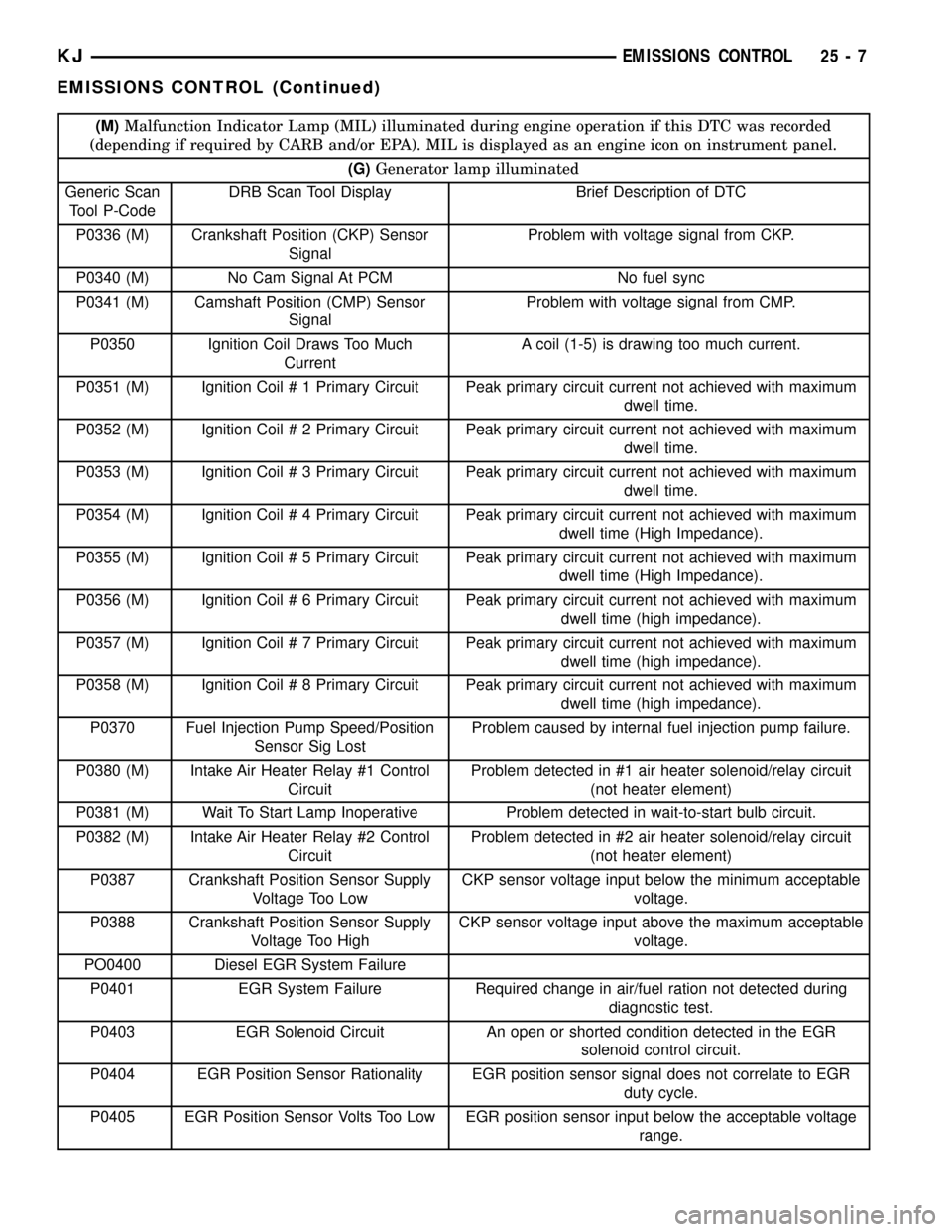
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0336 (M) Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CKP.
P0340 (M) No Cam Signal At PCM No fuel sync
P0341 (M) Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CMP.
P0350 Ignition Coil Draws Too Much
CurrentA coil (1-5) is drawing too much current.
P0351 (M) Ignition Coil # 1 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0352 (M) Ignition Coil # 2 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0353 (M) Ignition Coil # 3 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0354 (M) Ignition Coil # 4 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0355 (M) Ignition Coil # 5 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0356 (M) Ignition Coil # 6 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0357 (M) Ignition Coil # 7 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0358 (M) Ignition Coil # 8 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0370 Fuel Injection Pump Speed/Position
Sensor Sig LostProblem caused by internal fuel injection pump failure.
P0380 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #1 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #1 air heater solenoid/relay circuit
(not heater element)
P0381 (M) Wait To Start Lamp Inoperative Problem detected in wait-to-start bulb circuit.
P0382 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #2 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #2 air heater solenoid/relay circuit
(not heater element)
P0387 Crankshaft Position Sensor Supply
Voltage Too LowCKP sensor voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0388 Crankshaft Position Sensor Supply
Voltage Too HighCKP sensor voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
PO0400 Diesel EGR System Failure
P0401 EGR System Failure Required change in air/fuel ration not detected during
diagnostic test.
P0403 EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR
solenoid control circuit.
P0404 EGR Position Sensor Rationality EGR position sensor signal does not correlate to EGR
duty cycle.
P0405 EGR Position Sensor Volts Too Low EGR position sensor input below the acceptable voltage
range.
KJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 7
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)